Characterization of the Ejector Pump Performance for the Assisted Bidirectional Glenn Procedure
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Method
2.1. Modified Assisted Bidirectional Glenn
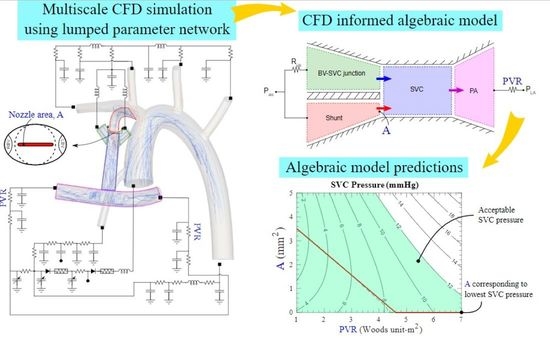
2.2. Geometry Construction and CFD Simulation
2.3. Algebraic Model
2.3.1. Model Construction
2.3.2. Parameter Identification
3. Results
3.1. CFD and Algebraic Model Comparison
3.2. Algebraic Model Predictions
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. LPN Model and Values
| Parameter | Value | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| 28.0899 | mmHg s/mL | |
| 0.04430 | mL/mmHg | |
| 0.02138 | mmHg s/mL | |
| 0.64510 | mmHg s/mL | |
| 0.15515 | mL/mmHg | |
| 0.16529 | mmHg s/mL | |
| 2.03945 | mL/mmHg | |
| 0.83376 | mmHg s/mL | |
| 0.02039 | mL/mmHg | |
| 0.02194 | mmHg s/mL | |
| 0.44375 | mL/mmHg | |
| 7.02239 | mmHg s/mL | |
| 0.07758 | mL/mmHg | |
| 0.01069 | mmHg s/mL | |
| 0.64510 | mmHg s/mL | |
| 0.07758 | mL/mmHg | |
| 0.16529 | mmHg s/mL | |
| 2.03945 | mL/mmHg | |
| 10.6739 | mmHg s/mL | |
| 1.9435 × | mL/mmHg | |
| 10.6739 | mmHg s/mL | |
| 5.1827 × | mL/mmHg | |
| 21.3477 | mmHg s/mL | |
| 7.7741 × | mL/mmHg | |
| 10.6739 | mmHg s/mL | |
| 0.05 × | mL/mmHg | |
| 18.5 | mmHg/mL | |
| −0.042 | mmHg/mL | |
| 4.0 | mL | |
| 0.9 | mmHg | |
| 0.062 | 1/mL | |
| 7.35 | mmHg/mL | |
| 1.0 | mL | |
| 0.17 | mmHg | |
| 0.484 | 1/mL | |
| 4 × | mmHg s/mL | |
| 4 × | mmHg s/mL | |
| 0.09 | mmHg s/mL | |
| 0.001 | mmHg s/mL | |
| 0.041555 | mL/mmHg |
References
- Norwood, W.I.; Kirklin, J.K.; Sanders, S.P. Hypoplastic left heart syndrome: Experience with palliative surgery. Am. J. Cardiol. 1980, 45, 87–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norwood, W.I.; Lang, P.; Casteneda, A.; Campbell, D. Experience with operations for hypoplastic left heart syndrome. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 1981, 82, 511–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glenn, W.W. Circulatory bypass of the right side of the heart: Shunt between superior vena cava and distal right pulmonary artery—Report of clinical application. N. Engl. J. Med. 1958, 259, 117–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glenn, W.W.; Ordway, N.K.; Talner, N.S.; Call, E.P., Jr. Circulatory Bypass of the Right Side of the Heart: VI. Shunt between Superior Vena Cava and Distal Right Pulmonary Artery; Report of Clinical Application in Thirty-eight Cases. Circulation 1965, 31, 172–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fontan, F.; Baudet, E. Surgical repair of tricuspid atresia. Thorax 1971, 26, 240–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fontan, F.; Kirklin, J.W.; Fernandez, G.; Costa, F.; Naftel, D.C.; Tritto, F.; Blackstone, E.H. Outcome after a “perfect” Fontan operation. Circulation 1990, 81, 1520–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- D’Udekem, Y.; Xu, M.Y.; Galati, J.C.; Lu, S.; Iyengar, A.J.; Konstantinov, I.E.; Wheaton, G.R.; Ramsay, J.M.; Grigg, L.E.; Millar, J.; et al. Predictors of survival after single-ventricle palliation: The impact of right ventricular dominance. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2012, 59, 1178–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bartram, U.; Grünenfelder, J.; Richard Van Praagh, M. Causes of death after the modified Norwood procedure: A study of 122 postmortem cases. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 1997, 64, 1795–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Migliavacca, F.; Dubini, G.; Pennati, G.; Pietrabissa, R.; Fumero, R.; Hsia, T.Y.; de Leval, M.R. Computational model of the fluid dynamics in systemic-to-pulmonary shunts. J. Biomech. 2000, 33, 549–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, M.H.; Sato, M.; Ueda, Y. Three-dimensional simulation of the Blalock-Taussig shunt using computational fluid dynamics. Surg. Today 2001, 31, 688–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Migliavacca, F.; Pennati, G.; Di Martino, E.; Dubini, G.; Pietrabissa, R. Pressure drops in a distensible model of end-to-side anastomosis in systemic-to-pulmonary shunts. Comput. Methods Biomech. Biomed. Eng. 2002, 5, 243–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waniewski, J.; Kurowska, W.; Mizerski, J.K.; Trykozko, A.; Nowiński, K.; Brzezińska-Rajszys, G.; Kościesza, A. The effects of graft geometry on the patency of a systemic-to-pulmonary shunt: A computational fluid dynamics study. Artif. Organs 2005, 29, 642–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bove, E.L.; Migliavacca, F.; de Leval, M.R.; Balossino, R.; Pennati, G.; Lloyd, T.R.; Khambadkone, S.; Hsia, T.Y.; Dubini, G. Use of mathematic modeling to compare and predict hemodynamic effects of the modified Blalock–Taussig and right ventricle–pulmonary artery shunts for hypoplastic left heart syndrome. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2008, 136, 312–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Esmaily-Moghadam, M.; Murtuza, B.; Hsia, T.Y.; Marsden, A. Simulations reveal adverse hemodynamics in patients with multiple systemic to pulmonary shunts. J. Biomech. Eng. 2015, 137, 031001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moghadam, M.E.; Migliavacca, F.; Vignon-Clementel, I.E.; Hsia, T.Y.; Marsden, A.L. Optimization of shunt placement for the Norwood surgery using multi-domain modeling. J. Biomech. Eng. 2012, 134, 051002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Migliavacca, F.; Pennati, G.; Dubini, G.; Fumero, R.; Pietrabissa, R.; Urcelay, G.; Bove, E.L.; Hsia, T.Y.; de Leval, M.R. Modeling of the Norwood circulation: Effects of shunt size, vascular resistances, and heart rate. Am. J. Physiol.-Heart Circ. Physiol. 2001, 280, H2076–H2086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Carlo, D.; Williams, W.G.; Freedom, R.M.; Trusler, G.A.; Rowe, R.D. The role of cava-pulmonary (Glenn) anastomosis in the palliative treatment of congenital heart disease. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 1982, 83, 437–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopf, G.S.; Laks, H.; Stansel, H.C.; Hellenbrand, W.E.; Kleinman, C.S.; Talner, N.S. Thirty-year follow-up of superior vena cava-pulmonary artery (Glenn) shunts. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 1990, 100, 662–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warrier, G.; Dharan, B.S.; Koshy, S.; Kumar, S.; Krishnanaik, S.; Rao, S.G. Bidirectional Glenn operation in infancy. Indian J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2004, 20, 159–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaquiss, R.D.; Ghanayem, N.S.; Hoffman, G.M.; Fedderly, R.T.; Cava, J.R.; Mussatto, K.A.; Tweddell, J.S. Early cavopulmonary anastomosis in very young infants after the Norwood procedure: Impact on oxygenation, resource utilization, and mortality. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2004, 127, 982–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Petrucci, O.; Khoury, P.R.; Manning, P.B.; Eghtesady, P. Outcomes of the bidirectional Glenn procedure in patients less than 3 months of age. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2010, 139, 562–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Caspi, J.; Pettitt, T.W.; Mulder, T.; Stopa, A. Development of the pulmonary arteries after the Norwood procedure: Comparison between Blalock-Taussig shunt and right ventricular–pulmonary artery conduit. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2008, 86, 1299–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griselli, M.; McGuirk, S.P.; Ofoe, V.; Stümper, O.; Wright, J.G.; de Giovanni, J.V.; Barron, D.J.; Brawn, W.J. Fate of pulmonary arteries following Norwood procedure. Eur. J. Cardio-Thorac. Surg. 2006, 30, 930–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Esmaily-Moghadam, M.; Hsia, T.Y.; Marsden, A.L.; Modeling of Congenital Hearts Alliance (MOCHA) Investigators. The assisted bidirectional Glenn: A novel surgical approach for first-stage single-ventricle heart palliation. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2015, 149, 699–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shang, J.K.; Esmaily, M.; Verma, A.; Reinhartz, O.; Figliola, R.S.; Hsia, T.Y.; Feinstein, J.A.; Marsden, A.L. Patient-specific multiscale modeling of the assisted bidirectional Glenn. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2019, 107, 1232–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, A.; Esmaily, M.; Shang, J.; Figliola, R.; Feinstein, J.A.; Hsia, T.Y.; Marsden, A.L. Optimization of the assisted bidirectional Glenn procedure for first stage single ventricle repair. World J. Pediatr. Congenit. Heart Surg. 2018, 9, 157–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Esmaily-Moghadam, M.; Conover, T.A.; Hsia, T.Y.; Marsden, A.L.; Figliola, R.S. In vitro assessment of the assisted bidirectional Glenn procedure for stage one single ventricle repair. Cardiovasc. Eng. Technol. 2015, 6, 256–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleeter, C.M.; Geraci, G.; Schiavazzi, D.E.; Kahn, A.M.; Marsden, A.L. Multilevel and multifidelity uncertainty quantification for cardiovascular hemodynamics. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2020, 365, 113030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jia, D.; Peroni, M.; Khalapyan, T.; Esmaily, M. An Efficient Assisted Bidirectional Glenn Design With Lowered Superior Vena Cava Pressure for Stage-One Single Ventricle Patients. J. Biomech. Eng. 2021, 143, 071008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeCampli, W.M. The steam locomotive makes a comeback: A new solution to staged single-ventricle palliation? J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2015, 149, 706–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morgan, C.D.; Wolf, M.S.; Le, T.M.; Shannon, C.N.; Wellons, J.C.; Mettler, B.A. Cerebral ventriculomegaly after the bidirectional Glenn (BDG) shunt: A single-institution retrospective analysis. Child’s Nerv. Syst. 2015, 31, 2131–2134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heinemann, M.; Breuer, J.; Steger, V.; Steil, E.; Sieverding, L.; Ziemer, G. Incidence and impact of systemic venous collateral development after Glenn and Fontan procedures. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2001, 49, 172–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pasta, S.; Gentile, G.; Raffa, G.M.; Scardulla, F.; Bellavia, D.; Luca, A.; Pilato, M.; Scardulla, C. Three-dimensional parametric modeling of bicuspid aortopathy and comparison with computational flow predictions. Artif. Organs 2017, 41, E92–E102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scardulla, F.; Pasta, S.; D’Acquisto, L.; Sciacca, S.; Agnese, V.; Vergara, C.; Quarteroni, A.; Clemenza, F.; Bellavia, D.; Pilato, M. Shear stress alterations in the celiac trunk of patients with a continuous-flow left ventricular assist device as shown by in-silico and in-vitro flow analyses. J. Heart Lung Transplant. 2017, 36, 906–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ficial, B.; Finnemore, A.E.; Cox, D.J.; Broadhouse, K.M.; Price, A.N.; Durighel, G.; Ekitzidou, G.; Hajnal, J.V.; Edwards, A.D.; Groves, A.M. Validation study of the accuracy of echocardiographic measurements of systemic blood flow volume in newborn infants. J. Am. Soc. Echocardiogr. 2013, 26, 1365–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ruano, R.; de Fatima Yukie Maeda, M.; Niigaki, J.I.; Zugaib, M. Pulmonary artery diameters in healthy fetuses from 19 to 40 weeks’ gestation. J. Ultrasound Med. 2007, 26, 309–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Box, F.M.; van der Geest, R.J.; Rutten, M.C.; Reiber, J.H. The influence of flow, vessel diameter, and non-Newtonian blood viscosity on the wall shear stress in a carotid bifurcation model for unsteady flow. Investig. Radiol. 2005, 40, 277–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moghadam, M.E.; Vignon-Clementel, I.E.; Figliola, R.; Marsden, A.L.; Modeling of Congenital Hearts Alliance (MOCHA) Investigators. A modular numerical method for implicit 0D/3D coupling in cardiovascular finite element simulations. J. Comput. Phys. 2013, 244, 63–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsden, A.L.; Esmaily-Moghadam, M. Multiscale modeling of cardiovascular flows for clinical decision support. Appl. Mech. Rev. 2015, 67, 030804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esmaily-Moghadam, M.; Bazilevs, Y.; Marsden, A.L. A bi-partitioned iterative algorithm for solving linear systems arising from incompressible flow problems. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2015, 286, 40–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esmaily-Moghadam, M.; Bazilevs, Y.; Marsden, A.L. A new preconditioning technique for implicitly coupled multidomain simulations with applications to hemodynamics. Comput. Mech. 2013, 52, 1141–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghadam, M.E.; Bazilevs, Y.; Hsia, T.Y.; Vignon-Clementel, I.E.; Marsden, A.L. A comparison of outlet boundary treatments for prevention of backflow divergence with relevance to blood flow simulations. Comput. Mech. 2011, 48, 277–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, A.N.; Hughes, T.J. Streamline upwind/Petrov-Galerkin formulations for convection dominated flows with particular emphasis on the incompressible Navier-Stokes equations. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 1982, 32, 199–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazilevs, Y.; Calo, V.; Cottrell, J.; Hughes, T.; Reali, A.; Scovazzi, G. Variational multiscale residual-based turbulence modeling for large eddy simulation of incompressible flows. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2007, 197, 173–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esmaily-Moghadam, M.; Bazilevs, Y.; Marsden, A. Impact of data distribution on the parallel performance of iterative linear solvers with emphasis on CFD of incompressible flows. Comput. Mech. 2015, 55, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckmann, D.M.; Bowers, S.; Stecker, M.; Cheung, A.T. Hematocrit, volume expander, temperature, and shear rate effects on blood viscosity. Anesth. Analg. 2000, 91, 539–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The Mathworks, Inc. MATLAB Version 9.11.0.1751886 (R2021b); The Mathworks, Inc.: Natick, MA, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Lakshminrusimha, S.; Swartz, D.D.; Gugino, S.F.; Ma, C.X.; Wynn, K.A.; Ryan, R.M.; Russell, J.A.; Steinhorn, R.H. Oxygen concentration and pulmonary hemodynamics in newborn lambs with pulmonary hypertension. Pediatr. Res. 2009, 66, 539–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mazza, E.; Taichman, D.B. Chapter 1—Functions and control of the pulmonary circulation. In Pulmonary Vascular Disease; Mandel, J., Taichman, D., Eds.; W.B. Saunders: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2006; pp. 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, G.O. The History of the Darcy-Weisbach Equation for Pipe Flow Resistance. In Environmental and Water Resources History; American Society of Civil Engineers: Reston, VA, USA, 2002; pp. 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]














Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jia, D.; Esmaily, M. Characterization of the Ejector Pump Performance for the Assisted Bidirectional Glenn Procedure. Fluids 2022, 7, 31. https://doi.org/10.3390/fluids7010031
Jia D, Esmaily M. Characterization of the Ejector Pump Performance for the Assisted Bidirectional Glenn Procedure. Fluids. 2022; 7(1):31. https://doi.org/10.3390/fluids7010031
Chicago/Turabian StyleJia, Dongjie, and Mahdi Esmaily. 2022. "Characterization of the Ejector Pump Performance for the Assisted Bidirectional Glenn Procedure" Fluids 7, no. 1: 31. https://doi.org/10.3390/fluids7010031
APA StyleJia, D., & Esmaily, M. (2022). Characterization of the Ejector Pump Performance for the Assisted Bidirectional Glenn Procedure. Fluids, 7(1), 31. https://doi.org/10.3390/fluids7010031