Salinity Changes the Dynamics of Pyrethroid Toxicity in Terms of Behavioral Effects on Newly Hatched Delta Smelt Larvae
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Larval Fish Source
2.2. Experimental Larvae Exposure
2.3. Analytical Chemistry
2.4. Locomotor Behavior Assay
2.5. Behavioral Parameters
2.6. Data Analysis
3. Results
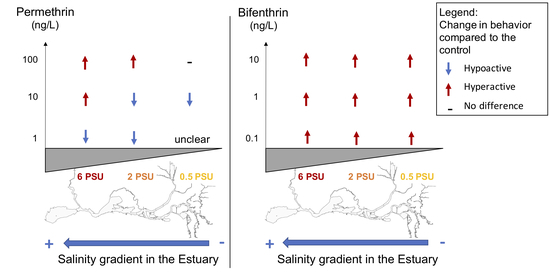
3.1. Pyrethroids Effect on Delta Smelt Larvae Behavior across A Salinity Gradient
3.1.1. Permethrin
3.1.2. Bifenthrin
3.2. Effect of the Salinity on the Toxicity of Pyrethroid Insecticides on Delta Smelt Larvae
3.2.1. Permethrin
3.2.2. Bifenthrin
4. Discussion
4.1. Low Pyrethroid Concentrations Impact Early Larval Delta Smelt Behavior and Decrease Their Anxiety-Related Response
4.2. Salinity Increases Pyrethroid Toxicity, Resulting in Behavior Change
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hobbs, J.A.; Lewis, L.S.; Willmes, M.; Denney, C.; Bush, E. Complex Life Histories Discovered in a Critically Endangered Fish. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, W.A. Critical Assessment of the Delta Smelt Population in the San Francisco Estuary, California. San Franc. Estuary Watershed Sci. 2005, 3. [Google Scholar]
- Moyle, P.B.; Herbold, B.; Stevens, D.E.; Miller, L.W. Life History and Status of Delta Smelt in the Sacramento-San Joaquin Estuary, California. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 1992, 121, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- California Department of Fish and Wildlife (CDFW). State & Federally Listed Endangered & Threatened Animals of California, Department of Fish and Wildlife, Bio-Geographic Data Branch; CDFW: Sacramento, CA, USA, 2014.
- IUCN. Hypomesus Transpacificus: NatureServe: The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species; IUCN: Gland, Switzerland, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Sommer, T.; Armor, C.; Baxter, R.; Breuer, R.; Brown, L.; Chotkowski, M.; Culberson, S.; Feyrer, F.; Gingras, M.; Herbold, B.; et al. The Collapse of Pelagic Fishes in the Upper San Francisco Estuary: El Colapso de Los Peces Pelagicos En La Cabecera Del Estuario San Francisco. Fisheries 2007, 32, 270–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuivila, K.M.; Moon, G.E. Potential Exposure of Larval and Juvenile Delta Smelt to Dissolved Pesticides in the Sacramento-San Joaquin Delta, California. Am. Fish. Soc. Symp. 2004, 39, 229–241. [Google Scholar]
- Brooks, M.L.; Fleishman, E.; Brown, L.R.; Lehman, P.W.; Werner, I.; Scholz, N.; Mitchelmore, C.; Lovvorn, J.R.; Johnson, M.L.; Schlenk, D.; et al. Life Histories, Salinity Zones, and Sublethal Contributions of Contaminants to Pelagic Fish Declines Illustrated with a Case Study of San Francisco Estuary, California, USA. Estuaries Coasts 2012, 35, 603–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moyle, P.; Brown, L.; Durand, J.; Hobbs, J. Delta Smelt: Life History and Decline of a Once-Abundant Species in the San Francisco Estuary. SFEWS 2016, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fong, S.; Louie, S.; Werner, I.; Connon, R.E. Contaminant Effects on California Bay–Delta Species and Human Health. SFEWS 2016, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Connon, R.; Hasenbein, S.; Brander, S.; Poynton, H.; Holland, E.; Schlenk, D.; Orlando, J.; Hladik, M.; Collier, T.; Scholz, N.; et al. Review of and Recommendations for Monitoring Contaminants and Their Effects in the San Francisco Bay−Delta. SFEWS 2019, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weston, D.; Moschet, C.; Young, T.; Johanif, N.; Poynton, H.; Major, K.; Connon, R.; Hasenbein, S. Chemical and Toxicological Impacts to Cache Slough Following Storm-Driven Contaminant Inputs. SFEWS 2019, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weston, D.P.; Lydy, M.J. Stormwater Input of Pyrethroid Insecticides to an Urban River. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2012, 31, 1579–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weston, D.P.; Schlenk, D.; Riar, N.; Lydy, M.J.; Brooks, M.L. Effects of Pyrethroid Insecticides in Urban Runoff on Chinook Salmon, Steelhead Trout, and Their Invertebrate Prey. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2015, 34, 649–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weston, D.P.; Asbell, A.M.; Lesmeister, S.A.; Teh, S.J.; Lydy, M.J. Urban and Agricultural Pesticide Inputs to a Critical Habitat for the Threatened Delta Smelt (Hypomesus Transpacificus). Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2014, 33, 920–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deanovic, L.A.; Stillway, M.; Hammock, B.G.; Fong, S.; Werner, I. Tracking Pyrethroid Toxicity in Surface Water Samples: Exposure Dynamics and Toxicity Identification Tools for Laboratory Tests with Hyalella Azteca (Amphipoda). Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2018, 37, 462–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, X. Study 321. Surface Water Monitoring for Pesticides in Agricultural Areas in Central Coast and Southern California; Department of Pesticide Regulation Environmental Monitoring Branch 1001 I Street: Sacramento, California, USA, 2019.
- Costa, C.; Rapisarda, V.; Catania, S.; Di Nola, C.; Ledda, C.; Fenga, C. Cytokine Patterns in Greenhouse Workers Occupationally Exposed to α-Cypermethrin: An Observational Study. Environ. Toxicol. Pharm. 2013, 36, 796–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soderlund, D.M. Molecular Mechanisms of Pyrethroid Insecticide Neurotoxicity: Recent Advances. Arch. Toxicol. 2012, 86, 165–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brander, S.M.; Gabler, M.K.; Fowler, N.L.; Connon, R.E.; Schlenk, D. Pyrethroid Pesticides as Endocrine Disruptors: Molecular Mechanisms in Vertebrates with a Focus on Fishes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 8977–8992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, J.M.; Matsumura, F. Two Different Types of Inhibitory Effects of Pyrethroids on Nerve Ca- and Ca + Mg-ATPase Activity in the Squid, Loligo Pealei. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 1982, 18, 180–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.B.; Singh, V. Cypermethrin Induced Histological Changes in Gonadotrophic Cells, Liver, Gonads, Plasma Levels of Estradiol-17β and 11-Ketotestosterone, and Sperm Motility in Heteropneustes Fossilis (Bloch). Chemosphere 2008, 72, 422–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werner, I.; Moran, K. Effects of Pyrethroid Insecticides on Aquatic Organisms. In Synthetic Pyrethroids; ACS Symposium Series; American Chemical Society: Washington, DC, USA, 2008; Volume 991, pp. 310–334. ISBN 978-0-8412-7433-4. [Google Scholar]
- Brander, S.M.; He, G.; Smalling, K.L.; Denison, M.S.; Cherr, G.N. The in Vivo Estrogenic and in Vitro Anti-Estrogenic Activity of Permethrin and Bifenthrin. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2012, 31, 2848–2855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brander, S.M.; Jeffries, K.M.; Cole, B.J.; DeCourten, B.M.; White, J.W.; Hasenbein, S.; Fangue, N.A.; Connon, R.E. Transcriptomic Changes Underlie Altered Egg Protein Production and Reduced Fecundity in an Estuarine Model Fish Exposed to Bifenthrin. Aquat. Toxicol. 2016, 174, 247–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tyler, C.R.; Beresford, N.; van der Woning, M.; Sumpter, J.P.; Tchorpe, K. Metabolism and Environmental Degradation of Pyrethroid Insecticides Produce Compounds with Endocrine Activities. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2000, 19, 801–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeGroot, B.C.; Brander, S.M. The Role of P450 Metabolism in the Estrogenic Activity of Bifenthrin in Fish. Aquat. Toxicol. 2014, 156, 17–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nillos, M.G.; Chajkowski, S.; Rimoldi, J.M.; Gan, J.; Lavado, R.; Schlenk, D. Stereoselective Biotransformation of Permethrin to Estrogenic Metabolites in Fish. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2010, 23, 1568–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeCourten, B.M.; Brander, S.M. Combined Effects of Increased Temperature and Endocrine Disrupting Pollutants on Sex Determination, Survival, and Development across Generations. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Duffy, T.A.; McElroy, A.E.; Conover, D.O. Variable Susceptibility and Response to Estrogenic Chemicals in Menidia Menidia. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2009, 380, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kidd, K.A.; Blanchfield, P.J.; Mills, K.H.; Palace, V.P.; Evans, R.E.; Lazorchak, J.M.; Flick, R.W. Collapse of a Fish Population after Exposure to a Synthetic Estrogen. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 8897–8901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kimmerer, W.J.; MacWilliams, M.; Gross, E.S. Variation of Fish Habitat and Extent of the Low-Salinity Zone with Freshwater Flow in the San Francisco Estuary. SFEWS 2013, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brown, L.R.; Bennett, W.A.; Wagner, R.W.; Morgan-King, T.; Knowles, N.; Feyrer, F.; Schoellhamer, D.H.; Stacey, M.T.; Dettinger, M. Implications for Future Survival of Delta Smelt from Four Climate Change Scenarios for the Sacramento–San Joaquin Delta, California. Estuaries Coasts 2013, 36, 754–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saranjampour, P.; Vebrosky, E.N.; Armbrust, K.L. Salinity Impacts on Water Solubility and N-Octanol/Water Partition Coefficients of Selected Pesticides and Oil Constituents. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2017, 36, 2274–2280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Cheng, Q.; Lin, L.; Wang, X.; Chen, B.; Luan, T.; Tam, N.F.Y. Partitions and Vertical Profiles of 9 Endocrine Disrupting Chemicals in an Estuarine Environment: Effect of Tide, Particle Size and Salinity. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 211, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hladik, M.L. Partitioning of Six Pyrethroid Insecticides at Varying Salinities: U.S. Geological Survey Data Release; U.S. Geological Survey: Sacramento, CA, USA, 2020. [CrossRef]
- Basnet, R.M.; Zizioli, D.; Taweedet, S.; Finazzi, D.; Memo, M. Zebrafish Larvae as a Behavioral Model in Neuropharmacology. Biomedicines 2019, 7, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fraser, T.W.K.; Khezri, A.; Jusdado, J.G.H.; Lewandowska-Sabat, A.M.; Henry, T.; Ropstad, E. Toxicant Induced Behavioural Aberrations in Larval Zebrafish Are Dependent on Minor Methodological Alterations. Toxicol. Lett. 2017, 276, 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Xu, T.; Huang, G.; Yin, D.; Zhang, Q.; Yang, X. Neurobehavioral Effects of Two Metabolites of BDE-47 (6-OH-BDE-47 and 6-MeO-BDE-47) on Zebrafish Larvae. Chemosphere 2018, 200, 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, L.D.; Seibert, J.; Soanes, K.H. Distinct Models of Induced Hyperactivity in Zebrafish Larvae. Brain Res. 2012, 1449, 46–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irons, T.D.; MacPhail, R.C.; Hunter, D.L.; Padilla, S. Acute Neuroactive Drug Exposures Alter Locomotor Activity in Larval Zebrafish. Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 2010, 32, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandara, S.B.; Carty, D.R.; Singh, V.; Harvey, D.J.; Vasylieva, N.; Pressly, B.; Wulff, H.; Lein, P.J. Susceptibility of Larval Zebrafish to the Seizurogenic Activity of GABA Type A Receptor Antagonists. NeuroToxicology 2020, 76, 220–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeMicco, A.; Cooper, K.R.; Richardson, J.R.; White, L.A. Developmental Neurotoxicity of Pyrethroid Insecticides in Zebrafish Embryos. Toxicol. Sci. 2010, 113, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nunes, M.E.M.; Schimith, L.E.; da Costa-Silva, D.G.; Lopes, A.R.; Leandro, L.P.; Martins, I.K.; de Mello, R.S.; Hartmann, D.D.; de Carvalho, N.R.; da Rosa, P.C.; et al. Acute Exposure to Permethrin Modulates Behavioral Functions, Redox, and Bioenergetics Parameters and Induces DNA Damage and Cell Death in Larval Zebrafish. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2019, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, D.F.; Miller, G.W.; Harvey, D.J.; Brander, S.M.; Geist, J.; Connon, R.E.; Lein, P.J. Bifenthrin Causes Transcriptomic Alterations in MTOR and Ryanodine Receptor-Dependent Signaling and Delayed Hyperactivity in Developing Zebrafish (Danio Rerio). Aquat. Toxicol. 2018, 200, 50–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Frank, D.F.; Brander, S.M.; Hasenbein, S.; Harvey, D.J.; Lein, P.J.; Geist, J.; Connon, R.E. Developmental Exposure to Environmentally Relevant Concentrations of Bifenthrin Alters Transcription of MTOR and Ryanodine Receptor-Dependent Signaling Molecules and Impairs Predator Avoidance Behavior across Early Life Stages in Inland Silversides (Menidia Beryllina). Aquat. Toxicol. 2019, 206, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mundy, P.C.; Carte, M.F.; Brander, S.M.; Hung, T.-C.; Fangue, N.; Connon, R.E. Bifenthrin Exposure Causes Hyperactivity in Early Larval Stages of an Endangered Fish Species at Concentrations That Occur during Their Hatching Season. Aquat. Toxicol. 2020, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mundy, P.; Huff Hartz, K.; Fulton, C.; Lydy, M.; Brander, S.; Hung, T.; Fangue, N.; Connon, R. Exposure to Permethrin or Chlorpyrifos Causes Differential Dose- and Time-Dependent Behavioral Effects at Early Larval Stages of an Endangered Teleost Species. Endang. Species Res. 2020, 44, 89–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weis, J.; Candelmo, A. Pollutants and Fish Predator/Prey Behavior: A Review of Laboratory and Field Approaches. Curr. Zool. 2012, 58, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baskerville-Bridges, B.; Lindberg, J.C.; Doroshov, S.I. Manual for the Intensive Culture of Delta Smelt (Hypomesus Transpacificus); University of California Davis: Sacramento, CA, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- ASTM E1192-97 Guide for Conducting Acute Toxicity Tests on Aqueous Ambient Samples and Effluents with Fishes, Macroinvertebrates, and Amphibians; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2014.
- Hladik, M.; Smalling, K.L.; Kuivila, K. Methods of Analysis: Determination of Pyrethroid Insecticides in Water and Sediment Using Gas Chromatography/Mass Spectrometry; U.S. Geological Survey Techniques and Methods 5–C2, 18 p; U.S. Geological Survey: Reston, Virginia, USA, 2009.
- Connon, R.E.; Geist, J.; Pfeiff, J.; Loguinov, A.V.; D’Abronzo, L.S.; Wintz, H.; Vulpe, C.D.; Werner, I. Linking Mechanistic and Behavioral Responses to Sublethal Esfenvalerate Exposure in the Endangered Delta Smelt; Hypomesus Transpacificus (Fam. Osmeridae). BMC Genom. 2009, 10, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deng, X. Study 304. Surface Water Monitoring for Pesticides in Agricultural Areas in Central Coast and Southern California; Department of Pesticide Regulation Environmental Monitoring Branch 1001 I Street: Sacramento, CA, USA, 2017.
- Weston, D.P.; Holmes, R.W.; Lydy, M.J. Residential Runoff as a Source of Pyrethroid Pesticides to Urban Creeks. Environ. Pollut. 2009, 157, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, P.; Dupuis, R.; Costentin, J. Thigmotaxis as an Index of Anxiety in Mice: Influence of Dopaminergic Transmissions. Behav. Brain Res. 1994, 61, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldwin, H.A.; Johnston, A.L.; File, S.E. Antagonistic Effects of Caffeine and Yohimbine in Animal Tests of Anxiety. Eur. J. Pharm. 1989, 159, 211–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodman, J.; McIntyre, C.K. Impaired Spatial Memory and Enhanced Habit Memory in a Rat Model of Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder. Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Packard, M.G.; Wingard, J.C. Amygdala and “Emotional” Modulation of the Relative Use of Multiple Memory Systems. Neurobiol. Learn. Mem. 2004, 82, 243–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasuti, C.; Fattoretti, P.; Carloni, M.; Fedeli, D.; Ubaldi, M.; Ciccocioppo, R.; Gabbianelli, R. Neonatal Exposure to Permethrin Pesticide Causes Lifelong Fear and Spatial Learning Deficits and Alters Hippocampal Morphology of Synapses. J. Neurodev. Disord. 2014, 6, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- El-Sayed, Y.S.; Saad, T.T. Subacute Intoxication of a Deltamethrin-Based Preparation (Butox® 5% EC) in Monosex Nile Tilapia, Oreochromis Niloticus L. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2008, 102, 293–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, H.T.; Silvestre, F.; Meulder, B.D.; Thome, J.-P.; Phuong, N.T.; Kestemont, P. Combined Effects of Deltamethrin, Temperature and Salinity on Oxidative Stress Biomarkers and Acetylcholinesterase Activity in the Black Tiger Shrimp (Penaeus Monodon). Chemosphere 2012, 86, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.-C.; Chen, J.-C. Acute Toxicity of Nitrite on Litopenaeus Vannamei (Boone) Juveniles at Different Salinity Levels. Aquaculture 2003, 224, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeLorenzo, M.E.; Wallace, S.C.; Danese, L.E.; Baird, T.D. Temperature and Salinity Effects on the Toxicity of Common Pesticides to the Grass Shrimp, Palaemonetes Pugio. J. Environ. Sci. Health B 2009, 44, 455–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- DeLorenzo, M.E.; Danese, L.E.; Baird, T.D. Influence of Increasing Temperature and Salinity on Herbicide Toxicity in Estuarine Phytoplankton. Environ. Toxicol. 2013, 28, 359–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeCourten, B.; Romney, A.; Brander, S. Chapter 2—The Heat Is On: Complexities of Aquatic Endocrine Disruption in a Changing Global Climate. In Separation Science and Technology; Ahuja, S., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2019; Volume 11, pp. 13–49. ISBN 1877-1718. [Google Scholar]
- Velasco, J.; Gutiérrez-Cánovas, C.; Botella-Cruz, M.; Sánchez-Fernández, D.; Arribas, P.; Carbonell, J.A.; Millán, A.; Pallarés, S. Effects of Salinity Changes on Aquatic Organisms in a Multiple Stressor Context. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2019, 374, 20180011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Staton, J.L.; Schizas, N.V.; Klosterhaus, S.L.; Griffitt, R.J.; Chandler, G.T.; Coull, B.C. Effect of Salinity Variation and Pesticide Exposure on an Estuarine Harpacticoid Copepod, Microarthridion Littorale (Poppe), in the Southeastern US. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2002, 278, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasenbein, S.; Poynton, H.; Connon, R.E. Contaminant Exposure Effects in a Changing Climate: How Multiple Stressors Can Multiply Exposure Effects in the Amphipod Hyalella Azteca. Ecotoxicology 2018, 27, 845–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Grisle, S.; Schlenk, D. Effects of Salinity on Aldicarb Toxicity in Juvenile Rainbow Trout (Oncorhynchus Mykiss) and Striped Bass (Morone Saxatilis × Chrysops). Toxicol. Sci. 2001, 64, 200–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brecken-Folse, J.A.; Mayer, F.L.; Pedigo, L.E.; Marking, L.L. Acute Toxicity of 4-Nitrophenol, 2,4-Dinitrophenol, Terbufos and Trichlorfon to Grass Shrimp (Palaemonetes Spp.) and Sheepshead Minnows (Cyprinodon Variegatus) as Affected by Salinity and Temperature. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 1994, 13, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, L.W.; Ziegenfuss, M.C.; Anderson, R.D.; Spittler, T.D.; Leichtweis, H.C. Influence of Salinity on Atrazine Toxicity to a Chesapeake Bay Copepod (Eurytemora Affinis) and Fish (Cyprinodon Variegatus). Estuaries 1994, 17, 181–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laskowski, D.A. Physical and Chemical Properties of Pyrethroids. Rev. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2002, 174, 49–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gammon, D.W.; Liu, Z.; Chandrasekaran, A.; El-Naggar, S.F.; Kuryshev, Y.A.; Jackson, S. Pyrethroid Neurotoxicity Studies with Bifenthrin Indicate a Mixed Type I/II Mode of Action. Pest Manag. Sci. 2019, 75, 1190–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradberry, S.M.; Cage, S.A.; Proudfoot, A.T.; Vale, J.A. Poisoning Due to Pyrethroids. Toxicol. Rev. 2005, 24, 93–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, L.G. The Neurotoxicity of Organochlorine and Pyrethroid Pesticides. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2015, 131, 135–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wakeling, E.N.; Neal, A.; Atchison, W. Pyrethroids and Their Effects on Ion Channels. In Pesticides—Advances in Chemical and Botanical Pesticides; InTech: Rijeka, Croatia, 2012; pp. 39–66. [Google Scholar]
- Vieira, C.E.D.; dos Reis Martinez, C.B. The Pyrethroid λ-Cyhalothrin Induces Biochemical, Genotoxic, and Physiological Alterations in the Teleost Prochilodus Lineatus. Chemosphere 2018, 210, 958–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Correlation (Spearman) | Condition | Periods | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dark | Light | |||||
| rs | p | rs | p | |||
| Permethrin | Concentration vs. TDM | 0.5 PSU | 0.00 | ns | −0.02 | ns |
| 2 PSU | 0.09 | * | −0.04 | ns | ||
| 6 PSU | 0.06 | * | 0.02 | ns | ||
| Concentration vs. anti-thigmotaxis | 0.5 PSU | 0.11 | * | 0.21 | * | |
| 2 PSU | 0.05 | * | −0.01 | ns | ||
| 6 PSU | 0.05 | * | 0.08 | * | ||
| Salinity vs. TDM | Control | 0.01 | ns | −0.05 | ns | |
| 1 ng/L | −0.09 | * | 0.08 | * | ||
| 10 ng/L | 0.09 | * | −0.06 | ns | ||
| 100 ng/L | 0.03 | ns | 0.04 | ns | ||
| Salinity vs. anti-thigmotaxis | Control | −0.14 | ns | −0.01 | ns | |
| 1 ng/L | −0.19 | * | −0.02 | ns | ||
| 10 ng/L | −0.24 | * | −0.22 | * | ||
| 100 ng/L | −0.28 | * | −0.16 | * | ||
| Bifenthrin | Concentration vs. TDM | 0.5 PSU | 0.04 | * | 0.10 | * |
| 2 PSU | 0.00 | ns | 0.32 | * | ||
| 6 PSU | 0.05 | * | 0.07 | * | ||
| Concentration vs. anti-thigmotaxis | 0.5 PSU | 0.07 | * | 0.18 | * | |
| 2 PSU | 0.09 | * | 0.43 | * | ||
| 6 PSU | 0.11 | * | 0.33 | * | ||
| Salinity vs. TDM | Control | −0.02 | ns | −0.10 | * | |
| 0.1 ng/L | 0.00 | ns | 0.13 | * | ||
| 1 ng/L | −0.01 | ns | −0.18 | * | ||
| 10 ng/L | 0.01 | ns | −0.02 | ns | ||
| Salinity vs. anti-thigmotaxis | Control | 0.05 | * | 0.16 | * | |
| 0.1 ng/L | 0.14 | * | 0.67 | * | ||
| 1 ng/L | 0.10 | * | 0.83 | * | ||
| 10 ng/L | 0.14 | * | 0.46 | * | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Segarra, A.; Mauduit, F.; Amer, N.R.; Biefel, F.; Hladik, M.L.; Connon, R.E.; Brander, S.M. Salinity Changes the Dynamics of Pyrethroid Toxicity in Terms of Behavioral Effects on Newly Hatched Delta Smelt Larvae. Toxics 2021, 9, 40. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics9020040
Segarra A, Mauduit F, Amer NR, Biefel F, Hladik ML, Connon RE, Brander SM. Salinity Changes the Dynamics of Pyrethroid Toxicity in Terms of Behavioral Effects on Newly Hatched Delta Smelt Larvae. Toxics. 2021; 9(2):40. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics9020040
Chicago/Turabian StyleSegarra, Amelie, Florian Mauduit, Nermeen R. Amer, Felix Biefel, Michelle L. Hladik, Richard E. Connon, and Susanne M. Brander. 2021. "Salinity Changes the Dynamics of Pyrethroid Toxicity in Terms of Behavioral Effects on Newly Hatched Delta Smelt Larvae" Toxics 9, no. 2: 40. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics9020040
APA StyleSegarra, A., Mauduit, F., Amer, N. R., Biefel, F., Hladik, M. L., Connon, R. E., & Brander, S. M. (2021). Salinity Changes the Dynamics of Pyrethroid Toxicity in Terms of Behavioral Effects on Newly Hatched Delta Smelt Larvae. Toxics, 9(2), 40. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics9020040