Quality Parameters and Consumer Acceptance of Jelly Candies Based on Pomegranate Juice “Mollar de Elche”
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
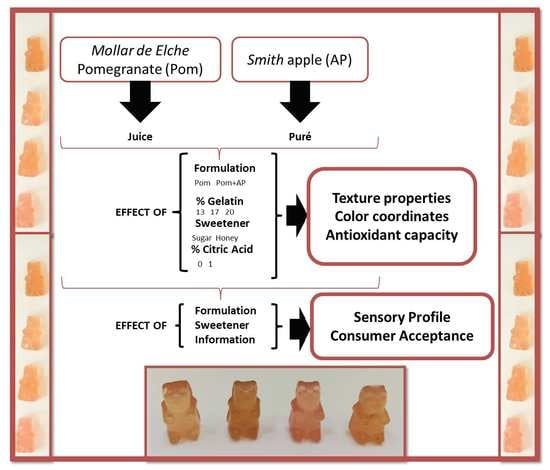
2.1. Experimental Design
2.2. Chemicals
2.3. Plant Material and Jelly Candy Preparation
- Purée preparation: apples were cut, ground, and heated at 80 °C in Thermomix device (Vorwerk, Wuppertal, Germany); 10 mL of citric acid per 1 kg of fruit was added to prevent enzymatic browning of the fruit [25]. Finally, the particle size of the mixture was reduced in a blender until a thin purée was obtained (apple purée, AP).
- Pomegranate juice preparation: pomegranate fruits were cut in halves, arils were manually separated from the husk, and juices were prepared using only arils (pomegranate juice, PJ).
- Gelatin hydration: gelatin was hydrated with water at 25 °C for 10 min (using ratios of 13%, 17%, and 20 %).
- Heat treatment and homogenization: the final blend included 25% of sweetener (sucrose or honey) and 31%, 29%, and 27.5% of pomegranate juice for the product with 13%, 17%, and 20% of gelatin, respectively. These blends were heated at 60 °C for 4 min in a Thermomix device (Vorwerk, Wuppertal, Germany) and then the same percentage (31%, 29%, and 27.5%) of pomegranate juice or apple purée was added and mixed at 60 °C for 2 min. Finally, the different formulations were obtained (Table 1).
2.4. Antioxidant Capacity (DPPH, FRAP, ABTS+) and Total Polyphenol Content
2.5. Color Parameters
2.6. Texture
2.7. Descriptive Sensory Analysis
2.8. Consumer Study
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Percentage of Gelatin Selection
3.2. Addition of 1% Citric Acid
3.3. Descriptive Sensory Analysis, Consumer Acceptability, and Driving Sensory Attributes
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hani, N.M.; Romli, S.R.; Ahmad, M. Influences of red pitaya fruit puree and gelling agents on the physico-mechanical properties and quality changes of gummy confections. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 50, 331–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartel, R.W.; Elbe, J.H.V.; Hofberger, R. Confectionery Science and Technology; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- De Moura, S.C.S.R.; Berling, C.L.; Garcia, A.O.; Queiroz, M.B.; Alvim, I.D.; Hubinger, M.D. Release of anthocyanins from the hibiscus extract encapsulated by ionic gelation and application of microparticles in jelly candy. Food Res. Int. 2019, 121, 542–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delgado, P.; Bañón, S. Effects of replacing starch by inulin on the physicochemical, texture and sensory characteristics of gummy jellies. CyTA J. Food 2018, 16, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mutlu, C.; Tontul, S.A.; Erbaş, M. Production of a minimally processed jelly candy for children using honey instead of sugar. LWT 2018, 93, 499–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cappa, C.; Lavelli, V.; Mariotti, M. Fruit candies enriched with grape skin powders: Physicochemical properties. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 62, 569–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olza, J.; Martínez de Victoria, E.; Aranceta-Bartrina, J.; González-Gross, M.; Ortega, R.M.; Serra-Majem, L.; Varela-Moreiras, G.; Gil, Á. Adequacy of Critical Nutrients Affecting the Quality of the Spanish Diet in the ANIBES Study. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rippe, J.M.; Angelopoulos, T.J. Relationship between Added Sugars Consumption and Chronic Disease Risk Factors: Current Understanding. Nutrients 2016, 8, 697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khawaja, A.H.; Qassim, S.; Hassan, N.A.G.M.; Arafa, E.-S.A. Added sugar: Nutritional knowledge and consumption pattern of a principal driver of obesity and diabetes among undergraduates in UAE. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Clin. Res. Rev. 2019, 13, 2579–2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chepulis, L.M.; Starkey, N.J.; Waas, J.R.; Molan, P.C. The effects of long-term honey, sucrose or sugar-free diets on memory and anxiety in rats. Physiol. Behav. 2009, 97, 359–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacques, A.; Chaaya, N.; Beecher, K.; Ali, S.A.; Belmer, A.; Bartlett, S. The impact of sugar consumption on stress driven, emotional and addictive behaviors. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2019, 103, 178–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Čižauskaitė, U.; Jakubaitytė, G.; Žitkevičius, V.; Kasparavičienė, G. Natural Ingredients-Based Gummy Bear Composition Designed According to Texture Analysis and Sensory Evaluation In Vivo. Molecules 2019, 24, 1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rubio-Arraez, S.; Capella, J.V.; Castelló, M.L.; Ortolá, M.D. Physicochemical characteristics of citrus jelly with non cariogenic and functional sweeteners. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 53, 3642–3650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rivero, R.; Archaina, D.; Sosa, N.; Leiva, G.; Baldi Coronel, B.; Schebor, C. Development of healthy gummy jellies containing honey and propolis. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2020, 100, 1030–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batada, A.; Jacobson, M.F. Prevalence of Artificial Food Colors in Grocery Store Products Marketed to Children. Clin. Pediatr. 2016, 55, 1113–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cano-Lamadrid, M.; Nowicka, P.; Hernández, F.; Carbonell-Barrachina, A.A.; Wojdyło, A. Phytochemical composition of smoothies combining pomegranate juice (Punica granatum L) and Mediterranean minor crop purées (Ficus carica, Cydonia oblonga, and Ziziphus jujube). J. Sci. Food Agric. 2018, 98, 5731–5741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cano-Lamadrid, M.; Lech, K.; Michalska, A.; Wasilewska, M.; Figiel, A.; Wojdyło, A.; Carbonell-Barrachina, Á.A. Influence of osmotic dehydration pre-treatment and combined drying method on physico-chemical and sensory properties of pomegranate arils, cultivar Mollar de Elche. Food Chem. 2017, 232, 306–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cano-Lamadrid, M.; Trigueros, L.; Wojdyło, A.; Carbonell-Barrachina, Á.A.; Sendra, E. Anthocyanins decay in pomegranate enriched fermented milks as a function of bacterial strain and processing conditions. LWT 2017, 80, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berenguer, M.; Vegara, S.; Barrajón, E.; Saura, D.; Valero, M.; Martí, N. Physicochemical characterization of pomegranate wines fermented with three different Saccharomyces cerevisiae yeast strains. Food Chem. 2016, 190, 848–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedigheh, A.; Mahtab, K.; Amirhossein, S.; Nizal, S. Pomegranate Consumption and Blood Pressure: A Review. Curr. Pharmaceut. Des. 2017, 23, 1042–1050. [Google Scholar]
- Faria, A.; Calhau, C. The Bioactivity of Pomegranate: Impact on Health and Disease. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2011, 51, 626–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Royer, G.; Madieta, E.; Symoneaux, R.; Jourjon, F. Preliminary study of the production of apple pomace and quince jelly. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2006, 39, 1022–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrido, J.I.; Lozano, J.E.; Genovese, D.B. Effect of formulation variables on rheology, texture, colour, and acceptability of apple jelly: Modelling and optimization. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 62, 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ventura, J.; Alarcón-Aguilar, F.; Roman-Ramos, R.; Campos-Sepulveda, E.; Reyes-Vega, M.L.; Daniel Boone-Villa, V.; Jasso-Villagómez, E.I.; Aguilar, C.N. Quality and antioxidant properties of a reduced-sugar pomegranate juice jelly with an aqueous extract of pomegranate peels. Food Chem. 2013, 136, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorantes-Álvarez, L.; Chiralt, A. Color of minimally processed fruits and vegetables as affected by some chemical and biochemical changes. In Minimally Processed Fruits and Vegetables; Alzamora, S., Tapia, M., Lopez-Malo, A., Eds.; Aspen Publishers: Gaithersburg, MA, USA, 2000; pp. 111–126. [Google Scholar]
- Re, R.; Pellegrini, N.; Proteggente, A.; Pannala, A.; Yang, M.; Rice-Evans, C. Antioxidant activity applying an improved ABTS radical cation decolorization assay. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1999, 26, 1231–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benzie, I.F.F.; Strain, J.J. The Ferric Reducing Ability of Plasma (FRAP) as a Measure of “Antioxidant Power”: The FRAP Assay. Anal. Biochem. 1996, 239, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cano-Lamadrid, M.; Vázquez-Araújo, L.; Sánchez-Rodríguez, L.; Wodyło, A.; Carbonell-Barrachina, Á.A. Consumers’ Opinion on Dried Pomegranate Arils to Determine the Best Processing Conditions. J. Food Sci. 2018, 83, 3085–3091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cano-Lamadrid, M.; Turkiewicz, I.P.; Tkacz, K.; Sánchez-Rodríguez, L.; López-Lluch, D.; Wojdyło, A.; Sendra, E.; Carbonell-Barrachina, A.A. A Critical Overview of Labeling Information of Pomegranate Juice-Based Drinks: Phytochemicals Content and Health Claims. J. Food Sci. 2019, 84, 886–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koppel, K.; Chambers, E., IV. Development and application of a lexicon to describe the flavor of pomegranate juice. J. Sens. Stud. 2010, 25, 819–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vázquez-Araújo, L.; Nuncio-Jáuregui, P.N.; Cherdchu, P.; Hernández, F.; Chambers, E., IV; Carbonell-Barrachina, Á.A. Physicochemical and descriptive sensory characterization of Spanish pomegranates: Aptitudes for processing and fresh consumption. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 49, 1663–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil, M.I.; Tomás-Barberán, F.A.; Hess-Pierce, B.; Holcroft, D.M.; Kader, A.A. Antioxidant Activity of Pomegranate Juice and Its Relationship with Phenolic Composition and Processing. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2000, 48, 4581–4589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, S.I.F.S.; Jongen, W.M.F.; van Boekel, M.A.J.S. A review of Maillard reaction in food and implications to kinetic modelling. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2000, 11, 364–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deutch, C.E. Browning in apples: Exploring the biochemical basis of an easily-observable phenotype. Biochem. Mol. Biol. Educ. 2018, 46, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeMars, L.L.; Ziegler, G.R. Texture and structure of gelatin/pectin-based gummy confections. Food Hydrocolloids 2001, 15, 643–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holcroft, D.M.; Gil, M.I.; Kader, A.A. Effect of Carbon Dioxide on anthocyanins, phenylalanine ammonia lyase and glucosyltransferase in the arils of stored pomegranate. J. Am. Soc. Hortic. Sci. 1998, 123, 136–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brouillard, R.; Figueiredo, P.; Elhabiri, M.; Dangles, O. Molecular interactions of phenolic compounds in relation to the colour of fruit and vegetables. In Phytochemistry of Fruit and Vegetables; Tomás-Barberán, F.A., Robins, R.J., Eds.; Clarendon Press: Oxford, UK, 1997; pp. 29–49. [Google Scholar]
- Hassimotto, N.M.A.; Genovese, M.I.; Lajolo, F.M. Antioxidant Activity of Dietary Fruits, Vegetables, and Commercial Frozen Fruit Pulps. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 2928–2935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.-O.; Padilla-Zakour, O.I. Jam Processing Effect on Phenolics and Antioxidant Capacity in Anthocyanin-rich Fruits: Cherry, Plum, and Raspberry. J. Food Sci. 2004, 69, S395–S400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, V.S.; Damiani, C.; Asquieri, E.R.; Orsi, D.C.; Nishi, A.C.F. Development and antioxidant capacity of sapota pulp Jelly (Quararibea cordata Vischer). Ciência Agrotecnol. 2012, 36, 341–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Choi, Y.; Lee, S.M.; Chun, J.; Lee, H.B.; Lee, J. Influence of heat treatment on the antioxidant activities and polyphenolic compounds of Shiitake (Lentinus edodes) mushroom. Food Chem. 2006, 99, 381–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maizura, M.; Aminah, A.; Wan Aida, W. Total phenolic content and antioxidant activity of kesum (Polygonum minus), ginger (Zingiber officinale) and turmeric (Curcuma longa) extract. Int. Food Res. J. 2011, 18, 529–534. [Google Scholar]
- Mohd Rasidek, N.A.; Mad Nordin, M.F.; Shameli, K. Formulation and evaluation of semisolid jelly produced by Musa acuminata Colla (AAA Group) peels. Asian Pacific J. Trop. Biomed. 2016, 6, 55–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.; Asmah, R. Comparison of total phenolic contents and antioxidant activities of turmeric leaf, pandan leaf and torch ginger flower. Int. Food Res. J. 2010, 17, 417–423. [Google Scholar]
- Gacche, R.N.; Shinde, B.T.; Dhole, N.A.; Pund, M.M.; Jadhav, A.D. Evaluation of floral honey for inhibition of polyphenol oxidase-mediated browning, antioxidant and antimicrobial activities. J. Food Biochem. 2009, 33, 693–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cano-Lamadrid, M.; Galindo, A.; Collado-González, J.; Rodríguez, P.; Cruz, Z.N.; Legua, P.; Burló, F.; Morales, D.; Carbonell-Barrachina, Á.A.; Hernández, F. Influence of deficit irrigation and crop load on the yield and fruit quality in Wonderful and Mollar de Elche pomegranates. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2018, 98, 3098–3108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higa, F.; Koppel, K.; Chambers, E. Effect of Additional Information on Consumer Acceptance: An Example with Pomegranate Juice and Green Tea Blends. Beverages 2017, 3, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]


| Code † | Gelatin | Honey | Sucrose | Juice | Purée | Citric Acid |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (%) ‡ | ||||||
| PJH-13 | 13 | 25 | - | 62 | 0 | |
| PJH-17 | 17 | 25 | - | 58 | 0 | |
| PJH-20 | 20 | 25 | - | 55 | 0 | |
| PJS-13 | 13 | - | 25 | 62 | 0 | |
| PJS-17 | 17 | - | 25 | 58 | 0 | |
| PJS-20 | 20 | - | 25 | 55 | 0 | |
| PJAPH-13 | 13 | 25 | - | 31 | 31 | 0 |
| PJAPH-17 | 17 | 25 | - | 29 | 29 | 0 |
| PJAPH-20 | 20 | 25 | - | 27.5 | 27.5 | 0 |
| PJAPS-13 | 13 | - | 25 | 31 | 31 | 0 |
| PJAPS-17 | 17 | - | 25 | 29 | 29 | 0 |
| PJAPS-20 | 20 | - | 25 | 27.5 | 27.5 | 0 |
| PJH-20c | 20 | 25 | - | 55 | 1 | |
| PJS-20c | 20 | - | 25 | 55 | 1 | |
| PJAPH-20c | 20 | 25 | - | 27.5 | 27.5 | 1 |
| PJAPS-20c | 20 | - | 25 | 27.5 | 27.5 | 1 |
| Samples | Antioxidant Capacity | Color | Texture Properties γ | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ABTS+ | DPPH | FRAP | TPC | H | A | S | Co | G | Ch | ||||
| (mg/100 g fw) | L* | a* | b* | (g) | (g s−1) | (g) | (g) | (g mm−1) | |||||
| PJH-13 | 2.61cd | 14.8a | 4.51a | 159a | 25.1d | 0.74c | 3.12d | 885.0d | −4790abc | 0.74 | 0.31 | 269.6 | 209.5 |
| PJH-17 | 2.51d | 13.8b | 3.30b | 133b | 23.9de | 0.65cde | 3.15d | 1224cd | −7191.8bcde | 0.55 | 0.31 | 384.8 | 226.9 |
| PJH-20 | 2.48d | 11.9de | 3.57b | 77.8f | 22.6ef | 0.49ef | 3.19d | 3664a | −8629cde | 0.76 | 0.26 | 959.0 | 791.6 |
| PJS-13 | 2.70bcd | 11.1ef | 4.59a | 116cd | 24.8d | 1.24a | 2.25ef | 1542c | −2138a | 0.94 | 0.30 | 467.2 | 444.6 |
| PJS-17 | 3.64a | 12.1d | 4.27a | 115de | 25.7d | 0.70cd | 1.90f | 820.9d | −4248abc | 1.06 | 0.45 | 203.4 | 213.8 |
| PJS-20 | 2.90bcd | 14.9a | 1.47f | 108d | 21.4f | 0.68cd | 2.43e | 2795b | −3304ab | 1.05 | 0.30 | 847.8 | 900.8 |
| PJAPH-13 | 3.13b | 12.6cd | 1.86df | 127bc | 30.7abc | 0.55de | 4.19bc | 791.5d | −4535abc | 1.08 | 0.56 | 442.8 | 478.9 |
| PJAPH-17 | 2.89bcd | 10.8f | 2.44cd | 106d | 29.07bc | 0.13g | 3.70c | 1080cd | −8026cde | 0.90 | 0.66 | 716.2 | 643.8 |
| PJAPH-20 | 2.79bcd | 12.1cd | 1.41f | 72.0f | 29.6bc | 0.38f | 4.20b | 1298cd | −9898e | 1.02 | 0.53 | 692.7 | 704.7 |
| PJAPS-13 | 3.69a | 12.2cd | 2.67c | 92.2e | 32.7a | 0.47ef | 5.25a | 747.3d | −4309abc | 1.02 | 0.52 | 386.8 | 393.8 |
| PJAPS-17 | 3.09bc | 12.9c | 3.21b | 159a | 31.1ab | 0.93b | 3.76bc | 836.8d | −7018bcde | 0.93 | 0.71 | 595.2 | 551.3 |
| PJAPS-20 | 2.46d | 10.6f | 2.04de | 109d | 28.9c | −0.15h | 1.66f | 950.5d | 5662.7bcd | 0.99 | 0.58 | 551.5 | 550.4 |
| Multifactor ANOVA † | |||||||||||||
| Formulation (F) | NS | ** | *** | NS | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | ** | *** | NS | NS |
| % Gelatin (G) | ** | * | *** | ** | *** | *** | *** | ** | *** | NS | *** | NS | NS |
| Sweetener (Sw) | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | *** | *** | NS | *** | ** | NS | NS | NS |
| F × G | ** | NS | *** | *** | NS | NS | NS | *** | NS | NS | NS | *** | *** |
| F × Sw | NS | NS | *** | *** | NS | NS | NS | NS | * | ** | NS | NS | NS |
| G × Sw | NS | * | *** | *** | * | * | NS | *** | *** | NS | * | NS | |
| F × G × S | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | NS | NS | NS | NS |
| Tukey Test ‡ | |||||||||||||
| F | |||||||||||||
| PJ γ | 2.80 | 13.1a | 3.62a | 118 | 23.9b | 0.75a | 2.68b | 16345a | −5180a | 0.84 b | 0.32 b | 478.4 | 418.9 |
| PJAP | 3.01 | 11.9b | 2.27b | 111 | 30.3a | 0.38b | 3.82a | 642.6b | −6643b | 1.00a | 0.57a | 372.7 | 372.4 |
| G | |||||||||||||
| 13% | 4.01a | 12.7a | 4.13a | 145a | 28.3a | 0.75a | 3.70a | 991.6b | −3943a | 0.94 | 0.42 b | 391.6 | 381.7 |
| 17% | 3.60ab | 12.2ab | 3.26b | 129ab | 27.4a | 0.60b | 3.13b | 787.0b | −6462b | 0.86 | 0.50 a | 323.0 | 275.8 |
| 20% | 2.81b | 11.5b | 2.43b | 107b | 25.6b | 0.35c | 2.92b | 1638a | −7320b | 0.94 | 0.42 b | 561.9 | 526.4 |
| S | |||||||||||||
| Honey | 3.42 | 12.2 | 3.55 | 122 | 26.8 | 0.49b | 3.59a | 1223 | −7249b | 0.84b | 0.42 | 403.5 | 384.7 |
| Sucrose | 3.53 | 12.1 | 2.99 | 133 | 27.4 | 0.65a | 2.91b | 1054 | −4568a | 1.00a | 0.47 | 447.6 | 406.6 |
| Samples | L* | a* | b* | ABTS+ | DPPH | FRAP | TPC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (mg/100 g fw) | |||||||
| PJH-20 | 23.9bc | 0.65c | 3.15b | 2.51c | 13.8ab | 3.30b | 74.1d |
| PJS-20 | 25.7b | 0.70c | 1.90c | 3.34b | 12.1c | 4.27a | 124bc |
| PJAPH-20 | 29.1a | 0.13d | 3.70b | 2.99bc | 10.8d | 2.44bc | 107c |
| PJAPS-20 | 31.1a | 0.93bc | 3.76b | 3.09bc | 12.9bc | 3.21b | 139ab |
| PJH-20c | 19.7d | 0.85bc | 1.72cd | 2.45c | 13.9ab | 1.18d | 133abc |
| PJS-20c | 23.2c | 1.94a | 0.98d | 3.68b | 13.6ab | 3.31b | 115bc |
| PJAPH-20c | 29.6a | 1.06b | 6.24a | 4.83a | 14.4a | 2.81bc | 107c |
| PJAPS-20c | 28.7a | 0.17d | 5.82a | 2.46c | 12.5c | 1.17d | 160a |
| Multifactor ANOVA † | |||||||
| Formulation (F) | *** | *** | *** | NS | NS | NS | NS |
| Citric acid (C) | *** | *** | *** | NS | *** | *** | * |
| Sweetener (Sw) | *** | *** | ** | NS | NS | NS | * |
| F × C | * | NS | *** | NS | NS | NS | NS |
| F × Sw | * | NS | *** | *** | NS | *** | NS |
| C × Sw | NS | NS | NS | *** | NS | NS | NS |
| F × C × Sw | *** | *** | * | * | *** | ** | *** |
| Tukey Test ‡ | |||||||
| F | |||||||
| PJA γ | 23.1b | 1.05a | 1.95b | 3.07 | 13.3 | 3.02 | 112 |
| PJAP | 29.6a | 0.58b | 4.89a | 3.32 | 12.6 | 2.41 | 128 |
| C | |||||||
| 0% | 27.4a | 0.61b | 3.14b | 3.03 | 12.4b | 3.31a | 111b |
| 1% | 25.3b | 1.02a | 3.70a | 3.35 | 13.6a | 2.11b | 129a |
| Sw | |||||||
| H | 25.6b | 0.69b | 3.13b | 3.17 | 13.2 | 2.43 | 105b |
| S | 27.2a | 0.94a | 3.72a | 3.22 | 12.8 | 2.99 | 134a |
| Samples | Color | Brightness | Sweetness | Sourness | Fruity | Pomegranate ID | Honey ID | Apple ID | Solubility | Hardness |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PJH-20c | 0.6b | 8.8a | 1.8b | 0.9 | 2.3ab | 0.8 | 0.2b | 1.8a | 5.7 | 3.4 |
| PJS-20c | 4.0a | 8.4a | 1.5b | 0.4 | 1.9b | 0.3 | 0.3b | 0.3b | 6.3 | 2.9 |
| PJAPH-20c | 0.1b | 6.3b | 2.1ab | 0.4 | 2.2ab | 0.5 | 0.4b | 1.5a | 5.9 | 3.1 |
| PJAPS-20c | 0.1b | 6.3b | 2.7a | 0.8 | 2.7a | 0.8 | 1.4a | 1.6a | 5.0 | 3.3 |
| ANOVA Multifactor † | ||||||||||
| Formulation (F) | *** | *** | * | NS | NS | NS | ** | * | * | NS |
| Sweetener (Sw) | *** | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | ** | ** | NS | NS |
| F × Sw | *** | *** | *** | NS | * | NS | ** | ** | ** | NS |
| Tukey Test ‡ | ||||||||||
| F | ||||||||||
| PJc γ | 2.3a | 8.6a | 1.6b | 0.7 | 2.1 | 0.5 | 0.2b | 1.0b | 6.0a | 3.2 |
| PJAPc | 0.1b | 6.3b | 2.4a | 0.6 | 2.4 | 0.6 | 0.9a | 1.5a | 5.5b | 3.2 |
| Sw | ||||||||||
| Honey | 0.3b | 7.5 | 1.9 | 0.7 | 2.2 | 0.6 | 0.3b | 1.6a | 5.8 | 3.3 |
| Sucrose | 2.0a | 7.4 | 2.1 | 0.6 | 2.3 | 0.5 | 0.8a | 0.9b | 5.7 | 3.1 |
| Samples | Overall | Color | Appearance | Fruity ID | Pom ID | Sweetness | Sourness | Hardness | Solubility | Adhesiveness |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PJH-20c | 4.8b | 4.4b | 5.0c | 4.4b | 4.3 | 5.2 | 5.0 | 5.1 | 5.7 | 5.5 |
| PJS-20c | 5.9a | 6.1a | 6.2ab | 5.1ab | 4.7 | 5.2 | 4.8 | 5.5 | 5.2 | 5.7 |
| PJAPH-20c | 4.8b | 4.4b | 5.0c | 4.4B | 4.3 | 5.2 | 5.0 | 5.1 | 5.7 | 5.5 |
| PJAPS-20c | 5.0ab | 4.6b | 5.3bc | 4.6ab | 4.3 | 5.1 | 5.0 | 5.2 | 5.5 | 5.5 |
| PJH-20c+inf | 5.2ab | 4.7b | 5.5abc | 4.5b | 4.4 | 5.1 | 5.1 | 5.5 | 5.7 | 5.9 |
| PJS-20c+inf | 6.0a | 6.0a | 6.5a | 5.5a | 5.0 | 5.7 | 5.5 | 6.0 | 6.0 | 6.0 |
| PJAPH-20c+inf | 5.2ab | 4.7b | 5.5abc | 4.5b | 4.4 | 5.1 | 5.1 | 5.5 | 5.7 | 5.9 |
| PJAPS-20c+inf | 5.5ab | 5.1ab | 6.0ab | 4.9ab | 4.9 | 5.2 | 5.4 | 5.4 | 5.7 | 5.8 |
| ANOVA Multifactor † | ||||||||||
| Formulation (F) | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS |
| Sweetener (Sw) | * | *** | ** | ** | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS |
| Information (Inf) | * | NS | ** | NS | * | NS | *** | * | ** | * |
| F × Sw | *** | *** | *** | ** | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS |
| F × Inf | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS |
| Sw × Inf | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS |
| F × Sw × Inf | *** | *** | *** | ** | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS |
| Tukey Test ‡ | ||||||||||
| F | ||||||||||
| PJc γ | 5.5 | 5.3 | 5.8 | 4.9 | 4.6 | 5.3 | 5.1 | 5.5 | 5.6 | 5.8 |
| PJAPc | 5.4 | 5.1 | 5.7 | 4.8 | 4.6 | 5.0 | 5.2 | 5.3 | 5.4 | 5.6 |
| Sw | ||||||||||
| H | 5.2b | 4.9b | 5.6b | 4.6b | 4.5 | 5.1 | 5.1 | 5.3 | 5.5 | 5.7 |
| S | 5.6a | 5.6a | 6.0a | 5.1a | 4.7 | 5.3 | 5.2 | 5.5 | 5.5 | 5.7 |
| Inf | ||||||||||
| Yes | 5.6a | 5.3 | 6.0a | 4.9 | 4.8a | 5.3 | 5.4a | 5.6a | 5.8a | 5.9a |
| No | 5.2b | 5.2 | 5.5b | 4.7 | 4.4b | 5.1 | 4.8b | 5.2b | 5.3b | 5.5b |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cano-Lamadrid, M.; Calín-Sánchez, Á.; Clemente-Villalba, J.; Hernández, F.; Carbonell-Barrachina, Á.A.; Sendra, E.; Wojdyło, A. Quality Parameters and Consumer Acceptance of Jelly Candies Based on Pomegranate Juice “Mollar de Elche”. Foods 2020, 9, 516. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9040516
Cano-Lamadrid M, Calín-Sánchez Á, Clemente-Villalba J, Hernández F, Carbonell-Barrachina ÁA, Sendra E, Wojdyło A. Quality Parameters and Consumer Acceptance of Jelly Candies Based on Pomegranate Juice “Mollar de Elche”. Foods. 2020; 9(4):516. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9040516
Chicago/Turabian StyleCano-Lamadrid, Marina, Ángel Calín-Sánchez, Jesús Clemente-Villalba, Francisca Hernández, Ángel A. Carbonell-Barrachina, Esther Sendra, and Aneta Wojdyło. 2020. "Quality Parameters and Consumer Acceptance of Jelly Candies Based on Pomegranate Juice “Mollar de Elche”" Foods 9, no. 4: 516. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9040516
APA StyleCano-Lamadrid, M., Calín-Sánchez, Á., Clemente-Villalba, J., Hernández, F., Carbonell-Barrachina, Á. A., Sendra, E., & Wojdyło, A. (2020). Quality Parameters and Consumer Acceptance of Jelly Candies Based on Pomegranate Juice “Mollar de Elche”. Foods, 9(4), 516. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9040516