Polyelectrolyte Gels Formed by Filamentous Biopolymers: Dependence of Crosslinking Efficiency on the Chemical Softness of Divalent Cations
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Rheology of Gels Formed by Pf1 and Divalent Cations
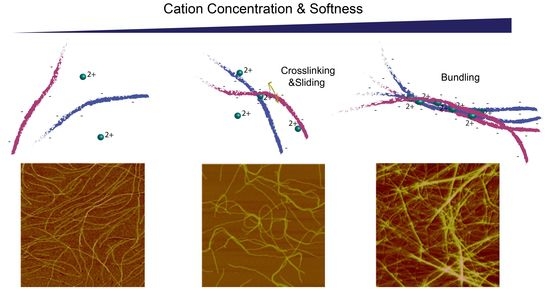
2.2. Divalent Counterion Specificity in Promoting Attractions between Like-Charged Filaments
2.3. Comparison of Counterion-Mediated Attractions in Networks of PF1 and Vimentin
2.4. Polyelectrolyte Aggregation Efficiency Correlates with Metal Ion Softness But Not Size
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| DLS | dynamic light scattering |
| HSAB | hard/soft acid/base |
| PE | polyelectrolyte |
| PMF | potential of mean force |
| VIF | vimentin intermediate filament |
References
- Janmey, P.A.; Slochower, D.R.; Wang, Y.H.; Wen, Q.; Cebers, A. Polyelectrolyte properties of filamentous biopolymers and their consequences in biological fluids. Soft Matter 2014, 10, 1439–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hosek, M.; Tang, J.X. Polymer-induced bundling of F actin and the depletion force. Phys. Rev. E 2004, 69, 051907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tang, J.X.; Janmey, P.A. The polyelectrolyte nature of F-actin and the mechanism of actin bundle formation. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 8556–8563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gurmessa, B.; Francis, M.; Rust, M.J.; Das, M.; Ross, J.L.; Robertson-Anderson, R.M. Counterion crossbridges enable robust multiscale elasticity in actin networks. Phys. Rev. Res. 2019, 1, 013016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tang, J.X.; Wong, S.E.; Tran, P.T.; Janmey, P.A. Counterion induced bundle formation of rodlike polyelectrolytes. Ber. Der Bunsen-Ges. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 1996, 100, 796–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bucki, R.; Durnas, B.; Watek, M.; Piktel, E.; Cruz, K.; Wolak, P.; Savage, P.B.; Janmey, P.A. Targeting polyelectrolyte networks in purulent body fluids to modulate bactericidal properties of some antibiotics. Infect. Drug Resist. 2018, 11, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- O’Reilly, S.A.; Roedica, J.; Nagy, D.; Hallewell, R.A.; Alderson, K.; Marklund, S.L.; Kuby, J.; Kushner, P.D. Motor neuron-astrocyte interactions and levels of Cu,Zn superoxide dismutase in sporadic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Exp. Neurol. 1995, 131, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yemets, A.; Horiunova, I.; Blume, Y. Cadmium, nickel, copper, and zinc influence on microfilament organization in Arabidopsis root cells. Cell Biol. Int. 2021, 45, 211–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrmann, H.; Haner, M.; Brettel, M.; Muller, S.A.; Goldie, K.N.; Fedtke, B.; Lustig, A.; Franke, W.W.; Aebi, U. Structure and assembly properties of the intermediate filament protein vimentin: The role of its head, rod and tail domains. J. Mol. Biol. 1996, 264, 933–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.J.; Day, L.A. Pf1 virus structure: Helical coat protein and DNA with paraxial phosphates. Science 1994, 265, 671–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huisman, E.M.; Wen, Q.; Wang, Y.H.; Cruz, K.; Kitenbergs, G.; Erglis, K.; Zeltins, A.; Cebers, A.; Janmey, P.A. Gelation of semiflexible polyelectrolytes by multivalent counterions. Soft Matter 2011, 7, 7257–7261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Horkay, F.; Basser, P.J.; Hecht, A.M.; Geissler, E. Ionic effects in semi-dilute biopolymer solutions: A small angle scattering study. J. Chem. Phys. 2018, 149, 163312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.T.; Lin, C.; Zhang, J.S.; Tan, Z.J. Ion-mediated interactions between like-charged polyelectrolytes with bending flexibility. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 21586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apelblat, A.; Manzurola, E. Solubilities of magnesium, calcium, barium, cobalt, nickel, copper, and zinc acetates in water from T = (278.15 to 348.15) K. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 1999, 31, 1347–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.X.; Janmey, P.A.; Lyubartsev, A.; Nordenskiold, L. Metal ion-induced lateral aggregation of filamentous viruses fd and M13. Biophys. J. 2002, 83, 566–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Slochower, D.R.; Huwe, P.J.; Radhakrishnan, R.; Janmey, P.A. Quantum and all-atom molecular dynamics simulations of protonation and divalent ion binding to phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (PIP2). J. Phys. Chem. B 2013, 117, 8322–8329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Perez-Sala, D.; Oeste, C.L.; Martinez, A.E.; Carrasco, M.J.; Garzon, B.; Canada, F.J. Vimentin filament organization and stress sensing depend on its single cysteine residue and zinc binding. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 7287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Monico, A.; Zorrilla, S.; Rivas, G.; Perez-Sala, D. Zinc Differentially Modulates the Assembly of Soluble and Polymerized Vimentin. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wu, H.Y.; Shen, Y.N.; Wang, D.Z.; Herrmann, H.; Goldman, R.D.; Weitz, D.A. Effect of Divalent Cations on the Structure and Mechanics of Vimentin Intermediate Filaments. Biophys. J. 2020, 119, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Zhang, J.; Yang, H.; Wu, C.; Dang, X.; Liu, Y. Copper depletion inhibits CoCl2-induced aggressive phenotype of MCF-7 cells via downregulation of HIF-1 and inhibition of Snail/Twist-mediated epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 12410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, P.; Hawkins, J.; Linthicum, W.H.; Wang, M.; Li, N.; Zhou, N.; Wen, Q.; Timme-Laragy, A.; Song, X.; Sun, Y. Heavy Metal Exposure Leads to Rapid Changes in Cellular Biophysical Properties. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 6, 1965–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dammann, C.; Koster, S. Dynamics of counterion-induced attraction between vimentin filaments followed in microfluidic drops. Lab Chip 2014, 14, 2681–2687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ricketts, S.N.; Khanal, P.; Rust, M.J.; Das, M.; Ross, J.L.; Robertson-Anderson, R.M. Triggering Cation-Induced Contraction of Cytoskeleton Networks via Microfluidics. Front. Phys. 2020, 8, 6699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Xu, D.C.; Wang, Y. Natural Indices for the Chemical Hardness/Softness of Metal Cations and Ligands. ACS Omega 2017, 2, 7185–7193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manning, G.S.; Ray, J. Counterion condensation revisited. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 1998, 16, 461–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xian, W.; Tang, J.X.; Janmey, P.A.; Braunlin, W.H. The polyelectrolyte behavior of actin filaments: A 25Mg NMR study. Biochemistry 1999, 38, 7219–7226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janmey, P.A.; Euteneuer, U.; Traub, P.; Schliwa, M. Viscoelastic properties of vimentin compared with other filamentous biopolymer networks. J. Cell Biol. 1991, 113, 155–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tang, J.X.; Ito, T.; Tao, T.; Traub, P.; Janmey, P.A. Opposite effects of electrostatics and steric exclusion on bundle formation by F-actin and other filamentous polyelectrolytes. Biochemistry 1997, 36, 12600–12607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, O.I.; Lifshitz, J.; Janmey, P.A.; Linden, M.; McIntosh, T.K.; Leterrier, J.F. Mechanisms of mitochondria-neurofilament interactions. J. Neurosci. 2003, 23, 9046–9058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cruz, K.; Wang, Y.-H.; Oake, S.A.; Janmey, P.A. Polyelectrolyte Gels Formed by Filamentous Biopolymers: Dependence of Crosslinking Efficiency on the Chemical Softness of Divalent Cations. Gels 2021, 7, 41. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels7020041
Cruz K, Wang Y-H, Oake SA, Janmey PA. Polyelectrolyte Gels Formed by Filamentous Biopolymers: Dependence of Crosslinking Efficiency on the Chemical Softness of Divalent Cations. Gels. 2021; 7(2):41. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels7020041
Chicago/Turabian StyleCruz, Katrina, Yu-Hsiu Wang, Shaina A. Oake, and Paul A. Janmey. 2021. "Polyelectrolyte Gels Formed by Filamentous Biopolymers: Dependence of Crosslinking Efficiency on the Chemical Softness of Divalent Cations" Gels 7, no. 2: 41. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels7020041
APA StyleCruz, K., Wang, Y. -H., Oake, S. A., & Janmey, P. A. (2021). Polyelectrolyte Gels Formed by Filamentous Biopolymers: Dependence of Crosslinking Efficiency on the Chemical Softness of Divalent Cations. Gels, 7(2), 41. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels7020041