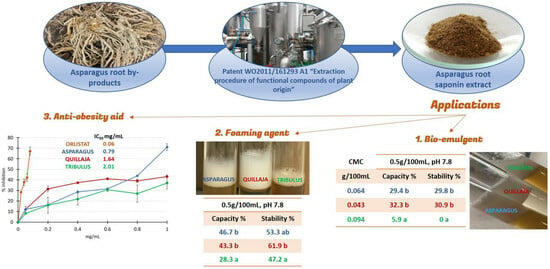
Applications of Saponin Extract from Asparagus Roots as Functional Ingredient
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Obtaining Saponin Extracts
2.2. Chemical Characterization of the Extracts
2.2.1. Saponin Content
2.2.2. Phenolic Compounds by Folin–Ciocalteu Assay
2.2.3. Phenolic Compounds by HPLC-DAD
2.2.4. Protein Concentration
2.2.5. Ash Content
2.3. Critical Micelle Concentration Assay (CMC)
2.4. Determination of Emulsifying Capacity and Emulsion Stability
2.5. Determination of Foaming Capacity and Foam Stability
2.6. Influence of Environmental Conditions (pH, Presence of Sodium Chloride, and Sucrose) on Emulsifying and Foaming Properties
2.7. Determination of the Inhibitory Effect of Saponin Extracts on Pancreatic Lipase
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Characterization of the Different Saponin Extracts
3.2. Emulsifying Properties
3.2.1. Critical Micelle Concentration Assays
3.2.2. Influence of Concentration on Emulsifying Properties
3.2.3. Influence of pH
3.2.4. Influence of Other Additives
3.3. Foaming Properties
3.3.1. Influence of Concentration on Foaming Properties
3.3.2. Influence of pH
3.3.3. Influence of Other Additives
3.4. Pancreatic Lipase Inhibition Assay
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schreiner, T.B.; Dias, M.M.; Barreiro, M.F.; Pinho, S.P. Saponins as Natural Emulsifiers for Nanoemulsions. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 6573–6590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aditivos Alimentarios. Available online: https://www.aditivos-alimentarios.com/ (accessed on 18 October 2023).
- Johnson, P.; Trybala, A.; Starov, V.; Pinfield, V.J. Effect of Synthetic Surfactants on the Environment and the Potential for Substitution by Biosurfactants. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 288, 102340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lapworth, D.J.; Baran, N.; Stuart, M.E.; Ward, R.S. Emerging Organic Contaminants in Groundwater: A Review of Sources, Fate and Occurrence. Environ. Pollut. 2012, 163, 287–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Effendi, I.; Nedi, S.; Ellizal; Nursyirwani; Feliatra; Fikar; Tanjung; Pakpahan, R.; Pratama. Detergent Disposal into Our Environmentand Its Impact on Marine Microbes. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2017, 97, 012030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masakorala, K.; Turner, A.; Brown, M.T. Toxicity of Synthetic Surfactants to the Marine Macroalga, Ulva Lactuca. Water. Air. Soil Pollut. 2011, 218, 283–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, M.J.; Jones, M.N. The Biodegradation of Surfactants in the Environment. Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA-Biomembr. 2000, 1508, 235–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oleszek, M.; Oleszek, W. Saponins in Food. In Handbook of Dietary Phytochemicals; Xiao, J., Sarker, S.D., Asakawa, Y., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2020; pp. 1–40. ISBN 9789811317453. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, T.-T.; Liu, X.-T.; Chen, Q.-X.; Shi, Y. Lipase Inhibitors for Obesity: A Review. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 128, 110314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, G.; Suresh, S.; Bayineni, V.K.; Kadeppagari, R.K. Lipase Inhibitors from Plants and Their Medical Applications. Int. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 7, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Reichert, C.L.; Salminen, H.; Weiss, J. Quillaja Saponin Characteristics and Functional Properties. Annu. Rev. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 10, 43–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaramillo, S.; Muriana, F.J.G.; Guillén, R.; Jiménez-Araujo, A.; Rodríguez-Arcos, R.; López, S. Saponins from Edible Spears of Wild Asparagus Inhibit AKT, P70S6K, and ERK Signalling, and Induce Apoptosis through G0/G1 Cell Cycle Arrest in Human Colon Cancer HCT-116 Cells. J. Funct. Foods 2016, 26, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vázquez-Castilla, S.; Jaramillo-Carmona, S.; Fuentes-Alventosa, J.M.; Jiménez-Araujo, A.; Rodríguez-Arcos, R.; Cermeño-Sacristán, P.; Espejo-Calvo, J.A.; Guillén-Bejarano, R. Saponin Profile of Green Asparagus Genotypes. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 11098–11108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vázquez-Castilla, S.; Jaramillo-Carmona, S.; Fuentes-Alventosa, J.M.; Jiménez-Araujo, A.; Rodríguez-Arcos, R.; Cermeño-Sacristán, P.; Espejo-Calvo, J.A.; Guillén-Bejarano, R. Optimization of a Method for the Pofiling and Quantification of Saponins in Different Green Asparagus Genotypes. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 6250–6258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaramillo-Carmona, S.; Rodriguez-Arcos, R.; Jiménez-Araujo, A.; López, S.; Gil, J.; Moreno, R.; Guillén-Bejarano, R. Saponin Profile of Wild Asparagus Species. J. Food Sci. 2017, 82, 638–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamdi, A.; Jaramillo-Carmona, S.; Beji, R.; Tej, R.; Zaoui, S.; Rodríguez-Arcos, R.; Jiménez-Araujo, A.; Kasri, M.; Lachaal, M.; Bouraoui, N.K.; et al. The Phytochemical and Bioactivity Profiles of Wild Asparagus albus L. Plant. Food Res. Int. 2017, 99, 720–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamdi, A.; Jaramillo-Carmona, S.; Rodríguez-Arcos, R.; Jiménez-Araujo, A.; Lachaal, M.; Karray-Bouraoui, N.; Guillén-Bejarano, R. Phytochemical Characterization and Bioactivity of Asparagus acutifolius: A Focus on Antioxidant, Cytotoxic, Lipase Inhibitory and Antimicrobial Activities. Molecules 2021, 26, 3328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Moreno, F.J.; Atero-Calvo, S.; Navarro-León, E.; Blasco, B.; Soriano, T.; Ruiz, J.M. Evaluation of Physiological and Quality Parameters of Green Asparagus Spears Subjected to Three Treatments against the Decline Syndrome. Agronomy 2021, 11, 937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brizuela, A.M.; De la Lastra, E.; Marín-Guirao, J.I.; Gálvez, L.; de Cara-García, M.; Capote, N.; Palmero, D. Fusarium Consortium Populations Associated with Asparagus Crop in Spain and Their Role on Field Decline Syndrome. J. Fungi 2020, 6, 336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato-Noguchi, H.; Nakamura, K.; Ohno, O.; Suenaga, K.; Okuda, N. Asparagus Decline: Autotoxicity and Autotoxic Compounds in Asparagus Rhizomes. J. Plant Physiol. 2017, 213, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartung, A.C.; Stephens, C.T. Effects of Allelopathic Substances Produced by Asparagus on Incidence and Severity of Asparagus Decline Due to Fusarium Crown Rot. J. Chem. Ecol. 1983, 9, 1163–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onlom, C.; Nuengchamnong, N.; Phrompittayarat, W.; Putalun, W.; Waranuch, N.; Ingkaninan, K. Quantification of Saponins in Asparagus racemosus by HPLC-Q-TOF-MS/MS. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2017, 12, 7–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, S.; Manivel, P.; Singh, R.; Dhanani, T.; Kumar, S. Varation of Saponin Content in Asparagus Adscendens Germplasms from Western Himalayan Region of India Using High Performance Liquid Chromatography-Evaporative Light Scattering Detector. J. Pharm. Appl. Chem. 2018, 4, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ralla, T.; Salminen, H.; Edelmann, M.; Dawid, C.; Hofmann, T.; Weiss, J. Oat Bran Extract (Avena sativa L.) from Food by-Product Streams as New Natural Emulsifier. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 81, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillén-Bejarano, R.; Rodríguez-Gutiérrez, G.; Fuentes-Alventosa, J.M.; Jaramillo-Carmona, S.; Rodríguez-Arcos, R.; Jiménez-Araujo, A.; Fernández-Bolaños, J. CSIC Procedimiento de Obtención de Compuestos Funcionales de Origen Vegetal; CSIC: Madrid, Spain, 2012.
- Singleton, V.L.; Rossi, J.A.J. Colorimetry of Total Phenolics with Phosphomolibdic-Phosphotungstic Acid Reagents. Am. J. Enol. Vitic. 1965, 16, 144–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paz, S.M.-d.l.; Martinez-Lopez, A.; Villanueva-Lazo, A.; Pedroche, J.; Millan, F.; Millan-Linares, M.C. Identification and Characterization of Novel Antioxidant Protein Hydrolysates from Kiwicha (Amaranthus caudatus L.). Antioxidants 2021, 10, 645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreiner, T.B.; Colucci, G.; Santamaria-Echart, A.; Fernandes, I.P.; Dias, M.M.; Pinho, S.P.; Barreiro, M.F. Evaluation of Saponin-Rich Extracts as Natural Alternative Emulsifiers: A Comparative Study with Pure Quillaja Bark Saponin. Colloids Surf. Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2021, 623, 126748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.C.; Kinsella, J.E. Functional Properties of Novel Proteins: Alfalfa Leaf Protein. J. Food Sci. 1976, 41, 286–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cano-Medina, A.; Jiménez-Islas, H.; Dendooven, L.; Herrera, R.P.; González-Alatorre, G.; Escamilla-Silva, E.M. Emulsifying and Foaming Capacity and Emulsion and Foam Stability of Sesame Protein Concentrates. Food Res. Int. 2011, 44, 684–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.-J.; Lee, Y.M.; Lee, C.-K.; Jung, J.K.; Han, S.B.; Hong, J.T. Therapeutic Applications of Compounds in the Magnolia Family. Pharmacol. Ther. 2011, 130, 157–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaradat, N.; Zaid, A.; Hussein, F.; Zaqzouq, M.; Aljammal, H.; Ayesh, O. Anti-Lipase Potential of the Organic and Aqueous Extracts of Ten Traditional Edible and Medicinal Plants in Palestine; A Comparison Study with Orlistat. Medicines 2017, 4, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böttcher, S.; Drusch, S. Saponins—Self-Assembly and Behavior at Aqueous Interfaces. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 243, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chhatre, S.; Nesari, T.; Kanchan, D.; Somani, G.; Sathaye, S. Phytopharmacological Overview of Tribulus terrestris. Pharmacogn. Rev. 2014, 8, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Semerdjieva, I.B.; Zheljazkov, V.D. Chemical Constituents, Biological Properties, and Uses of Tribulus terrestris: A Review. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2019, 14, 1934578X1986839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, Q.; Liu, Z.; Zhi, L.; Jiao, B.; Hu, H.; Ma, X.; Agyei, D.; Shi, A. Plant Protein-Based Emulsifiers: Mechanisms, Techniques for Emulsification Enhancement and Applications. Food Hydrocoll. 2023, 144, 109008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walkowicz, W.E.; Fernández-Tejada, A.; George, C.; Corzana, F.; Jiménez-Barbero, J.; Ragupathi, G.; Tan, D.S.; Gin, D.Y. Quillaja Saponin Variants with Central Glycosidic Linkage Modifications Exhibit Distinct Conformations and Adjuvant Activities. Chem. Sci. 2016, 7, 2371–2380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Z.; Wen, Y.; Yi, J.; Cao, Y.; Liu, F.; McClements, D.J. Comparison of Natural and Synthetic Surfactants at Forming and Stabilizing Nanoemulsions: Tea Saponin, Quillaja Saponin, and Tween 80. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 536, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karthik, S.; Raghavan, C.V.; Marslin, G.; Rahman, H.; Selvaraj, D.; Balakumar, K.; Franklin, G. Quillaja Saponin: A Prospective Emulsifier for the Preparation of Solid Lipid Nanoparticles. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2016, 147, 274–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdolmaleki, K.; Mohammadifar, M.A.; Mohammadi, R.; Fadavi, G.; Meybodi, N.M. The Effect of PH and Salt on the Stability and Physicochemical Properties of Oil-in-Water Emulsions Prepared with Gum Tragacanth. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 140, 342–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Strobel, B.W.; Cedergreen, N.; Cao, Y.; Hansen, H.C.B. Stability of Saponin Biopesticides: Hydrolysis in Aqueous Solutions and Lake Waters. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2019, 21, 1204–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Leser, M.E.; Sher, A.A.; McClements, D.J. Formation and Stability of Emulsions Using a Natural Small Molecule Surfactant: Quillaja Saponin (Q-Naturale®). Food Hydrocoll. 2013, 30, 589–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ereifej, K.I.; Rababah, T.M.; Al-Rababah, M.A. Quality Attributes of Halva by Utilization of Proteins, Non-Hydrogenated Palm Oil, Emulsifiers, Gum Arabic, Sucrose, and Calcium Chloride. Int. J. Food Prop. 2005, 8, 415–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, C.; Sher, A.; Rousset, P.; McClements, D.J. Use of Natural Emulsifiers in Model Coffee Creamers: Physical Properties of Quillaja Saponin-Stabilized Emulsions. Food Hydrocoll. 2017, 67, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böttcher, S.; Drusch, S. Interfacial Properties of Saponin Extracts and Their Impact on Foam Characteristics. Food Biophys. 2016, 11, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badve, M.; Humbare, T. Foaming and Emulsifying Properties of Saponin Glycosides: A Natural Non-Ionic Surfactant. Proc. Indian Natl. Sci. Acad. 2023, 89, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Chu, X.; Li, X.; Su, E.; Cao, F.; Zhu, W.; Li, S.; Wang, J. Insight into Foam Properties of Natural Saponins with Low-pH and High-Temperature Tolerance from Xanthoceras sorbifolium Bunge Leaves for Industry Applications. Food Biophys. 2023, 18, 545–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, S.S.; Gandhi, I.S.R.; Khwairakpam, S. State-of-the-Art Review on the Characteristics of Surfactants and Foam from Foam Concrete Perspective. J. Inst. Eng. India Ser. A 2018, 99, 391–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro Del Hierro, J.; Casado-Hidalgo, G.; Reglero, G.; Martin, D. The Hydrolysis of Saponin-Rich Extracts from Fenugreek and Quinoa Improves Their Pancreatic Lipase Inhibitory Activity and Hypocholesterolemic Effect. Food Chem. 2021, 338, 128113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshizumi, K.; Hirano, K.; Ando, H.; Hirai, Y.; Ida, Y.; Tsuji, T.; Tanaka, T.; Satouchi, K.; Terao, J. Lupane-Type Saponins from Leaves of Acanthopanax sessiliflorus and Their Inhibitory Activity on Pancreatic Lipase. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 335–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| ARS | QS | TS | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Saponin | 47.64 1 | >10 2,3 | 12.32 2 |
| Phenolics 1,4 | 3.35 | 1.10 | 9.42 |
| Protein | 10.74 1 | 0.26 1 | 4.10 2 |
| Ash | 0.60 1 | 0.90 1 | 0.22 2 |
| Emulsifying capacity | ||||
| Sap. conc. | Saponin | Water | NaCl 1M | Sucrose 5% |
| 0.50 | ARS | 29.41 ± 0.62 b A | 47.69 ± 4.35 b B | 30.30 ± 0.64 c A |
| QS | 32.35 ± 2.08 b B | 48.10 ± 3.74 b C | 26.13 ± 0.55 b A | |
| TS | 5.88 ± 0.04 a B | 29.63 ± 0.74 a C | 0.00 ± 0.00 a A | |
| 0.03 | ARS | 18.66 ± 1.06 b B | 33.58 ± 1.06 a C | 5.88 ± 0.04 b A |
| QS | 28.36 ± 0.42 c A | 44.78 ± 2.11 b B | 29.63 ± 0.31 c A | |
| TS | 0.00 ± 0.00 a A | 29.85 ± 0.63 a B | 0.00 ± 0.00 a A | |
| Emulsion stability | ||||
| Sap. conc. | Saponin | Water | NaCl 1M | Sucrose 5% |
| 0.50 | ARS | 29.85 ± 1.06 b B | 7.46 ± 0.21 b A | 28.79 ± 2.14 b B |
| QS | 31.11 ± 0.33 b A | 40.60 ± 0.43 c B | 31.82 ± 0.43 b A | |
| TS | 0.00 ± 0.00 a A | 0.00 ± 0.00 a A | 7.65 ± 0.11 a B | |
| 0.03 | ARS | 22.22 ± 0.23 b C | 0.00 ± 0.00 a A | 7.63 ± 0.08 b B |
| QS | 28.15 ± 0.29 c B | 0.00 ± 0.00 a A | 27.27 ± 0.43 c B | |
| TS | 0.00 ± 0.00 a A | 0.00 ± 0.00 a A | 0.00 ± 0.00 a A | |
| Foaming capacity | ||||
| Sap. conc. | Saponin | Water | Sodium chloride 1M | Sucrose 5% |
| 0.50 | ARS | 46.67 ± 4.71 b A | 46.67 ± 1.89 b A | 45.00 ± 2.36 c A |
| QS | 43.33 ± 4.71 b B | 26.67 ± 3.30 a A | 27.47 ± 2.30 b A | |
| TS | 28.33 ± 2.36 a B | 25.00 ± 2.83 a B | 13.33 ± 0.94 a A | |
| 0.03 | ARS | 20.00 ± 2.36 b A | 33.33 ± 2.83 b B | 25.00 ± 1.89 b A |
| QS | 28.36 ± 0.42 c B | 38.33 ± 2.36 b C | 23.33 ± 1.41 b A | |
| TS | 0.00 ± 0.00 a A | 13.33 ± 0.94 a C | 6.67 ± 0.47 a B | |
| Foam stability | ||||
| Sap. conc. | Saponin | Water | Sodium chloride 1M | Sucrose 5% |
| 0.50 | ARS | 53.33 ± 4.71 b B | 35.74 ± 1.44 b A | 51.92 ± 2.72 b B |
| QS | 61.91 ± 6.74 c A | 75.58 ± 9.35 c A | 68.73 ± 0.33 c A | |
| TS | 47.22 ± 3.93 a B | 33.12 ± 3.80 b A | 37.34 ± 4.43 a AB | |
| 0.03 | ARS | 74.83 ± 2.97 b B | 24.32 ± 4.30 b A | 73.19 ± 3.91 b B |
| QS | 71.84 ± 2.61 b B | 64.96 ± 8.30 c A | 71.56 ± 4.34 b B | |
| TS | 0.00 ± 0.00 a | 0.00 ± 0.00 a | 0.00 ± 0.00 a | |
| Regression Model | R2 (%) | a | b | IC50 (mg/mL) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Orlistat | 95.70 | 0.4517 | 27.5093 | 0.058 | |
| ARS | 93.22 | 3.2900 | 59.2210 | 0.7887 | |
| QS | 93.77 | −37.0366 | 1983.12 | 1.6366 | |
| TS | 96.54 | 0.2352 | 35.0949 | 2.0107 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hamdi, A.; Viera-Alcaide, I.; Jiménez-Araujo, A.; Rodríguez-Arcos, R.; Guillén-Bejarano, R. Applications of Saponin Extract from Asparagus Roots as Functional Ingredient. Foods 2024, 13, 274. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13020274
Hamdi A, Viera-Alcaide I, Jiménez-Araujo A, Rodríguez-Arcos R, Guillén-Bejarano R. Applications of Saponin Extract from Asparagus Roots as Functional Ingredient. Foods. 2024; 13(2):274. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13020274
Chicago/Turabian StyleHamdi, Amel, Isabel Viera-Alcaide, Ana Jiménez-Araujo, Rocío Rodríguez-Arcos, and Rafael Guillén-Bejarano. 2024. "Applications of Saponin Extract from Asparagus Roots as Functional Ingredient" Foods 13, no. 2: 274. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13020274
APA StyleHamdi, A., Viera-Alcaide, I., Jiménez-Araujo, A., Rodríguez-Arcos, R., & Guillén-Bejarano, R. (2024). Applications of Saponin Extract from Asparagus Roots as Functional Ingredient. Foods, 13(2), 274. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13020274