City Scale Modeling of Ultrafine Particles in Urban Areas with Special Focus on Passenger Ferryboat Emission Impact
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Emission Size Spectra
2.2.1. Ferryboat Traffic
2.2.2. Shipping
2.2.3. Road Traffic
2.2.4. Residential Heating
2.2.5. Other Emission Sources
2.3. Model Description
2.4. Model Input
2.5. Measurements
2.5.1. Sampling Equipment
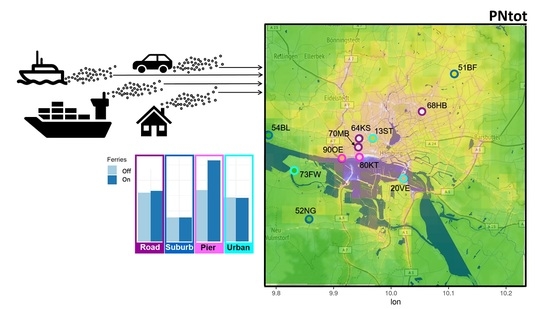
2.5.2. Measurement Sites
3. Results
3.1. Modeled Spatial Distribution
3.2. Modeled Particle Size Distribution
3.3. Modeled Diurnal Variation
3.4. Ultrafine Particles versus Total PN
3.5. Contribution of Ferryboats
3.5.1. Share of Ferryboats in the Total Concentration
3.5.2. Spatial Distribution of Ferryboat Emissions
4. Discussion
4.1. Discrepancies between Modeled PN and Measurements
4.1.1. Modeled PN at Traffic Stations
4.1.2. Modeled PN at Ferryboat Piers
4.1.3. Representativeness of Background PN without Temporal Variation
4.2. Influence of Meteorology on Modeled PN
4.2.1. Day-to-Day Variations
4.2.2. Clean Air Event on Day 1
4.2.3. Challenges for Adequate Modeling of Meteorology
4.3. Limitations of the Current Methodology Application
4.3.1. Missing Emissions from Airport Activities
4.3.2. Nucleation Events
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Meteorological Data Map Showing Locations of Virtual Weather Stations



Appendix B. List of the Monitoring Stations Considered in This Study
| Station | Code | Category | Coordinates | Properties | Measurement Days |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sternschanze | 13ST | Urban background | 53.56; 9.96 | Residential heating; in a park without influence of direct emission sources | Day 1 (8 February 2021) |
| Övelgönne | 90OE | Close to shore/pier | 53.54; 9.91 | Ferryboat emissions; located at the Övelgönne pier, passively influenced by urban background | Day 2 (12 February 2021) and Day 5 (22 February 2021) |
| Max-Brauer Allee | 70MB | Road traffic | 53.55; 9.94 | Road traffic emissions; enclosed by a busy four-lane road, passively influenced by urban background | Day 3 (16 February 2021) |
| Neugraben | 52NG | Suburban background | 53.48; 9.85 | Background concentration; on the edge of a suburban neighborhood and a nature reserve | Day 4 (19 February 2021) |
| Wedel BSH | 15WE | Suburban background | 53.56; 9.71 | Bases for boundary conditions, on the edge of the model extent | June–December 2021 |
| Bramfeld | 51BF | Suburban background | 53.63; 10.11 | Within the suburbs in the Northwesterly edge of the city | - |
| Blankenese | 54BL | Suburban background | 53.56; 9.78 | In a quarter at the left edge of the model domain | - |
| Finkenwerder | 73FW | Urban background | 53.53; 9.83 | At a central location at the southside of the river | - |
| Habichtstraße | 68HB | Road traffic | 53.59; 10.05 | At a major traffic lane in a densely populated area in the northwest | - |
| Altona Elbhang | 80KT | Close to shore/pier | 53.54; 9.94 | Halfway up the slope along the northern shore of the river | - |
| Kieler Straße | 64KS | Road traffic | 53.56; 9.94 | Next to a four-lane street with street-canyon effect | - |
| Veddel | 20VE | Urban background | 53.52; 10.02 | In a residential surrounded by mainly surrounded by port area | - |
References
- European Environment Agency Healthy Environment, Healthy Lives: How the Environment Influences Health and Well-Being in Europe. Available online: https://www.eea.europa.eu/publications/healthy-environment-healthy-lives (accessed on 25 January 2021).
- Caiazzo, F.; Ashok, A.; Waitz, I.A.; Yim, S.H.L.; Barrett, S.R.H. Air Pollution and Early Deaths in the United States. Part I: Quantifying the Impact of Major Sectors in 2005. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 79, 198–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dedoussi, I.C.; Barrett, S.R.H. Air Pollution and Early Deaths in the United States. Part II: Attribution of PM2.5 Exposure to Emissions Species, Time, Location and Sector. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 99, 610–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donaldson, K.; Stone, V.; Clouter, A.; Renwick, L.; MacNee, W. Ultrafine Particles. Occup. Environ. Med. 2001, 58, 211–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wilke, S. Emission von Feinstaub der Partikelgröße PM2.5. Available online: https://www.umweltbundesamt.de/daten/luft/luftschadstoff-emissionen-in-deutschland/emission-von-feinstaub-der-partikelgroesse-pm25 (accessed on 25 January 2021).
- Ibald-Mulli, A.; Wichmann, H.-E.; Kreyling, W.; Peters, A. Epidemiological Evidence on Health Effects of Ultrafine Particles. J. Aerosol Med. 2002, 15, 189–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, H.-S.; Ryu, M.H.; Carlsten, C. Ultrafine Particles: Unique Physicochemical Properties Relevant to Health and Disease. Exp. Mol. Med. 2020, 52, 318–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puustinen, A.; Hämeri, K.; Pekkanen, J.; Kulmala, M.; de Hartog, J.; Meliefste, K.; ten Brink, H.; Kos, G.; Katsouyanni, K.; Karakatsani, A.; et al. Spatial Variation of Particle Number and Mass over Four European Cities. Atmos. Environ. 2007, 41, 6622–6636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morawska, L.; Thomas, S.; Bofinger, N.; Wainwright, D.; Neale, D. Comprehensive Characterization of Aerosols in a Subtropical Urban Atmosphere: Particle Size Distribution and Correlation with Gaseous Pollutants. Atmos. Environ. 1998, 32, 2467–2478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Salma, I.; Borsós, T.; Weidinger, T.; Aalto, P.; Hussein, T.; Dal Maso, M.; Kulmala, M. Production, Growth and Properties of Ultrafine Atmospheric Aerosol Particles in an Urban Environment. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 1339–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Jesus, A.L.; Rahman, M.M.; Mazaheri, M.; Thompson, H.; Knibbs, L.D.; Jeong, C.; Evans, G.; Nei, W.; Ding, A.; Qiao, L.; et al. Ultrafine Particles and PM2.5 in the Air of Cities around the World: Are They Representative of Each Other? Environ. Int. 2019, 129, 118–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morawska, L.; Ristovski, Z.; Jayaratne, E.R.; Keogh, D.U.; Ling, X. Ambient Nano and Ultrafine Particles from Motor Vehicle Emissions: Characteristics, Ambient Processing and Implications on Human Exposure. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 8113–8138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cass, G.; Hughes, L.; Bhave, P.; Kleeman, M.; Allen, J.; Salmon, L. The Chemical Composition of Atmospheric Ultrafine Particles. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2000, 358, 2581–2592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geller, M.D.; Kim, S.; Misra, C.; Sioutas, C.; Olson, B.A.; Marple, V.A. A Methodology for Measuring Size-Dependent Chemical Composition of Ultrafine Particles. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2002, 36, 748–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donaldson, K.; Brown, D.; Clouter, A.; Duffin, R.; MacNee, W.; Renwick, L.; Tran, L.; Stone, V. The Pulmonary Toxicology of Ultrafine Particles. J. Aerosol Med. 2002, 15, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oberdörster, G.; Utell, M.J. Ultrafine Particles in the Urban Air: To the Respiratory Tract—And beyond? Environ. Health Perspect. 2002, 110, A440–A441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Araujo Jesus, A.; Barajas, B.; Kleinman, M.; Wang, X.; Bennett, B.J.; Gong, K.W.; Navab, M.; Harkema, J.; Sioutas, C.; Lusis Aldons, J.; et al. Ambient Particulate Pollutants in the Ultrafine Range Promote Early Atherosclerosis and Systemic Oxidative Stress. Circ. Res. 2008, 102, 589–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Oberdörster, G.; Oberdörster, E.; Oberdörster, J. Nanotoxicology: An Emerging Discipline Evolving from Studies of Ultrafine Particles. Environ. Health Perspect. 2005, 113, 823–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eyring, V.; Köhler, H.W.; van Aardenne, J.; Lauer, A. Emissions from International Shipping: 1. The Last 50 Years. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2005, 110, D17305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzei, F.; D’Alessandro, A.; Lucarelli, F.; Nava, S.; Prati, P.; Valli, G.; Vecchi, R. Characterization of Particulate Matter Sources in an Urban Environment. Sci. Total Environ. 2008, 401, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viana, M.; Hammingh, P.; Colette, A.; Querol, X.; Degraeuwe, B.; de Vlieger, I.; van Aardenne, J. Impact of Maritime Transport Emissions on Coastal Air Quality in Europe. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 90, 96–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, Y.; Rodríguez, S.; Guerra García, J.C.; Trujillo, J.L.; García, R. Ultrafine Particles Pollution in Urban Coastal Air Due to Ship Emissions. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 4907–4914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merico, E.; Conte, M.; Grasso, F.M.; Cesari, D.; Gambaro, A.; Morabito, E.; Gregoris, E.; Orlando, S.; Alebić-Juretić, A.; Zubak, V.; et al. Comparison of the Impact of Ships to Size-Segregated Particle Concentrations in Two Harbour Cities of Northern Adriatic Sea. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 266, 115175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Healy, R.M.; O’Connor, I.P.; Hellebust, S.; Allanic, A.; Sodeau, J.R.; Wenger, J.C. Characterisation of Single Particles from In-Port Ship Emissions. Atmos. Environ. 2009, 43, 6408–6414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirjola, L.; Pajunoja, A.; Walden, J.; Jalkanen, J.-P.; Rönkkö, T.; Kousa, A.; Koskentalo, T. Mobile Measurements of Ship Emissions in Two Harbour Areas in Finland. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2014, 7, 149–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Karl, M.; Pirjola, L.; Karppinen, A.; Jalkanen, J.-P.; Ramacher, M.O.P.; Kukkonen, J. Modeling of the Concentrations of Ultrafine Particles in the Plumes of Ships in the Vicinity of Major Harbors. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lopes, M.; Russo, A.; Gouveia, C.; Ferreira, F. Monitoring of Ultrafine Particles in the Surrounding Urban Area of In-Land Passenger Ferries. J. Environ. Prot. 2019, 10, 838–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jonsson, Å.M.; Westerlund, J.; Hallquist, M. Size-Resolved Particle Emission Factors for Individual Ships. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2011, 38, L13809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moldanová, J.; Fridell, E.; Winnes, H.; Holmin-Fridell, S.; Boman, J.; Jedynska, A.; Tishkova, V.; Demidjian, B.; Joulie, S.; Bladt, H. Physical and Chemical Characterisation of PM Emissions from Two Ships Operating in European Emission Control Areas. Atmos. Meas. Tech. Discuss. 2013, 6, 3577–3596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hofman, J.; Staelens, J.; Cordell, R.; Stroobants, C.; Zikova, N.; Hama, S.M.L.; Wyche, K.P.; Kos, G.P.A.; van der Zee, S.; Smallbone, K.L.; et al. Ultrafine Particles in Four European Urban Environments: Results from a New Continuous Long-Term Monitoring Network. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 136, 68–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lopes, M.; Russo, A.; Monjardino, J.; Gouveia, C.; Ferreira, F. Monitoring of Ultrafine Particles in the Surrounding Urban Area of a Civilian Airport. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2019, 10, 1454–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molnár, P.; Janhäll, S.; Hallquist, M. Roadside Measurements of Fine and Ultrafine Particles at a Major Road North of Gothenburg. Atmos. Environ. 2002, 36, 4115–4123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabaliauskas, K.; Jeong, C.-H.; Yao, X.; Jun, Y.-S.; Jadidian, P.; Evans, G.J. Five-Year Roadside Measurements of Ultrafine Particles in a Major Canadian City. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 49, 245–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwack, L.M.; Hanna, S.R.; Spengler, J.D.; Levy, J.I. Using Advanced Dispersion Models and Mobile Monitoring to Characterize Spatial Patterns of Ultrafine Particles in an Urban Area. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 4822–4829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asmi, A.; Wiedensohler, A.; Laj, P.; Fjaeraa, A.-M.; Sellegri, K.; Birmili, W.; Weingartner, E.; Baltensperger, U.; Zdimal, V.; Zikova, N.; et al. Number Size Distributions and Seasonality of Submicron Particles in Europe 2008–2009. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 5505–5538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Putaud, J.-P.; van Dingenen, R.; Alastuey, A.; Bauer, H.; Birmili, W.; Cyrys, J.; Flentje, H.; Fuzzi, S.; Gehrig, R.; Hansson, H.C.; et al. A European Aerosol Phenomenology—3: Physical and Chemical Characteristics of Particulate Matter from 60 Rural, Urban, and Kerbside Sites across Europe. Atmos. Environ. 2010, 44, 1308–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerminen, V.-M.; Chen, X.; Vakkari, V.; Petäjä, T.; Kulmala, M.; Bianchi, F. Atmospheric New Particle Formation and Growth: Review of Field Observations. Environ. Res. Lett. 2018, 13, 103003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kristensson, A.; Dal Maso, M.; Swietlicki, E.; Hussein, T.; Zhou, J.; Kerminen, V.-M.; Kulmala, M. Characterization of New Particle Formation Events at a Background Site in Southern Sweden: Relation to Air Mass History. Tellus B Chem. Phys. Meteorol. 2008, 60, 330–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karl, M.; Walker, S.-E.; Solberg, S.; Ramacher, M.O.P. The Eulerian Urban Dispersion Model EPISODE—Part 2: Extensions to the Source Dispersion and Photochemistry for EPISODE–CityChem v1.2 and Its Application to the City of Hamburg. Geosci. Model Dev. 2019, 12, 3357–3399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Karl, M. City-Scale Chemistry Transport Model Citychem-EPISODE, Version 1.0; Zenodo; Helmholtz Centre Geesthacht—Centre for Materials and Coastal Research: Geesthacht, Germany, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Deutscher Wetterdienst Wetter Und Klima—Deutscher Wetterdienst—Leistungen—Windkarten Zur Mittleren Windgeschwindigkeit. Available online: https://www.dwd.de/DE/leistungen/windkarten/deutschland_und_bundeslaender.html (accessed on 27 January 2021).
- Statista Jahresniederschlagsmenge in Ausgewählten Städten in Deutschland. 2020. Available online: https://de.statista.com/statistik/daten/studie/583161/umfrage/jahresniederschlagsmenge-in-ausgewaehlten-staedten-in-deutschland/ (accessed on 27 January 2021).
- Hamburger Luftmessnetz Hamburger Luftmessnetz—Schadstoffe—Übersicht—FHH. Available online: https://luft.hamburg.de/clp/schadstoffe/ (accessed on 26 March 2021).
- Struschka, M.; Kilgus, D.; Springmann, M.; Baumbach, G. Effiziente Bereitstellung Aktueller Emissionsdaten für die Luftreinhaltung. Umweltbundesamt. 2009. Available online: https://www.umweltbundesamt.de/publikationen/effiziente-bereitstellung-aktueller-emissionsdaten (accessed on 18 January 2021).
- Umweltbundesamt Umweltbundesamt—Feinstaub (PM2.5) Im Jahr. 2019. Available online: https://www.umweltbundesamt.de/sites/default/files/w21ad_luftdaten/annualtabulation/PDF/pm2_2019.pdf (accessed on 30 November 2021).
- European City Air Quality Viewer—European Environment Agency. Available online: https://www.eea.europa.eu/themes/air/urban-air-quality/european-city-air-quality-viewer (accessed on 1 November 2021).
- Ramacher, M.O.P.; Matthias, V.; Aulinger, A.; Quante, M.; Bieser, J.; Karl, M. Contributions of Traffic and Shipping Emissions to City-Scale NOx and PM2.5 Exposure in Hamburg. Atmos. Environ. 2020, 237, 117674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Morawska, L.; Birmili, W.; Paasonen, P.; Hu, M.; Kulmala, M.; Harrison, R.M.; Norford, L.; Britter, R. Ultrafine Particles in Cities. Environ. Int. 2014, 66, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paasonen, P.; Visshedjik, A.; Kupiainen, K.; Klimont, Z.; van der Gon, H.D.; Kulmala, M. Aerosol Particle Number Emissions and Size Distributions: Implementation in the GAINS Model and Initial Results; IIASA Interim Report; IIASA: Laxenburg, Austria, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Böhm, J.; Wahler, G. Luftreinhalteplan Für Hamburg—1. Fortschreibung. 2012. Available online: https://www.hamburg.de/contentblob/3744850/f3984556074bbb1e95201d67d8085d22/data/fortschreibung-luftreinhalteplan.pdf (accessed on 14 November 2021).
- Winnes, H.; Fridell, E. Particle Emissions from Ships: Dependence on Fuel Type. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2009, 59, 1391–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beecken, J.; Mellqvist, J.; Salo, K.; Ekholm, J.; Jalkanen, J.P.; Johansson, L.; Litvinenko, V.; Volodin, K.; Frank-Kamenetsky, D.A. Emission Factors of SO2, NOx and Particles from Ships in Neva Bay from Ground-Based and Helicopter-Borne Measurements and AIS-Based Modeling. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 5229–5241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ban-Weiss, G.A.; Lunden, M.M.; Kirchstetter, T.W.; Harley, R.A. Measurement of Black Carbon and Particle Number Emission Factors from Individual Heavy-Duty Trucks. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 1419–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Karl, M.; Kukkonen, J.; Keuken, M.P.; Lützenkirchen, S.; Pirjola, L.; Hussein, T. Modeling and Measurements of Urban Aerosol Processes on the Neighborhood Scale in Rotterdam, Oslo and Helsinki. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 4817–4835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Agrawal, H.; Welch, W.A.; Henningsen, S.; Miller, J.W.; Cocker, D.R. Emissions from Main Propulsion Engine on Container Ship at Sea. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2010, 115, D23205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alföldy, B.; Lööv, J.; Lagler, F. Measurements of Air Pollution Emission Factors for Marine Transportation in SECA. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2013, 16, 1777–1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ban-Weiss, G.A.; Lunden, M.M.; Kirchstetter, T.W.; Harley, R.A. Size-Resolved Particle Number and Volume Emission Factors for on-Road Gasoline and Diesel Motor Vehicles. J. Aerosol Sci. 2010, 41, 5–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rivas, I.; Beddows, D.C.S.; Amato, F.; Green, D.C.; Järvi, L.; Hueglin, C.; Reche, C.; Timonen, H.; Fuller, G.W.; Niemi, J.V.; et al. Source Apportionment of Particle Number Size Distribution in Urban Background and Traffic Stations in Four European Cities. Environ. Int. 2020, 135, 105345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R’Mili, B.; Boréave, A.; Meme, A.; Vernoux, P.; Leblanc, M.; Noël, L.; Raux, S.; D’Anna, B. Physico-Chemical Characterization of Fine and Ultrafine Particles Emitted during Diesel Particulate Filter Active Regeneration of Euro5 Diesel Vehicles. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 3312–3319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casati, R.; Scheer, V.; Vogt, R.; Benter, T. Measurement of Nucleation and Soot Mode Particle Emission from a Diesel Passenger Car in Real World and Laboratory in Situ Dilution. Atmos. Environ. 2007, 41, 2125–2135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, R.M.; Rob MacKenzie, A.; Xu, H.; Alam, M.S.; Nikolova, I.; Zhong, J.; Singh, A.; Zeraati-Rezaei, S.; Stark, C.; Beddows, D.C.S.; et al. Diesel Exhaust Nanoparticles and Their Behaviour in the Atmosphere. Proc. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2018, 474, 20180492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Minutolo, P.; D’Anna, A.; Commodo, M.; Pagliara, R.; Toniato, G.; Accordini, C. Emission of Ultrafine Particles from Natural Gas Domestic Burners. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2008, 25, 1357–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozgen, S.; Ripamonti, G.; Cernuschi, S.; Giugliano, M. Ultrafine Particle Emissions for Municipal Waste-to-Energy Plants and Residential Heating Boilers. Rev. Env. Sci. Biotechnol. 2012, 11, 407–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stacey, B. Measurement of Ultrafine Particles at Airports: A Review. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 198, 463–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mertens, J.; Lepaumier, H.; Rogiers, P.; Desagher, D.; Goossens, L.; Duterque, A.; Le Cadre, E.; Zarea, M.; Blondeau, J.; Webber, M. Fine and Ultrafine Particle Number and Size Measurements from Industrial Combustion Processes: Primary Emissions Field Data. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2020, 11, 803–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kukkonen, J.; Karl, M.; Keuken, M.P.; van der Gon, D.; Hugo, A.C.; Denby, B.R.; Singh, V.; Douros, J.; Manders, A.; Samaras, Z.; et al. Modelling the Dispersion of Particle Numbers in Five European Cities. Geosci. Model Dev. 2016, 9, 451–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hamer, P.D.; Walker, S.-E.; Sousa-Santos, G.; Vogt, M.; Vo-Thanh, D.; Lopez-Aparicio, S.; Schneider, P.; Ramacher, M.O.P.; Karl, M. The Urban Dispersion Model EPISODE V10.0—Part 1: An Eulerian and Sub-Grid-Scale Air Quality Model and Its Application in Nordic Winter Conditions. Geosci. Model Dev. 2020, 13, 4323–4353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karl, M.; Ramacher, M. City-Scale Chemistry Transport Model EPISODE-CityChem, Version 1.5; Zenodo; Helmholtz Centre Hereon: Geesthacht, Germany, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Petersen, W.B. User’s Guide for Hiway-2: A Highway Air Pollution Model; EPA-600/8-80-018; U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: Research Triangle Park, NC, USA, 1980.
- Walker, S.-E.; Grønskei, K.E. Spredningsberegninger for On-line Overvåking i Grenland. Programbeskrivelse og Brukerveiledning; NILU: Kjeller, Norway, 1992; ISBN 978-82-425-0395-4. [Google Scholar]
- Walker, S.E. WORM: A new open road line source model for low wind speed conditions. Int. J. Environ. Pollut. 2011, 47, 348–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sič, B.; El Amraoui, L.; Marécal, V.; Josse, B.; Arteta, J.; Guth, J.; Joly, M.; Hamer, P.D. Modelling of Primary Aerosols in the Chemical Transport Model MOCAGE: Development and Evaluation of Aerosol Physical Parameterizations. Geosci. Model Dev. 2015, 8, 381–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schwarzkopf, D.A.; Petrik, R.; Matthias, V.; Quante, M.; Majamäki, E.; Jalkanen, J.-P. A Ship Emission Modeling System with Scenario Capabilities. Atmos. Environ. X 2021, 12, 100132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badeke, R.; Matthias, V.; Grawe, D. Parameterizing the Vertical Downward Dispersion of Ship Exhaust Gas in the near Field. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2021, 21, 5935–5951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramacher, M.O.P.; Kakouri, A.; Speyer, O.; Feldner, J.; Karl, M.; Timmermans, R.; van der Gon, H.D.; Kuenen, J.; Gerasopoulos, E.; Athanasopoulou, E. The UrbEm Hybrid Method to Derive High-Resolution Emissions for City-Scale Air Quality Modeling. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramacher, M.O.P.; Karl, M. Integrating Modes of Transport in a Dynamic Modelling Approach to Evaluate Population Exposure to Ambient NO2 and PM2.5 Pollution in Urban Areas. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 2099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kuik, F.; Kerschbaumer, A.; Lauer, A.; Lupascu, A.; von Schneidemesser, E.; Butler, T.M. Top–down Quantification of NOx Emissions from Traffic in an Urban Area Using a High-Resolution Regional Atmospheric Chemistry Model. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 8203–8225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ketzel, M.; Wåhlin, P.; Berkowicz, R.; Palmgren, F. Particle and Trace Gas Emission Factors under Urban Driving Conditions in Copenhagen Based on Street and Roof-Level Observations. Atmos. Environ. 2003, 37, 2735–2749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klose, S.; Birmili, W.; Voigtländer, J.; Tuch, T.; Wehner, B.; Wiedensohler, A.; Ketzel, M. Particle Number Emissions of Motor Traffic Derived from Street Canyon Measurements in a Central European City. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2009, 9, 3763–3809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urban Atlas 2012—Copernicus Land Monitoring Service. Available online: https://land.copernicus.eu/local/urban-atlas/urban-atlas-2012 (accessed on 8 December 2021).
- Batista e Silva, F.; Poelman, H.; Martens, V.; Lavalle, C. Population Estimation for the Urban Atlas Polygons. In JRC Technical Reports 2013; Publication Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2013; JRC 87300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramacher, M.; Bieser, J. Emission inventories for residential heating: A bottom-up model for the city of Hamburg. In Proceedings of the 18th GEIA Conference, Hamburg, Germany, 13−15 September 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- TSI Incorporated. P-Trak Ultrafine Particle Counter Model 8525. Available online: https://tsi.com/getmedia/f30434e0-ccea-4eb8-a15a-8d6bf42fbd0e/PTrakSpec2980197?ext=.pdf (accessed on 14 November 2021).
- Zhu, Y.; Yu, N.; Kuhn, T.; Hinds, W.C. Field Comparison of P-Trak and Condensation Particle Counters. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 422–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gidhagen, L.; Johansson, C.; Langner, J.; Foltescu, V.L. Urban Scale Modeling of Particle Number Concentration in Stockholm. Atmos. Environ. 2005, 39, 1711–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansson, C.; Norman, M.; Gidhagen, L. Spatial & Temporal Variations of PM10 and Particle Number Concentrations in Urban Air. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2007, 127, 477–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.; Shen, S.; Sioutas, C.; Zhu, Y.; Hinds, W.C. Size Distribution and Diurnal and Seasonal Trends of Ultrafine Particles in Source and Receptor Sites of the Los Angeles Basin. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2002, 52, 297–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, J.; Birmili, W.; Hermann, M.; Tuch, T.; Weinhold, K.; Spindler, G.; Schladitz, A.; Bastian, S.; Löschau, G.; Cyrys, J.; et al. Variability of Black Carbon Mass Concentrations, Sub-Micrometer Particle Number Concentrations and Size Distributions: Results of the German Ultrafine Aerosol Network Ranging from City Street to High Alpine Locations. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 202, 256–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carslaw, D.C.; Ropkins, K. Openair—An R Package for Air Quality Data Analysis. Environ. Model. Softw. 2012, 27–28, 52–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lonati, G.; Crippa, M.; Gianelle, V.; van Dingenen, R. Daily Patterns of the Multi-Modal Structure of the Particle Number Size Distribution in Milan, Italy. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 2434–2442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, V.K.; Kumar, P.; van Poppel, M.; Bleux, N.; Frijns, E.; Reggente, M.; Berghmans, P.; Int Panis, L.; Samson, R. Wintertime Spatio-Temporal Variation of Ultrafine Particles in a Belgian City. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 431, 307–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, Y.; Hinds, W.C.; Kim, S.; Sioutas, C. Concentration and Size Distribution of Ultrafine Particles Near a Major Highway. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2002, 52, 1032–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Birmili, W.; Sun, J.; Weinhold, K.; Merkel, M.; Rasch, F.; Spindler, G.; Wiedensohler, A.; Bastian, S.; Löschau, G.; Schladitz, A.; et al. Atmospheric Aerosol Measurements in the German Ultrafine Aerosol Network (GUAN)—Part III: Black Carbon Mass and Particle Number Concentrations 2009–2014. Gefahrst. Reinhalt. Luft 2015, 75, 479–488. [Google Scholar]
- Birmili, W.; Weinhold, K.; Nordmann, S.; Wiedensohler, A.; Spindler, G.; Mueller, K.; Herrmann, H.; Gnauk, T.; Pitz, M.; Cyrys, J.; et al. Atmospheric Aerosol Measurements in the German Ultrafine Aerosol Network (GUAN). Gefahrst. Reinhalt. Luft 2009, 69, 137–145. [Google Scholar]
- Morawska, L.; Jayaratne, E.R.; Mengersen, K.; Jamriska, M.; Thomas, S. Differences in Airborne Particle and Gaseous Concentrations in Urban Air between Weekdays and Weekends. Atmos. Environ. 2002, 36, 4375–4383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brines, M.; Dall’Osto, M.; Beddows, D.C.S.; Harrison, R.M.; Gómez-Moreno, F.; Núñez, L.; Artíñano, B.; Costabile, F.; Gobbi, G.P.; Salimi, F.; et al. Traffic and Nucleation Events as Main Sources of Ultrafine Particles in High-Insolation Developed World Cities. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 5929–5945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ruellan, S.; Cachier, H. Characterisation of Fresh Particulate Vehicular Exhausts near a Paris High Flow Road. Atmos. Environ. 2001, 35, 453–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rönkkö, T.; Kuuluvainen, H.; Karjalainen, P.; Keskinen, J.; Hillamo, R.; Niemi, J.V.; Pirjola, L.; Timonen, H.J.; Saarikoski, S.; Saukko, E.; et al. Traffic Is a Major Source of Atmospheric Nanocluster Aerosol. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 7549–7554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Birmili, W.; Weinhold, K.; Rasch, F.; Sonntag, A.; Sun, J.; Merkel, M.; Wiedensohler, A.; Bastian, S.; Schladitz, A.; Löschau, G.; et al. Long-Term Observations of Tropospheric Particle Number Size Distributions and Equivalent Black Carbon Mass Concentrations in the German Ultrafine Aerosol Network (GUAN). Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2016, 8, 355–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schaap, M.; Timmermans, R.M.A.; Roemer, M.; Boersen, G.A.C.; Builtjes, P.; Sauter, F.; Velders, G.; Beck, J. The LOTOS?EUROS Model: Description, Validation and Latest Developments. Int. J. Environ. Pollut. 2008, 32, 270–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Birmili, W.; Hermann, M.; Tuch, T.; Weinhold, K.; Merkel, M.; Rasch, F.; Müller, T.; Schladitz, A.; Bastian, S.; et al. Decreasing Trends of Particle Number and Black Carbon Mass Concentrations at 16 Observational Sites in Germany from 2009 to 2018. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 7049–7068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Bismarck-Osten, C.; Birmili, W.; Ketzel, M.; Massling, A.; Petäjä, T.; Weber, S. Characterization of Parameters Influencing the Spatio-Temporal Variability of Urban Particle Number Size Distributions in Four European Cities. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 77, 415–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birmili, W.; Wiedensohler, A.; Heintzenberg, J.; Lehmann, K. Atmospheric Particle Number Size Distribution in Central Europe: Statistical Relations to Air Masses and Meteorology. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2001, 106, 32005–32018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deutscher Wetterdienst Monatlicher Klimastatus Deutschland Februar 2021. Available online: www.dwd.de/klimastatus (accessed on 27 January 2021).
- Law, K.S.; Stohl, A. Arctic Air Pollution: Origins and Impacts. Science 2007, 315, 1537–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Galindo, N.; Varea, M.; Gil-Moltó, J.; Yubero, E.; Nicolás, J. The Influence of Meteorology on Particulate Matter Concentrations at an Urban Mediterranean Location. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2011, 215, 365–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Hartog, J.J.; Hoek, G.; Mirme, A.; Tuch, T.; Kos, G.P.A.; ten Brink, H.M.; Brunekreef, B.; Cyrys, J.; Heinrich, J.; Pitz, M.; et al. Relationship between Different Size Classes of Particulate Matter and Meteorology in Three European Cities. J. Environ. Monit. 2005, 7, 302–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Ketzel, M.; Vardoulakis, S.; Pirjola, L.; Britter, R. Dynamics and Dispersion Modelling of Nanoparticles from Road Traffic in the Urban Atmospheric Environment—A Review. J. Aerosol Sci. 2011, 42, 580–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fujitani, Y.; Kumar, P.; Tamura, K.; Fushimi, A.; Hasegawa, S.; Takahashi, K.; Tanabe, K.; Kobayashi, S.; Hirano, S. Seasonal Differences of the Atmospheric Particle Size Distribution in a Metropolitan Area in Japan. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 437, 339–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Westerdahl, D.; Fruin, S.A.; Fine, P.L.; Sioutas, C. The Los Angeles International Airport as a Source of Ultrafine Particles and Other Pollutants to Nearby Communities. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 3143–3155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudda, N.; Fruin, S.A. International Airport Impacts to Air Quality: Size and Related Properties of Large Increases in Ultrafine Particle Number Concentrations. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 3362–3370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Németh, Z.; Rosati, B.; Zíková, N.; Salma, I.; Bozó, L.; Dameto de España, C.; Schwarz, J.; Ždímal, V.; Wonaschütz, A. Comparison of Atmospheric New Particle Formation Events in Three Central European Cities. Atmos. Environ. 2018, 178, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dall’Osto, M.; Querol, X.; Alastuey, A.; O’Dowd, C.; Harrison, R.M.; Wenger, J.; Gómez-Moreno, F.J. On the Spatial Distribution and Evolution of Ultrafine Particles in Barcelona. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 741–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hussein, T.; Mølgaard, B.; Hannuniemi, H.; Martikainen, J.; Järvi, L.; Wegner, T.; Ripamonti, G.; Weber, S.; Vesala, T.; Hämeri, K. Finger-Prints of Urban Particle Number Size Distribution in Helsinki—Finland: Local versus Regional Characteristics. Boreal Environ. Res. 2014, 19, 1–20. [Google Scholar]










| Area (nm) | Background | Residential | Street/Ferryboat | Ships |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| <5 | 0% | 2% | 2% | 0% |
| <10 | 8.5% | 5% | 6% | 5% |
| <50 | 38% | 22% | 77% | 75% |
| <100 | 89.5% | 93% | 92% | 95% |
| <400 | 100% | 97% | 98% | 99% |
| <1000 | 100% | 99% | 100% | 100% |
| <5000 | 100% | 100% | 100% | 100% |
| <10,000 | 100% | 100% | 100% | 100% |
| Day (Date) | Wind Speed (m/s) | Wind Direction (°) | Temperature (°C) | Rel. Humidity (%) | PN Measurement Station |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Day 1 (8 February 2021) | 4.4 (0.8–5.2) | 83 (73–105) | −2.8 (−5.3–−1.6) | 50.5 (43.6–76.3) | Sternschanze (13ST) |
| Day 2 (12 February 2021) | 1.2 (0.5–1.8) | 65 (31–81) | −5.1 (−7.8–−1.3) | 61.6 (42.7–75.7) | Övelgönne (90OE) |
| Day 3 (16 February 2021) | 0.7 (0.3–2.1) | 167 (89–260) | 3.2 (1.4–5.3) | 89 (83–91) | Max-Brauer-Allee (70MB) |
| Day 4 (19 February 2021) | 1.3 (0.5–2.8) | 198 (97–265) | 6.4 (4.3–9.7) | 75.7 (59.6–89) | Neugraben (52NG) |
| Day 5 (22 February 2021) | 0.6 (0.3–1.3) | 182 (91–242) | 10.3 (2.8–19.5) | 60.8 (32.2–84.3) | Övelgönne (90OE) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lauenburg, M.; Karl, M.; Matthias, V.; Quante, M.; Ramacher, M.O.P. City Scale Modeling of Ultrafine Particles in Urban Areas with Special Focus on Passenger Ferryboat Emission Impact. Toxics 2022, 10, 3. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10010003
Lauenburg M, Karl M, Matthias V, Quante M, Ramacher MOP. City Scale Modeling of Ultrafine Particles in Urban Areas with Special Focus on Passenger Ferryboat Emission Impact. Toxics. 2022; 10(1):3. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10010003
Chicago/Turabian StyleLauenburg, Marvin, Matthias Karl, Volker Matthias, Markus Quante, and Martin Otto Paul Ramacher. 2022. "City Scale Modeling of Ultrafine Particles in Urban Areas with Special Focus on Passenger Ferryboat Emission Impact" Toxics 10, no. 1: 3. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10010003
APA StyleLauenburg, M., Karl, M., Matthias, V., Quante, M., & Ramacher, M. O. P. (2022). City Scale Modeling of Ultrafine Particles in Urban Areas with Special Focus on Passenger Ferryboat Emission Impact. Toxics, 10(1), 3. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10010003