Waste Orange Peels as a Source of Cellulose Nanocrystals and Their Use for the Development of Nanocomposite Films
Abstract
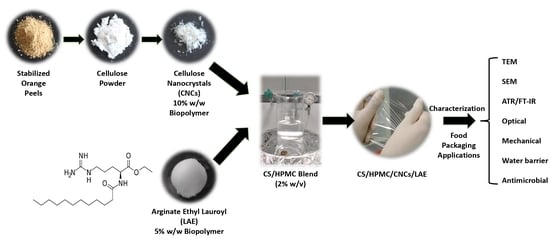
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Reagents
2.2. Pre-Treatment and Chemical Composition Analysis of Orange Peels
2.3. Cellulose Isolation
2.4. Production of Cellulose Nanocrystals (CNCs) and Yield Calculation
2.5. Preparation of Film-Forming Solutions and Nanocomposite Films
2.6. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM) and X-ray Diffraction (XRD)
2.7. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
2.8. Attenuated Total Reflection (ATR)/Fourier-Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FT-IR)
2.9. Thickness and Mechanical Properties
2.10. UV-Vis Light Transmittance, Opacity, and Color
2.11. Water Content (WC) and Water Solubility (WS)
2.12. Water Vapor Permeability (WVP)
2.13. In Vitro Antimicrobial Activity
2.14. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Chemical Analysis of Orange Peel, CNC Yield, and Visual Appearance
3.2. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM) and X-ray Diffraction (XRD)
3.3. Characterization of CS/HPMC Nanocomposite Films
3.3.1. Surface and Cross-Section Morphology
3.3.2. ATR/FT-IR Spectroscopy
3.3.3. Thickness and Mechanical Properties
3.3.4. Color
3.3.5. UV Barrier, Light Transmittance, and Opacity Value
3.3.6. Water Content, Water Solubility, and Water Vapor Permeability
3.3.7. In Vitro Antimicrobial Activity
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Amjadi, S.; Almasi, H.; Ghadertaj, A.; Mehryar, L. Whey Protein Isolate-based Films Incorporated with Nanoemulsions of Orange Peel (Citrus Sinensis) Essential Oil: Preparation and Characterization. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2021, 45, e15196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patanè, C.; Malvuccio, A.; Saita, A.; Rizzarelli, P.; Siracusa, L.; Rizzo, V.; Muratore, G. Nutritional Changes during Storage in Fresh-Cut Long Storage Tomato as Affected by Biocompostable Polylactide and Cellulose Based Packaging. LWT 2019, 101, 618–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Gaikwad, K.K.; Lee, Y.S. Antimicrobial and Antioxidant Properties of Polyvinyl Alcohol Bio Composite Films Containing Seaweed Extracted Cellulose Nano-Crystal and Basil Leaves Extract. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 107, 1879–1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bigi, F.; Haghighi, H.; Siesler, H.W.; Licciardello, F.; Pulvirenti, A. Characterization of Chitosan-Hydroxypropyl Methylcellulose Blend Films Enriched with Nettle or Sage Leaf Extract for Active Food Packaging Applications. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 120, 106979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, W.; Zhao, Y.; Xiao, D.; Cheng, J.; Zhao, J. A Biodegradable Water-Triggered Chitosan/Hydroxypropyl Methylcellulose Pesticide Mulch Film for Sustained Control of Phytophthora Sojae in Soybean (Glycine Max L. Merr.). J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 245, 118943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Filippo, M.F.; Dolci, L.S.; Liccardo, L.; Bigi, A.; Bonvicini, F.; Gentilomi, G.A.; Passerini, N.; Panzavolta, S.; Albertini, B. Cellulose Derivatives-Snail Slime Films: New Disposable Eco-Friendly Materials for Food Packaging. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 111, 106247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-González, L.; Vargas, M.; González-Martínez, C.; Chiralt, A.; Cháfer, M. Characterization of Edible Films Based on Hydroxypropylmethylcellulose and Tea Tree Essential Oil. Food Hydrocoll. 2009, 23, 2102–2109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, T.A.; Cabral, B.R.; de Oliveira, A.C.S.; Dias, M.V.; de Oliveira, C.R.; Borges, S.V. Release of Papain Incorporated in Chitosan Films Reinforced with Cellulose Nanofibers. Food Process. Preserv. 2021, 45, e15900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huq, T.; Khan, A.; Brown, D.; Dhayagude, N.; He, Z.; Ni, Y. Sources, Production and Commercial Applications of Fungal Chitosan: A Review. J. Bioresour. Bioprod. 2022, 7, 85–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madni, A.; Kousar, R.; Naeem, N.; Wahid, F. Recent Advancements in Applications of Chitosan-Based Biomaterials for Skin Tissue Engineering. J. Bioresour. Bioprod. 2021, 6, 11–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, B.R.; Facchi, S.P.; de Oliveira, A.C.; Nunes, C.S.; Souza, P.R.; Vilsinski, B.H.; Popat, K.C.; Kipper, M.J.; Muniz, E.C.; Martins, A.F. Bactericidal Pectin/Chitosan/Glycerol Films for Food Pack Coatings: A Critical Viewpoint. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rotta, J.; Ozório, R.Á.; Kehrwald, A.M.; de Oliveira Barra, G.M.; de Melo Castanho Amboni, R.D.; Barreto, P.L.M. Parameters of Color, Transparency, Water Solubility, Wettability and Surface Free Energy of Chitosan/Hydroxypropylmethylcellulose (HPMC) Films Plasticized with Sorbitol. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2009, 29, 619–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Feng, H.; Wu, M.; Chen, L.; Xia, W.; Zhang, W. Preparation and Characterization of Arginine-Modified Chitosan/Hydroxypropyl Methylcellose Antibacterial Film. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 145, 750–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doh, H.; Dunno, K.D.; Whiteside, W.S. Cellulose Nanocrystal Effects on the Biodegradability with Alginate and Crude Seaweed Extract Nanocomposite Films. Food Biosci. 2020, 38, 100795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coelho, C.C.d.S.; Silva, R.B.S.; Carvalho, C.W.P.; Rossi, A.L.; Teixeira, J.A.; Freitas-Silva, O.; Cabral, L.M.C. Cellulose Nanocrystals from Grape Pomace and Their Use for the Development of Starch-Based Nanocomposite Films. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 159, 1048–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Shi, H.; He, Y.; Fei, X.; Peng, L. Preparation and Characterization of Carboxymethyl Cellulose-Based Composite Films Reinforced by Cellulose Nanocrystals Derived from Pea Hull Waste for Food Packaging Applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 164, 4104–4112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pezo, D.; Navascués, B.; Salafranca, J.; Nerín, C. Analytical Procedure for the Determination of Ethyl Lauroyl Arginate (LAE®) to Assess the Kinetics and Specific Migration from a New Antimicrobial Active Food Packaging. Anal. Chim. Acta 2012, 745, 92–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Duan, G.; Zhang, G.; Yang, H.; He, S.; Jiang, S. Electrospun Functional Materials toward Food Packaging Applications: A Review. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, H.; Ou, S.; Huang, Y.; Huang, H. Utilization of Pineapple Peel for Production of Nanocellulose and Film Application. Cellulose 2018, 25, 1743–1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanjanzadeh, H.; Behrooz, R.; Bahramifar, N.; Gindl-Altmutter, W.; Bacher, M.; Edler, M.; Griesser, T. Surface Chemical Functionalization of Cellulose Nanocrystals by 3-Aminopropyltriethoxysilane. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 106, 1288–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Han, X.; Zhang, C.; Liu, K.; Duan, G. Source of Nanocellulose and Its Application in Nanocomposite Packaging Material: A Review. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 3158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coelho, C.C.S.; Michelin, M.; Cerqueira, M.A.; Gonçalves, C.; Tonon, R.V.; Pastrana, L.M.; Freitas-Silva, O.; Vicente, A.A.; Cabral, L.M.C.; Teixeira, J.A. Cellulose Nanocrystals from Grape Pomace: Production, Properties and Cytotoxicity Assessment. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 192, 327–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, F.; Hsieh, Y.-L. Cellulose Nanocrystal Isolation from Tomato Peels and Assembled Nanofibers. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 122, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A.; Negi, Y.S.; Choudhary, V.; Bhardwaj, N.K. Sugarcane Bagasse: A Promising Source for the Production of Nanocellulose. J. Polym. Compos. 2014, 2, 23–27. [Google Scholar]
- Tibolla, H.; Pelissari, F.M.; Menegalli, F.C. Cellulose Nanofibers Produced from Banana Peel by Chemical and Enzymatic Treatment. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 59, 1311–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naz, S.; Ahmad, N.; Akhtar, J.; Ahmad, N.M.; Ali, A.; Zia, M. Management of Citrus Waste by Switching in the Production of Nanocellulose. IET Nanobiotechnology 2016, 10, 395–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melikoğlu, A.Y.; Bilek, S.E.; Cesur, S. Optimum Alkaline Treatment Parameters for the Extraction of Cellulose and Production of Cellulose Nanocrystals from Apple Pomace. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 215, 330–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodsamran, P.; Sothornvit, R. Extraction of Phenolic Compounds from Lime Peel Waste Using Ultrasonic-Assisted and Microwave-Assisted Extractions. Food Biosci. 2019, 28, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becerril, R.; Manso, S.; Nerin, C.; Gómez-Lus, R. Antimicrobial Activity of Lauroyl Arginate Ethyl (LAE®), against Selected Food-Borne Bacteria. Food Control 2013, 32, 404–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haghighi, H.; Leugoue, S.K.; Pfeifer, F.; Siesler, H.W.; Licciardello, F.; Fava, P.; Pulvirenti, A. Development of Antimicrobial Films Based on Chitosan-Polyvinyl Alcohol Blend Enriched with Ethyl Lauroyl Arginate (LAE®) for Food Packaging Applications. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 100, 105419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Official Methods of Analysis, AOAC International 2012, 19th ed.; AOAC International: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 2012.
- Van Soest, P.J. Use of Detergents in the Analysis of Fibrous Feeds. II. A Rapid Method for the Determination of Fiber and Lignin. J. Assoc. Off. Agric. Chem. 1963, 46, 825–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leceta, I.; Guerrero, P.; Ibarburu, I.; Dueñas, M.T.; de la Caba, K. Characterization and Antimicrobial Analysis of Chitosan-Based Films. J. Food Eng. 2013, 116, 889–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.Y.; Garcia, C.V.; Shin, G.H.; Kim, J.T. Antibacterial and Antioxidant Properties of Hydroxypropyl Methylcellulose-Based Active Composite Films Incorporating Oregano Essential Oil Nanoemulsions. LWT 2019, 106, 164–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirviö, J.A.; Visanko, M.; Heiskanen, J.P.; Liimatainen, H. UV-Absorbing Cellulose Nanocrystals as Functional Reinforcing Fillers in Polymer Nanocomposite Films. J. Mater. Chem. A 2016, 4, 6368–6375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, S.; French, A.D.; Condon, B.D.; Concha, M. Segal Crystallinity Index Revisited by the Simulation of X-Ray Diffraction Patterns of Cotton Cellulose Iβ and Cellulose II. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 135, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oudiani, A.E.; Chaabouni, Y.; Msahli, S.; Sakli, F. Crystal Transition from Cellulose I to Cellulose II in NaOH Treated Agave Americana L. Fibre. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 86, 1221–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haghighi, H.; Gullo, M.; La China, S.; Pfeifer, F.; Siesler, H.W.; Licciardello, F.; Pulvirenti, A. Characterization of Bio-Nanocomposite Films Based on Gelatin/Polyvinyl Alcohol Blend Reinforced with Bacterial Cellulose Nanowhiskers for Food Packaging Applications. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 113, 106454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Standard Test Method for Tensile Properties of Thin Plastic Sheeting; ASTM International Designation D882-12; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2015.
- Haghighi, H.; De Leo, R.; Bedin, E.; Pfeifer, F.; Siesler, H.W.; Pulvirenti, A. Comparative Analysis of Blend and Bilayer Films Based on Chitosan and Gelatin Enriched with LAE® (Lauroyl Arginate Ethyl) with Antimicrobial Activity for Food Packaging Applications. Food Packag. Shelf Life 2019, 19, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gontard, N.; Guilbert, S.; Cuq, J.-L. Edible Wheat Gluten Films: Influence of the Main Process Variables on Film Properties Using Response Surface Methodology. J. Food Sci. 1992, 57, 190–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, P.; Hsieh, Y.-L. Preparation and Characterization of Cellulose Nanocrystals from Rice Straw. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 87, 564–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdul Khalil, H.P.S.; Davoudpour, Y.; Islam, M.N.; Mustapha, A.; Sudesh, K.; Dungani, R.; Jawaid, M. Production and Modification of Nanofibrillated Cellulose Using Various Mechanical Processes: A Review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 99, 649–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oun, A.A.; Rhim, J.-W. Isolation of Cellulose Nanocrystals from Grain Straws and Their Use for the Preparation of Carboxymethyl Cellulose-Based Nanocomposite Films. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 150, 187–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, J.; Li, J.; Xu, J.; Xiang, Z.; Mo, L. Research on Cellulose Nanocrystals Produced from Cellulose Sources with Various Polymorphs. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 33486–33493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariño, M.; Lopes da Silva, L.; Durán, N.; Tasic, L. Enhanced Materials from Nature: Nanocellulose from Citrus Waste. Molecules 2015, 20, 5908–5923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bigi, F.; Haghighi, H.; De Leo, R.; Ulrici, A.; Pulvirenti, A. Multivariate Exploratory Data Analysis by PCA of the Combined Effect of Film-Forming Composition, Drying Conditions, and UV-C Irradiation on the Functional Properties of Films Based on Chitosan and Pectin. LWT 2021, 137, 110432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, S.M.; Ferreira, D.P.; Teixeira, P.; Ballesteros, L.F.; Teixeira, J.A.; Fangueiro, R. Active Natural-Based Films for Food Packaging Applications: The Combined Effect of Chitosan and Nanocellulose. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 177, 241–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dechant, J. Ultrarotspektroskopische Untersuchungen an Polymeren; De Gruyter: Berlin, Germany, 1973; ISBN 9783112480878. [Google Scholar]
- Li, N.; Yang, X.; Lin, D. Development of Bacterial Cellulose Nanofibers/Konjac Glucomannan-Based Intelligent Films Loaded with Curcumin for the Fresh-Keeping and Freshness Monitoring of Fresh Beef. Food Packag. Shelf Life 2022, 34, 100989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kale, R.D.; Gorade, V.G. Potential Application of Medical Cotton Waste for Self-Reinforced Composite. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 124, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perumal, A.B.; Nambiar, R.B.; Sellamuthu, P.S.; Sadiku, E.R.; Li, X.; He, Y. Extraction of Cellulose Nanocrystals from Areca Waste and Its Application in Eco-Friendly Biocomposite Film. Chemosphere 2022, 287, 132084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamarra, A.; Missagia, B.; Urpí, L.; Morató, J.; Muñoz-Guerra, S. Ionic Coupling of Hyaluronic Acid with Ethyl N-Lauroyl l-Arginate (LAE®): Structure, Properties and Biocide Activity of Complexes. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 197, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, O.; Gil, À.; Atarés, L.; Chiralt, A. Active Starch-Gelatin Films for Shelf-Life Extension of Marinated Salmon. LWT 2017, 84, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Du, M.; Liu, H.; Zhang, K.; Xu, X.; Liu, K.; Tu, J.; Liu, Q. Chitosan Films Incorporating Litchi Peel Extract and Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles and Their Application as Coatings on Watercored Apples. Prog. Org. Coat. 2021, 151, 106103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, J.; Ren, X.; Zhu, S.; Gao, Y. Cellulose Nanocrystals from Pomegranate Peel: Isolation, Characterization, and Its Reinforcement for Chitosan Film. J. Mater. Sci. 2022, 57, 11062–11076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, T.A.; Oliveira, A.C.S.; Lago, A.M.T.; Yoshida, M.I.; Dias, M.V.; Borges, S.V. Properties of Chitosan–Papain Biopolymers Reinforced with Cellulose Nanofibers. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2021, 45, e15740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.; Rhim, J.-W. Gelatin/Cellulose Nanofiber-Based Functional Films Added with Mushroom-Mediated Sulfur Nanoparticles for Active Packaging Applications. J. Nanostructure Chem. 2022, 12, 979–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaikwad, K.K.; Lee, S.M.; Lee, J.S.; Lee, Y.S. Development of Antimicrobial Polyolefin Films Containing Lauroyl Arginate and Their Use in the Packaging of Strawberries. Food Meas. 2017, 11, 1706–1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, S.F.; Rezaei, M.; Zandi, M.; Farahmandghavi, F. Fabrication of Bio-Nanocomposite Films Based on Fish Gelatin Reinforced with Chitosan Nanoparticles. Food Hydrocoll. 2015, 44, 172–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukyai, P.; Anongjanya, P.; Bunyahwuthakul, N.; Kongsin, K.; Harnkarnsujarit, N.; Sukatta, U.; Sothornvit, R.; Chollakup, R. Effect of Cellulose Nanocrystals from Sugarcane Bagasse on Whey Protein Isolate-Based Films. Food Res. Int. 2018, 107, 528–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.-F.; Shankar, S.; Rhim, J.-W. Properties of Alginate-Based Films Reinforced with Cellulose Fibers and Cellulose Nanowhiskers Isolated from Mulberry Pulp. Food Hydrocoll. 2017, 63, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Willis, S.; Jordan, K.; Sismour, E. Chitosan Nanocomposite Films Incorporating Cellulose Nanocrystals and Grape Pomace Extracts. Packag. Technol. Sci. 2018, 31, 631–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.A.S.S.; Jimat, D.N.; Nawawi, W.M.F.W.; Sulaiman, S. Antibacterial, Mechanical and Thermal Properties of PVA/Starch Composite Film Reinforced with Cellulose Nanofiber of Sugarcane Bagasse. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2022, 47, 5747–5754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Ren, T.; Harper, D.; Li, M. Development of Antimicrobial Films with Cinnamaldehyde Stabilized by Ethyl Lauroyl Arginate and Cellulose Nanocrystals. Food Packag. Shelf Life 2022, 33, 100886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jantrawut, P.; Chaiwarit, T.; Jantanasakulwong, K.; Branchais, C.H.; Chambin, O. Effect of Plasticizer Type on Tensile Property and In Vitro Indomethacin Release of Thin Films Based on Low-Methoxyl Pectin. Polymers 2017, 9, 289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, A.; Gastelú, G.; Barrera, G.N.; Ribotta, P.D.; Álvarez Igarzabal, C.I. Preparation and Characterization of Soy Protein Films Reinforced with Cellulose Nanofibers Obtained from Soybean By-Products. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 89, 758–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, O.; Díaz, R.; Atarés, L.; Chiralt, A. Influence of the Processing Method and Antimicrobial Agents on Properties of Starch-Gelatin Biodegradable Films: Starch-Gelatin Biodegradable Films. Polym. Int. 2016, 65, 905–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, Y.; Li, F.; Jiao, X.; Li, Q. The Effects of Cellulose Nanocrystal and Cellulose Nanofiber on the Properties of Pumpkin Starch-Based Composite Films. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 192, 444–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, S.F.; Ghaderi, J.; Gómez-Guillén, M.C. Trans-Cinnamaldehyde-Doped Quadripartite Biopolymeric Films: Rheological Behavior of Film-Forming Solutions and Biofunctional Performance of Films. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 112, 106339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadi, A.; Nawab, A.; Alam, F.; Zehra, K. Physical, Mechanical, Optical, Barrier, and Antioxidant Properties of Sodium Alginate–Aloe Vera Biocomposite Film. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2021, 45, e15444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguirre-Loredo, R.Y.; Rodríguez-Hernández, A.I.; Morales-Sánchez, E.; Gómez-Aldapa, C.A.; Velazquez, G. Effect of Equilibrium Moisture Content on Barrier, Mechanical and Thermal Properties of Chitosan Films. Food Chem. 2016, 196, 560–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noshirvani, N.; Hong, W.; Ghanbarzadeh, B.; Fasihi, H.; Montazami, R. Study of Cellulose Nanocrystal Doped Starch-Polyvinyl Alcohol Bionanocomposite Films. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 107, 2065–2074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matta, E.; Bertola, N. Development and Characterization of High Methoxyl Pectin Film by Using Isomalt as Plasticizer. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2020, 44, e14568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cazón, P.; Velazquez, G.; Ramírez, J.A.; Vázquez, M. Polysaccharide-Based Films and Coatings for Food Packaging: A Review. Food Hydrocoll. 2017, 68, 136–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Zhong, Q. Physical and Antimicrobial Properties of Chitosan Films Incorporated with Lauric Arginate, Cinnamon Oil, and Ethylenediaminetetraacetate. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 65, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muriel-Galet, V.; López-Carballo, G.; Gavara, R.; Hernández-Muñoz, P. Antimicrobial Effectiveness of Lauroyl Arginate Incorporated into Ethylene Vinyl Alcohol Copolymers to Extend the Shelf-Life of Chicken Stock and Surimi Sticks. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2015, 8, 208–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.; Davidson, P.M.; Critzer, F.; Zhong, Q. Antimicrobial Activities of Lauric Arginate and Cinnamon Oil Combination against Foodborne Pathogens: Improvement by Ethylenediaminetetraacetate and Possible Mechanisms. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 72, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, S.G.-G.; Almasi, H. Physical Characteristics, Release Properties, and Antioxidant and Antimicrobial Activities of Whey Protein Isolate Films Incorporated with Thyme (Thymus Vulgaris L.) Extract-Loaded Nanoliposomes. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2018, 11, 1552–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muriel-Galet, V.; López-Carballo, G.; Gavara, R.; Hernández-Muñoz, P. Antimicrobial Food Packaging Film Based on the Release of LAE® from EVOH. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2012, 157, 239–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alwi, N.A.; Ali, A. Reduction of Escherichia coli O157, Listeria monocytogenes and Salmonella enterica Sv. Typhimurium Populations on Fresh-Cut Bell Pepper Using Gaseous Ozone. Food Control 2014, 46, 304–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Film Sample | Crystallinity Index % |
|---|---|
| CS/HPMC | 7.65 ± 0.06 a |
| CS/HPMC/LAE® | 7.42 ± 0.13 a |
| CS/HPMC/CNCs | 24.96 ± 1.05 b |
| CS/HPMC/CNCs/LAE® | 26.81 ± 1.36 b |
| CNC orange peel | 61.93 ± 3.46 c |
| Film Sample | Thickness (µm) | TS (MPa) | E (%) | YM (MPa) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CS/HPMC | 32.7 ± 2.0 a | 17.5 ± 1.0 a | 18.9 ± 0.9 a | 644.7 ± 25.2 c |
| CS/HPMC/CNCs | 35.3 ± 1.8 b | 25.4 ± 2.7 b | 19.9 ± 1.6 a | 705.8 ± 57.2 d |
| CS/HPMC/LAE® | 34.1 ± 2.6 ab | 15.1 ± 0.9 a | 23.9 ± 1.0 b | 407.0 ± 28.9 a |
| CS/HPMC/CNCs/LAE® | 38.1 ± 1.8 c | 26.4 ± 1.4 b | 27.8 ± 1.9 c | 529.1 ± 48.8 b |
| Film Sample | Color Parameters | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| L* | a* | b* | ΔE | |
| CS/HPMC | 97.2 ± 0.3 c | −1.1 ± 0.1 a | 7.2 ± 0.6 a | 7.5 ± 0.6 a |
| CS/HPMC/CNCs | 95.6 ± 0.2 a | −0.9 ± 0.06 b | 10.2 ± 0.4 c | 10.8 ± 0.4 b |
| CS/HPMC/LAE® | 97.5 ± 0.3 c | −0.8 ± 0.06 c | 7.5 ± 0.6 a | 7.8 ± 0.7 a |
| CS/HPMC/CNCs/LAE® | 96.3 ± 0.2 b | −0.9 ± 0.03 b | 8.9 ± 0.8 b | 10.0 ± 1.0 b |
| Film Sample | Light Transmission (%) at Different Wavelengths (nm) | Opacity (600 nm) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 200 | 280 | 350 | 400 | 500 | 600 | 700 | 800 | ||
| CS/HPMC | <0.1 | 25.5 | 45.7 | 69.2 | 83.2 | 87.2 | 89.4 | 90.2 | 1.5 ± 0.1 a |
| CS/HPMC/CNCs | <0.1 | 12.4 | 31.8 | 54.4 | 67.2 | 73.1 | 76.2 | 78.0 | 3.1 ± 0.2 d |
| CS/HPMC/LAE® | <0.1 | 26.8 | 51.2 | 71.7 | 83.7 | 87.4 | 88.7 | 89.4 | 1.9 ± 0.06 b |
| CS/HPMC/CNCs/LAE® | <0.1 | 22.3 | 44.6 | 64.4 | 76.8 | 81.2 | 83.8 | 85.1 | 2.4 ± 0.2 c |
| Film Sample | WC (%) | WS (%) | WVP (g·mm/kPa·Day·m2) |
|---|---|---|---|
| CS/HPMC | 22.6 ± 2.6 b | 52.5 ± 1.8 b | 7.2 ± 0.5 b |
| CS/HPMC/CNCs | 19.7 ± 0.8 a | 35.6 ± 0.8 a | 5.8 ± 0.3 a |
| CS/HPMC/LAE® | 23.9 ± 1.1 b | 62.5 ± 1.2 d | 9.5 ± 0.7 c |
| CS/HPMC/CNCs/LAE® | 22.8 ± 0.7 b | 56.9 ± 1.0 c | 6.8 ± 0.5 ab |
| Film Sample | S. enterica | E. coli | L. monocytogenes | P. fluorescens |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CS/HPMC | N.D. | N.D. | N.D. | N.D. |
| CS/HPMC/CNCs | N.D. | N.D. | N.D. | N.D. |
| CS/HPMC/LAE® | 0.9 ± 0.09 bA | 4.4 ± 0.4 bB | 6.7 ± 0.6 aC | 8.5 ± 0.7 bD |
| CS/HPMC/CNCs/LAE® | 0.5 ± 0.07 aA | 3.4 ± 0.4 aB | 6.5 ± 0.6 aD | 5.7 ± 0.4 aC |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bigi, F.; Maurizzi, E.; Haghighi, H.; Siesler, H.W.; Licciardello, F.; Pulvirenti, A. Waste Orange Peels as a Source of Cellulose Nanocrystals and Their Use for the Development of Nanocomposite Films. Foods 2023, 12, 960. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12050960
Bigi F, Maurizzi E, Haghighi H, Siesler HW, Licciardello F, Pulvirenti A. Waste Orange Peels as a Source of Cellulose Nanocrystals and Their Use for the Development of Nanocomposite Films. Foods. 2023; 12(5):960. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12050960
Chicago/Turabian StyleBigi, Francesco, Enrico Maurizzi, Hossein Haghighi, Heinz Wilhelm Siesler, Fabio Licciardello, and Andrea Pulvirenti. 2023. "Waste Orange Peels as a Source of Cellulose Nanocrystals and Their Use for the Development of Nanocomposite Films" Foods 12, no. 5: 960. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12050960
APA StyleBigi, F., Maurizzi, E., Haghighi, H., Siesler, H. W., Licciardello, F., & Pulvirenti, A. (2023). Waste Orange Peels as a Source of Cellulose Nanocrystals and Their Use for the Development of Nanocomposite Films. Foods, 12(5), 960. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12050960