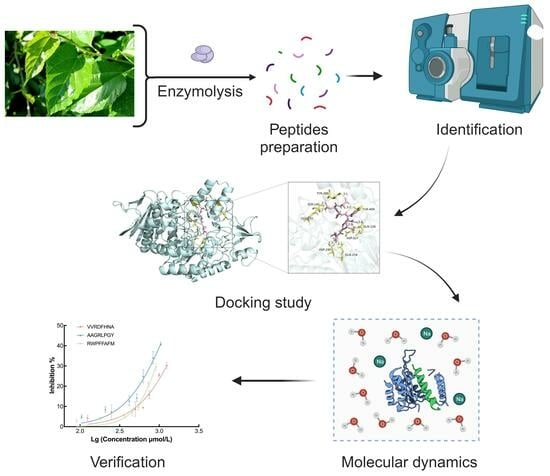
Development and Identification of Novel α-Glucosidase Inhibitory Peptides from Mulberry Leaves
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Mulberry Leaf Protein
2.3. Preparation of Mulberry Leaf Peptides
2.3.1. Single-Factor Test
2.3.2. Optimization of Enzymatic Hydrolysis Parameters via Response Surface Method (RSM)
2.4. Degree of Hydrolysis (DH) Determination
2.5. Yield of Soluble Peptides (YSP) Determination
2.6. Molecular Weight Distribution Determination
2.7. Determination of α-Glucosidase Inhibitory Activity
2.8. Crude Separation of α-Glucosidase Inhibitory Peptides
2.9. Peptide Sequence Identification
2.10. Virtual Screening and Molecular Docking
2.11. Molecular Dynamics Simulation
2.12. Peptide Synthesis
2.13. Statistics Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Optimization of Enzymatic Hydrolysis
3.1.1. Results of Single-Factor Experiments
3.1.2. Results of Enzymatic Hydrolysis Optimization
3.2. Evaluation, Separation, and Identification of α-Glucosidase Inhibitory Peptides
3.2.1. Evaluation of Enzymatic Hydrolysis Products
3.2.2. Separation and Identification of α-Glucosidase Inhibitory Peptides
3.3. Virtual Screening and Molecular Docking
3.3.1. Binding Energy Analysis
3.3.2. Binding Site Analysis
3.4. Molecular Dynamics Simulation
3.4.1. Root Mean Square Deviation Analysis
3.4.2. Root Mean Square Fluctuation Analysis
3.4.3. Radius of Gyration Analysis
3.4.4. Analysis of the Number of Hydrogen Bonds
3.4.5. Solvent Accessible Surface Area Analysis
3.5. Verification of the Inhibitory Bioability of Selected Peptides
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- International Diabetes Federation. IDF Diabetes Atlas; International Diabetes Federation: Brussels, Belgium, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Blahova, J.; Martiniakova, M.; Babikova, M.; Kovacova, V.; Mondockova, V.; Omelka, R. Pharmaceutical Drugs and Natural Therapeutic Products for the Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dirir, A.M.; Daou, M.; Yousef, A.F.; Yousef, L.F. A Review of Alpha-Glucosidase Inhibitors from Plants as Potential Candidates for the Treatment of Type-2 Diabetes. Phytochem. Rev. 2022, 21, 1049–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhameja, M.; Gupta, P. Synthetic Heterocyclic Candidates as Promising α-Glucosidase Inhibitors: An Overview. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 176, 343–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, J.T.; Ross, R.P.; Bolton, D.; Fitzgerald, G.F.; Stanton, C. Bioactive Peptides from Muscle Sources: Meat and Fish. Nutrients 2011, 3, 765–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, Z.; Comer, J.; Li, Y. Bioinformatics Approaches to Discovering Food-Derived Bioactive Peptides: Reviews and Perspectives. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2023, 162, 117051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, J.Z.H.; Mei, Y. Evaluation of the Coupled Two-Dimensional Main Chain Torsional Potential in Modeling Intrinsically Disordered Proteins. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2017, 57, 267–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidal-Limon, A.; Aguilar-Toalá, J.E.; Liceaga, A.M. Integration of Molecular Docking Analysis and Molecular Dynamics Simulations for Studying Food Proteins and Bioactive Peptides. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 934–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Li, H.; Wen, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, J.; Sun, B. Molecular Mechanism for the α-Glucosidase Inhibitory Effect of Wheat Germ Peptides. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 15231–15239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Z.; Yin, Y.; Zhao, W.; Liu, J.; Chen, F. Anti-Diabetic Activity Peptides from Albumin against α-Glucosidase and α-Amylase. Food Chem. 2012, 135, 2078–2085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Yin, Y.; Zhao, W.; Yu, Y.; Liu, B.; Liu, J.; Chen, F. Novel Peptides Derived from Egg White Protein Inhibiting Alpha-Glucosidase. Food Chem. 2011, 129, 1376–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Wang, S.; Wu, J.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Z.; Gan, L.; He, J.; Shi, H.; Hou, J. The Kinetics and Mechanism of α-Glucosidase Inhibition by F5-SP, a Novel Compound Derived from Sericin Peptides. Food Funct. 2017, 8, 323–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mojica, L.; Mejía, E.G. de Optimization of Enzymatic Production of Anti-Diabetic Peptides from Black Bean (Phaseolus Vulgaris L.) Proteins, Their Characterization and Biological Potential. Food Funct. 2016, 7, 713–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Fan, Y.; Xu, F.; Xie, J.; Gao, X.; Li, L.; Tian, Y.; Sheng, J. Characterization of the Structure, Stability, and Activity of Hypoglycemic Peptides from Moringa Oleifera Seed Protein Hydrolysates. Food Funct. 2022, 13, 3481–3494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mu, X.; Wang, R.; Cheng, C.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, W. Preparation, Structural Properties, and in Vitro and in Vivo Activities of Peptides against Dipeptidyl Peptidase IV (DPP-IV) and α-Glucosidase: A General Review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Lu, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Shen, B. Amino Acid Composition and Nutritional Evaluation of Mulberry Leaves. Food Sci. 2015, 36, 225–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, G.; Chai, X.; Hou, G.; Zhao, F.; Meng, Q. Phytochemistry, Bioactivities and Future Prospects of Mulberry Leaves: A Review. Food Chem. 2022, 372, 131335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchetti, L.; Truzzi, E.; Frosi, I.; Papetti, A.; Cappellozza, S.; Saviane, A.; Pellati, F.; Bertelli, D. In Vitro Bioactivity Evaluation of Mulberry Leaf Extracts as Nutraceuticals for the Management of Diabetes Mellitus. Food Funct. 2022, 13, 4344–4359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, C.; Tang, X.; Ren, Y.; Wang, E.; Shi, L.; Wu, X.; Wu, H. Novel Antioxidant Peptides Purified from Mulberry (Morus Atropurpurea Roxb.) Leaf Protein Hydrolysates with Hemolysis Inhibition Ability and Cellular Antioxidant Activity. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 7650–7659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.-L.; Zhao, M.; Xu, J.-Y.; Lv, T.-M.; Liu, X.-C.; Sun, S.; Guan, Q.; Zhou, Z.-C.; Wu, J.; Zhao, M.-Y.; et al. Inhibitory Mechanism of Prenylated Flavonoids Isolated from Mulberry Leaves on α-Glucosidase by Multi-Spectroscopy and Molecular Dynamics Simulation. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2023, 71, 9135–9147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, J. Preparation of Mulberry Leaf protein and Study on the Quality of Leaf Protein. Master’s Theis, Northwest A&F University, Xianyang, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Arrutia, F.; Puente, Á.; Riera, F.A.; Menéndez, C.; González, U.A. Influence of Heat Pre-Treatment on BSA Tryptic Hydrolysis and Peptide Release. Food Chem. 2016, 202, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, B.-B.; Lee, E.-J.; Ramachandraiah, K.; Hong, G.-P. Characterization of Bovine Serum Albumin Hydrolysates Prepared by Subcritical Water Processing. Food Chem. 2019, 278, 203–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, H.-L.; Liu, M.-L.; Li, S.-Y.; Song, W.-Q.; Ouyang, H.; Xiao, Z.-P.; Zhu, H.-L. Identification, Potency Evaluation, and Mechanism Clarification of α-Glucosidase Inhibitors from Tender Leaves of Lithocarpus polystachyus Rehd. Food Chem. 2022, 371, 131128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Liu, X.; Wang, W.; Wang, J.; Li, X.; Sun, S. Preparation and Identification of Peptides with α-Glucosidase Inhibitory Activity from Shiitake Mushroom (Lentinus edodes) Protein. Foods 2023, 12, 2534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, Y.; Liang, K.; Jin, Y.; Zhang, M.; Chen, Y.; Wu, H.; Lai, F. Identification and Characterization of Two Novel α-Glucosidase Inhibitory Oligopeptides from Hemp (Cannabis Sativa L.) Seed Protein. J. Funct. Foods 2016, 26, 439–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.; Ma, H.; Zhou, C.; Luo, M.; Liu, W.; Qu, W.; He, R.; Luo, L.; Yagoub, A.E.-G.A. Effect of Degree of Hydrolysis on the Bioavailability of Corn Gluten Meal Hydrolysates. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2015, 95, 2501–2509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Wu, F.; He, Z.; Fang, X.; Liu, X. Optimization and Molecular Mechanism of Novel α-Glucosidase Inhibitory Peptides Derived from Camellia Seed Cake through Enzymatic Hydrolysis. Foods 2023, 12, 393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Deng, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Liu, L.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, J.; Xie, P.; Huang, L. Screening and Evaluation of Novel α-Glucosidase Inhibitory Peptides from Ginkgo Biloba Seed Cake Based on Molecular Docking Combined with Molecular Dynamics Simulation. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2023, 71, 10326–10337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, G.; Zhao, Q.; Wang, D.; Fan, Y.; Shi, Y.; Huang, A. Novel ACE Inhibitory, Antioxidant and α-Glucosidase Inhibitory Peptides Identified from Fermented Rubing Cheese through Peptidomic and Molecular Docking. LWT 2022, 159, 113196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Matos, F.M.; de Lacerda, J.T.J.G.; Zanetti, G.; de Castro, R.J.S. Production of Black Cricket Protein Hydrolysates with α-Amylase, α-Glucosidase and Angiotensin I-Converting Enzyme Inhibitory Activities Using a Mixture of Proteases. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2022, 39, 102276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Feng, D.; Xiang, Y.; Guo, J.; Huang, N.; Yu, N.; Yang, H.; Liu, C.; Zou, K. Synthesis and Inhibitory Activity of Euparin Derivatives as Potential Dual Inhibitors against α-Glucosidase and Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase 1B (PTP1B). Fitoterapia 2023, 169, 105596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Zhao, H.; Pan, X.; Orfila, C.; Lu, W.; Ma, Y. Preparation of Bioactive Peptides with Antidiabetic, Antihypertensive, and Antioxidant Activities and Identification of α-Glucosidase Inhibitory Peptides from Soy Protein. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 7, 1848–1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramírez Fuentes, L.; Richard, C.; Chen, L. Sequential Alcalase and Flavourzyme Treatment for Preparation of α-Amylase, α-Glucosidase, and Dipeptidyl Peptidase (DPP)-IV Inhibitory Peptides from Oat Protein. J. Funct. Foods 2021, 87, 104829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, M.A.; Bester, M.J.; Neitz, A.W.; Gaspar, A.R.M. Rational in Silico Design of Novel α-Glucosidase Inhibitory Peptides and in Vitro Evaluation of Promising Candidates. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 107, 234–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Wang, D.; Dai, Y.; Zhao, L.; Wang, W.; Ding, X. Identification and Molecular Binding Mechanism of Novel α-Glucosidase Inhibitory Peptides from Hot-Pressed Peanut Meal Protein Hydrolysates. Foods 2023, 12, 663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ernits, K.; Kjeldsen, C.; Persson, K.; Grigor, E.; Alamäe, T.; Visnapuu, T. Structural Insight into a Yeast Maltase—The BaAG2 from Blastobotrys Adeninivorans with Transglycosylating Activity. J. Fungi 2021, 7, 816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.; Xu, S.; He, R.; Liang, G. Application of Molecular Simulation Methods in Food Science: Status and Prospects. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2023, 71, 2684–2703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebenezer, O.; Damoyi, N.; Shapi, M.; Wong, G.K.-S.; Tuszynski, J.A. A Molecular Docking Study Reveals That Short Peptides Induce Conformational Changes in the Structure of Human Tubulin Isotypes αβI, αβII, αβIII and αβIV. J. Funct. Biomater. 2023, 14, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Fan, R.; Meng, T.; Wang, L. Exploration of the Inhibitory Mechanisms of Trans-Polydatin/Resveratrol on α-Glucosidase by Multi-Spectroscopic Analysis, in Silico Docking and Molecular Dynamics Simulation. Spectrochim. Acta. A. Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2023, 299, 122866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chouhan, H.; Purohit, A.; Ram, H.; Chowdhury, S.; Kashyap, P.; Panwar, A.; Kumar, A. The Interaction Capabilities of Phytoconstituents of Ethanolic Seed Extract of Cumin (Cuminum cyminum L.) with HMG-CoA Reductase to Subside the Hypercholesterolemia: A Mechanistic Approach. Food Front. 2022, 3, 300–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Chi, H.; Ma, S.; Zhao, L.; Cai, S. Identification of Novel α-Glucosidase Inhibitory Peptides in Rice Wine and Their Antioxidant Activities Using in Silico and in Vitro Analyses. LWT 2023, 178, 114629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Wei, G.; Li, K.; Duan, S.; Ye, R.; Huang, A. Identification and Molecular Docking of Novel α-Glucosidase Inhibitory Peptides from Hydrolysates of Binglangjiang Buffalo Casein. LWT 2022, 156, 113062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yap, P.G.; Gan, C.Y. In Vivo Challenges of Anti-Diabetic Peptide Therapeutics: Gastrointestinal Stability, Toxicity and Allergenicity. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 105, 161–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsen, J.V.; Ong, S.-E.; Mann, M. Trypsin Cleaves Exclusively C-Terminal to Arginine and Lysine Residues. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2004, 3, 608–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mudgil, P.; Kamal, H.; Priya Kilari, B.; Mohd Salim, M.A.S.; Gan, C.-Y.; Maqsood, S. Simulated Gastrointestinal Digestion of Camel and Bovine Casein Hydrolysates: Identification and Characterization of Novel Anti-Diabetic Bioactive Peptides. Food Chem. 2021, 353, 129374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, Z.; Yan, R.; Jiang, Y.; Feng, S.; Sun, H.; Sun, J.; Zhao, D.; Li, H.; Wang, B.; Zhang, N. Identification of Peptides in Qingke Baijiu and Evaluation of Its Angiotensin Converting Enzyme (ACE) Inhibitory Activity and Stability. Food Chem. 2022, 395, 133551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Deng, Y.; Xie, P.; Liu, L.; Zhang, C.; Cheng, J.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Huang, L.; Jiang, J. Novel Bioactive Peptides from Ginkgo Biloba Seed Protein and Evaluation of Their α-Glucosidase Inhibition Activity. Food Chem. 2023, 404, 134481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Coefficient Source | Sum of Squares | Degrees of Freedom | Mean Square | F-Value | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Models | 76.62 | 9 | 8.51 | 78.44 | <0.0001 |
| A-Temperature | 5.97 | 1 | 5.97 | 55.00 | 0.0001 |
| B-Time | 8.82 | 1 | 8.82 | 81.27 | <0.0001 |
| C-Enzyme Amount | 7.94 | 1 | 7.94 | 73.16 | <0.0001 |
| AB | 2.74 | 1 | 2.74 | 25.24 | 0.0015 |
| AC | 0.026 | 1 | 0.026 | 0.24 | 0.6420 |
| BC | 0.087 | 1 | 0.087 | 0.80 | 0.4003 |
| A2 | 35.28 | 1 | 35.28 | 325.04 | <0.0001 |
| B2 | 7.25 | 1 | 7.25 | 66.78 | <0.0001 |
| C2 | 4.42 | 1 | 4.42 | 40.72 | 0.0004 |
| Residual sum of squares | 0.76 | 7 | 0.11 | ||
| Misfit term | 0.46 | 3 | 0.15 | 2.08 | 0.2458 |
| Pure error | 0.30 | 4 | 0.074 | ||
| Total deviation | 77.37 | 16 | |||
| R2 = 0.9902 | R2adj = 0.9776 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Deng, F.; Liang, Y.; Lei, Y.; Xiong, S.; Rong, J.; Hu, Y. Development and Identification of Novel α-Glucosidase Inhibitory Peptides from Mulberry Leaves. Foods 2023, 12, 3917. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12213917
Deng F, Liang Y, Lei Y, Xiong S, Rong J, Hu Y. Development and Identification of Novel α-Glucosidase Inhibitory Peptides from Mulberry Leaves. Foods. 2023; 12(21):3917. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12213917
Chicago/Turabian StyleDeng, Fanghui, Yihao Liang, Yuelei Lei, Shanbai Xiong, Jianhua Rong, and Yang Hu. 2023. "Development and Identification of Novel α-Glucosidase Inhibitory Peptides from Mulberry Leaves" Foods 12, no. 21: 3917. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12213917
APA StyleDeng, F., Liang, Y., Lei, Y., Xiong, S., Rong, J., & Hu, Y. (2023). Development and Identification of Novel α-Glucosidase Inhibitory Peptides from Mulberry Leaves. Foods, 12(21), 3917. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12213917