Revelation for the Influence Mechanism of Long-Chain Fatty Acid Ethyl Esters on the Baijiu Quality by Multicomponent Chemometrics Combined with Modern Flavor Sensomics
Abstract
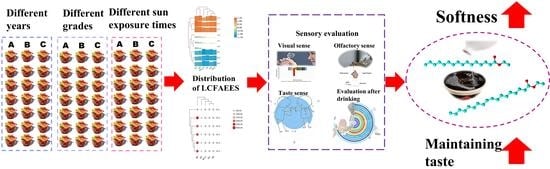
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Standard Information
2.2. Baijiu Sample Information
2.3. Pretreatment Methods for Baijiu Samples
2.4. Analytical Parameters with GC-MS Detection
2.5. Qualitative Analysis of LCFAEEs
2.6. Quantitative Analysis of LCFAEEs
2.7. Modern Flavor Sensomics Evaluation
2.7.1. Baijiu Evaluation Environment and Conditions
2.7.2. Descriptive Profile Tests
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Parameter Description
3.2. Analysis of the Distribution for Six LCFAEEs in Baijiu Produced Different Years
3.3. Analysis of the Distribution of Six LCFAEEs in Different Grades of Baijiu
3.4. Analysis of the Distribution of Six LCFAEEs in Baijiu under Different Sun Exposure Times
3.5. Modern Flavor Sensomics Analysis of Different Baijiu Samples
3.5.1. Visual Sense
3.5.2. Olfactory Sense
3.5.3. Taste Sense
3.5.4. Evaluation after Drinking
3.5.5. Comprehensive Analysis of Sensory Evaluation for Baijiu Samples
3.6. Baijiu Sample Addition Experiment
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, J.; Chen, H.; Wu, Y.; Zhao, D. Uncover the flavor code of strong-aroma baijiu: Research progress on the revelation of aroma compounds in strong-aroma baijiu by means of modern separation technology and molecular sensory evaluation. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2022, 109, 104499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Y.; Zhao, W.; Xiao, Z.; Zhu, J.; Xiong, W.; Chen, F. Characterization of aroma compounds and effects of amino acids on the release of esters in laimao baijiu. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2022, 103, 1784–1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yunsong, J.; Jinyuan, S.; Zhongtian, Y.; Hehe, L.; Xiaotao, S.; Fuping, Z. Evaluation of antioxidant peptides generated from jiuzao (residue after baijiu distillation) protein hydrolysates and their effect of enhancing healthy value of chinese baijiu. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2020, 100, 59–73. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, J.; Tian, W.; Zhao, D. Research progress of trace components in sesame-aroma type of baijiu. Food Res. Int. 2020, 137, 109695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin-Yuan, S.; Zhong-Tian, Y.; Dong-Rui, Z.; Bao-Guo, S.; Fu-Ping, Z. Qualitative and quantitative research of propyl lactate in brewed alcoholic beverages. Int. J. Food Prop. 2018, 21, 1351–1361. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, D.; Shi, D.; Sun, J.; Li, A.; Sun, B.; Zhao, M.; Chen, F.; Sun, X.; Li, H.; Huang, M.; et al. Characterization of key aroma compounds in gujinggong chinese baijiu by gas chromatography-olfactometry, quantitative measurements, and sensory evaluation. Food Res. Int. 2018, 105, 616–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Zhao, J.; Liu, X.; Zhang, C.; Zhao, Z.; Li, X.; Sun, B. Flavor mystery of chinese traditional fermented baijiu: The great contribution of ester compounds. Food Chem. 2022, 369, 130920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Sun, B. Effect of fermentation processing on the flavor of baijiu. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 5425–5432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, L.; Tan, Y.; Wang, H.; Yang, F.; Chen, L.; Hao, F.; Lv, X.; Du, H.; Xu, Y. Effect of pichia on shaping the fermentation microbial community of sauce-flavor baijiu. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2021, 336, 108898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Q.; Sun, J.; Wang, B.; Sun, B. Wine, beer and chinese baijiu in relation to cardiovascular health: The impact of moderate drinking. Food Sci. Human Wellness 2023, 12, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, Z.; Hao, H.; Yan, R.; Wang, X.; Wang, B.; Sun, J.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, B. Individualization of chinese alcoholic beverages: Feasibility towards a regulation of organic acids. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 172, 114168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Q.; Meng, L.; Mei, Z.; Liu, Q.; Chai, L.; Zhong, X.; Zheng, L.; Liu, G.; Wang, S.; Shen, C.; et al. Volatile compound abundance correlations provide a new insight into odor balances in sauce-aroma baijiu. Foods 2022, 11, 3916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Hou, Y.; Chen, H.; Wang, J.; Zhang, C.; Zhao, Z.; Ao, R.; Huang, H.; Hong, J.; Zhao, D.; et al. “key factor“ for baijiu quality: Research progress on acid substances in baijiu. Foods 2022, 11, 2959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, W.; Du, A.; Fan, Z.; Wang, Y.; Shi, L. Effects of short-chain peptides on the flavor profile of baijiu by the density functional theory: Peptidomics, sensomics, flavor reconstitution, and sensory evaluation. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 9547–9556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Qiao, Z.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, X.; Sun, X.; Han, S.; Pan, C. Comprehensive evaluation of luzhou-flavor liquor quality based on fuzzy mathematics and principal component analysis. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 10, 1780–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhao, J.; Huang, H.; Wu, M.; Li, X.; Li, W.; Sun, X.; Sun, B. An efficient phthalate ester-degrading bacillus subtilis: Degradation kinetics, metabolic pathway, and catalytic mechanism of the key enzyme. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 273, 116461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruis, A.J.; Bohnenkamp, A.C.; Patinios, C.; van Nuland, Y.M.; Levisson, M.; Mars, A.E.; van den Berg, C.; Kengen, S.W.M.; Weusthuis, R.A. Microbial production of short and medium chain esters: Enzymes, pathways, and applications. Biotechnol. Adv. 2019, 37, 107407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Sun, B.; Fan, G.; Teng, C.; Xiong, K.; Zhu, Y.; Li, J.; Li, X. The brewing process and microbial diversity of strong flavour chinese spirits: A review. J. Inst. Brew. 2017, 123, 5–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wei, Y.; Zou, W.; Shen, C.; Yang, J. Basic flavor types and component characteristics of chinese traditional liquors: A review. J. Food Sci. 2020, 85, 4096–4107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Power, A.C.; Jones, J.; Nineil, C.; Geoghegan, S.; Warren, S.; Currivan, S.; Cozzolino, D. What & apos;s in this drink? Classification and adulterant detection in irish whiskey samples using near infrared spectroscopy combined with chemometrics. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2021, 101, 5256–5263. [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez-Solana, R.; Esteves, E.; Mansinhos, I.; Goncalves, S.; Perez-Santin, E.; Galego, L.; Romano, A. Influence of elaboration process on chemical, biological, and sensory characteristics of european pennyroyal liqueurs. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2021, 101, 4076–4089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Wu, Y.; Wang, J.; Hong, J.; Tian, W.; Zhao, D.; Sun, J.; Huang, M.; Li, H.; Zheng, F.; et al. Uncover the flavor code of roasted sesame for sesame flavor baijiu: Advance on the revelation of aroma compounds in sesame flavor baijiu by means of modern separation technology and molecular sensory evaluation. Foods 2022, 11, 998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, J.; Wang, J.; Zhang, C.; Zhao, Z.; Tian, W.; Wu, Y.; Chen, H.; Zhao, D.; Sun, J. Unraveling variation on the profile aroma compounds of strong aroma type of baijiu in different regions by molecular matrix analysis and olfactory analysis. Rsc Adv. 2021, 11, 33511–33521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, D.; Jiang, Y.; Sun, J.; Li, H.; Huang, M.; Sun, X.; Zhao, M. Elucidation of the anti-inflammatory effect of vanillin in lps-activated thp-1 cells. J. Food Sci. 2019, 84, 1920–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, W.; Chen, X.; Zhou, D.; Xiong, F. Applications and prospects of the automation of compound flavor baijiu production by solid-state fermentation. Int. J. Food Eng. 2022, 18, 737–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, J.; Yang, S.; Shen, Y.; Cheng, W.; Li, H.; Sun, J.; Huang, M.; Sun, B. What are the main factors that affect the flavor of sauce-aroma baijiu. Foods 2022, 11, 3534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.; Du, H.; Zhang, H.; Fang, C.; Jin, G.; Chen, S.; Wu, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Xu, Y. Geographically associated fungus-bacterium interactions contribute to the formation of geography-dependent flavor during high-complexity spontaneous fermentation. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e01844-22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, W.; Cao, X.; Cheng, J.; Li, L.; Zhang, T.; Wu, Q.; Xiang, P.; Shen, C.; Li, Q. Chinese baijiu: The perfect works of microorganisms. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 919044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Chen, Q.; Jia, X.; Wang, Y.; Huang, M.; Wang, G.; Chen, H.; Gao, P. The effects of gamma irradiation and natural aging on the composition of nongxiangxing baijiu. J. Food Process Preserv. 2022, 46, e17146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, W.; Fan, Z.; Du, A.; Shi, L. Molecular mechanism of mare nectaris and magnetic field on the formation of ethyl carbamate during 19 years aging of feng-flavor baijiu. Food Chem. 2022, 382, 132357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Huang, Q.; Fei, Y.; Zhao, W.; Brennan, C.; Bai, W. The effect of aged pork fat on the quality and volatile compounds of chi-aroma baijiu. Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 43, e109922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Huang, H.; Lu, H.; Wu, M.; Lin, M.; Zhang, C.; Zhao, Z.; Li, W.; Zhang, C.; Li, X.; et al. Characterization of an aspergillus niger for efficient fatty acid ethyl ester synthesis in aqueous phase and the molecular mechanism. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 4292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, W.; Fan, Z.; Du, A.; Shi, L. Molecular mechanism of high pressure shear grinding on feng-flavour chinese baijiu ageing. Food Res. Int. 2022, 153, 110957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Meng, L.; Lu, Z.; Chai, L.; Wang, S.; Shi, J.; Shen, C.; Xu, Z. Identification of age-markers based on profiling of baijiu volatiles over a two-year maturation period: Case study of lu-flavor baijiu. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 141, 110913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rendall, R.; Pereira, A.C.; Reis, M.S. Advanced predictive methods for wine age prediction: Part I-a comparison study of single-block regression approaches based on variable selection, penalized regression, latent variables and tree-based ensemble methods. Talanta 2017, 171, 341–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razungles, A.J.; Baumes, R.L.; Dufour, C.; Sznaper, C.N.; Bayonove, C.L. Effect of sun exposure on carotenoids and c13-norisoprenoid glycosides in syrah berries (vitisvinifera l.). Sci. Des Aliment. 1998, 18, 361–373. [Google Scholar]
- Brock, P.E.; Pan, B.; Sacks, G.; Lakso, A.; Acree, T.; Lawless, H.; Henick-Kling, T. Chemistry and sensory effects of vineyard sun exposure on cabernet franc wines. Am. J. Enol. Vitic. 2008, 59, 111A. [Google Scholar]
- Piombino, P.; Genovese, A.; Gambuti, A.; Lamorte, S.A.; Lisanti, M.T.; Moio, L. Effects of off-vine bunches shading and cryomaceration on free and glycosilated flavours of malvasia delle lipari wine. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2010, 45, 234–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swinchatt, J.P.; Howell, D.G.; Macdonald, S.L. The scale dependence of wine and terroir: Examples from coastal california and the napa valley (usa). Elements. 2018, 14, 179–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, X.; Jia, F.; Cai, J.; Shi, Y.; Duan, C.; Lan, Y. Characterization and evolution of volatile compounds of cabernet sauvignon wines from two different clones during oak barrel aging. Foods 2022, 11, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wei, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, T.; Huang, M.; Wu, J.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wang, B. A new method to predict the content changes of aroma compounds during the aging process of niulanshan baijiu using the gm (1,1) gray model. Flavour Frag. J. 2022, 37, 5–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin-Vertedor, D.; Rodrigues, N.; Marx, I.M.G.; Veloso, A.C.A.; Peres, A.M.; Alberto Pereira, J. Impact of thermal sterilization on the physicochemical-sensory characteristics of californian-style black olives and its assessment using an electronic tongue. Food Control 2020, 117, 107369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Rodriguez, L.; Cano-Lamadrid, M.; Carbonell-Barrachina, A.A.; Hernandez, F.; Sendra, E. Impact of gastrointestinal in vitro digestion and deficit irrigation on antioxidant activity and phenolic content bioaccessibility of "manzanilla" table olives. J. Food Qual. 2020, 2020, 6348194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]










| Name | Abbreviation of Chart Name | CAS | Source of Standard | Fineness |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ethyl tetradecanoate | ET | 124-06-1 | Shanghai Yuanye Biotechnology Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China | GC ≥ 98.0% |
| Ethyl palmitate | EP | 628-97-7 | Shanghai Yuanye Biotechnology Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China | GC ≥ 98.0% |
| Ethyl octadecanoate | EO | 111-61-5 | Tanmo Quality Inspection-Reference Material Center, Changzhou, China | GC ≥ 99.0% |
| Ethyl 9-octadecenoate | E9 | 111-62-6 | Tanmo Quality Inspection-Reference Material Center, Changzhou, China | GC ≥ 98.5% |
| Ethyl 9,12-octadecadienoate | E912 | 544-35-4 | Shanghai Aladdin Biochemical Technology Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China | GC ≥ 97.0% |
| Ethyl 9,12,15-octadecatrienoate | E91215 | 1191-41-9 | Beijing North Weiye Measurement Technology Research Institute, Beijing, China | GC ≥ 98.0% |
| Baijiu Sample Groups | Baijiu Information Description | Alcohol/° |
|---|---|---|
| A1 | 2014-premium | 60 |
| B1 | 2014-excellent | 60 |
| C1 | 2014-level 1 | 60 |
| A2 | 2015-premium | 60 |
| C2 | 2018-level 1 | 60 |
| C3-1 | 2022-level 1-exposure-0 days | 60 |
| C3-2 | 2022-level 1-exposure-6 days | 60 |
| C3-3 | 2022-level 1-exposure-12 days | 60 |
| C3-4 | 2022-level 1-exposure-20 days | 60 |
| C3-5 | 2022-level 1-exposure-30 days | 60 |
| C3-6 | 2022-level 1-exposure-50 days | 60 |
| One-Level Indicators | Two-Level Indicators | Specific Description | Rating Score (Points) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Visual sense | Clear and transparent without impurities | Clear and transparent, with no suspension and no precipitate. | 0–10 |
| Olfactory sense | Fruity aroma | The aroma of Baijiu presents a fruit aroma (i.e., banana, apple, pineapple, etc.), and the fruit aroma smells comfortable. | 0–5 |
| Aged fragrant | With an obvious special aroma except Baijiu, it can be described as oak barrel aroma. | 0–5 | |
| Pit aroma | Rich cellar aroma with natural earthy astringency. | 0–5 | |
| Grain fragrance | Comfortable aroma of cooked grain. | 0–5 | |
| Floral aroma | Sweet flower fragrance (i.e., rose, chrysanthemum, etc.). | 0–5 | |
| Taste sense | Inlet taste | The complex trace components in Baijiu can cause irritation, but the time is short and the irritation is not strong. | 0–10 |
| Aroma sensation in the mouth | The full-blown Baijiu aroma resembled a volcanic eruption and filled the mouth. | 0–10 | |
| Middle laryngeal taste | No irritant sensation to the throat, and Baijiu is soft. | 0–10 | |
| Evaluation after drinking | Drunkenness | After drinking an appropriate amount of Baijiu (5–25 mL), you may get drunk within 30 min, but your body is not uncomfortable. | 0–25 |
| Remaining taste | After swallowing Baijiu, the time is more than 15 s until the aroma disappears in the mouth. | 0–10 |
| Compounds | Qualitative Ion | Quantitative Ion | LOD/(μg/L) | LOQ/(μg/L) | Interday Precision/(%) | Intraday Precision/(%) | Recovery Rate/(%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ET | 88, 101, 157, 211, 256 | 88, 256 | 0.24 | 0.76 | 1.1 | 2.57 | 95–103 |
| EP | 88, 101, 157, 239, 284 | 88, 284 | 0.32 | 1.91 | 1.15 | 1.73 | 105–108 |
| EO | 88, 101, 157, 269, 312 | 88, 312 | 0.11 | 1.13 | 2.11 | 3.79 | 95–101 |
| E9 | 55, 180, 222, 264, 310 | 55, 310 | 0.18 | 1.18 | 1.13 | 1.15 | 96–106 |
| E912 | 67, 81, 109, 263, 308 | 67, 308 | 0.24 | 3.32 | 2.14 | 8.62 | 98–107 |
| E91215 | 79, 95, 108, 121, 306 | 79, 306 | 0.44 | 1.15 | 2.35 | 0.85 | 102–103 |
| Compounds | Regression Equation | R2 |
|---|---|---|
| ET | y = 307753x − 80514 | 0.9989 |
| EP | y = 308141x − 217577 | 0.9976 |
| EO | y = 1000000x − 929800 | 0.9896 |
| E9 | y = 968421x − 943401 | 0.9958 |
| E912 | y = 1000000x − 1000000 | 0.9950 |
| E91215 | y = 1000000x − 1000000 | 0.9799 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, Y.; Chen, H.; Huang, H.; Chen, F.; Hong, J.; Zhao, D.; Zhang, C.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, S.; Ao, R.; et al. Revelation for the Influence Mechanism of Long-Chain Fatty Acid Ethyl Esters on the Baijiu Quality by Multicomponent Chemometrics Combined with Modern Flavor Sensomics. Foods 2023, 12, 1267. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12061267
Wu Y, Chen H, Huang H, Chen F, Hong J, Zhao D, Zhang C, Zhao Z, Wang S, Ao R, et al. Revelation for the Influence Mechanism of Long-Chain Fatty Acid Ethyl Esters on the Baijiu Quality by Multicomponent Chemometrics Combined with Modern Flavor Sensomics. Foods. 2023; 12(6):1267. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12061267
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Yashuai, Hao Chen, He Huang, Fangyuan Chen, Jiaxin Hong, Dongrui Zhao, Chunsheng Zhang, Zhigang Zhao, Shimin Wang, Ran Ao, and et al. 2023. "Revelation for the Influence Mechanism of Long-Chain Fatty Acid Ethyl Esters on the Baijiu Quality by Multicomponent Chemometrics Combined with Modern Flavor Sensomics" Foods 12, no. 6: 1267. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12061267
APA StyleWu, Y., Chen, H., Huang, H., Chen, F., Hong, J., Zhao, D., Zhang, C., Zhao, Z., Wang, S., Ao, R., & Sun, B. (2023). Revelation for the Influence Mechanism of Long-Chain Fatty Acid Ethyl Esters on the Baijiu Quality by Multicomponent Chemometrics Combined with Modern Flavor Sensomics. Foods, 12(6), 1267. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12061267