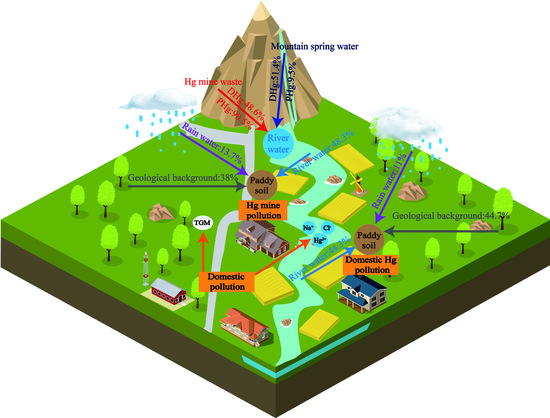
Mercury Biogeochemical Cycle in Yanwuping Hg Mine and Source Apportionment by Hg Isotopes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sample Collection
2.3. Analytical Methods
2.4. Hg Isotopes Analysis
2.5. Quality Control
2.6. Data Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Hg Pollution in Mine Wastes
3.2. Atmospheric Hg
3.3. Surface Water Hg and Source Apportionment
3.3.1. Surface Water Hg Pollution
3.3.2. Source Apportionment by Hg Isotopes
3.4. Paddy Soil Hg and Source Apportionment
3.4.1. Paddy Soil Hg Pollution
3.4.2. Source Apportionment by Hg Isotopes
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Feng, X.; Foucher, D.; Hintelmann, H.; Yan, H.; He, T.; Qiu, G. Tracing mercury contamination sources in sediments using mercury isotope compositions. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 3363–3368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, P.; Du, B.; Maurice, L.; Laffont, L.; Lagane, C.; Point, D.; Sonke, J.E.; Yin, R.; Lin, C.-J.; Feng, X. Mercury isotope signatures of methylmercury in rice samples from the Wanshan mercury mining area, China: Environmental implications. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 12321–12328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, L.P.; Zhang, L.; Cheng, I.; Aherne, J.; Wentworth, G.R. Impacts and effects indicators of atmospheric deposition of major pollutants to various ecosystems—A review. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2018, 18, 1953–1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Donovan, P.M.; Blum, J.D.; Singer, M.B.; Marvin-DiPasquale, M.; Tsui, M.T.K. Isotopic Composition of Inorganic Mercury and Methylmercury Downstream of a Historical Gold Mining Region. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 1691–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gerson, J.R.; Topp, S.N.; Vega, C.M.; Gardner, J.R.; Yang, X.; Fernandez, L.E.; Bernhardt, E.S.; Pavelsky, T.M. Artificial lake expansion amplifies mercury pollution from gold mining. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, 4953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.; Wang, C.; Ding, L.; Chen, M.; Hu, Y.; Li, P.; Zhang, L.; Feng, X. Soil mercury pollution caused by typical anthropogenic sources in China: Evidence from stable mercury isotope measurement and receptor model analysis. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 288, 125687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brocza, F.M.; Biester, H.; Richard, J.-H.; Kraemer, S.M.; Wiederhold, J.G. Mercury Isotope Fractionation in the Subsurface of a Hg(II) Chloride-Contaminated Industrial Legacy Site. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 7296–7305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, P.; Feng, X.; Shang, L.; Qiu, G.; Meng, B.; Liang, P.; Zhang, H. Mercury pollution from artisanal mercury mining in Tongren, Guizhou, China. Appl. Geochem. 2008, 23, 2055–2064. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, G.L.; Feng, X.B.; Wang, S.F.; Fu, X.W.; Shang, L.H. Mercury distribution and speciation in water and fish from abandoned Hg mines in Wanshan, Guizhou province, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2009, 407, 5162–5168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.-H.; Kabir, E.; Jahan, S.A. A review on the distribution of Hg in the environment and its human health impacts. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 306, 376–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Feng, X.; Qiu, G.; Shang, L.; Li, G. Human hair mercury levels in the Wanshan mercury mining area, Guizhou Province, China. Environ. Geochem. Health 2009, 31, 683–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Qiu, G.L.; Anderson, C.W.N.; Zhang, H.; Meng, B.; Liang, L.; Feng, X.B. Effect of Atmospheric Mercury Deposition on Selenium Accumulation in Rice (Oryza sativa L.) at a Mercury Mining Region in Southwestern China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 3540–3547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, J.C.; Wang, J.X.; Zhang, L.M.; Anderson, C.W.N.; Wang, X.; Zhang, H.; Dai, Z.H.; Feng, X.B. Screening of native low mercury accumulation crops in a mercury—Polluted mining region: Agricultural planning to manage mercury risk in farming communities. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 262, 121324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Li, P.; Qiu, G.; Wang, S.; Li, G.; Shang, L.; Meng, B.; Jiang, H.; Bai, W.; Li, Z. Human exposure to methylmercury through rice intake in mercury mining areas, Guizhou Province, China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 326–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, Z.; Feng, X.; Sommar, J.; Li, P.; Fu, X. Spatial distribution of mercury deposition fluxes in Wanshan Hg mining area, Guizhou province, China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2012, 12, 6207–6218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Du, B.; Feng, X.; Li, P.; Yin, R.; Yu, B.; Sonke, J.E.; Guinot, B.; Anderson, C.W.; Maurice, L. Use of mercury isotopes to quantify mercury exposure sources in inland populations, China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 5407–5416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, Y.; Wang, J.; Xia, J.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Du, Y.; Wei, W. A pilot study on using biochars as sustainable amendments to inhibit rice uptake of Hg from a historically polluted soil in a Karst region of China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 170, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhou, X.; Ma, W.; Yin, D.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Wang, D. Distribution of Mercury and Methylmercury in Farmland Soils Affected by Manganese Mining and Smelting Activities. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 10288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, S.Y.; Blum, J.D.; Yin, R.; Tsui, M.T.-K.; Yang, Y.H.; Choi, J.W. Mercury stable isotopes for monitoring the effectiveness of the Minamata Convention on Mercury. Earth Sci. Rev. 2020, 203, 103111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimenez-Moreno, M.; Barre, J.P.G.; Perrot, V.; Berail, S.; Rodriguez Martin-Doimeadios, R.C.; Amouroux, D. Sources and fate of mercury pollution in Almaden mining district (Spain): Evidences from mercury isotopic compositions in sediments and lichens. Chemosphere 2016, 147, 430–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiederhold, J.G.; Smith, R.S.; Siebner, H.; Jew, A.D.; Brown, G.E., Jr.; Bourdon, B.; Kretzschmar, R. Mercury Isotope Signatures as Tracers for Hg Cycling at the New Idria Hg Mine. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 6137–6145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stetson, S.J.; Gray, J.E.; Wanty, R.B.; Macalady, D.L. Isotopic Variability of Mercury in Ore, Mine-Waste Calcine, and Leachates of Mine-Waste Calcine from Areas Mined for Mercury. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 7331–7336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bergquist, B.A.; Blum, J.D. Mass-dependent and-independent fractionation of Hg isotopes by photoreduction in aquatic systems. Science 2007, 318, 417–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blum, J.D.; Sherman, L.S.; Johnson, M.W. Mercury isotopes in earth and environmental sciences. Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 2014, 42, 249–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Feng, X.; Larssen, T.; Qiu, G.; Vogt, R.D. In inland China, rice, rather than fish, is the major pathway for methylmercury exposure. Environ. Health Perspect. 2010, 118, 1183–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smith, R.S.; Wiederhold, J.G.; Jew, A.D.; Brown, G.E., Jr.; Bourdon, B.; Kretzschmar, R. Stable Hg Isotope Signatures in Creek Sediments Impacted by a Former Hg Mine. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 767–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Feng, X.; Yin, R.; Zhu, W.; Li, Z. Mercury distributions and mercury isotope signatures in sediments of Dongjiang, the Pearl River Delta, China. Chem. Geol. 2011, 287, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, R.; Feng, X.; Chen, B.; Zhang, J.; Wang, W.; Li, X. Identifying the Sources and Processes of Mercury in Subtropical Estuarine and Ocean Sediments Using Hg Isotopic Composition. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 1347–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, R.; Feng, X.; Wang, J.; Li, P.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, J.; Zheng, L.; Hu, T. Mercury speciation and mercury isotope fractionation during ore roasting process and their implication to source identification of downstream sediment in the Wanshan mercury mining area, SW China. Chem. Geol. 2013, 336, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Li, R.; Ali, M.U.; Wang, C.; Wang, B.; Jin, X.; Shao, M.; Li, P.; Zhang, L.; Feng, X. Mercury migration to surface water from remediated mine waste and impacts of rainfall in a karst area—Evidence from Hg isotopes. Water Res. 2023, 230, 119592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Marusczak, N.; Wang, X.; Gheusi, F.; Sonke, J.E. Isotopic Composition of Gaseous Elemental Mercury in the Free Troposphere of the Pic du Midi Observatory, France. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 5641–5650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hua, Y.; Cui, M. Wanshan Mercury Deposit in Guizhou Province; China Geological Press: Beijing, China, 1994. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yan, J.; Wang, C.; Wang, Z.; Yang, S.; Li, P. Mercury concentration and speciation in mine wastes in Tongren mercury mining area, southwest China and environmental effects. Appl. Geochem. 2019, 106, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Feng, X.; Zhu, J.; Sapkota, A.; Meng, B.; Yao, H.; Qin, H.; Larssen, T. Selenium in soil inhibits mercury uptake and translocation in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 10040–10046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, G.; Feng, X.; Meng, B.; Zhang, C.; Gu, C.; Du, B.; Lin, Y. Environmental geochemistry of an abandoned mercury mine in Yanwuping, Guizhou Province, China. Environ. Res. 2013, 125, 124–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Gu, C.; Feng, X.; Qiu, G.; Shang, L.; Xu, Z.; Lu, Q.; Xiao, D.; Wang, H.; Lin, Y.; et al. Weir building: A potential cost-effective method for reducing mercury leaching from abandoned mining tailings. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 651, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Feng, X.; Qiu, G.; Zhang, J.; Meng, B.; Wang, J. Mercury speciation and mobility in mine wastes from mercury mines in China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2013, 20, 8374–8381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shao, M.; Liu, Z.; Sun, H.; Lai, C.; Ma, Z.; He, X.; Fang, Y.; Chai, Q. C-N-P driven changes to phytoplankton community structure and gross primary productivity in river-fed reservoir ecosystems on the Chinese Loess Plateau. J. Hydrol. 2023, 616, 128781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, R.; Krabbenhoft, D.P.; Bergquist, B.A.; Zheng, W.; Lepak, R.F.; Hurley, J.P. Effects of mercury and thallium concentrations on high precision determination of mercury isotopic composition by Neptune Plus multiple collector inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2016, 31, 2060–2068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Lin, C.-J.; Yuan, W.; Sun, G.; Fu, X.; Feng, X. An improved method for recovering and preconcentrating mercury in natural water samples for stable isotope analysis. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2019, 34, 2303–2313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Feng, X.; Yin, R.; Zhang, H. Diurnal variations of total mercury, reactive mercury, and dissolved gaseous mercury concentrations and water/air mercury flux in warm and cold seasons from freshwaters of southwestern China. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2013, 32, 2256–2265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estrade, N.; Carignan, J.; Donard, O.F. Tracing and quantifying anthropogenic mercury sources in soils of northern France using isotopic signatures. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 1235–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, C.; Du, B.; Yin, R.; Meng, B.; Fu, X.; Li, P.; Zhang, L.; Feng, X. Isotopic Fractionation and Source Appointment of Methylmercury and Inorganic Mercury in a Paddy Ecosystem. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 14334–14342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blum, J.D.; Bergquist, B.A. Reporting of variations in the natural isotopic composition of mercury. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2007, 388, 353–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Estrade, N.; Carignan, J.; Sonke, J.E.; Donard, O.F. Measuring Hg isotopes in bio-geo-environmental reference materials. Geostand. Geoanal. Res. 2010, 34, 79–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssen, S.E.; Johnson, M.W.; Blum, J.D.; Barkay, T.; Reinfelder, J.R. Separation of monomethylmercury from estuarine sediments for mercury isotope analysis. Chem. Geol. 2015, 411, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pribil, M.J.; Rimondi, V.; Costagliola, P.; Lattanzi, P.; Rutherford, D.L. Assessing mercury distribution using isotopic fractionation of mercury processes and sources adjacent and downstream of a legacy mine district in Tuscany, Italy. Appl. Geochem. 2020, 117, 104600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Ecology and Environment of China (MEE). Soil Environmental Qualityrisk Control Standard for Soil Contamination of Development Land (GB3600–2018); Environmental Science Press of China: Beijing, China, 2018. (In Chinese)
- Ministry of Ecology and Environment of China (MEE). Soil Environmental Quality Risk Control Standard for Soil Contamination of Agricultural Land (GB15618–2018); Environmental Science Press of China: Beijing, China, 2018. (In Chinese)
- China National Environmental Monitoring Center (CNEMC). The Soil Environmental Background Value in the People’s Republic of China; China Environmental Press: Beijing, China, 1990. (In Chinese)
- Dai, Z.; Feng, X.; Zhang, C.; Wang, J.; Jiang, T.; Xiao, H.; Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Qiu, G. Assessing anthropogenic sources of mercury in soil in Wanshan Hg mining area, Guizhou, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2013, 20, 7560–7569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, G.; Feng, X.; Meng, B.; Sommar, J.; Gu, C. Environmental geochemistry of an active Hg mine in Xunyang, Shaanxi Province, China. Appl. Geochem. 2012, 27, 2280–2288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Lin, Y.; Meng, B.; Feng, X.; Xu, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Zhong, W.; Hu, Y.; Qiu, G. The impact of an abandoned mercury mine on the environment in the Xiushan region, Chongqing, southwestern China. Appl. Geochem. 2018, 88, 267–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ministry of Environment Protection of China (MEP). Ambient Air Quality Standards (GB3095–2012); Environmental Science Press of China: Beijing, China, 2012. (In Chinese)
- Xu, X.; Liu, N.; Landis, M.S.; Feng, X.; Qiu, G. Characteristics and distributions of atmospheric mercury emitted from anthropogenic sources in Guiyang, southwestern China. Acta Geochim. 2016, 35, 240–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, L.; Qiu, G.; Anderson, C.W.; Meng, B.; Wang, D.; Shang, L.; Yan, H.; Feng, X. Mercury methylation in rice paddies and its possible controlling factors in the Hg mining area, Guizhou province, Southwest China. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 215, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, X.; Zhang, H.; Yu, B.; Wang, X.; Lin, C.-J.; Feng, X. Observations of atmospheric mercury in China: A critical review. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 9455–9476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Z.G.; Feng, X.; Li, P.; Liang, L.; Tang, S.L.; Wang, S.F.; Fu, X.W.; Qiu, G.L.; Shang, L.H. Emissions of air-borne mercury from five municipal solid waste landfills in Guiyang and Wuhan, China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2010, 10, 3353–3364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Das, R.; Wang, X.; Khezri, B.; Webster, R.D.; Sikdar, P.K.; Datta, S. Mercury isotopes of atmospheric particle bound mercury for source apportionment study in urban Kolkata, India. Elem. Sci. Anthr. 2016, 4, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, G.; Liu, C.-Q.; Wu, P.; Yang, Y. The geochemical characteristics of mine-waste calcines and runoff from the Wanshan mercury mine, Guizhou, China. Appl. Geochem. 2004, 19, 1735–1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Environmental Protection Administration of China (EPA). Chinese Standards for Surface Water Quality (GB3838–2002); Environmental Protection Administration of China: Beijing, China, 2002. (In Chinese)
- Qiu, G.; Feng, X.; Wang, S.; Xiao, T. Mercury contaminations from historic mining to water, soil and vegetation in Lanmuchang, Guizhou, southwestern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2006, 368, 56–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokoo, Y.; Nakano, T.; Nishikawa, M.; Quan, H. Mineralogical variation of Sr–Nd isotopic and elemental compositions in loess and desert sand from the central Loess Plateau in China as a provenance tracer of wet and dry deposition in the northwestern Pacific. Chem. Geol. 2004, 204, 45–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Jin, Z.; Yu, J.; Zhou, Y.; Zhou, L. Hydrogeochemical processes between surface and groundwaters on the northeastern Chinese Loess Plateau: Implications for water chemistry and environmental evolutions in semi-arid regions. J. Geochem. Explor. 2015, 159, 115–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Liu, C.-Q. Water geochemistry of the Xijiang basin rivers, South China: Chemical weathering and CO2 consumption. Appl. Geochem. 2010, 25, 1603–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, C.; Yang, H.; Wang, J.; Guo, J.; Tang, X.; Chen, J. Combined use of stable nitrogen and oxygen isotopes to constrain the nitrate sources in a karst lake. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2020, 303, 107089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaillardet, J.; Dupre, B.; Allegre, C.J.; Negrel, P. Chemical and physical denudation in the Amazon River basin. Chem. Geol. 1997, 142, 141–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaillardet, J.; Dupre, B.; Louvat, P.; Allegre, C.J. Global silicate weathering and CO2 consumption rates deduced from the chemistry of large rivers. Chem. Geol. 1999, 159, 3–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Liu, C.; Harue, M.; Li, S.; Liu, X. The use of environmental isotopic (C, Sr, S) and hydrochemical tracers to characterize anthropogenic effects on karst groundwater quality: A case study of the Shuicheng Basin, SW China. Appl. Geochem. 2010, 25, 1924–1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Li, S.; Lang, Y.; Xiao, H. Using δ15N-and δ18O-values to identify nitrate sources in karst ground water, Guiyang, Southwest China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 6928–6933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Y.; Cheng, L.; Ma, B.; Cai, Y. The fate of mercury in municipal wastewater treatment plants in China: Significance and implications for environmental cycling. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 306, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Feng, X.B.; Larssen, T.; Shang, L.H.; Vogt, R.D.; Lin, Y.; Li, P.; Zhang, H.I. Fractionation, distribution and transport of mercury in rivers and tributaries around Wanshan Hg mining district, Guizhou Province, Southwestern China: Part 2-Methylmercury. Appl. Geochem. 2010, 25, 642–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Washburn, S.J.; Blum, J.D.; Kurz, A.Y.; Pizzuto, J.E. Spatial and temporal variation in the isotopic composition of mercury in the South River, VA. Chem. Geol. 2018, 494, 96–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiederhold, J.G.; Skyllberg, U.; Drott, A.; Jiskra, M.; Jonsson, S.; Bjorn, E.; Bourdon, B.; Kretzschmar, R. Mercury isotope signatures in contaminated sediments as a tracer for local industrial pollution sources. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gehrke, G.E.; Blum, J.D.; Marvin-DiPasquale, M. Sources of mercury to San Francisco Bay surface sediment as revealed by mercury stable isotopes. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2011, 75, 691–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonke, J.E.; Schäfer, J.; Chmeleff, J.; Audry, S.; Blanc, G.; Dupré, B. Sedimentary mercury stable isotope records of atmospheric and riverine pollution from two major European heavy metal refineries. Chem. Geol. 2010, 279, 90–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, D.; He, T.; Yin, R.; Zeng, L. Effects of soil properties on production and bioaccumulation of methylmercury in rice paddies at a mercury mining area, China. J. Environ. Sci. 2018, 68, 194–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, J.; Liu, F.; Zhao, L.; Liu, C.; Fu, Z.; Teng, Y. Mercury horizontal spatial distribution in paddy field and accumulation of mercury in rice as well as their influencing factors in a typical mining area of Tongren City, Guizhou, China. J. Environ. Health Sci. Eng. 2021, 19, 1555–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Yin, R.; Yu, B.; Du, B. Mercury isotope variations in surface soils in different contaminated areas in Guizhou Province, China. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2013, 58, 249–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, H.; Yin, R.-S.; Feng, X.-B.; Sommar, J.; Anderson, C.W.; Sapkota, A.; Fu, X.-W.; Larssen, T. Atmospheric mercury inputs in montane soils increase with elevation: Evidence from mercury isotope signatures. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 3322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, Z.H.; Chen, J.B.; Feng, X.B.; Hintelmann, H.; Yuan, S.L.; Cai, H.M.; Huang, Q.; Wang, S.X.; Wang, F.Y. Mass-dependent and mass-independent fractionation of mercury isotopes in precipitation from Guiyang, SW China. Comptes Rendus Geosci. 2015, 347, 358–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jin, X.; Yan, J.; Ali, M.U.; Li, Q.; Li, P. Mercury Biogeochemical Cycle in Yanwuping Hg Mine and Source Apportionment by Hg Isotopes. Toxics 2023, 11, 456. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11050456
Jin X, Yan J, Ali MU, Li Q, Li P. Mercury Biogeochemical Cycle in Yanwuping Hg Mine and Source Apportionment by Hg Isotopes. Toxics. 2023; 11(5):456. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11050456
Chicago/Turabian StyleJin, Xingang, Junyao Yan, Muhammad Ubaid Ali, Qiuhua Li, and Ping Li. 2023. "Mercury Biogeochemical Cycle in Yanwuping Hg Mine and Source Apportionment by Hg Isotopes" Toxics 11, no. 5: 456. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11050456
APA StyleJin, X., Yan, J., Ali, M. U., Li, Q., & Li, P. (2023). Mercury Biogeochemical Cycle in Yanwuping Hg Mine and Source Apportionment by Hg Isotopes. Toxics, 11(5), 456. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11050456