Effect of Gamma-Radiation on Zearalenone—Degradation, Cytotoxicity and Estrogenicity
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
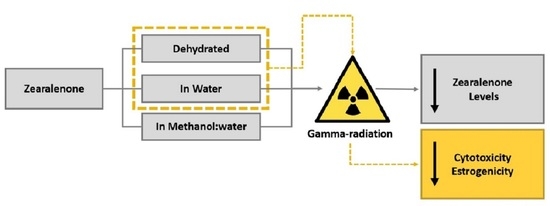
2.2. Preparation of ZEA Solutions and Irradiation Process
2.3. Determination of ZEA Levels
2.4. Cytotoxicity Studies
2.4.1. Cells Culture and Exposure
2.4.2. AB, CFDA-AM and NR Uptake (NRU) Assays
2.5. Estrogenicity Studies
2.5.1. Cell Culture and Exposure
2.5.2. Transactivation Assay
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. ZEA Concentration after Irradiation
3.2. Cytotoxicity of Irradiated ZEA
3.3. Estrogenicity of Irradiated ZEA
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Palumbo, R.; Crisci, A.; Venâncio, A.; Cortiñas Abrahantes, J.; Dorne, J.-L.; Battilani, P.; Toscano, P. Occurrence and co-occurrence of mycotoxins in cereal-based feed and food. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 74. [Google Scholar]
- Ayed-Boussema, I.; Bouaziz, C.; Rjiba, K.; Valenti, K.; Laporte, F.; Bacha, H.; Hassen, W. The mycotoxin Zearalenone induces apoptosis in human hepatocytes (HepG2) via p53-dependent mitochondrial signaling pathway. Toxicol. In Vitro Int. J. Publ. Assoc. BIBRA 2008, 22, 1671–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- IARC. Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans. Some Traditional Herbal Medicines, Some Mycotoxins, Naphthalene and Styrene. In IARC Monographs on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans; IARC Press: Lyon, France, 2002; Volume 82, p. 276. [Google Scholar]
- Rogowska, A.; Pomastowski, P.; Sagandykova, G.; Buszewski, B. Zearalenone and its metabolites: Effect on human health, metabolism and neutralisation methods. Toxicon Off. J. Int. Soc. Toxinol. 2019, 162, 46–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zinedine, A.; Soriano, J.M.; Molto, J.C.; Manes, J. Review on the toxicity, occurrence, metabolism, detoxification, regulations and intake of zearalenone: An oestrogenic mycotoxin. Food Chem. Toxicol. J. Publ. Br. Ind. Biol. Res. Assoc. 2007, 45, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, J.W.; Klich, M. Mycotoxins. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2003, 16, 497–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kriszt, R.; Krifaton, C.; Szoboszlay, S.; Cserhati, M.; Kriszt, B.; Kukolya, J.; Czeh, A.; Feher-Toth, S.; Torok, L.; Szoke, Z.; et al. A new zearalenone biodegradation strategy using non-pathogenic Rhodococcus Pyridinivorans K408 strain. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e43608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bullerman, L.B.; Bianchini, A. Stability of mycotoxins during food processing. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2007, 119, 140–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, N.H.; Attia, E.S.A.; Farag, S.A. Effect of gamma-irradiation on the natural occurrence of Fusarium mycotoxins in wheat, flour and bread. Food Nahrung 1997, 41, 34–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortinovis, C.; Pizzo, F.; Spicer, L.; Caloni, F. Fusarium mycotoxins: Effects on reproductive function in domesticanimals—A review. Theriogenology 2013, 80, 557–564. [Google Scholar]
- Gutleb, A.C.; Morrison, E.; Murk, A.J. Cytotoxicity assays for mycotoxins produced by Fusarium strains: A review. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2002, 11, 309–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuiper-Goodman, T.; Scott, P.M.; Watanabe, H. Risk assessment of the mycotoxin zearalenone. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 1987, 7, 253–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Videmann, B.; Mazallon, M.; Tep, J.; Lecoeur, S. Metabolism and transfer of the mycotoxin zearalenone in human intestinal Caco-2 cells. Food Chem. Toxicol. Int. J. Publ. Br. Indust. Biol. Res. Assoc. 2008, 46, 3279–3286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tatay, E.; Meca, G.; Font, G.; Ruiz, M.J. Interactive effects of zearalenone and its metabolites on cytotoxicity and metabolization in ovarian CHO-K1 cells. Toxicol. In Vitro Int. J. Publ. Assoc. BIBRA 2014, 28, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biehl, M.L.; Prelusky, D.B.; Koritz, G.D.; Hartin, K.E.; Buck, W.B.; Trenholm, H.L. Biliary excretion and enterohepatic cycling of zearalenone in immature pigs. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 1993, 121, 152–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Burns, K.A.; Arao, Y.; Luh, C.J.; Korach, K.S. Differential estrogenic actions of endocrine-disrupting chemicals bisphenol A, bisphenol AF, and zearalenone through estrogen receptor alpha and beta in vitro. Environ. Health Perspec. 2012, 120, 1029–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ayed-Boussema, I.; Ouanes, Z.; Bacha, H.; Abid, S. Toxicities induced in cultured cells exposed to zearalenone: Apoptosis or mutagenesis? J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2007, 21, 136–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marin, D.E.; Taranu, I.; Burlacu, R.; Tudor, D.S. Effects of zearalenone and its derivatives on the innate immune response of swine. Toxicon Offic. J. Int. Soc. Toxinol. 2010, 56, 956–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abid-Essefi, S.; Ouanes, Z.; Hassen, W.; Baudrimont, I.; Creppy, E.; Bacha, H. Cytotoxicity, inhibition of DNA and protein syntheses and oxidative damage in cultured cells exposed to zearalenone. Toxicol. In Vitro Int. J. Publ. Assoc. BIBRA 2004, 18, 467–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marin, D.E.; Taranu, I.; Burlacu, R.; Manda, G.; Motiu, M.; Neagoe, I.; Dragomir, C.; Stancu, M.; Calin, L. Effects of zearalenone and its derivatives on porcine immune response. Toxicol. In Vitro Int. J. Publ. Assoc. BIBRA 2011, 25, 1981–1988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Z.; Liu, M.; Qu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Yin, S.; Shan, A. Toxic effects of zearalenone on oxidative stress, inflammatory cytokines, biochemical and pathological changes induced by this toxin in the kidney of pregnant rats. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2014, 37, 580–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrer, E.; Juan-Garcia, A.; Font, G.; Ruiz, M.J. Reactive oxygen species induced by beauvericin, patulin and zearalenone in CHO-K1 cells. Toxicol. In Vitro Int. J. Publ. Assoc. BIBRA 2009, 23, 1504–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prouillac, C.; Videmann, B.; Mazallon, M.; Lecoeur, S. Induction of cells differentiation and ABC transporters expression by a myco-estrogen, zearalenone, in human choriocarcinoma cell line (BeWo). Toxicology 2009, 263, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salah-Abbes, J.B.; Abbes, S.; Haous, Z.; Oueslati, R. Raphanus sativus extract prevents and ameliorates zearalenone-induced peroxidative hepatic damage in Balb/c mice. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2009, 61, 1545–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cetin, Y.; Bullerman, L.B. Evaluation of reduced toxicity of zearalenone by extrusion processing as measured by the MTT cell proliferation assay. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 6558–6563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, Â.; Antonio, A.L.; Oliveira, M.B.P.; Martins, A.; Ferreira, I.C. Effect of gamma and electron beam irradiation on the physico-chemical and nutritional properties of mushrooms: A review. Food Chem. 2012, 135, 641–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calado, T.; Venâncio, A.; Abrunhosa, L. Irradiation for Mold and Mycotoxin Control: A Review. Compr. Rev. Food Saf. 2014, 13, 1049–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, F.; Xie, F.; Xue, X.; Wang, Z.; Fan, B.; Ha, Y. Structure elucidation and toxicity analyses of the radiolytic products of aflatoxin B1 in methanol-water solution. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 192, 1192–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Getoff, N. Factors influencing the efficiency of radiation-induced degradation of water pollutants. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2002, 65, 437–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rychlik, M.; Humpf, H.U.; Marko, D.; Danicke, S.; Mally, A.; Berthiller, F.; Klaffke, H.; Lorenz, N. Proposal of a comprehensive definition of modified and other forms of mycotoxins including “masked” mycotoxins. Mycotoxin Res. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eisenbrand, G.; Pool-Zobel, B.; Baker, V.; Balls, M.; Blaauboer, B.J.; Boobis, A.; Carere, A.; Kevekordes, S.; Lhuguenot, J.C.; Pieters, R.; et al. Methods of in vitro toxicology. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2002, 40, 193–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, B.; He, X.; Cheng, W.H.; Xu, W.; Luo, Y.; Liang, R.; Luo, H.; Huang, K. Analysis of individual and combined effects of ochratoxin A and zearalenone on HepG2 and KK-1 cells with mathematical models. Toxins 2014, 6, 1177–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dayeh, V.R.; Chow, S.L.; Schirmer, K.; Lynn, D.H.; Bols, N.C. Evaluating the toxicity of Triton X-100 to protozoan, fish, and mammalian cells using fluorescent dyes as indicators of cell viability. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2004, 57, 375–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dayeh, V.R.; Lynn, D.H.; Bols, N.C. Cytotoxicity of metals common in mining effluent to rainbow trout cell lines and to the ciliated protozoan, Tetrahymena thermophila. Toxicol. In Vitro 2005, 19, 399–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riley, R.T.; Voss, K.A.; Pestka, J.J.; Williams, D.E. Developing mechanism-based and exposure biomarkers for mycotoxins in animals. In Determining Mycotoxins and Mycotoxigenic Fungi in Food and Feed; De Saeger, S., Ed.; Elsevier Science: Cambridge, UK, 2011; pp. 262–265. [Google Scholar]
- Fink-Gremmels, J.; Malekinejad, H. Clinical effects and biochemical mechanisms associated with exposure to the mycoestrogen zearalenone. Anim. Feed Sci. Tech. 2007, 137, 326–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maaroufi, K.; Chekir, L.; Ekue Creppy, E.; Ellouz, F.; Bacha, H. Zearalenone induces modifications of haematological and biochemical parameters in rats. Toxicon Offic. J. Int. Soc. Toxinol. 1996, 34, 535–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Čonková, E.; Laciaková, A.; Pástorová, B.; Seidel, H.; Kováč, G. The effect of zearalenone on some enzymatic parameters in rabbits. Toxicol. Lett. 2001, 121, 145–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urani, C.; Doldi, M.; Crippa, S.; Camatini, M. Human-derived cell lines to study xenobiotic metabolism. Chemosphere 1998, 37, 2785–2795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javitt, N.B. Hep G2 cells as a resource for metabolic studies: Lipoprotein, cholesterol, and bile acids. FASEB J. 1990, 4, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OECD. Test No. 455: The Stably Transfected Human Estrogen Receptor-Alpha Transcriptional Activation Assay for Detection of Estrogenic Agonist-Activity of Chemicals; OECD: Paris, France, 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM. Practice for using the Fricke reference standard dosimetry system. In ASTM-E 1026 Annual Book of ASTM Standards; ASTM: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Keller, L.; Abrunhosa, L.; Keller, K.; Rosa, C.A.; Cavaglieri, L.; Venâncio, A. Zearalenone and its derivatives α-zearalenol and β-zearalenol decontamination by Saccharomyces cerevisiae strains isolated from bovine forage. Toxins 2015, 7, 3297–3308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Calado, T.; Fernández-Cruz, M.L.; Verde, S.C.; Venâncio, A.; Abrunhosa, L. Gamma irradiation effects on ochratoxin A: Degradation, cytotoxicity and application in food. Food Chem. 2018, 240, 463–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lammel, T.; Boisseaux, P.; Fernández-Cruz, M.L.; Navas, J.M. Internalization and cytotoxicity of graphene oxide and carboxyl graphene nanoplatelets in the human hepatocellular carcinoma cell line Hep G2. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2013, 10, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hooshmand, H.; Klopfenstein, C.F. Effects of gamma irradiation on mycotoxin disappearance and amino acid contents of corn, wheat, and soybeans with different moisture contents. Plant. Food Hum. Nutr. 1995, 47, 227–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sebaei, A.S.; Sobhy, H.M.; Fouzy, A.S.M.; Hussain, O.A. Occurrence of zearalenone in grains and its reduction by gamma radiation. Int. J. Environ. Analyt. Chem. 2020, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalili, M.; Jinap, S.; Noranizan, M.A. Aflatoxins and ochratoxin a reduction in black and white pepper by gamma radiation. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2012, 81, 1786–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalili, M.; Jinap, S.; Noranizan, A. Effect of gamma radiation on reduction of mycotoxins in black pepper. Food Control 2010, 21, 1388–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutluer, B.; Erkoç, F. Effects of gamma irradiation on aflatoxins. Z. Lebensm. Unters. Forch. 1987, 185, 398–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Caër, S. Water radiolysis: Influence of oxide surfaces on H2 production under ionizing radiation. Water 2011, 3, 235–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Dyck, P.J.; Tobback, P.; Feyes, M.; van de Voorde, H. Sensitivity of aflatoxin B1 to ionizing radiation. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1982, 43, 1317–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kalagatur, N.K.; Kamasani, J.R.; Mudili, V. Assessment of detoxification efficacy of irradiation on zearalenone mycotoxin in various fruit juices by response surface methodology and elucidation of its in-vitro toxicity. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Z.-S.; Xie, Q.-F.; Che, L.-M. Effects of gamma irradiation on aflatoxin B1 levels in soybean and on the properties of soybean and soybean oil. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 2018, 139, 224–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Rahman, G.N.; Sultan, Y.Y.; Salem, S.H.; Amer, M.M. Identify the natural levels of mycotoxins in Egyptian roasted peanuts and the destructive effect of gamma radiation. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. Food Sci. 2019, 2019, 1174–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EC. Commission Regulation no 1881/2006 of 19 December 2006 setting maximum levels for certain contaminants in foodstuffs (consolidated version from 01/07/2020). In Official Journal of the European Communities; EC: Brussels, Belgium, 2020; pp. 4–24. [Google Scholar]






Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Calado, T.; Abrunhosa, L.; Cabo Verde, S.; Alté, L.; Venâncio, A.; Fernández-Cruz, M.L. Effect of Gamma-Radiation on Zearalenone—Degradation, Cytotoxicity and Estrogenicity. Foods 2020, 9, 1687. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9111687
Calado T, Abrunhosa L, Cabo Verde S, Alté L, Venâncio A, Fernández-Cruz ML. Effect of Gamma-Radiation on Zearalenone—Degradation, Cytotoxicity and Estrogenicity. Foods. 2020; 9(11):1687. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9111687
Chicago/Turabian StyleCalado, Thalita, Luís Abrunhosa, Sandra Cabo Verde, Luis Alté, Armando Venâncio, and María Luisa Fernández-Cruz. 2020. "Effect of Gamma-Radiation on Zearalenone—Degradation, Cytotoxicity and Estrogenicity" Foods 9, no. 11: 1687. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9111687
APA StyleCalado, T., Abrunhosa, L., Cabo Verde, S., Alté, L., Venâncio, A., & Fernández-Cruz, M. L. (2020). Effect of Gamma-Radiation on Zearalenone—Degradation, Cytotoxicity and Estrogenicity. Foods, 9(11), 1687. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9111687