A Highly Mechanical, Conductive, and Cryophylactic Double Network Hydrogel for Flexible and Low-Temperature Tolerant Strain Sensors
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Mechanical Properties of Hydrogels
2.2. Modulation on Mechanical Performance of DN Hydrogel
2.3. Mechanical Flexibility at Low Temperatures
2.4. Sensing Performance of Hydrogel Flexible Sensor
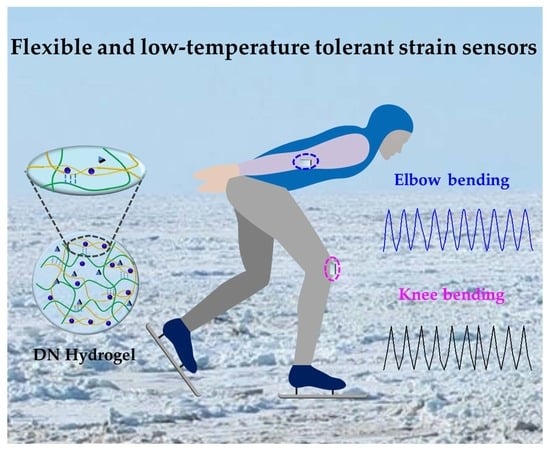
2.5. Human Motion Detection
2.6. Low-Temperature Strain Responsiveness
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Fabrication of CS/P (AA-co-AM) DN Hydrogel
4.3. Fabrication of the Hydrogel-Based Flexible Sensor
4.4. Characterization
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gao, Y.; Peng, J.; Zhou, M.; Yang, Y.; Wang, X.; Wang, J.; Cao, Y.; Wang, W.; Wu, D. A multi-model, large range and anti-freezing sensor based on a multi-crosslinked poly(vinyl alcohol) hydrogel for human-motion monitoring. J. Mater. Chem. B 2020, 8, 11010–11020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, G.; Wang, J.; Qian, K.; Chen, J.; Li, S.; Lee, P.S. Extremely stretchable strain sensors based on conductive self-healing dynamic cross-links hydrogels for human-motion detection. Adv. Sci. 2017, 4, 1600190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, J.; Wan, L.; Gao, Y.; Fang, X.; Lu, T.; Pan, L.; Xuan, F. Highly stretchable and self-healable mxene/polyvinyl alcohol hydrogel electrode for wearable capacitive electronic skin. Adv. Electron. Mater. 2019, 5, 1900285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Chen, G.; Tian, J.; Wan, X. Chitin/Ca solvent-based conductive and stretchable organohydrogel with anti-freezing and anti-drying. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 207, 484–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.-W.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.-Y.; Wang, P. Textile-based flexible pressure sensors: A review. Polym. Rev. 2022, 62, 65–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, J.; Wang, S.; Wang, L.; Wu, M. Neuron-inspired multifunctional conductive hydrogels for flexible wearable sensors. J. Mater. Chem. C 2022, 10, 4327–4335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Wang, X.; Zhang, H.J.; You, X.; Yue, O. Self-healable, high-strength hydrogel electrode for flexible sensors and supercapacitors. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 36240–36252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.; Choi, H.; Kang, K.; Shin, M.; Son, D. Soft stretchable conductive carboxymethylcellulose hydrogels for wearable sensors. Gels 2022, 8, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, Y.; Wei, Q.; Wang, Y.; Lei, M.; Li, M.; Li, D.; Zhang, L.; Wu, Y. Self-healing mechanism and conductivity of the hydrogel flexible sensors: A review. Gels 2021, 7, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Z.; Kuroki, M.; Otsuka, Y.; Maeda, S. Contraction waves in self-oscillating polymer gels. Extrem. Mech. Lett. 2020, 39, 100830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeda, S.; Hara, Y.; Yoshida, R.; Hashimoto, S. Peristaltic motion of polymer gels. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2008, 47, 6690–6693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rukmanikrishnan, B.; Lee, J. Anti-freezing and thermally self-healing polymer composite comprising polyvinyl alcohol, polyethylene oxide, and sodium carboxymethyl cellulose. Eur. Polym. J. 2021, 154, 110565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Huang, J.; Zhou, Z.; Chen, Q.; Hong, M.; Yang, S.; Heqing, F. Highly elastic anti-fatigue and anti-freezing conductive double network hydrogel for human body sensors. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2021, 60, 6162–6172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Q.; Wu, Z.; Tao, K.; Wei, Y.; Wang, W.; Yang, B.R.; Xie, X.; Wu, J. Environment tolerant, adaptable and stretchable organohydrogels: Preparation, optimization, and applications. Mater. Horiz. 2022, 9, 1356–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.; Li, C.; Li, G.; Yu, D.; Song, Z.; Wang, H.; Liu, X.; Liu, H.; Liu, W. Development of conductive hydrogels for fabricating flexible strain sensors. Small 2022, 18, e2101518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Dai, T.; Zhou, Y.; Mohamed, A.; Yuan, G.; Jia, H. Adhesive and high-sensitivity modified Ti3C2TX (MXene)-based organohydrogels with wide work temperature range for wearable sensors. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 613, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, Q.; Lei, W.; Chen, L.; Yin, Y.; Zhou, J.; Liu, M. Anti-freezing, conductive self-healing organohydrogels with stable strain-sensitivity at subzero temperatures. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 14159–14163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Chen, D.; Sun, X.; Xu, Z.; Yang, Y.; Song, Y.; Jiang, F. An environmentally tolerant, highly stable, cellulose nanofiber-reinforced, conductive hydrogel multifunctional sensor. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 284, 119199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Wu, Z.; Huang, W.; Yang, X.; Liang, Y.; Tao, K.; Yang, B.R.; Shi, W.; Xie, X. Stretchable, stable, and room-temperature gas sensors based on self-healing and transparent organohydrogels. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 52070–52081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, W.; Gu, K.; Yao, J.; Shao, Z.; Chen, X. Poly(vinyl alcohol) hydrogels with integrated toughness, conductivity, and freezing tolerance based on ionic liquid/water binary solvent systems. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 29008–29020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Li, Q.; Li, K.; Sun, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhuang, T.; Yan, J.; Wang, H. Ultra-high electrical conductivity in filler-free polymeric hydrogels toward thermoelectrics and electromagnetic interference shielding. Adv. Mater. 2022, 34, e2109904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morelle, X.P.; Illeperuma, W.R.; Tian, K.; Bai, R.; Suo, Z.; Vlassak, J.J. Highly stretchable and tough hydrogels below water freezing temperature. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, e1801541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, Q.; Gao, G. Solvent-resistant and nonswellable hydrogel conductor toward mechanical perception in diverse liquid media. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 13709–13717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, C.; Zhu, T.; Liu, H.; Yang, G.; He, Z.; Wang, M.; Ji, M.; Cong, G.; Yu, J.; Zhu, C.; et al. A one-step aqueous route to prepare polyacrylonitrile-based hydrogels with excellent ionic conductivity and extreme low temperature tolerance. J. Mater. Chem. A 2020, 8, 22090–22099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.; Liu, Y.; Ruan, Y.; Qiu, H.; Song, P.; Kong, J.; Zhang, H.; Gu, J. Multifunctional sponges with flexible motion sensing and outstanding thermal insulation for superior electromagnetic interference shielding. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2020, 139, 106143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Cong, Y.; Fu, J. Stretchable and tough conductive hydrogels for flexible pressure and strain sensors. J. Mater. Chem. B 2020, 8, 3437–3459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Wang, X.; Cao, Y.; Yang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Gao, Y.; Ma, Z.; Wang, J.; Wang, W.; Wu, D. Freezing-tolerant, highly sensitive strain and pressure sensors assembled from ionic conductive hydrogels with dynamic cross-links. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 25334–25344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Chen, L.; Shen, B.; Mo, J.; Tang, F.; Feng, J. Highly stretchable and self-healing double network hydrogel based on polysaccharide and polyzwitterion for wearable electric skin. Polymer 2020, 194, 122381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Chen, L.; Shen, B.; Wang, Y.; Peng, P.; Tang, F.; Feng, J. Highly transparent, self-healing, injectable and self-adhesive chitosan/polyzwitterion-based double network hydrogel for potential 3D printing wearable strain sensor. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2020, 117, 111298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, M.; Pan, S.; Li, H.; Yi, X.; Zhan, Y.; Sun, Z.; Jiang, X.; Zhang, Y. Hybrid double-network hydrogel for highly stretchable, excellent sensitive, stabilized, and transparent strain sensors. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2021, 32, 1548–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zheng, H.; Tan, Y.J.; Tor, S.B.; Zhou, K. Development of an ultrastretchable double-network hydrogel for flexible strain sensors. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 12814–12823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Cao, Y.; Wang, X.; Chen, Y.; Liu, H.; Gao, Y.; Wang, J.; Liu, C.; Wang, W.; et al. Anti-freezing, resilient and tough hydrogels for sensitive and large-range strain and pressure sensors. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 403, 126431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Wu, D. Energy-dissipative and soften resistant hydrogels based on chitosan physical network: From construction to application. Chin. J. Chem. 2022, 40, 2118–2134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.F.; Ma, X.; Hou, T.; Guo, K.; Yin, J.; Wang, Z.; Shu, L.; He, M.; Yao, J. Inorganic salts induce thermally reversible and anti-freezing cellulose hydrogels. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 7366–7370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Wang, X.; Yang, Y. Chitosan-based high-mechanical double-network hydrogels: Construction, modulation and applications. Acta Chim. Sin. 2021, 79, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Meijer, H.E.H.; Govaert, L.E. Mechanical performance of polymer systems: The relation between structure and properties. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2005, 30, 915–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Ren, Z.; Liu, X.; Ling, Q.; Li, Z.; Gu, H. A Multifunctional, Self-healing, self-adhesive, and conductive sodium alginate/poly(vinyl alcohol) composite hydrogel as a flexible strain sensor. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 11344–11355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]











| CS Content | Elastic Modulus (MPa) | Fracture Strength (MPa) | Fracture Strain (%) | Toughness (MJ/m3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0% | 0.09 | 0.26 | 702 | 1.11 |
| 2.5% | 0.17 | 0.73 | 623 | 2.24 |
| 5% | 0.36 | 1.46 | 576 | 4.65 |
| 7.5% | 0.50 | 2.44 | 539 | 6.80 |
| 10% | 0.78 | 2.71 | 460 | 6.95 |
| n(AA):n(AM) | Elastic Modulus (MPa) | Fracture Strength (MPa) | Fracture Strain (%) | Toughness (MJ/m3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5% | 0.29 | 1.24 | 629 | 4.35 |
| 10% | 0.39 | 1.64 | 594 | 5.29 |
| 15% | 0.50 | 2.44 | 539 | 6.79 |
| 20% | 0.73 | 2.47 | 474 | 6.64 |
| 25% | 0.80 | 2.63 | 433 | 6.26 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Diao, Q.; Liu, H.; Yang, Y. A Highly Mechanical, Conductive, and Cryophylactic Double Network Hydrogel for Flexible and Low-Temperature Tolerant Strain Sensors. Gels 2022, 8, 424. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels8070424
Diao Q, Liu H, Yang Y. A Highly Mechanical, Conductive, and Cryophylactic Double Network Hydrogel for Flexible and Low-Temperature Tolerant Strain Sensors. Gels. 2022; 8(7):424. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels8070424
Chicago/Turabian StyleDiao, Quan, Hongyan Liu, and Yanyu Yang. 2022. "A Highly Mechanical, Conductive, and Cryophylactic Double Network Hydrogel for Flexible and Low-Temperature Tolerant Strain Sensors" Gels 8, no. 7: 424. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels8070424
APA StyleDiao, Q., Liu, H., & Yang, Y. (2022). A Highly Mechanical, Conductive, and Cryophylactic Double Network Hydrogel for Flexible and Low-Temperature Tolerant Strain Sensors. Gels, 8(7), 424. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels8070424