Highly Selective Detection of Hydrogen Sulfide by Simple Cu-CNTs Nanocomposites
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. CNTs Synthesis and Functionalization
2.2. Metal Deposition
- (1)
- Physical method—electron beam evaporation (EBE): the sample is placed in the vacuum (10−2 Torr) chamber of the Angstrom Engineering Equipment and very thin (5 nm) pure Cu (99.99%) was deposited on its surface using the e-beam evaporation method. The thickness of the deposited Cu layer was controlled by a special sensor placed in the chamber.
- (2)
- Chemical method—electrochemical deposition: 4 g of CuSO4 salt was dissolved in 16 mL of distilled water and added to electrolyte. A graphite or copper electrode was used for the cathode, and a structure consisting of a network of closely spaced MWCNTs on the substrate was used for the anode. When the required voltage was applied to the electrodes, the current generated between the electrodes carried the Cu2+ ions onto the MWCNTs. This process resulted in the deposition of Cu atoms on MWCNTs. The process was repeated a number of different times and the optimal condition was chosen for the deposition of a very thin metal layer.
2.3. Scanning Electron Microscopy
2.4. Raman Spectroscopy
2.5. Gas Sensing Test
3. Results
3.1. Material Characterization
3.2. H2S Sensing Characteristics
4. Discussion
H2S Sensing Mechanism
5. Conclusions
- -
- The functionalization of CNTs with oxygen-containing groups increases their sensitivity to environmental effects.
- -
- The morphological analyses carried out by SEM have revealed that there are noticeable changes in the morphology of the f-MWCNTs/Cu obtained by both physical and chemical methods.
- -
- The nanocomposites prepared by both the physical and chemical methods have good sensing properties for H2S gas detection.
- -
- The sensor structure of f-MWCNTs/Cu demonstrated high sensitivity to H2S gas at room temperature.
- -
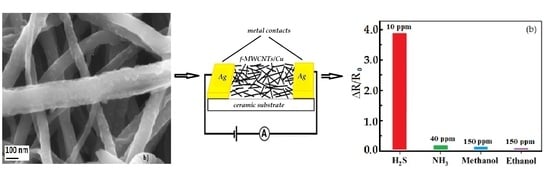
- It was established that the sensor element based on f-MWCNTs/Cu obtained by the chemical method is more highly sensitive to H2S gas than to methanol, ethanol, and ammonia.
- -
- The tests carried out to study the selectivity of the developed new sensors to other gases and vapors, including ammonia, ethanol, methanol and several organic solvents have demonstrated their lower sensitivity to the mentioned gases compared to H2S (physically prepared: 5 times lower; chemically prepared: 10 times lower), with the exception of their insignificant response to ammonia.
- -
- The f-MWCNTs/Cu prepared by the chemical method demonstrates about 5 times (~400%) higher sensitivity to H2S gas at room temperature in comparison with the same structure prepared by physical deposition method.
- -
- It is possible to reduce the recovery time of the f-MWCNTs/Cu structure by heating it up to 50 °C after the H2S gas sensing process.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Khalilova, H.K.; Mammadov, V.A. The assessment of anthropogenic impact on heavy metal pollution of soils and sediments in urban areas of oil industrial region of Azerbaijan. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2016, 1, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kan, H.; Chen, R.; Tong, S. Ambient air pollution, climate change, and population health in China. Environ. Int. 2012, 42, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manucci, P.M.; Franchini, M. Health effects of ambient air pollution in developing countries. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalilova, H.K. The problems of the negative environmental impact of chemical pollutants and possible ways of their prevention. Chem. Probl. 2019, 4, 500–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazardous Substance Fact Sheet. Available online: https://nj.gov/health/eoh/rtkweb/documents/fs/1017.pdf (accessed on 15 February 2023).
- Delaware Health and Social Services—Division of Public Health. (2013, September, Revised). Frequently Asked Questions: Hydrogen Sulfide [PDF]. Available online: https://dhss.delaware.gov/dhss/dph/files/hydsulffaq.pdf (accessed on 15 February 2023).
- Romero-Guzman, L.; Reyes-Guttierrez, L.R.; Romero-Guzman, E.T.; Savedra-Labastida, E. Carbon nanotube filters for removal of air pollutants from mobile sources. JMMCE 2018, 6, 105–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cinke, M.; Li, J.; Charles, W.; Bauschlicher, J.; Ricca, A.; Meyyappan, M. CO2 Adsorption in Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes. Chem. Phys. Let. 2003, 376, 761–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, M.; Koel, A.; Rang, T.; Mehadi, Z. Simulations of Benzene and Hydrogen-Sulfide Gas Detector Based on Single-Walled Carbon Nanotube over Intrinsic 4H-SiC Substrate. Micromachines 2020, 11, 453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, G.; Najaf, Z.; Mehmood, A.; Bilal, S.; Shah, A.; Mian, S.; Ali, G. An Overview of the Recent Progress in the Synthesis and Applications of Carbon Nanotubes. C J. Carbon Res. 2019, 5, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xin, F.; Li, L. Decoration of carbon nanotubes with silver nanoparticles for advanced CNT/polymer nanocomposites. Compos. Part A 2011, 42, 961–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgakilas, V.; Gournis, D.; Tzitzios, V.; Pasquato, L.; Guldi, D.M.; Prato, M. Decorating carbon nanotubes with metal or semiconductor nanoparticles. J. Mat. Chem. 2007, 17, 2679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.D.; Zhang, W.H. Carbon Nanotubes as Active Components for Gas Sensors. J. Sens. 2009, 2009, 160698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zanolli, Z.; Leghrib, R.; Felten, A.; Pireaux, J.-J.; Llobet, E.; Charlier, J.-C. Gas Sensing with Au-Decorated Carbon Nanotubes. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 4592–4599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, G.; Sun, Y.; Sun, J.; Chen, Q. Mechanical properties of carbon nanotube–copper nanocomposites. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2008, 18, 035013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, G.; Ocola, L.E.; Chen, J. Room-Temperature Gas Sensing Based on Electron Transfer between Discrete Tin Oxide Nanocrystals and Multiwalled Carbon Nanotubes. Adv. Mater. 2009, 21, 2487–2491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashutosh, S.T.; Ram, P.; Sanjay, A.R.; Koti, V. An overview of processing and properties of Cu/CNT nanocomposites. Mater. Today Proc. 2017, 4, 3872–3881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, J.F.; Rajule, N.; Mun, S.D. Novel Characterizations of Mechanical Properties for a Copper/Single-Walled Carbon Nanotube Nanocomposite Synthesized by Laser Surface Implanting. C J. Carbon Res. 2020, 6, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, Q.; Chai, G.; Li, B. Exploration Study of Multifunctional Metallic Nanocomposite Utilizing Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes for Micro/Nano Devices. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part N J. Nanoeng. Nanosyst. 2005, 219, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shewalea, P.S.; Patil, V.B.; Shinc, S.W.; Kimc, J.H.; Uplane, M.D. H2S gas sensing properties of nanocrystalline Cu-doped ZnO thin films prepared by advanced spray pyrolysis. Sens. Actuators 2013, 186, 226–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donarelli, M.; Prezioso, S.; Perrozzi, F.; Giancaterini, L.; Cantalini, C.; Treossi, E.; Palermo, V.; Santucci, S.; Ottaviano, L. Graphene oxide for gas detection under standard humidity conditions. 2D Materials 2015, 2, 0350182D. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, R.J.; Franklin, N.R.; Kong, J.; Cao, J.; Tombler, T.W.; Zhang, Y.; Dai, H. Molecular photodesorption from single-walled carbon nanotubes. Appl. Phys. Let. 2001, 79, 2258–2260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, G.; Wu, J.; Qi, X.; Wan, X.; Liu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Xu, L. Molecularly imprinted polypyrrole film-coated poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene):polystyrene sulfonate-functionalized black phosphorene for the selective and robust detection of norfloxacin. Mater. Today Chem. 2022, 26, 101043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balouria, V.; Ramgir, N.S.; Singh, A.; Debnath, A.; Mahajan, A.; Bedi, R.; Aswal, D.; Gupta, S. Gupta Enhanced H2S sensing characteristics of Au modified Fe2O3 thin films. Sens. Actuators B 2015, 219, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girija, K.G.; Somasundaram, K.; Topkar, A.; Vatsa, R.K. Highly selective H2S gas sensor based on Cu-doped ZnO nanocrystalline films deposited by RF magnetron sputtering of powder target. J. Alloys Compd. 2016, 684, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Cao, J.; Kong, F.; Xia, H.; Zhang, J.; Wu, S. Low-temperature H2S sensors based on Ag-doped α-Fe2O3 nanoparticles. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2008, 131, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Yin, L.; Zhang, L.; Xiang, D.; Gao, R. Metal Oxide Gas Sensors: Sensitivity and Influencing Factors. Sensors 2010, 10, 2088–2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wetchakuna, K.; Samerjai, T.; Tamaekonga, N.; Liewhirana, C.; Siriwonga, C.; Kruefua, V.; Wisitsoraat, A.; Tuantranont, A.; Phanichphant, S. Semiconducting metal oxides as sensors for environmentally hazardous gases. Sens. Actuators 2011, 160, 580–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, C.; Attolini, G.; Bosi, M.; Frigeri, C.; Frigeri, P.; Gombia, E.; Lazzarini, L.; Rossi, F.; Seravalli, L.; Trevisi, G.; et al. Detection of Nitroaromatic Explosives in Air by Amino-Functionalized Carbon Nanotubes. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadova, S.; Musayeva, N.; Trevisi, G. Carbon nanotubes decorated with nickel nanoparticles for ammonia detection. In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference MTP-Modern Trends in Physics, Baku, Azerbaijan, 15–17 December 2021; pp. 7–13. [Google Scholar]
- Bang, J.H.; Mirzaei, A.; Choi, M.S.; Han, S.; Lee, H.Y.; Kim, S.S.; Kim, H.W. Decoration of multi-walled carbon nanotubes with CuO/Cu2O nanoparticles for selective sensing of H2S gas. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021, 344, 130176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, B.; Chen, P.; Hong, Q.; Lin, J.; Tan, K.L. Growth of Pd, Pt, Ag and Au nanoparticles on carbon nanotubes. J. Mat. Chem. 2001, 11, 2378–2381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horastani, Z.K.; Hashemifar, S.J.; Sayedi, S.M.; Sheikhi, M.H. First-principles study of H2 adsorption on the pristine and oxidized (8,0) carbon nanotube. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2013, 38, 13680–13686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musayeva, N.; Orujov, T.; Hasanov, R.; Sultanov, C.; Ferrari, C.; Frigeri, C.; Trevisi, G.; Beretta, S.; Bosi, M.; Verucchi, R.; et al. Baldini. Growth and functionalization of carbon nanotubes for nitroaromatic explosive detection. Mater. Today Proc. 2020, 20, 46–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullayeva, S.; Musayeva, N.; Hasanov, R.F. Characterization of high quality carbon nanotubes synthesized via Aerosol –CVD. J. Adv. Phys. 2015, 11, 3229–3240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Menezes, B.R.C.; Ferreira, F.V.; Silva, B.C.; Simonetti EA, N.; Bastos, T.M.; Cividanes, L.S.; Thim, G.P. Effects of octadecylamine functionalization of carbon nanotubes on dispersion, polarity, and mechanical properties of CNT/HDPE nanocomposites. J. Mat. Sci. 2018, 53, 14311–14327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setaro, A. Advanced Carbon Nanotubes Functionalization. J. Phys. Condens. Matter. 2017, 29, 423003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, Y.S.; Kim, Y.T.; Lee, K. Low Temperature Volatile-Organic-Compound (VOC) Sensor Based on Tungsten Oxide Nanorods. Technical. In Proceedings of the 2005 NSTI Nanotechnology Conference and Trade Show, Anaheim, CA, USA, 22 June 2005; Volume 3, pp. 169–172. [Google Scholar]
- Asad, M.; Sheikhi, M.H.; Pourfath, M.; Moradi, M. High sensitive and selective flexible H2S gas sensors based on Cu nanoparticle decorated SWCNTs. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 210, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, S.J.; Lin, Z.D. Ammonia gas sensors with Au-decorated carbon nanotubes. Microsyst. Technol. 2018, 24, 4207–4210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]











Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Musayeva, N.; Khalilova, H.; Izzatov, B.; Trevisi, G.; Ahmadova, S.; Alizada, M. Highly Selective Detection of Hydrogen Sulfide by Simple Cu-CNTs Nanocomposites. C 2023, 9, 25. https://doi.org/10.3390/c9010025
Musayeva N, Khalilova H, Izzatov B, Trevisi G, Ahmadova S, Alizada M. Highly Selective Detection of Hydrogen Sulfide by Simple Cu-CNTs Nanocomposites. C. 2023; 9(1):25. https://doi.org/10.3390/c9010025
Chicago/Turabian StyleMusayeva, Nahida, Hadiya Khalilova, Bakhtiyar Izzatov, Giovanna Trevisi, Shahla Ahmadova, and Muhammad Alizada. 2023. "Highly Selective Detection of Hydrogen Sulfide by Simple Cu-CNTs Nanocomposites" C 9, no. 1: 25. https://doi.org/10.3390/c9010025
APA StyleMusayeva, N., Khalilova, H., Izzatov, B., Trevisi, G., Ahmadova, S., & Alizada, M. (2023). Highly Selective Detection of Hydrogen Sulfide by Simple Cu-CNTs Nanocomposites. C, 9(1), 25. https://doi.org/10.3390/c9010025