Potential Risks of PM2.5-Bound Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons and Heavy Metals from Inland and Marine Directions for a Marine Background Site in North China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling Site and Sample Collection
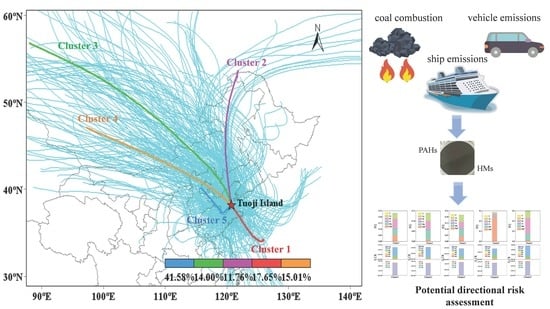
2.1.1. Sampling Site
2.1.2. PM2.5 Sample Collection
2.2. Sample Chemical Analysis
2.2.1. Conventional Components Analysis
2.2.2. Organic Components Analysis
2.3. Quality Assurance and Quality Control
2.4. Health Risk Assessment for Different Directions
2.4.1. Step 1: Back-Trajectory Calculation and Cluster Analysis
2.4.2. Step 2: Source Identification for Different Directions
2.4.3. Step 3: Cancer and Non-Cancer Risk Assessment for Different Directions
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characteristics of PM2.5 and Component Concentrations
3.2. Seasonal Variations of Cancer and Non-Cancer Risks
3.3. Directional Variations of Compositions
3.4. Directional Variations of Risks
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jin, L.; Xie, J.W.; Wong, C.K.C.; Chan, S.K.Y.; Abbaszade, G.; Schnelle-Kreis, J.; Zimmermann, R.; Li, J.; Zhang, G.; Fu, P.Q.; et al. Contributions of City-Specific Fine Particulate Matter (PM2.5) to Differential In Vitro Oxidative Stress and Toxicity Implications between Beijing and Guangzhou of China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 2881–2891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, S.F.; Yan, Q.; Zheng, H.; Liu, H.B.; Wang, W.; Zheng, S.R.; Yang, G.W.; Zheng, M.M.; Wu, J.; Qi, S.H.; et al. Substantial reductions in ambient PAHs pollution and lives saved as a co-benefit of effective long-term PM2.5 pollution controls. Environ. Int. 2018, 114, 266–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Idowu, O.; Semple, K.T.; Ramadass, K.; O’Connor, W.; Hansbro, P.; Thavamani, P. Beyond the obvious: Environmental health implications of polar polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Environ. Int. 2019, 123, 543–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, Y.Z.; Li, Y.X.; Liang, Y.L.; Xue, Q.Q.; Feng, X.; Feng, Y.C. Size distributions of source-specific risks of atmospheric heavy metals: An advanced method to quantify source contributions to size-segregated respiratory exposure. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 407, 124355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thiankhaw, K.; Chattipakorn, N.; Chattipakorn, S.C. PM2.5 exposure in association with AD-related neuropathology and cognitive outcomes. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 292, 118320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alves, C.; Rienda, I.C.; Vicente, A.; Vicente, E.; Gonçalves, C.; Candeias, C.; Rocha, F.; Lucarelli, F.; Pazzi, G.; Kováts, N.; et al. Morphological properties, chemical composition, cancer risks and toxicological potential of airborne particles from traffic and urban background sites. Atmos. Res. 2021, 264, 105837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juda-Rezler, K.; Zajusz-Zubek, E.; Reizer, M.; Maciejewska, K.; Kurek, E.; Bulska, E.; Klejnowski, K. Bioavailability of elements in atmospheric PM2.5 during winter episodes at Central Eastern European urban background site. Atmos. Environ. 2021, 245, 117993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, L.L.; Engling, G.; Zhang, X.Y.; Sun, J.Y.; Zhang, Y.M.; Xu, W.Y.; Liu, C.; Zhang, G.; Liu, X.Y.; Ma, Q.L. Chemical characteristics of PM2.5 during summer at a background site of the Yangtze River Delta in China. Atmos. Res. 2017, 198, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.P.; Zong, Z.; Tian, C.G.; Chen, Y.J.; Luo, C.L.; Tang, J.H.; Li, J.; Zhang, G. Assessing on toxic potency of PM2.5-bound polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons at a national atmospheric background site in North China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 612, 330–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.M.; Yang, L.X.; Mellouki, A.; Wen, L.; Yang, Y.M.; Gao, Y.; Jiang, P.; Li, Y.Y.; Wang, W.X. Chemical characteristics and influence of continental outflow on PM1.0, PM2.5 and PM10 measured at Tuoji island in the Bohai Sea. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 573, 699–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.M.; Yang, L.X.; Mellouki, A.; Chen, J.M.; Chen, X.F.; Gao, Y.; Jiang, P.; Li, Y.Y.; Yu, H.; Wang, W.X. Diurnal concentrations, sources, and cancer risk assessments of PM2.5-bound PAHs, NPAHs, and OPAHs in urban, marine and mountain environments. Chemosphere 2018, 209, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mamoudou, I.; Zhang, F.; Chen, Q.; Wang, P.; Chen, Y. Characteristics of PM2.5 from ship emissions and their impacts on the ambient air: A case study in Yangshan Harbor, Shanghai. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 640–641, 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, C.; Han, Y.M.; Bandowe, B.A.M.; Cao, J.J.; Huang, R.J.; Ni, H.Y.; Tian, J.; Wilcke, W. Occurrence, gas/particle partitioning and carcinogenic risk of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and their oxygen and nitrogen containing derivatives in Xi’an, central China. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 505, 814–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broome, R.A.; Cope, M.E.; Goldsworthy, B.; Goldsworthy, L.; Emmerson, K.; Jegasothy, E.; Morgan, G.G. The mortality effect of ship-related fine particulate matter in the Sydney greater metropolitan region of NSW, Australia. Environ. Int. 2016, 87, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, J.; Wang, X.J.; Zhang, Y.J.; Zhu, H.X.; Chen, Q.; Tian, Y.Z.; Shi, X.R.; Shi, G.L.; Feng, Y.C. PM2.5 source profiles and relative heavy metal risk of ship emissions: Source samples from diverse ships, engines, and navigation processes. Atmos. Environ. 2018, 191, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.Z.; Liu, X.; Huo, R.Q.; Shi, Z.B.; Sun, Y.M.; Feng, Y.C.; Harrison, R.M. Organic compound source profiles of PM2.5 from traffic emissions, coal combustion, industrial processes and dust. Chemosphere 2021, 278, 130429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.M.; Tian, Y.Z.; Xue, Q.Q.; Jia, B.; Wei, Y.; Song, D.L.; Huang, F.X.; Feng, Y.C. Source-specific risks of synchronous heavy metals and PAHs in inhalable particles at different pollution levels: Variations and health risks during heavy pollution. Environ. Int. 2021, 146, 106162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ravindra, K.; Sokhi, R.; Van Grieken, R. Atmospheric polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons: Source attribution, emission factors and regulation. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 2895–2921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ravindra, K.; Wauters, E.; Van Grieken, R. Variation in particulate PAHs levels and their relation with the transboundary movement of the air masses. Sci. Total Environ. 2008, 396, 100–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Park, M.K.; Choi, S.D. Monitoring and risk assessment of arsenic species and metals in the Taehwa River in Ulsan, the largest industrial city in South Korea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2021, 172, 112862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodins, V.; Lucht, S.; Ohlwein, S.; Hennig, F.; Soppa, V.; Erbel, R.; Jockel, K.H.; Weimar, C.; Hermann, D.M.; Schramm, S.; et al. Long-term exposure to ambient source-specific particulate matter and its components and incidence of cardiovascular events-The Heinz Nixdorf Recall study. Environ. Int. 2020, 142, 105854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Q.Q.; Jiang, Z.; Wang, X.; Song, D.L.; Huang, F.X.; Tian, Y.Z.; Huangfu, Y.Q.; Feng, Y.C. Comparative study of PM10-bound heavy metals and PAHs during six years in a Chinese megacity: Compositions, sources, and source-specific risks. Ecotox. Environ. Saf. 2019, 186, 109740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, R.; Jia, B.; Tian, Y.Z.; Feng, Y.C. Source-specific health risk assessment of PM2.5-bound heavy metals based on high time-resolved measurement in a Chinese megacity: Insights into seasonal and diurnal variations. Ecotox. Environ. Saf. 2021, 216, 112167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esmaeilirad, S.; Lai, A.; Abbaszade, G.; Schnelle-Kreis, J.; Zimmermann, R.; Uzu, G.; Daellenbach, K.; Canonaco, F.; Hassankhany, H.; Arhami, M.; et al. Source apportionment of fine particulate matter in a Middle Eastern Metropolis, Tehran-Iran, using PMF with organic and inorganic markers. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 705, 135330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galvao, E.S.; Reis, N.C., Jr.; Lima, A.T.; Stuetz, R.M.; D’Azeredo, O.M.T.; Santos, J.M. Use of inorganic and organic markers associated with their directionality for the apportionment of highly correlated sources of particulate matter. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 651, 1332–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, M.J.; Ren, L.J.; Ren, H.; Zhao, Y.; Kawamura, K.; Zhang, H.L.; Wei, L.F.; Sun, Y.L.; Wang, Z.F.; Fu, P.Q. Primary biogenic and anthropogenic sources of organic aerosols in Beijing, China: Insights from saccharides and n-alkanes. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 243, 1579–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, G.M.; Teinila, K.; Custodio, D.; Santos, A.G.; Xian, H.; Hillamo, R.; Alves, C.A.; de Andrade, J.B.; da Rocha, G.O.; Kumar, P.; et al. Particulate pollutants in the Brazilian city of Sao Paulo: 1-year investigation for the chemical composition and source apportionment. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 11943–11969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Souza, M.R.R.; Suzarte, J.S.; Carmo, L.O.; Santos, E.; Soares, L.S.; Júnior, A.R.V.; Santos, L.G.G.V.; Krause, L.C.; Damasceno, F.C.; Frena, M.; et al. Assessment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in three environmental components from a tropical estuary in Northeast Brazil. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2021, 171, 112726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaezzadeh, V.; Yi, X.; Rais, F.R.; Bong, C.W.; Thomes, M.W.; Lee, C.W.; Zakaria, M.P.; Wang, A.J.; Zhong, G.C.; Zhang, G. Distribution of black carbon and PAHs in sediments of Peninsular Malaysia. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2021, 172, 112871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stein, A.F.; Draxler, R.R.; Rolph, G.D.; Stunder, B.J.B.; Cohen, M.D.; Ngan, F. NOAA’s HYSPLIT atmospheric transport and dispersion modeling system. Bull. Amer. Meteor. Soc. 2015, 96, 2059–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.Y.; Xing, J.; Wang, S.X.; Fu, X.; Zheng, H.T. Source-specific speciation profiles of PM2.5 for heavy metals and their anthropogenic emissions in China. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 239, 544–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, X.; Chen, Y.; Tian, C.; Huang, G.; Fang, Y.; Zhang, F.; Zong, Z.; Li, J.; Zhang, G. Impact of agricultural waste burning in the Shandong Peninsula on carbonaceous aerosols in the Bohai Rim, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 481, 311–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Chen, Y.J.; Tian, C.G.; Wang, X.P.; Huang, G.P.; Fang, Y.; Zong, Z. Identification and quantification of shipping emissions in Bohai Rim, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 497–498, 570–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, Q.L.; Bi, X.H.; Song, W.B.; Li, T.K.; Liu, B.S.; Ding, J.; Xu, J.; Song, C.B.; Yang, N.W.; Schulze, B.C.; et al. Residential coal combustion as a source of primary sulfate in Xi’an, China. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 196, 66–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, C.Y.; Chiang, H.C.; Chen, M.J.; Yang, T.T.; Wu, Y.S.; Chen, Y.C. Impacts of hazardous metals and PAHs in fine and coarse particles with long-range transports in Taipei City. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 250, 934–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.Z.; Shi, G.L.; Huang-Fu, Y.Q.; Song, D.L.; Liu, J.Y.; Zhou, L.D.; Feng, Y.C. Seasonal and regional variations of source contributions for PM10 and PM2.5 in urban environment. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 557–558, 697–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, Y.Z.; Shi, G.L.; Han, B.; Wu, J.H.; Zhou, X.Y.; Zhou, L.D.; Zhang, P.; Feng, Y.C. Using an improved Source Directional Apportionment method to quantify the PM2.5 source contributions from various directions in a megacity in China. Chemosphere 2015, 119, 750–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bogawski, P.; Borycka, K.; Grewling, Ł.; Kasprzyk, I. Detecting distant sources of airborne pollen for Poland: Integrating back-trajectory and dispersion modelling with a satellite-based phenology. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 689, 109–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rolph, G.; Stein, R.; Stunder, B. Real-time environmental applications and display system: READY. Environ. Model. Softw. 2017, 95, 210–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Draxler, R.R.; Hess, G.D. An overview of the HYSPLIT_4 modeling system for trajectories, dispersion, and deposition. Aust. Meteor. Mag. 1998, 47, 295–308. [Google Scholar]
- Han, D.; Fu, Q.; Gao, S.; Li, L.; Ma, Y.; Qiao, L.; Xu, H.; Liang, S.; Cheng, P.; Chen, X.; et al. Non-polar organic compounds in autumn and winter aerosols in a typical city of eastern China: Size distribution and impact of gas–particle partitioning on PM2.5 source apportionment. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 9375–9391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lyu, Y.; Xu, T.T.; Yang, X.; Chen, J.M.; Cheng, T.T.; Li, X. Seasonal contributions to size-resolved n-alkanes C8–C40 in the Shanghai atmosphere from regional anthropogenic activities and terrestrial plant waxes. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 579, 1918–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manoli, E.; Kouras, A.; Samara, C. Profile analysis of ambient and source emitted particle-bound polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons from three sites in northern Greece. Chemosphere 2004, 56, 867–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.P.; Cai, M.J.; Xu, C.; Zhang, N.; Zhou, J.B.; Yan, J.P.; Schwab, J.J.; Yuan, C.S. Chemical nature of PM2.5 and PM10 in the coastal urban Xiamen, China: Insights into the impacts of shipping emissions and health risk. Atmos. Environ. 2020, 227, 117383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- US EPA. Exposure Factors Handbook 2011 Edition (Final Report); EPA/600/R-09/052F; U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2011.
- US EPA. User’s Guide/Technical Background Document for US EPA Region. 9′s RSL Tables; US Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2013.
- Orosun, M.M.; Adewuyi, A.D.; Salawu, N.B.; Isinkaye, M.O.; Orosun, O.R.; Oniku, A.S. Monte Carlo approach to risks assessment of heavy metals at automobile spare part and recycling market in Ilorin, Nigeria. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 22084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayenuddin, M.; Md, A.J.; Ferdoushi, Z.; Begum, M.; Mondal, S. Carcinogenic and non-carcinogenic human health risk from exposure to heavy metals in surface water of padma river. Res. J. Environ. Toxicol. 2018, 12, 18–23. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.B.; Bae, G.N.; Moon, K.C.; Pyo, K.Y. Characteristics of TSP and PM2.5 measured at Tokchok Island in the Yellow Sea. Atmos. Environ. 2002, 36, 5427–5435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Ma, J.; Cao, Z.; Dove, A.; Zhang, L. Trend and climate signals in seasonal air concentration of organochlorine pesticides over the Great Lakes. J. Geophys. Res. Atmospheres 2010, 115, D15307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, N.; Yuan, S.; Yan, Q.L. Sea Ice in the Bohai Sea and Its Impact on Marine Ecological Environment. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 47, 20–25. [Google Scholar]
- Guan, Q.; Wang, F.; Xu, C.; Pan, N.; Lin, J.; Zhao, R.; Yang, Y.; Luo, H. Source apportionment of heavy metals in agricultural soil based on PMF: A case study in Hexi Corridor, northwest China. Chemosphere 2018, 193, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, P.H.; Kong, S.F.; Geng, C.M.; Han, B.; Lu, B.; Sun, R.F.; Zhao, R.J.; Bai, Z.P. Assessing the Hazardous Risks of Vehicle Inspection Workers’ Exposure to Particulate Heavy Metals in Their Work Places. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2013, 13, 255–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xue, M.; Yang, Y.; Ruan, J.; Xu, Z. Assessment of Noise and Heavy Metals (Cr, Cu, Cd, Pb) in the Ambience of the Production Line for Recycling Waste Printed Circuit Boards. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 494–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, H.L.; Yu, Y.X.; An, T.C. Bioaccessibilities of metal(loid)s and organic contaminants in particulates measured in simulated human lung fluids: A critical review. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 265, 115070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardoni, V.; Elser, M.; Valli, G.; Valentini, S.; Bigi, A.; Fermo, P.; Piazzalunga, A.; Vecchi, R. Size-segregated aerosol in a hot-spot pollution urban area: Chemical composition and three-way source apportionment. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 231, 601–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iakovides, M.; Iakovides, G.; Stephanou, E.G. Atmospheric particle-bound polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, n-alkanes, hopanes, steranes and trace metals: PM2.5 source identification, individual and cumulative multi-pathway lifetime cancer risk assessment in the urban environment. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 752, 141834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tobiszewski, M.; Namieśnik, J. PAH diagnostic ratios for the identification of pollution emission sources. Environ. Pollut. 2012, 162, 110–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.F.; Han, L.H.; Cheng, S.Y.; Wang, X.Q.; Zhang, H.Y. Characteristics and Sources of Carbon Pollution of Fine Particulate Matter in Typical Cities in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Region. Res. of Environ. Sci. 2020, 33, 1729–1739. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Duan, J.; Tan, J. Atmospheric heavy metals and Arsenic in China: Situation, sources and control policies. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 74, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotchenruther, R.A. Source apportionment of PM2.5 at multiple Northwest US sites: Assessing regional winter wood smoke impacts from residential wood combustion. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 142, 210–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Species | Cold Season (n = 32) | Warm Season (n = 23) | Annual (n = 55) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | |
| PM2.5 | 58 | 35 | 41 | 21 | 51 | 31 |
| Si | 2.18 | 1.85 | 0.86 | 0.54 | 1.65 | 1.33 |
| Al | 0.16 | 0.10 | 0.15 | 0.10 | 0.16 | 0.1 |
| Ca | 0.60 | 0.45 | 0.50 | 0.23 | 0.56 | 0.39 |
| K | 0.71 | 0.47 | 1.10 | 1.08 | 0.87 | 0.8 |
| Fe | 0.33 | 0.20 | 0.19 | 0.11 | 0.27 | 0.18 |
| Zn | 0.07 | 0.06 | 0.03 | 0.02 | 0.05 | 0.04 |
| Na | 0.55 | 0.35 | 1.29 | 0.80 | 0.85 | 0.68 |
| Mg | 0.08 | 0.05 | 0.12 | 0.07 | 0.09 | 0.06 |
| Cu | 9.15 × 10−3 | 7.89 × 10−3 | 1.30 × 10−3 | 1.28 × 10−3 | 4.50 × 10−3 | 8.90 × 10−4 |
| Ba | 3.42 × 10−3 | 2.36 × 10−3 | 4.35 × 10−3 | 2.95 × 10−3 | 3.80 × 10−3 | 2.60 × 10−3 |
| Ti | 2.51 × 10−2 | 1.93 × 10−2 | 5.58 × 10−3 | 2.99 × 10−3 | 1.70 × 10−2 | 1.60 × 10−2 |
| V | 4.78 × 10−3 | 4.73 × 10−3 | 1.56 × 10−3 | 1.28 × 10−3 | 3.50 × 10−3 | 3.20 × 10−3 |
| Mn | 1.64 × 10−2 | 1.33 × 10−2 | 7.92 × 10−3 | 3.92 × 10−3 | 1.30 × 10−2 | 1.10 × 10−2 |
| Cr | 5.71 × 10−2 | 4.07 × 10−2 | 7.05 × 10−3 | 6.54 × 10−3 | 3.70 × 10−2 | 3.60 × 10−2 |
| Ni | 5.64 × 10−3 | 4.01 × 10−3 | 7.49 × 10−3 | 3.95 × 10−3 | 6.40 × 10−3 | 6.30 × 10−3 |
| As | 4.98 × 10−3 | 4.86 × 10−3 | 1.88 × 10−3 | 1.10 × 10−3 | 3.70 × 10−3 | 3.40 × 10−3 |
| Pb | 2.17 × 10−2 | 2.16 × 10−2 | 7.41 × 10−3 | 6.90 × 10−3 | 1.60 × 10−2 | 1.50 × 10−2 |
| OC | 6.86 | 3.96 | 5.46 | 3.17 | 6.3 | 3.76 |
| EC | 2.30 | 1.62 | 1.41 | 0.70 | 1.94 | 1.41 |
| NO3− | 10.11 | 9.45 | 10.18 | 9.96 | 10.14 | 9.76 |
| SO42− | 7.10 | 6.22 | 5.84 | 4.70 | 6.59 | 6.48 |
| NH4+ | 5.40 | 4.79 | 5.35 | 4.27 | 5.38 | 4.63 |
| Cl− | 0.85 | 0.90 | 0.55 | 0.48 | 0.73 | 0.71 |
| Na+ | 0.44 | 0.18 | 1.07 | 1.04 | 0.69 | 0.64 |
| Mg2+ | 0.10 | 0.07 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 0.07 | 0.05 |
| Ca2+ | 0.55 | 0.51 | 0.13 | 0.07 | 0.38 | 0.3 |
| K+ | 0.62 | 0.40 | 0.93 | 0.84 | 0.74 | 0.64 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xue, Q.; Tian, Y.; Liu, X.; Wang, X.; Huang, B.; Zhu, H.; Feng, Y. Potential Risks of PM2.5-Bound Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons and Heavy Metals from Inland and Marine Directions for a Marine Background Site in North China. Toxics 2022, 10, 32. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10010032
Xue Q, Tian Y, Liu X, Wang X, Huang B, Zhu H, Feng Y. Potential Risks of PM2.5-Bound Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons and Heavy Metals from Inland and Marine Directions for a Marine Background Site in North China. Toxics. 2022; 10(1):32. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10010032
Chicago/Turabian StyleXue, Qianqian, Yingze Tian, Xinyi Liu, Xiaojun Wang, Bo Huang, Hongxia Zhu, and Yinchang Feng. 2022. "Potential Risks of PM2.5-Bound Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons and Heavy Metals from Inland and Marine Directions for a Marine Background Site in North China" Toxics 10, no. 1: 32. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10010032
APA StyleXue, Q., Tian, Y., Liu, X., Wang, X., Huang, B., Zhu, H., & Feng, Y. (2022). Potential Risks of PM2.5-Bound Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons and Heavy Metals from Inland and Marine Directions for a Marine Background Site in North China. Toxics, 10(1), 32. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10010032