Physical Stability of Oil-In-Water Emulsion Stabilized by Gelatin from Saithe (Pollachius virens) Skin
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Physicochemical Characterization
2.2. Mineral Composition
2.3. Electrophoretic Study (SDS-PAGE)
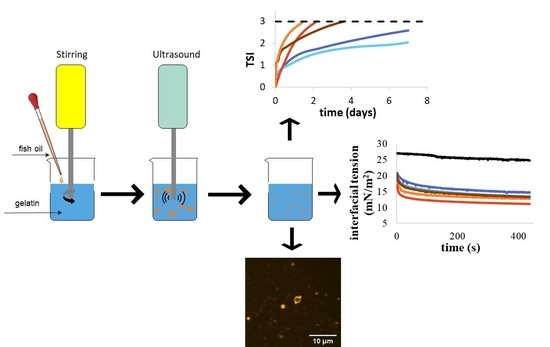
2.4. Emulsion Preparation
2.5. Emulsion Stability
2.6. Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS)
2.7. ζ-Potential Measurements
2.8. Viscosity Measurements
2.9. Interfacial Properties
2.10. Confocal Scanning Laser Microscopy (CLSM)
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Physicochemical Characterization
3.2. Mineral Composition
3.3. Protein Profile (SDS-PAGE)
3.4. Emulsion Stability
3.5. Hydrodynamic Diameter and ζ-Potential Measurements
3.6. Flow Behavior
3.7. Interfacial Tension
3.8. Confocal Scanning Laser Microscopy (CLSM)
4. Discussion
4.1. Physicochemical Characterization of Gelatins
4.2. In Bulk Emulsions
4.3. Absorption to the Oil–Water Interface
4.4. Physical Stability of Emulsions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- McClements, D.J. Food Emulsions—Principles, Practices and Techniques, 3rd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2016; ISBN 9781498726696. [Google Scholar]
- Farjami, T.; Madadlou, A. An overview on preparation of emulsion-filled gels and emulsion particulate gels. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 86, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, K.C.G.; Sato, A.C.K. Sonication technique to produce emulsions: The impact of ultrasonic power and gelatin concentration. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2019, 52, 286–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mosavian, M.T.H.; Hassani, A. Making oil-in-water emulsions by ultrasound and stability evaluation using Taguchi method. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 2010, 31, 293–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafari, S.M.; He, Y.; Bhandari, B. Production of sub-micron emulsions by ultrasound and microfluidization techniques. J. Food Eng. 2007, 82, 478–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafari, S.M.; Assadpoor, E.; He, Y.; Bhandari, B. Re-coalescence of emulsion droplets during high-energy emulsification. Food Hydrocoll. 2008, 22, 1191–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foegeding, E.A.; Davis, J.P. Food protein functionality: A comprehensive approach. Food Hydrocoll. 2011, 25, 1853–1864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burger, T.G.; Zhang, Y. Recent progress in the utilization of pea protein as an emulsifier for food applications. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 86, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shavandi, A.; Hou, Y.; Carne, A.; McConnell, M.; Bekhit, A.E.-d.A. Marine Waste Utilization as a Source of Functional and Health Compounds, 1st ed.; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; Volume 87, ISBN 9780128160497. [Google Scholar]
- Karim, A.A.; Bhat, R. Fish gelatin: Properties, challenges, and prospects as an alternative to mammalian gelatins. Food Hydrocoll. 2009, 23, 563–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, D.M.; Inada, T.; Iwamoto, T.; Scialabba, N. Fao Species Catalogue an Annotated and Illustrated Catalogue; FAO Fisheries Officers: Phnom Penh, Cambodia, 1990; ISBN 9251028907. [Google Scholar]
- Surh, J.; Decker, E.A.; McClements, D.J. Properties and stability of oil-in-water emulsions stabilized by fish gelatin. Food Hydrocoll. 2006, 20, 596–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casanova, F.; Mohammadifar, M.A.; Jahromi, M.; Petersen, H.O.; Eybye, K.L.; Kobbelgaard, S.; Jakobsen, G.; Jessen, F. Physico-chemical, structural and techno-functional properties of gelatin from saithe (Pollachius virens) skin. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 156, 918–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AOAC International. Standard Methods 930.15 and 942.05; AOAC International: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Dumas, J.B.A. Procedes de l’analyse organique. Ann. Chim. Phys. 1831, T47, 198–213. [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli, U.K. Cleavage of Structural Proteins during Assembly of Head of Bacteriophage-T4. Nature 1970, 227, 680–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabilloud, T.; Charmont, S. Detection of Proteins on Two-Dimensional Electrophoresis Gels. In Proteome Research: Two-Dimensional Gel Electrophoresis and Identification Methods; Rabilloud, T., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2000; pp. 107–126. ISBN 978-3-642-57105-3. [Google Scholar]
- Herrera, L.M. Analytical Techniques for Studying the Physical Properties of Lipid Emulsions; Hartel, W.R., Clark, J.P., Rodriguez-Lazaro, D., Topping, D., Eds.; Springer New York LLC: New York, NY, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- ISO/TR 13097. Guidelines for the Characterization of Dispersion Stability; ISO: Geneve, Switzerland, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Formulaction Turbiscan Stability Index|Formulaction—Smart Scientific Analysis. Available online: https://www.formulaction.com/en/knowledge-center/turbiscan-stability-index (accessed on 27 January 2020).
- Marcotte, M.; Hoshahili, A.R.T.; Ramaswamy, H.S. Rheological properties of selected hydrocolloids as a function of concentration and temperature. Food Res. Int. 2001, 34, 695–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schröder, A.; Berton-Carabin, C.; Venema, P.; Cornacchia, L. Interfacial properties of whey protein and whey protein hydrolysates and their influence on O/W emulsion stability. Food Hydrocoll. 2017, 73, 129–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beverung, C.J.; Radke, C.J.; Blanch, H.W. Protein adsorption at the oil/water interface: Characterization of adsorption kinetics by dynamic interfacial tension measurements. Biophys. Chem. 1999, 81, 59–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Trindade Alfaro, A.; Balbinot, E.; Weber, C.I.; Tonial, I.B.; Machado-Lunkes, A. Fish Gelatin: Characteristics, Functional Properties, Applications and Future Potentials. Food Eng. Rev. 2014, 7, 33–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjakul, S.; Oungbho, K.; Visessanguan, W.; Thiansilakul, Y.; Roytrakul, S. Characteristics of gelatin from the skins of bigeye snapper, Priacanthus tayenus and Priacanthus macracanthus. Food Chem. 2009, 116, 445–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savadkoohi, S.; Hoogenkamp, H.; Shamsi, K.; Farahnaky, A. Color, sensory and textural attributes of beef frankfurter, beef ham and meat-free sausage containing tomato pomace. Meat Sci. 2014, 97, 410–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro-González, M.I.; Méndez-Armenta, M. Heavy metals: Implications associated to fish consumption. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2008, 26, 263–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kołodziejska, I.; Skierka, E.; Sadowska, M.; Kołodziejski, W.; Niecikowska, C. Effect of extracting time and temperature on yield of gelatin from different fish offal. Food Chem. 2008, 107, 700–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damodaran, K.; Parkin, O.R.; Fennema, S. Fennema’s Food Chemistry, 4th ed.; CRC Press: New York, NY, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Fustier, P.; Achouri, A.; Taherian, A.R.; Britten, M.; Pelletier, M.; Sabik, H.; Villeneuve, S.; Mondor, M. Protein-Protein Multilayer Oil-in-Water Emulsions for the Microencapsulation of Flaxseed Oil: Effect of Whey and Fish Gelatin Concentration. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 9239–9250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amine, C.; Dreher, J.; Helgason, T.; Tadros, T. Investigation of emulsifying properties and emulsion stability of plant and milk proteins using interfacial tension and interfacial elasticity. Food Hydrocoll. 2014, 39, 180–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karefyllakis, D.; Octaviana, H.; van der Goot, A.J.; Nikiforidis, C.V. The emulsifying performance of mildly derived mixtures from sunflower seeds. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 88, 75–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Wang, B.; Barrow, C.J.; Adhikari, B. Relating the variation of secondary structure of gelatin at fish oil-water interface to adsorption kinetics, dynamic interfacial tension and emulsion stability. Food Chem. 2014, 143, 484–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murray, B.S. Interfacial rheology of food emulsifiers and proteins. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2002, 7, 426–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, A.; Nakai, S. Hydrophobicity determined by a fluorescence probe method and its correlation with surface properties of proteins. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1980, 624, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muijlwijk, K.; Huang, W.; Vuist, J.E.; Berton-Carabin, C.; Schroën, K. Convective mass transport dominates surfactant adsorption in a microfluidic Y-junction. Soft Matter 2016, 12, 9025–9029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vioque, J.; Sánchez-vioque, R.; Clemente, A.; Pedroche, J.; Millán, F. Partially hydrolyzed rapeseed protein isolates with improved functional properties. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2000, 77, 447–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amarowicz, R. Modification of emulsifying properties of food proteins by enzymatic hydrolysis. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2010, 112, 695–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slizyte, R.; Dauksas, E.; Falch, E.; Storo, I.; Rustad, T. Characteristic of protein fractions generated from hydrolysed cod (Gadus morhua) by-product. Process Biochem. 2005, 40, 2021–2033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comunian, T.A.; Ravanfar, R.; Selig, M.J.; Abbaspourrad, A. Influence of the protein type on the stability of fish oil in water emulsion obtained by glass microfluidic device. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 77, 96–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nejadmansouri, M.; Hosseini, S.M.H.; Niakosari, M.; Yousefi, G.H.; Golmakani, M.T. Physicochemical properties and storage stability of ultrasound-mediated WPI-stabilized fish oil nanoemulsions. Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 61, 801–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genot, C.; Meynier, A.; Riaublanc, A. Lipid oxidation in emulsions. In Lipid Oxidation Pathways; Kamal-Eldin, A., Ed.; AOCS Press: Champaign, IL, USA, 2003; pp. 190–244. [Google Scholar]








| Skin Washing | Pre Treatment | Washing | Step 1 | Step 2 | Step 3 | Step 4 | Step 5 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | Sigma (commercial sample) | |||||||
| B | Norland (commercial sample) | |||||||
| C | No | Neutrase | Water | HCl | 80 °C for 5 min | centrifugation 5 min at 2100× g | Adjusted pH at 6.5 | centrifugation 5 min at 2100× g |
| D | No | Citric acid | ||||||
| E | Yes | |||||||
| Sample | Water (%) | Ash (%) | Protein (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| A | 11.73 ± 0.08 | 0.18 ± 0.03 | 84.43 ± 0.72 |
| B | 11.97 ± 0.01 | 0.25 ± 0.03 | 81.91 ± 0.61 |
| C | 7.09 ± 0.06 | 27.62 ± 0.11 | 63.91 ± 0.34 |
| D | 4.81 ± 1.28 | 24.39 ± 1.06 | 54.06 ± 1.48 |
| E | 7.96 ± 0.13 | 1.17 ± 0.03 | 86.10 ± 0.34 |
| A | B | C | D | E | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Macroelements (g/kg dry matter) | Na | 0.08 | 0.13 | 115 | 72.70 | 1.43 |
| Mg | 0.01 | <0.01 | 0.88 | 0.87 | 0.39 | |
| K | 0.16 | <0.05 | 0.75 | 0.30 | 1.55 | |
| Ca | 0.51 | <0.20 | 2.85 | 17.70 | <0.20 | |
| Microelements (mg/kg dry matter) | Cr | 0.23 | 0.11 | 14.20 | 18.60 | 1.60 |
| Mn | 0.01 | 0.09 | 1.18 | 6.38 | 0.20 | |
| Fe | 76.40 | 1.30 | 101 | 127 | 8.75 | |
| Co | <0.01 | <0.01 | 0.10 | 0.19 | <0.01 | |
| Ni | 0.06 | <0.01 | 5.93 | 9.38 | <0.01 | |
| Zn | 0.36 | <0.01 | 0.83 | 97.10 | 2.83 | |
| Cu | 0.45 | 1.07 | 2.24 | 3.79 | 0.78 | |
| Se | 4.57 | <0.01 | 2.35 | 0.32 | <0.01 | |
| Sr | 2.16 | <0.05 | 37.20 | 147 | 11.1 | |
| Toxic elements (mg/kg dry matter) | Cd | 0.33 | <0.01 | 0.12 | <0.01 | <0.01 |
| Pb | <0.05 | <0.05 | <0.05 | 0.14 | <0.05 | |
| Hg | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Henriet, P.; Jessen, F.; Vall-llosera, M.; Marie, R.; Jahromi, M.; Mohammadifar, M.A.; Stampe-Villadsen, H.L.; Olander Petersen, H.; Sloth, J.J.; Loft Eybye, K.; et al. Physical Stability of Oil-In-Water Emulsion Stabilized by Gelatin from Saithe (Pollachius virens) Skin. Foods 2020, 9, 1718. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9111718
Henriet P, Jessen F, Vall-llosera M, Marie R, Jahromi M, Mohammadifar MA, Stampe-Villadsen HL, Olander Petersen H, Sloth JJ, Loft Eybye K, et al. Physical Stability of Oil-In-Water Emulsion Stabilized by Gelatin from Saithe (Pollachius virens) Skin. Foods. 2020; 9(11):1718. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9111718
Chicago/Turabian StyleHenriet, Pauline, Flemming Jessen, Mar Vall-llosera, Rodolphe Marie, Mastaneh Jahromi, Mohammad Amin Mohammadifar, Hanne Lilian Stampe-Villadsen, Heidi Olander Petersen, Jens J. Sloth, Karin Loft Eybye, and et al. 2020. "Physical Stability of Oil-In-Water Emulsion Stabilized by Gelatin from Saithe (Pollachius virens) Skin" Foods 9, no. 11: 1718. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9111718
APA StyleHenriet, P., Jessen, F., Vall-llosera, M., Marie, R., Jahromi, M., Mohammadifar, M. A., Stampe-Villadsen, H. L., Olander Petersen, H., Sloth, J. J., Loft Eybye, K., Jakobsen, G., & Casanova, F. (2020). Physical Stability of Oil-In-Water Emulsion Stabilized by Gelatin from Saithe (Pollachius virens) Skin. Foods, 9(11), 1718. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9111718