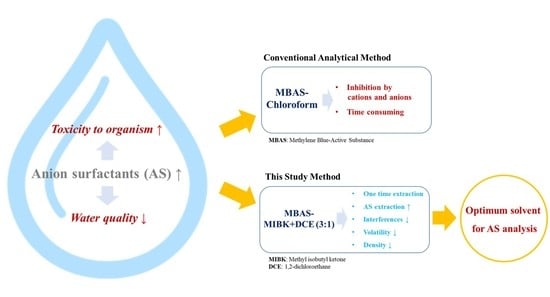
Screening of a Novel Solvent for Optimum Extraction of Anionic Surfactants in Water
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents
2.2. Physiochemical Properties of Organic Solvents
2.3. SDS Extraction Efficiency by an Individual Solvent
2.4. SDS Extraction Efficiency of SDS by a Mixture of Organic Solvents
2.5. Washing Effects on SDS Extraction by Screened Solvent
2.6. Factors Affecting SDS Extraction Efficiency by the Mixed Solvent
2.6.1. pH Effects
2.6.2. Ionic Strength Effects
2.6.3. Interference by Cations for SDS Extraction Efficiency
2.6.4. Interference by Anions for SDS Extraction Efficiency
3. Results
3.1. SDS Extraction Efficiency by an Individual Solvent
3.2. Physicochemical Properties of Solvents
3.3. Effects of Washing Process on SDS Extraction
3.4. Development of MIBK-DCE Mixed Solvent
3.5. Effect of pH and Ionic Strength on the SDS Extraction Efficiency by MIBK-DCE (3:1)
3.6. Interference of Cations on SDS Extraction Efficiency by MIBK-DCE (3:1) Mixed Solvent
3.7. Interference of Anions on SDS Extraction Efficiency by MIBK-DCE (3:1) Mixed Solvent
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Aboul-Kassim, T.A.; Simoneit, B.R.T. Detergents: A review of the nature, chemistry, and behavior in the aquatic environment. Part I. Chemical composition and analytical techniques. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1993, 23, 325–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cserhati, T.; Forgacs, E.; Oros, G. Biological activity and environmental impact of anionic surfactants. Environ. Int. 2002, 28, 337–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibanez, J.G.; Hernandez-Esparza, M.; Doria-Serrano, C.; Fregoso-Infante, A.; Singh, M.M. Environmental Chemistry: Fundamentals; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Ivanković, T.; Hernović, J. Surfactants in the environment. Arh. Hig. Rada. Toksikol. 2010, 61, 95–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jardak, K.; Drogui, P.; Daghrir, R. Surfactants in aquatic and terrestrial environment: Occurrence, behavior, and treatment processes. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 3195–3216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirisattha, S.; Momose, Y.; Kitagawa, E.; Iwahashi, H. Toxicity of anionic detergents by Saccharomyces cerevisiae microarray analysis. Water Res. 2004, 38, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ying, G.G. Fate, behavior and effects of surfactants and their degradation products in the environment. Environ. Int. 2006, 32, 417–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olmez-Hanci, T.; Arslan-Alston, I.; Basar, G. Multivariate analysis of anionic, cationic and nonionic textile surfactant degradation with the H2O2/UV-C process by using the capabilities of response surface methodology. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 185, 193–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farn, R.J. Chemistry and Technology of Surfactants; Wiley-Blackwell Publishing Ltd.: Oxford, UK, 2006; pp. 1–132. [Google Scholar]
- Rosen, M.J. Surfactants and Interfacial Phenomena, 3rd ed.; Wiley and Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Corazza, M.; Lauriola, M.M.; Zappaterra, M.; Bianchi, A.; Virgili, A. Surfactants, skin cleansing protagonists. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2010, 24, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olkowska, E.; Polkowska, Ż.; Namieśnik, J. Analytical procedures for the determination of surfactants in environmental samples. Talanta 2012, 88, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olkowska, E.; Polkowska, Ż.; Ruman, M.; Namieśnik, J. Similar concentration of surfactants in rural and urban areas. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2015, 13, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, S.; Garcia-Bennett, A.E.; Yokoi, T.; Sakamoto, K.; Kunieda, H.; Terasaki, O.; Tatsumi, T. A novel anionic surfactant templating route for synthesizing mesoporous silica with unique structure. Nat. Mat. 2003, 2, 801–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soni, A.; Rai, N.; Sar, S.K. A study of spectrophotometric determination of ion association complex, formed by anionic surfactant sodium dodecyl by using crystal violet as a cationic dye in Region Bilaspur (Chhattisgarh). Orient. J. Chem. 2014, 30, 1335–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jurado, E.; Fernández-Serrano, M.; Núñez-Olea, J.; Luzón, G.; Lechuga, M. Simplified spectrophotometric method using methylene blue for determining anionic surfactants: Applications to the study of primary biodegradation in aerobic screening tests. Chemosphere 2006, 65, 278–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lara-Martin, P.A.; Gomex-Parra, A.; Gonzalez-Mazo, E. Simultaneous extraction and determination of anionic surfactants in waters and sediments. J. Chromatogr. A 2006, 1114, 205–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedraza, A.; Sicilia, M.D.; Rubio, S.; Perez-Bendito, D. Assessment of the surfactant-dye binding degree method as an alternative to the methylene blue method for the determination of anionic surfactants in aqueous environmental samples. Anal. Chim. Acta 2007, 588, 252–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ródenas-Torralba, E.; Reis, B.F.; Morales-Rubio, Á.; de la Guardia, M. An environmentally friendly multicommutated alternative to the reference method for anionic surfactant determination in water. Talanta 2005, 66, 591–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sini, K.; Idouhar, M.; Ahmia, A.C.; Ferradj, A.; Tazerouti, A. Spectrophotometric determination of anionic surfactants: Optimization by response surface methodology and application to Algiers bay wastewater. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2017, 189, 646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballet, T.G.N.; Effebi, K.R.; Ako, O.Y.A.; Kpidi, Y.H.; Yapo, O.B. Anionic surfactants levels in M’Koa Lake Water (Jacqueville, Côte d’Ivoire). J. Water Res. Prot. 2018, 10, 1210–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cantarero, S.; Camino-Sanchez, F.J.; Zafra-Gomez, A.; Ballesteros, O.; Navalon, A.; Vilchez, J.L.; Verge, C.; Reis, M.S.; Paraiva, P.M. Evaluation of the presence of major anionic surfactants in marine sediments. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2012, 64, 587–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonough, K.; Casteel, K.; Itrich, N.; Menzies, J.; Belanger, S.; Wehmeyer, K.; Federle, T. Evaluation of anionic surfactant concentrations in US effluents and probabilistic determination of their combined ecological risk in mixing zones. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 572, 434–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korea Water Environment Monitoring System. Available online: http://water.nier.go.kr/ (accessed on 8 January 2022).
- Norfazrin, N.M.; Adnan, S.; Latif, M.T.; Zakaria, Z.; Abdullahand, M.; Othman, M. The composition of surfactants in river water and its influence to the amount of surfactants in drinking water. World Appl. Sci. J. 2012, 17, 970–975. [Google Scholar]
- Pastewski, S.; Mędrzycka, K. Monitoring surfactant concentrations in surface waters in tricity agglomeration. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2003, 12, 643–646. [Google Scholar]
- Robert-Peillard, F.; Coulomb, A.D.S.B.; Doumenq, P.; Malleret, L.; Asia, L.; Boudenne, J.L. Occurrence and fate of selected surfactants in seawater at the outfall of the Marseille urban sewerage system. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 12, 1527–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ministry of Environment (MOE). Water Quality and Aquatic Ecosystem Conservation Act; Ministry of Environment (MOE): Sejong City, Korea, 2015.
- American Public Health Association (APHA). Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 20th ed.; American Public Health Association, American Water Works Association and Water Environmental Federation: Washington, DC, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- ISO. Water Quality. Determination of Surfactants. Part 1: Determination of Anionic Surfactants by Measurement of the Methylene Blue Index (MBAS); ISO 7875-1, ISO/TC 147/SC 2; ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Wyrwas, B.; Zgoła-Grześkowiak, A. Continuous flow methylene blue active substances method for the determination of anionic surfactants in river water and biodegradation test samples. J. Surfact. Deterg. 2014, 17, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bidari, A.; Ganjali, M.R.; Norouzi, P. Development and evaluation of a dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction based test method for quantitation of total anionic surfactants; advantage against reference methods. Cent. Eur. J. Chem. 2010, 8, 702–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koga, M.; Yamamichi, Y.; Nomoto, Y.; Irie, M.; Tanimura, T.; Yoshinaga, T. Rapid determination of anionic surfactants by improved spectrophotometric method using methylene blue. Anal. Sci. 1999, 15, 563–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Feiteira, F.N.; dos Reis, L.G.T.; Pacheco, W.F.; Cassella, R.J. Solventless determination of total anionic surfactants in waters using polyurethane foam as support and analysis of digital images. Microchem. J. 2015, 119, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeerum, C.; Wongwilai, W.; Grudpan, K.; Vongboot, M. Green assay of anionic surfactant via ion-association with methylene blue sorbed on polyurethane foam monolithic rod and using smartphone. Talanta 2018, 190, 85–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Environment (MOE). Standard Methods for Examination of Water Quality; MOE: Sejong City, Korea, 2007.
- Yokoyama, Y.; Tai, E.; Sato, H. Spectrometric determination of anionic surfactants in environmental waters based on anisole extraction of their bis [2-(5-chloro-2-pyridylazo)-5-diethylaminophenolato] cobalt (III) ion pairs. Anal. Sci. 2011, 27, 845–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- George, A.L.; White, G.F. Optimization of the methylene blue assay for anionic surfactants added to estuarine and marine water. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2009, 18, 2232–2236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Lee, H.K. Low-density solvent-based solvent demulsification dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction for the fast determination of trace levels of sixteen priority polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in environmental water samples. J. Chromatogr. A 2011, 1218, 5040–5046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doumèche, B.; Heinemann, M.; Büchs, J.; Hartmeier, W.; Ansorge-Schumacher, M.B. Enzymatic catalysis in gel-stabilized two-phase systems: Improvement of the solvent phase. J. Mol. Catal. B Enzym. 2002, 18, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smallwood, I.M. Handbook of Organic Properties; Halsted Press: New York, NY, USA, 1996; pp. 3–183. [Google Scholar]
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). Available online: https://www.epa.gov/haps/health-effects-notebook-hazardous-air-pollutants (accessed on 8 January 2022).
- Moldoveanu, S.C.; David, V. Solvent extraction. In Sample Preparation in Chromatography; Moidoveanu, S., David, V., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2004; pp. 287–309. [Google Scholar]
- Rydberg, J.; Cox, M.; Musikas, C. Solvent Extraction Principles and Practice, 2nd ed.; 1-594; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2004; pp. 1–594. [Google Scholar]
- Turney, M.E.; Cannell, D.W. Alkaline methylene blue method for determination of anionic surfactants and for amine oxides in detergents. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 1965, 42, 544–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitt, T.M. Analysis of Surfactants, Surfactant Science Series Vol. 96, 2nd ed.; Marcel Dekker, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2001; p. 638. [Google Scholar]
- Nollet, L.M.L.; Gelder, L.S.O. Handbook of Water Analysis, 3rd ed.; CRC Press, Taylor & Francis Group, LLC: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2014; pp. 189–232. [Google Scholar]


| Solvents | Phase-Separation Time | Maximum Absorbance Wavelength | Absorbance | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Blank 1 | Sample 2 | BC 3 | |||
| min | nm | ||||
| Chloroform | 12~22 | 652 | 0.0278 | 0.5377 | 0.5099 |
| Dichloromethane | 29~42 | 653 | 0.1507 | 0.8222 | 0.6715 |
| 1,2-Dichloroethane (DCE) | 34~60 | 656 | 0.1145 | 0.7333 | 0.6188 |
| n-Hexane | 1~2 | 659 | 0.0025 | 0.0029 | 0.0004 |
| Methyl isobutyl ketone (MIBK) | 1~2 | 658 | 0.0278 | 0.5405 | 0.5127 |
| Benzene | 2~3 | 657 | −0.0012 | 0.0363 | 0.0401 |
| Solvents | Density 1 (g/mL) | Health Hazard Group 2 | Odor Threshold 1 (ppm) | Vapor Pressure 1 (mmHg, 20 °C) | Boiling Point 1 (°C) | Volatilization Rate 3 (mL min−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chloroform | 1.480 | B2 4 | 300 | 169 | 61 | 0.28 |
| Dichloromethane | 1.326 | B2 4 | 250 | 376 | 40 | 0.50 |
| 1,2-Dichloroethane | 1.253 | B2 4 | 400 | 71 | 83.5 | 0.12 |
| MIBK 6 | 0.801 | D 5 | 8 | 16.5 | 116 | 0.04 |
| Solvents | MIBK/DCE Mixing Ratios | Phase-Separation Time (min) | SDS Extraction Efficiency 1 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Absorbances | CV 2 (%) | |||
| MIBK/DCE 3 | 100:0 | 1 | 0.3802 ± 0.0021 | 0.6 |
| 95:5 | 1 | 0.4572 ± 0.0052 | 1.1 | |
| 90:10 | 1 | 0.5280 ± 0.0026 | 0.5 | |
| 85:15 | 1 | 0.5854 ± 0.0024 | 0.4 | |
| 80:20 | 2.5 | 0.6253 ± 0.0032 | 0.5 | |
| 75:25 | 2.5 | 0.6657 ± 0.0011 | 0.2 | |
| 70:30 | 3 | 0.6933 ± 0.0011 | 0.2 | |
| 0:100 | 87 | 0.8455 ± 0.0017 | 0.2 | |
| chloroform | 0.6057 ± 0.0090 | 1.5 | ||
| pH | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | |
| Concentration 1 (mg L−1) | 1.04 | 1.01 | 1.01 | 1.02 | 1.02 | 1.01 | 1.03 | 1.02 | 1.02 | 0.94 |
| SD 2 | 0.02 | 0.01 | <0.10 | 0.01 | <0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.02 |
| CV 3 (%) | 2.1 | 1.4 | 0.4 | 0.7 | 0.3 | 0.9 | 0.4 | 0.6 | 1.0 | 2.2 |
| Recovery (%) | 103 | 100 | 100 | 101 | 102 | 100 | 102 | 101 | 101 | 93 |
| Ionic Strength (M) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.05 | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.5 | 1.0 | 2.0 | |
| Concentration 1 (mg L−1) | 1.00 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.98 | 0.98 | 0.97 | 0.96 |
| SD 2 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | 0.01 | <0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | <0.01 | 0.01 |
| Recovery (%) | 100 | 99 | 99 | 99 | 99 | 98 | 97 | 97 | 96 |
| Compounds | Cations | Cation Conc. (M) | SDS Conc. 1 (mg L−1) | SD 2 (mg L−1) | Recovery (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Na2SO4 | Na+ | 0.10 | 0.97 b,c | 0.01 | 97 |
| K2SO4 | K+ | 0.10 | 0.97 c | 0.01 | 97 |
| (NH4)2SO4 | NH4+ | 0.10 | 0.96 c | <0.01 | 97 |
| MgSO4 | Mg2+ | 0.10 | 0.98 b | <0.01 | 98 |
| d-Water | - | ~0 | 0.999 a | <0.01 | 100 |
| Compounds | Anions | Treated Anion Concentration (M) | Anionic Interference Conc. 1 (mg L−1) | Interference Strength (IS) 2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NaF | F− | 0.5 | 0.049 ± 0.002 3 | 3.4 × 10−7 |
| NaCl | Cl− | 0.5 | 0.628 ± 0.004 | 4.4 × 10−6 |
| 1.0 | 0.972 ± 0.015 | 3.4 × 10−6 | ||
| KBr | Br− | 0.02 | 0.722 ± 0.012 | 1.3 × 10−4 |
| 0.05 | 1.222 ± 0.053 | 8.6 × 10−5 | ||
| KI | I− | 0.0001 | 0.917 ± 0.010 | 3.2 × 10−2 |
| 0.0002 | 1.250 ± 0.010 | 2.2 × 10−2 | ||
| 0.0005 | 1.696 ± 0.017 | 1.2 × 10−2 | ||
| NaNO2 | NO2− | 0.25 | 0.932 ± 0.011 | 1.3 × 10−5 |
| 0.50 | 1.618 ± 0.016 | 1.1 × 10−5 | ||
| KNO3 | NO3− | 0.0025 | 0.825 ± 0.007 | 1.2 × 10−3 |
| 0.0050 | 1.300 ± 0.027 | 9.1 × 10−4 | ||
| KCN | CN− | 0.2 | 0.647 ± 0.046 | 1.1 × 10−5 |
| 0.5 | 1.124 ± 0.137 | 7.9 × 10−6 | ||
| KH2PO4 | H2PO4− | 1.0 | 0.174 ± 0.004 | 6.1 × 10−7 |
| NaHCO3 | HCO3− | 1.0 | 0.143 ± 0.003 | 5.0 × 10−7 |
| Sodium acetate | Acetate | 1.0 | 0.203 ± 0.023 | 7.1 × 10−7 |
| Sodium tartrate | Tartrate | 0.5 | 0.162 ± 0.020 | 1.1 × 10−6 |
| Trisodium citrate | Citrate | 0.5 | 0.262 ± 0.036 | 1.8 × 10−6 |
| Sodium benzoate | Benzoate | 0.05 | 0.524 ± 0.018 | 3.7 × 10−5 |
| Potassium biphthalate | Biphthalate | 0.02 | 0.867 ± 0.031 | 1.5 × 10−4 |
| 0.05 | 0.899 ± 0.123 | 6.5 × 10−5 | ||
| Sodium salicylate | Salicylate | 0.0002 | 1.082 ± 0.016 | 1.9 × 10−2 |
| 0.0005 | 1.686 ± 0.027 | 1.2 × 10−2 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yoon, J.-H.; Shin, Y.G.; Kim, H.S.; Kirkham, M.B.; Yang, J.E. Screening of a Novel Solvent for Optimum Extraction of Anionic Surfactants in Water. Toxics 2022, 10, 80. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10020080
Yoon J-H, Shin YG, Kim HS, Kirkham MB, Yang JE. Screening of a Novel Solvent for Optimum Extraction of Anionic Surfactants in Water. Toxics. 2022; 10(2):80. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10020080
Chicago/Turabian StyleYoon, Jung-Hwan, Yong Geon Shin, Hyuck Soo Kim, M. B. Kirkham, and Jae E. Yang. 2022. "Screening of a Novel Solvent for Optimum Extraction of Anionic Surfactants in Water" Toxics 10, no. 2: 80. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10020080
APA StyleYoon, J.-H., Shin, Y. G., Kim, H. S., Kirkham, M. B., & Yang, J. E. (2022). Screening of a Novel Solvent for Optimum Extraction of Anionic Surfactants in Water. Toxics, 10(2), 80. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10020080