Evaluation of Oxygen Absorbers Using Food Simulants and Inductively Coupled Mass Spectrometry
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents and Materials
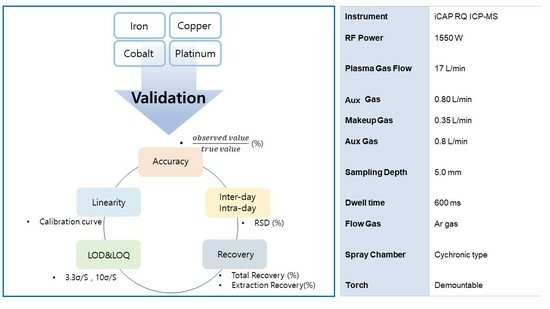
2.2. Instrumentation
2.3. Sample Preparation (Food Simulants)
2.4. Sample Digestion and Pre-Processing
2.4.1. Elution Test
2.4.2. Microwave Digestion
2.5. Method Validation
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. ICP-MS Method Validation
3.2. Cross-Validation of ICP-MS
3.3. Analysis of the Elution Test
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, S.; Brahma, S.; Mackay, J.; Cao, C.; Aliakbarian, B. The role of smart packaging system in food supply chain. J. Food Sci. 2020, 85, 517–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biji, K.; Ravishankar, C.; Mohan, C.; Srinivasa Gopal, T. Smart packaging systems for food applications: A review. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 52, 6125–6135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Firouz, M.S.; Mohi-Alden, K.; Omid, M. A critical review on intelligent and active packaging in the food industry: Research and development. Food Res. Int. 2021, 141, 110113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dey, A.; Neogi, S. Oxygen scavengers for food packaging applications: A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 90, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, P. Role of oxygen absorbers in food as packaging material, their characterization and applications. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 60, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cruz, R.S.; Camilloto, G.P.; dos Santos Pires, A.C. Oxygen scavengers: An approach on food preservation. Struct. Funct. Food Eng. 2012, 2, 21–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradley, E.; Driffield, M.; Leon, I.; Ticha, J.; van Stee, L.; Zondervan-van den Beuken, E.; Koster, S. Identification of Chemicals Specific to Active and Intelligent Packaging on the European Market and the Extent to Which They Migrate into Food; TNO Report; TNO: The Hague, The Netherlands, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Engwa, G.A.; Ferdinand, P.U.; Nwalo, F.N.; Unachukwu, M.N. Mechanism and health effects of heavy metal toxicity in humans. Poisoning Mod. World New Tricks Old Dog 2019, 10, 70–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parmar, M.; Thakur, L.S. Heavy metal Cu, Ni and Zn: Toxicity, health hazards and their removal techniques by low cost adsorbents: A short overview. Int. J. Plant Anim. Environ. Sci. 2013, 3, 143–157. [Google Scholar]
- Ćwiertnia, A.; Kozłowski, M.; Cymbaluk-Płoska, A. The Role of Iron and Cobalt in Gynecological Diseases. Cells 2022, 12, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teschke, R. Aluminum, arsenic, beryllium, cadmium, chromium, cobalt, copper, iron, lead, mercury, molybdenum, nickel, platinum, thallium, titanium, vanadium, and zinc: Molecular aspects in experimental liver injury. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 12213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perše, M. Cisplatin mouse models: Treatment, toxicity and translatability. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Food and Drug Administration. Guidance for industry: Preparation of premarket submissions for food contact substances: Chemistry recommendations. In Guidance Complience Regulatory Information; Food and Drug Administration: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- EFSA Panel on Food Contact Materials, Enzymes and Processing Aids (CEP); Silano, V.; Barat Baviera, J.M.; Bolognesi, C.; Chesson, A.; Cocconcelli, P.S.; Crebelli, R.; Gott, D.M.; Grob, K.; Lambré, C.; et al. Review and priority setting for substances that are listed without a specific migration limit in Table 1 of Annex 1 of Regulation 10/2011 on plastic materials and articles intended to come into contact with food. EFSA J. 2020, 18, e06124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ministry of Food and Drug. Standards and Specifications for Utensils, Containers and Packages; Korean Ministry of Food and Drug Safety: Cheongju, Republic of Korea, 2021.
- Manousi, N.; Zachariadis, G.A. Development and Validation of an ICP-AES Method for the Determination of Toxic and Nutrient Metals in Candies: Application for the Analysis of Different Samples from the Greek Market. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 10599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, H.-J.; Hwang, G.-H.; Ahn, S.-M.; Kim, Y.-Y.; Shin, H.-S. Risk assessment and determination of heavy metals in home meal replacement products by using inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry and direct mercury analyzer. Foods 2022, 11, 504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO); World Health Organization (WHO). Guidelines on Performance Criteria for Methods of Analysis for the Determination of Pesticide Residues in Food and Feed (cxg 90-2017). Available online: https://www.fao.org/fao-who-codexalimentarius/search/en/?cx=018170620143701104933%3Aqq82jsfba7w&q=CXG+90-2017&cof=FORID%3A9 (accessed on 23 June 2023).
- Gupta, K. Food safety guidelines for food packaging. In Green Substainable Process for Chemical and Environmental Engineering and Science; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2023; pp. 56–69. [Google Scholar]
- Jang, M.-K.; Son, M.-H.; Park, S.-H.; Cho, Y.-S.; Ku, E.-J.; Chae, S.-Y.; Jeon, J.-S.; Lee, M.-J. Safety Evaluation of Hazardous Metals Migrated in Tumbler Samples. Hangug Sigpum Wisaeng Anjeonseong Haghoeji 2022, 37, 166–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.-J.; Park, S.-R.; Kim, M.; Choi, J.C. A study on the migration of heavy metals from polycarbonate food contact materials using an inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS). Korean J. Packag. Sci. Technol. 2018, 24, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Type of Food | Food Simulants | |
|---|---|---|
| Oils and fatty foods (Food containing 20% or more of the total, surface, or part of the surface of the food) | n-Heptane | |
| Alcoholic beverages | Alcoholic beverages containing not more than 20% alcohol | 20% ethanol |
| Alcoholic beverages containing more than 20% alcohol | 50% ethanol | |
| Food other than oils and fatty foods and alcoholic beverages | Food with a pH of 5 or lower | 4% acetic acid |
| Food exceeding pH 5 | Water | |
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| RF power | 1550 W |
| Ar gas flow rate (mL/min) Sample uptake rate | Auxiliary: 0.8, nebulizer: 1.0 1.0 mL/min |
| Nebulizer Spray chamber Torch | Concentric type Cyclonic type Demountable |
| Interface cones | Nickel |
| Quadrupole chamber Dwell time (ms) | 1 × 10−6 torr 600 |
| Analytical masses | Fe (57), Co (59), Cu (63), Pt (195) |
| Analytes and measurement mode | KED |
| Matrix Type | Heavy Metal Element | LOD a (mg/kg) | LOQ b (mg/kg) | Linearity Equation c | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Water | Co | 0.00002 | 0.00007 | y = 37,537x + 7795.5 | 1.0000 |
| Cu | 0.0001 | 0.0003 | y = 29,064x + 26,736 | 1.0000 | |
| Pt | 0.0002 | 0.0005 | y = 3,982,718x − 229,619 | 1.0000 | |
| Fe | 0.1123 | 0.3404 | y = 330,348x + 23,425 | 1.0000 | |
| 4% acetic acid | Co | 0.0001 | 0.0002 | y = 37,542x + 7752.8 | 1.0000 |
| Cu | 0.0000 | 0.0001 | y = 28,891x + 30,671 | 0.9996 | |
| Pt | 0.0001 | 0.0003 | y = 3,971,346x + 55,332 | 0.9999 | |
| Fe | 0.1032 | 0.3129 | y = 345,386x − 31,532 | 0.9999 | |
| 20% ethanol | Co | 0.00002 | 0.0001 | y = 37,209x + 9605.6 | 0.9998 |
| Cu | 0.0001 | 0.0002 | y = 29,079x + 28,236 | 0.9986 | |
| Pt | 0.00002 | 0.0001 | y = 4,144,907x − 35,874 | 1.0000 | |
| Fe | 0.2190 | 0.6636 | y = 351,745x + 32,137 | 0.9998 | |
| 50% ethanol | Co | 0.0001 | 0.0004 | y = 38,615x + 7459.2 | 1.0000 |
| Cu | 0.0001 | 0.0002 | y = 30,523x + 21,463 | 1.0000 | |
| Pt | 0.00003 | 0.0001 | y = 4,289,917x − 21,839 | 1.0000 | |
| Fe | 0.0440 | 0.1333 | y = 380,607x + 42,364 | 0.9989 | |
| n-Heptane | Co | 0.0001 | 0.0003 | y = 40,494x + 9085.2 | 1.0000 |
| Cu | 0.0001 | 0.0002 | y = 31,664x + 41,842 | 0.9993 | |
| Pt | 0.0001 | 0.0003 | y = 4,388,571x + 118,922 | 1.0000 | |
| Fe | 0.0735 | 0.2228 | y = 427,438x + 39,190 | 0.9998 |
| Matrix Type | Heavy Metal Element | Intraday (n = 3) | Interday (n = 3) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Accuracy (Mean ± SD) | Precision (Mean ± SD) | Accuracy (Mean ± SD) | Precision (Mean ± SD) | ||
| Water | Co (μg/kg) | 100.68 ± 0.55 | 0.73 ± 0.48 | 100.21 ± 0.37 | 2.13 ± 0.55 |
| Cu (μg/kg) | 100.71 ± 1.01 | 0.79 ± 0.50 | 99.09 ± 1.49 | 2.44 ± 1.28 | |
| Pt (μg/kg) | 99.68 ± 2.44 | 0.94 ± 0.24 | 100.07 ± 2.45 | 2.19 ± 0.96 | |
| Fe (mg/kg) | 99.57 ± 1.24 | 1.33 ± 0.41 | 99.77 ± 1.17 | 10.37 ± 1.24 | |
| 4% acetic acid | Co (μg/kg) | 99.69 ± 0.95 | 0.63 ± 0.27 | 100.11 ± 0.59 | 1.15 ± 0.46 |
| Cu (μg/kg) | 96.72 ± 6.62 | 0.87 ± 0.69 | 97.33 ± 6.03 | 1.59 ± 0.38 | |
| Pt (μg/kg) | 100.62 ± 1.99 | 0.79 ± 0.51 | 100.73 ± 2.06 | 2.22 ± 1.05 | |
| Fe (mg/kg) | 96.04 ± 2.99 | 0.87 ± 0.38 | 98.45 ± 1.26 | 8.62 ± 0.96 | |
| 20% ethanol | Co (μg/kg) | 101.17 ± 1.48 | 0.66 ± 0.5 | 100.95 ± 1.06 | 1.35 ± 0.52 |
| Cu (μg/kg) | 99.76 ± 7.98 | 0.77 ± 0.54 | 99.98 ± 8.5 | 1.08 ± 0.42 | |
| Pt (μg/kg) | 100.14 ± 2.69 | 0.65 ± 0.23 | 100.75 ± 2.54 | 0.72 ± 0.4 | |
| Fe (mg/kg) | 100.35 ± 1.18 | 0.91 ± 0.52 | 101.52 ± 0.94 | 7.29 ± 0.75 | |
| 50% etnaol | Co (μg/kg) | 100.55 ± 0.49 | 0.82 ± 0.33 | 100.31 ± 0.57 | 1.91 ± 0.76 |
| Cu (μg/kg) | 99.76 ± 0.93 | 0.97 ± 0.89 | 99.44 ± 1.32 | 2.12 ± 1.07 | |
| Pt (μg/kg) | 100.58 ± 2.68 | 0.85 ± 0.46 | 100.76 ± 2.78 | 0.68 ± 0.3 | |
| Fe (mg/kg) | 95.52 ± 7.32 | 0.61 ± 0.35 | 96.52 ± 6.32 | 5.82 ± 1.07 | |
| n-Heptane | Co (μg/kg) | 101.62 ± 1.91 | 0.59 ± 0.47 | 101.45 ± 1.68 | 1.56 ± 0.93 |
| Cu (μg/kg) | 95.14 ± 6.44 | 0.95 ± 1.02 | 95.03 ± 6.88 | 2.58 ± 2.46 | |
| Pt (μg/kg) | 101.98 ± 3.24 | 0.81 ± 0.35 | 101.62 ± 3.13 | 1.07 ± 0.52 | |
| Fe (mg/kg) | 100.03 ± 0.40 | 0.58 ± 0.24 | 100.51 ± 0.51 | 3.6 ± 0.28 | |
| Matrix Type | Heavy Metal Element Concentration | Spike | A a Mean Value | B b Mean Value | C c Mean Value | Accuracy (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4% Acetic acid | Co (μg/kg) | 1 | 1.10 | 1.19 | 0.98 | 109.07 |
| 5 | 5.52 | 5.74 | 4.99 | 108.31 | ||
| 20 | 21.35 | 22.46 | 19.83 | 106.05 | ||
| Cu (μg/kg) | 1 | 1.09 | 1.21 | 0.99 | 109.33 | |
| 5 | 5.32 | 4.75 | 4.94 | 104.73 | ||
| 20 | 20.78 | 19.86 | 19.82 | 103.63 | ||
| Pt (μg/kg) | 1 | 1.02 | 1.00 | 0.95 | 98.87 | |
| 5 | 4.88 | 4.75 | 4.80 | 96.20 | ||
| 20 | 19.71 | 19.86 | 19.11 | 97.79 | ||
| Fe (mg/kg) | 1 | 1.09 | 1.11 | 1.00 | 106.67 | |
| 5 | 5.27 | 5.38 | 4.87 | 103.45 | ||
| 20 | 21.59 | 22.22 | 19.48 | 105.48 |
| Heavy Metal Element Concentration | Matrix Type | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Water | 4% Acetic Acid | n-Heptane | 20% Ethanol | 50% Ethanol | |
| Co (μg/kg) | 0.204 | 0.211 | 0.248 | 0.211 | 0.227 |
| Cu (μg/kg) | 0.661 | 1.013 | 1.300 | 0.938 | 0.877 |
| Pt (μg/kg) | 0.007 | 0.005 | 0.005 | 0.005 | 0.005 |
| Fe (mg/kg) | 0.053 | 0.054 | 0.058 | 0.056 | 0.056 |
| Oxygen Absorbers | Fe (mg/kg) | Co (μg/kg) | Cu (μg/kg) | Pt (μg/kg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Oxygen Absorber 1 | 0.40 ± 0.00 | 2.79 ± 0.00 | 15.62 ± 0.01 | ND a |
| Oxygen Absorber 2 | 0.30 ± 0.00 | 2.58 ± 0.00 | 13.88 ± 0.00 | ND |
| Oxygen Absorber 3 | 0.30 ± 0.00 | 1.91 ± 0.00 | 0.30 ± 0.00 | ND |
| Oxygen Absorber 4 | 0.30 ± 0.00 | 1.40 ± 0.00 | ND | ND |
| Oxygen Absorber 5 | 0.40 ± 0.00 | 1.49 ± 0.00 | ND | ND |
| Oxygen Absorber 6 | 0.30 ± 0.00 | 1.51 ± 0.00 | 4.52 ± 0.00 | ND |
| Oxygen Absorber 7 | 4.42 ± 0.00 | 6.63 ± 0.00 | 6.83 ± 0.00 | ND |
| Oxygen Absorber 8 | 6.56 ± 0.00 | 4.84 ± 0.00 | 209.60 ± 0.01 | ND |
| Oxygen Absorber 9 | 0.50 ± 0.00 | 1.81 ± 0.00 | 10.57 ± 0.00 | ND |
| Oxygen Absorber 10 | 1.30 ± 0.00 | 2.69 ± 0.00 | 17.56 ± 0.01 | ND |
| Oxygen Absorber 11 | 0.40 ± 0.00 | 1.20 ± 0.00 | 15.41 ± 0.01 | ND |
| Oxygen Absorber 12 | 0.60 ± 0.00 | 1.20 ± 0.00 | ND | ND |
| Oxygen Absorber 13 | 0.50 ± 0.00 | 1.30 ± 0.00 | ND | ND |
| Oxygen Absorber 14 | 1.61 ± 0.00 | 3.32 ± 0.00 | 19.11 ± 0.00 | ND |
| Oxygen Absorber 15 | 0.06 ± 0.00 | 3.31 ± 0.00 | 2.90 | ND |
| Oxygen Absorber 16 | 1.39 ± 0.00 | 1.79 ± 0.00 | 3.27 ± 0.01 | ND |
| Oxygen Absorber 17 | 1.71 ± 0.00 | 2.31 ± 0.00 | ND | ND |
| Oxygen Absorber 18 | 8.90 ± 0.00 | 8.60 ± 0.00 | 9.50 ± 0.01 | ND |
| Oxygen Absorber 19 | 2.31 ± 0.00 | 1.71 ± 0.00 | ND | ND |
| Oxygen Absorber 20 | 2.42 ± 0.00 | 2.83 ± 0.00 | 26.54 ± 0.01 | ND |
| Oxygen Absorbers | Fe (mg/kg) | Co (μg/kg) | Cu (μg/kg) | Pt (μg/kg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Oxygen Absorber 1 | 0.50 ± 0.00 | 0.69 ± 0.00 | 62.30 ± 0.00 | ND |
| Oxygen Absorber 2 | 1.49 ± 0.00 | 1.59 ± 0.00 | 170.87 ± 0.00 | ND |
| Oxygen Absorber 3 | ND | ND | 41.93 ± 0.00 | ND |
| Oxygen Absorber 4 | 0.10 ± 0.00 | 0.70 ± 0.00 | 539.25 ± 0.03 | ND |
| Oxygen Absorber 5 | ND | ND | 976.14 ± 0.04 | ND |
| Oxygen Absorber 6 | 0.20 ± 0.00 | ND | 283.82 ± 0.01 | ND |
| Oxygen Absorber 7 | 0.59 ± 0.00 | 0.50 ± 0.00 | ND | ND |
| Oxygen Absorber 8 | 1.81 ± 0.00 | 1.91 ± 0.00 | 9.63 ± 0.01 | ND |
| Oxygen Absorber 9 | 0.20 ± 0.00 | ND | 343.10 ± 0.02 | ND |
| Oxygen Absorber 10 | 0.69 ± 0.00 | 1.69 ± 0.00 | 6.75 ± 0.01 | ND |
| Oxygen Absorber 11 | 1.59 ± 0.00 | 1.79 ± 0.00 | 11.52 ± 0.00 | ND |
| Oxygen Absorber 12 | 53.08 ± 0.00 | 5.16 ± 0.00 | 9.13 ± 0.00 | ND |
| Oxygen Absorber 13 | 1.50 ± 0.00 | 2.90 ± 0.00 | 41.63 ± 0.01 | ND |
| Oxygen Absorber 14 | 1.00 ± 0.00 | 5.20 ± 0.00 | 112.02 ± 0.01 | ND |
| Oxygen Absorber 15 | 0.07 ± 0.00 | 2.72 ± 0.00 | 31.72 ± 0.00 | ND |
| Oxygen Absorber 16 | 3.40 ± 0.00 | 1.00 ± 0.01 | 15.11 ± 0.01 | ND |
| Oxygen Absorber 17 | 4.09 ± 0.00 | 0.70 ± 0.00 | 86.01 ± 0.01 | ND |
| Oxygen Absorber 18 | 0.60 ± 0.00 | 0.20 ± 0.00 | 2.80 ± 0.01 | ND |
| Oxygen Absorber 19 | 0.40 ± 0.00 | 0.20 ± 0.00 | ND | ND |
| Oxygen Absorber 20 | 1.70 ± 0.00 | 0.30 ± 0.00 | 6.31 ± 0.01 | ND |
| Oxygen Absorbers | Fe (mg/kg) | Co (μg/kg) | Cu (μg/kg) | Pt (μg/kg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Oxygen Absorber 1 | 1.10 ± 0.00 | 1.40 ± 0.00 | 3.60 ± 0.01 | ND |
| Oxygen Absorber 2 | 2.72 ± 0.00 | 4.03 ± 0.00 | 10.38 ± 0.01 | ND |
| Oxygen Absorber 3 | 1.20 ± 0.00 | 2.00 ± 0.00 | 1.20 ± 0.00 | ND |
| Oxygen Absorber 4 | 1.20 ± 0.00 | 2.20 ± 0.00 | 5.01 ± 0.00 | ND |
| Oxygen Absorber 5 | 4.81 ± 0.00 | 4.51 ± 0.00 | 57.76 ± 0.02 | ND |
| Oxygen Absorber 6 | 0.71 ± 0.00 | 1.92 ± 0.00 | ND | ND |
| Oxygen Absorber 7 | 0.50 ± 0.00 | 6.39 ± 0.00 | 2.10 ± 0.00 | ND |
| Oxygen Absorber 8 | 1.21 ± 0.00 | 7.77 ± 0.00 | 14.02 ± 0.00 | ND |
| Oxygen Absorber 9 | 2.79 ± 0.00 | 2.39 ± 0.00 | 2.69 ± 0.00 | ND |
| Oxygen Absorber 10 | 0.80 ± 0.00 | 1.39 ± 0.00 | 39.21 ± 0.00 | ND |
| Oxygen Absorber 11 | 1.19 ± 0.00 | 3.96 ± 0.00 | 1.49 ± 0.01 | ND |
| Oxygen Absorber 12 | 1.51 ± 0.00 | 3.62 ± 0.00 | ND | ND |
| Oxygen Absorber 13 | 32.46 ± 0.00 | 5.93 ± 0.00 | 77.19 ± 0.00 | ND |
| Oxygen Absorber 14 | 1.90 ± 0.00 | 6.01 ± 0.00 | 7.41 ± 0.00 | ND |
| Oxygen Absorber 15 | 0.06 ± 0.00 | ND | ND | ND |
| Oxygen Absorber 16 | 0.10 ± 0.00 | 10.54 ± 0.00 | ND | ND |
| Oxygen Absorber 17 | 0.90 ± 0.00 | 13.19 ± 0.01 | 176.73 ± 0.02 | ND |
| Oxygen Absorber 18 | 2.12 ± 0.00 | 19.29 ± 0.00 | 10.81 ± 0.00 | 0.10 ± 0.00 |
| Oxygen Absorber 19 | 1.00 ± 0.00 | 17.12 ± 0.00 | 57.17 ± 0.00 | ND |
| Oxygen Absorber 20 | 0.80 ± 0.00 | 13.79 ± 0.00 | 37.88 ± 0.01 | ND |
| Oxygen Absorbers | Fe (mg/kg) | Co (μg/kg) | Cu (μg/kg) | Pt (μg/kg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Oxygen Absorber 1 | 0.20 ± 0.00 | 0.10 ± 0.00 | 46.89 ± 0.00 | ND |
| Oxygen Absorber 2 | ND | ND | 2.83 ± 0.01 | ND |
| Oxygen Absorber 3 | 0.30 ± 0.00 | ND | 5.90 ± 0.00 | ND |
| Oxygen Absorber 4 | 0.20 ± 0.00 | ND | ND | ND |
| Oxygen Absorber 5 | 0.10 ± 0.00 | ND | 77.65 ± 0.01 | ND |
| Oxygen Absorber 6 | 0.30 ± 0.00 | ND | 51.04 ± 0.01 | ND |
| Oxygen Absorber 7 | 1.10 ± 0.00 | 4.80 ± 0.00 | 12.50 ± 0.01 | ND |
| Oxygen Absorber 8 | 0.70 ± 0.00 | 6.52 ± 0.00 | 4.21 ± 0.01 | ND |
| Oxygen Absorber 9 | 0.20 ± 0.00 | ND | 89.98 ± 0.01 | ND |
| Oxygen Absorber 10 | 0.30 ± 0.00 | 2.68 ± 0.00 | ND | ND |
| Oxygen Absorber 11 | 0.50 ± 0.00 | 2.58 ± 0.00 | ND | ND |
| Oxygen Absorber 12 | 0.61 ± 0.00 | 2.12 ± 0.00 | ND | ND |
| Oxygen Absorber 13 | 0.59 ± 0.00 | 3.57 ± 0.00 | 8.12 ± 0.01 | ND |
| Oxygen Absorber 14 | 10.14 ± 0.00 | 14.71 ± 0.00 | 83.47 ± 0.02 | ND |
| Oxygen Absorber 15 | 0.09 ± 0.00 | 7.46 ± 0.00 | 61.32 ± 0.01 | ND |
| Oxygen Absorber 16 | 0.70 ± 0.00 | 5.57 ± 0.00 | 10.14 ± 0.00 | ND |
| Oxygen Absorber 17 | 1.11 ± 0.00 | 5.65 ± 0.00 | 13.91 ± 0.01 | ND |
| Oxygen Absorber 18 | 0.60 ± 0.00 | 4.74 ± 0.00 | ND | ND |
| Oxygen Absorber 19 | 0.70 ± 0.00 | 5.94 ± 0.01 | ND | ND |
| Oxygen Absorber 20 | 1.00 ± 0.00 | 5.68 ± 0.00 | ND | ND |
| Oxygen Absorbers | Fe (mg/kg) | Co (μg/kg) | Cu (μg/kg) | Pt (μg/kg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Oxygen Absorber 1 | ND | ND | 4.97 ± 0.01 | ND |
| Oxygen Absorber 2 | 0.60 ± 0.00 | 0.89 ± 0.00 | 10.44 ± 0.00 | ND |
| Oxygen Absorber 3 | ND | ND | 17.86 ± 0.00 | ND |
| Oxygen Absorber 4 | 0.60 ± 0.00 | ND | 4.08 ± 0.01 | ND |
| Oxygen Absorber 5 | 1.20 ± 0.00 | ND | 0.30 ± 0.00 | ND |
| Oxygen Absorber 6 | 0.50 ± 0.00 | ND | 21.53 ± 0.01 | ND |
| Oxygen Absorber 7 | 0.71 ± 0.00 | 6.97 ± 0.00 | 6.16 ± 0.01 | ND |
| Oxygen Absorber 8 | 1.00 ± 0.00 | 6.29 ± 0.00 | 66.31 ± 0.01 | ND |
| Oxygen Absorber 9 | 0.20 ± 0.00 | 0.60 ± 0.00 | 41.84 ± 0.01 | ND |
| Oxygen Absorber 10 | 0.71 ± 0.00 | 5.55 ± 0.00 | 12.40 ± 0.01 | ND |
| Oxygen Absorber 11 | 0.30 ± 0.00 | 4.72 ± 0.00 | 9.14 ± 0.00 | ND |
| Oxygen Absorber 12 | 2.70 ± 0.00 | 8.31 ± 0.00 | 14.62 ± 0.01 | ND |
| Oxygen Absorber 13 | 0.80 ± 0.00 | 6.29 ± 0.00 | 11.69 ± 0.01 | ND |
| Oxygen Absorber 14 | 0.99 ± 0.00 | 6.35 ± 0.00 | 17.08 ± 0.01 | ND |
| Oxygen Absorber 15 | 0.07 ± 0.00 | 5.95 ± 0.00 | 10.12 ± 0.01 | ND |
| Oxygen Absorber 16 | 0.40 ± 0.00 | 5.05 ± 0.00 | 22.42 ± 0.00 | ND |
| Oxygen Absorber 17 | 1.11 ± 0.00 | 5.45 ± 0.00 | 30.69 ± 0.01 | ND |
| Oxygen Absorber 18 | 1.41 ± 0.00 | 4.34 ± 0.00 | 2.42 ± 0.00 | ND |
| Oxygen Absorber 19 | 2.93 ± 0.00 | 10.09 ± 0.00 | 29.66 ± 0.01 | ND |
| Oxygen Absorber 20 | 5.33 ± 0.00 | 7.94 ± 0.00 | 18.49 ± 0.01 | ND |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Oh, S.-Y.; Kang, E.-J.; Lim, K.-J.; Lee, Y.-H.; Shin, H.-S. Evaluation of Oxygen Absorbers Using Food Simulants and Inductively Coupled Mass Spectrometry. Foods 2023, 12, 3686. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12193686
Oh S-Y, Kang E-J, Lim K-J, Lee Y-H, Shin H-S. Evaluation of Oxygen Absorbers Using Food Simulants and Inductively Coupled Mass Spectrometry. Foods. 2023; 12(19):3686. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12193686
Chicago/Turabian StyleOh, Seung-Yeon, Eun-Ji Kang, Kyung-Jik Lim, Yoon-Hee Lee, and Han-Seung Shin. 2023. "Evaluation of Oxygen Absorbers Using Food Simulants and Inductively Coupled Mass Spectrometry" Foods 12, no. 19: 3686. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12193686
APA StyleOh, S. -Y., Kang, E. -J., Lim, K. -J., Lee, Y. -H., & Shin, H. -S. (2023). Evaluation of Oxygen Absorbers Using Food Simulants and Inductively Coupled Mass Spectrometry. Foods, 12(19), 3686. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12193686