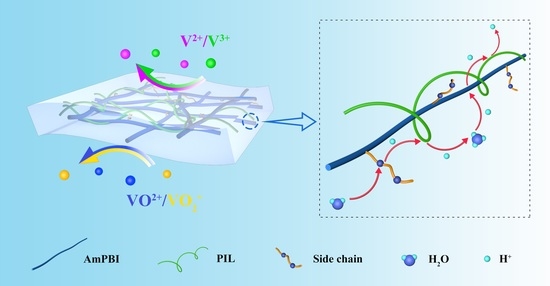
Low Vanadium Permeability Membranes Based on Flexible Hydrophilic Side Chain Grafted Polybenzimidazole/Polymeric Ionic Liquid for VRFBs
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of the AmPBI and Ionic Liquids
2.3. Synthesis of the AmPBI-MOE
2.4. Preparation of AmPBI-MOE-PIL-X Composite Membranes
2.5. Characterization and Measurements
2.5.1. Structural Characterizations
2.5.2. Scanning Electron Microscopy
2.5.3. Water Uptake, Swelling Ratio, and Ion Exchange Capacity
2.5.4. Vanadium Permeability
2.5.5. Area Resistance
2.5.6. Chemical Stability
2.5.7. VRFB Cell Performance
2.5.8. Proton Conductivity
2.5.9. Ion selectivity
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Synthesis and Characterization
3.2. Microscopic Morphology
3.3. Physicochemical Properties of Membranes
3.4. Vanadium Permeability, Ion Selectivity, and Area Resistance
3.5. Mechanical Properties
3.6. VRFB Performance
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jung, J.; Won, J.; Hwang, S.S. Highly selective composite membranes using ladder-like structured polysilsesquioxane for a non-aqueous redox flow battery. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 595, 117520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, M.; Dai, Q.; Li, F.; Li, T.; Hou, G.; Zhang, H.; Li, X. Membranes with Well-Defined Selective Layer Regulated by Controlled Solvent Diffusion for High Power Density Flow Battery. Adv. Energy Mater. 2020, 10, 2001382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Li, M.; Yuan, Z.; Li, X.; Zhang, H.; Vankelecom, I.F.J. Advanced Charged Sponge-Like Membrane with Ultrahigh Stability and Selectivity for Vanadium Flow Batteries. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2016, 26, 210–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, K.; Li, Y.; Xing, Y.; Wang, L.; Li, N. A novel polybenzimidazole membrane containing bulky naphthalene group for vanadium flow battery. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 586, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, C.; Liu, J.; Yan, C. A significantly improved membrane for vanadium redox flow battery. J. Power Sources 2010, 195, 4380–4383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, D.; Yu, L.; Liu, L.; Xi, J. Rice Paper Reinforced Sulfonated Poly(ether ether ketone) as Low-Cost Membrane for Vanadium Flow Batteries. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 2437–2444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Long, J.; Liu, J.; Luo, H.; Duan, H.; Zhang, Y.; Li, J.; Qi, X.; Chu, L. A novel porous polyimide mem-brane with ultrahigh chemical stability for application in vanadium redox flow battery. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 428, 131203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escorihuela, J.; Sahuquillo, O.; Garcia-Bernabe, A.; Gimenez, E.; Compan, V. Phosphoric Acid Doped Polybenzimid-azole (PBI)/Zeolitic Imidazolate Framework Composite Membranes with Significantly Enhanced Proton Conductivity under Low Humidity Conditions. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mukhopadhyay, S.; Das, A.; Jana, T.; Das, S.K. Fabricating a MOF Material with Polybenzimidazole into an Efficient Proton Exchange Membrane. ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 2020, 3, 7964–7977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Gao, L.; Di, M.; Jiang, X.; Wu, X.; Yan, X.; Li, X.; He, G. Ion/Molecule-selective transport nanochannels of membranes for redox flow batteries. Energy Storage Mater. 2021, 34, 648–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.; Wu, X.; Yan, X.; Gao, L.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, D.; Li, J.; Wang, Q.; He, G. Polybenzimidazole membranes with nanophase-separated structure induced by non-ionic hydrophilic side chains for vanadium flow batteries. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 3895–3905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aberoumand, S.; Woodfield, P.; Shabani, B.; Dao, D.V. Advances in electrode and electrolyte improvements in vanadium redox flow batteries with a focus on the nanofluidic electrolyte approach. Phys. Rep. 2020, 881, 1–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, J.; You, D.; Li, X. Step-by-Step Modification of Graphite Felt Electrode for Vanadium Redox Flow Battery. J. Electrochem. 2020, 26, 876–884. [Google Scholar]
- Jirabovornwisut, T.; Arpornwichanop, A. A review on the electrolyte imbalance in vanadium redox flow batteries. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2019, 44, 24485–24509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khataee, A.; Nederstedt, H.; Jannasch, P.; Lindström, R.W. Poly(arylene alkylene)s functionalized with perfluorosulfonic acid groups as proton exchange membranes for vanadium redox flow batteries. J. Membr. Sci. 2023, 671, 121390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tempelman, C.H.L.; Jacobs, J.F.; Balzer, R.M.; Degirmenci, V. Membranes for all vanadium redox flow batteries. J. Energy Storage 2020, 32, 101754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Ahn, Y.; Kim, D. Poly(arylene ether ketone) proton exchange membranes grafted with long aliphatic pendant sulfonated groups for vanadium redox flow batteries. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 2261–2270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gubler, L. Membranes and separators for redox flow batteries. Curr. Opin. Electrochem. 2019, 18, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Ling, L.; Xiao, M.; Han, D.; Wang, S.; Meng, Y. Effectively suppressing vanadium permeation in vanadium redox flow battery application with modified Nafion membrane with nacre-like nanoarchitectures. J. Power Sources 2017, 352, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.; Konovalova, A.; Tsoy, E.; Park, G.; Henkensmeier, D.; Kwon, Y. Alkaline naphthoquinone-based redox flow batteries with a crosslinked sulfonated polyphenylsulfone membrane. Int. J. Energy Res. 2022, 46, 12988–13002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Sang, X.; Wang, L.; Zhang, J.; Song, J.; Han, B. Incorporation of metal-organic framework in polymer mem-brane enhances vanadium flow battery performance. Electrochim. Acta 2017, 257, 243–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Zhao, T.; An, L.; Wei, L.; Zhang, C. The use of polybenzimidazole membranes in vanadium redox flow batteries leading to increased coulombic efficiency and cycling performance. Electrochim. Acta 2015, 153, 492–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.; Zhao, L.; Che, X.; Cai, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, H.; Chen, H.; He, H.; Liu, J.; Yang, J. Quaternary ammonium groups grafted polybenzimidazole membranes for vanadium redox flow battery applications. J. Power Sources 2020, 457, 228037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Feng, K.; Ding, L.; Wang, L.; Han, X. Influence of solvent on ion conductivity of polybenzimidazole proton exchange membranes for vanadium redox flow batteries. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2020, 28, 1701–1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.; Kwon, B.W.; Jung, M.; Serhiichuk, D.; Henkensmeier, D.; Kwon, Y. Iron-vanadium redox flow batteries with polybenzimidazole membranes: High coulomb efficiency and low capacity loss. J. Power Sources 2019, 439, 227079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noh, C.; Serhiichuk, D.; Malikah, N.; Kwon, Y.; Henkensmeier, D. Optimizing the performance of meta-polybenzimidazole membranes in vanadium redox flow batteries by adding an alkaline pre-swelling step. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 407, 126574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Pingitore, A.T.; Xie, W.; Yang, Z.; Perry, M.L.; Benicewicz, B.C. Sulfonated PBI Gel Membranes for Redox Flow Batteries. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2019, 166, A1449–A1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, J.-K.; Kim, T.-H.; Yoon, S.J.; Lee, J.Y.; Lee, J.-C.; Hong, Y.T. Highly proton conductive, dense polybenzimid-azole membranes with low permeability to vanadium and enhanced H2SO4 absorption capability for use in vanadium redox flow batteries. J. Mater. Chem. A 2016, 4, 14342–14355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noh, C.; Jung, M.; Henkensmeier, D.; Nam, S.W.; Kwon, Y. Vanadium Redox Flow Batteries Using me-ta-Polybenzimidazole-Based Membranes of Different Thicknesses. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 36799–36809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.; Yan, X.; Zhang, D.; Wu, X.; Luo, Y.; He, G. A H3PO4 preswelling strategy to enhance the proton conductivity of a H2SO4-doped polybenzimidazole membrane for vanadium flow batteries. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 23479–23488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, B.; Wu, X.; Guo, Y.; Yang, M.; Du, R.; Chen, W.; Yan, X.; Cui, F.; He, G. Anionic conductive group tunable amphoteric polybenzimidazole ion conductive membrane for vanadium redox flow battery. J. Membr. Sci. 2023, 670, 121351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Xiong, P.; Xiao, S.; Zhu, Y.; Peng, S.; He, G. Ion conductive mechanisms and redox flow battery applications of polybenzimidazole-based membranes. Energy Storage Mater. 2022, 45, 595–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do, X.H.; Abbas, S.; Ikhsan, M.M.; Choi, S.; Ha, H.Y.; Azizi, K.; Hjuler, H.A.; Henkensmeier, D. Membrane Assemblies with Soft Protective Layers: Dense and Gel-Type Polybenzimidazole Membranes and Their Use in Vanadium Redox Flow Batteries. Small 2022, 18, 2206284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, L.; Song, X.; Wang, L.; Zhao, Z. Enhancing proton conductivity of polybenzimidazole membranes by introducing sulfonate for vanadium redox flow batteries applications. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 578, 126–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Gao, L.; Hu, L.; Di, M.; Yan, X.; An, B.; He, G. The synergistic effect of protonated imidaz-ole-hydroxyl-quaternary ammonium on improving performances of anion exchange membrane assembled flow batteries. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 603, 118011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Ding, L.; Wang, L.; He, M.; Han, X. Polybenzimidazole membranes embedded with ionic liquids for use in high proton selectivity vanadium redox flow batteries. Electrochim. Acta 2019, 295, 1034–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.; Long, J.; Xuan, S.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, J.; Zhang, H. Branched sulfonated polyimide membrane with ionic cross-linking for vanadium redox flow battery application. J. Power Sources 2019, 438, 226993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, Y.; Kim, D. Ultra-low vanadium ion permeable electrolyte membrane for vanadium redox flow battery by pore filling of PTFE substrate. Energy Storage Mater. 2020, 31, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, D.; Wang, S.; Ma, W.; Wang, D.; Liu, G.; Liu, F.; Cui, Y.; Wang, X.; Yong, Z.; Wang, Z. A low vanadium permeability sulfonated polybenzimidazole membrane with a metal-organic framework for vanadium redox flow batteries. Electrochim. Acta 2022, 405, 139795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, T.; David, O.; Gendel, Y.; Wessling, M. Porous poly(benzimidazole) membrane for all vanadium redox flow battery. J. Power Sources 2016, 312, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Dong, Z.; Di, M.; Hu, L.; Zhang, C.; Pan, Y.; Zhang, N.; Jiang, X.; Wu, X.; Wang, J.; et al. A highly proton-conductive and vanadium-rejected long-side-chain sulfonated polybenzimidazole membrane for redox flow battery. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 596, 117616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Wang, S.; Tian, X.; Li, J.; Liu, F.; Wang, X.; Chen, H.; Mao, T.; Liu, G. Ethyl phosphoric acid grafted amino-modified polybenzimidazole with improved long-term stability for high-temperature proton exchange membrane applications. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2020, 45, 3176–3185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Wang, S.; Wang, D.; Liu, G.; Cui, Y.; Liang, D.; Wang, X.; Yong, Z.; Wang, Z. Multifunctional polymeric ionic liquids cross-linked polybenzimidazole membrane with excellent long-term stability for high temperature-proton exchange membranes fuel cells. J. Power Sources 2021, 494, 229732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Wang, S.; Li, J.; Liu, F.; Tian, X.; Wang, X.; Mao, T.; Xu, J.; Wang, Z. Novel cross-linked membranes based on polybenzimidazole and polymeric ionic liquid with improved proton conductivity for HT-PEMFC applications. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2019, 95, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Wang, S.; Wang, D.; Liu, G.; Liu, F.; Liang, D.; Wang, X.; Yong, Z.; Wang, Z. HT-PEMs based on carbazole grafted polybenzimidazole with high proton conductivity and excellent tolerance of phosphoric acid. J. Membr. Sci. 2021, 637, 119610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.; Yan, X.; Wu, X.; Zhang, D.; Luo, Y.; Su, L.; He, G. Thin skinned asymmetric polybenzimidazole membranes with readily tunable morphologies for high-performance vanadium flow batteries. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 1852–1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sizov, V.E.; Kondratenko, M.S.; Gallyamov, M.O.; Stevenson, K.J. Advanced porous polybenzimidazole membranes for vanadium redox batteries synthesized via a supercritical phase-inversion method. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2018, 137, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, X.; Zhao, H.; Ren, X.; Zhang, D.; Wei, H.; Liu, J.; Zhang, X.; Yang, J. Porous polybenzimidazole membranes with high ion selectivity for the vanadium redox flow battery. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 611, 118359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, T.; Tang, W.; Jin, Y.; Che, X.; Liu, J.; Yang, J. Ether-Free Poly(p-terphenyl-co-acetylpyridine) Membranes with Different Thicknesses for Vanadium Redox Flow Batteries. ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 2022, 5, 11713–11722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Samples | Thickness (µm) | Water Uptake (%) | Swelling Ratio (%) | IEC (mmol g−1) | Proton Conductivity (mS cm−1) | VO2+ Permeability (10−9 cm2 min−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AmPBI | 35 | 24.3 ± 0.5 | 13.2 ± 1.0 | 0.42 | 7.9 | 3.25 |
| AmPBI-MOE | 37 | 26.5 ± 0.3 | 14.9 ± 0.7 | 0.41 | 8.1 | 0.85 |
| AmPBI-MOE-PIL-5 | 36 | 27.7 ± 0.6 | 14.0 ± 0.4 | 0.47 | 8.5 | 0.88 |
| AmPBI-MOE-PIL-10 | 30 | 24.1 ± 0.4 | 14.1 ± 0.3 | 0.48 | 8.8 | 0.93 |
| AmPBI-MOE-PIL-20 | 34 | 15.4 ± 0.5 | 13.8 ± 0.7 | 0.39 | 9.4 | 0.98 |
| AmPBI-MOE-PIL-30 | 27 | 12.9 ± 0.5 | 14.4 ± 0.8 | 0.37 | 9.5 | 0.99 |
| Nafion117 | 180 | 22.7 ± 0.5 | 43.8 ± 1.2 | 1.10 | 49.2 | 60.67 |
| Membrane | Thickness (µm) | AR (Ω cm2) | Current Density (mA·cm−2) | CE (%) | VE (%) | EE (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AmPBI-MOE-PIL-5 | 36 | 0.70 | 60 | 94.3 | 87.9 | 82.9 |
| PBI-100 [46] | 0.70 | 60 | ~100 | ~82 | ~82 | |
| 50-SPBI [15] | 39 | ~2.7 | 60 | ~77 | ||
| PBI [22] | - | - | 60 | 99 | 74 | 74 |
| ScABPBI [47] | 65 | 0.34 | 60 | 97 | 85 | ~82 |
| 72P–24S PBI [30] | 76 | 0.43 | 60 | 97 | 85 | ~84 |
| mPBI [29] | 35 | 2.03 | 80 | ~98 | ~69 | ~68 |
| PBI-40-SiO2 [48] | - | ~0.28 | 80 | 99.5 | 77 | 76.8 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, X.; Wang, S.; Liang, D.; Cui, Y.; Wang, X.; Yong, Z.; Liu, F.; Wang, Z. Low Vanadium Permeability Membranes Based on Flexible Hydrophilic Side Chain Grafted Polybenzimidazole/Polymeric Ionic Liquid for VRFBs. Batteries 2023, 9, 141. https://doi.org/10.3390/batteries9020141
Wang X, Wang S, Liang D, Cui Y, Wang X, Yong Z, Liu F, Wang Z. Low Vanadium Permeability Membranes Based on Flexible Hydrophilic Side Chain Grafted Polybenzimidazole/Polymeric Ionic Liquid for VRFBs. Batteries. 2023; 9(2):141. https://doi.org/10.3390/batteries9020141
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Xiaorui, Shuang Wang, Dan Liang, Yinghe Cui, Xiaodong Wang, Zhipeng Yong, Fengxiang Liu, and Zhe Wang. 2023. "Low Vanadium Permeability Membranes Based on Flexible Hydrophilic Side Chain Grafted Polybenzimidazole/Polymeric Ionic Liquid for VRFBs" Batteries 9, no. 2: 141. https://doi.org/10.3390/batteries9020141
APA StyleWang, X., Wang, S., Liang, D., Cui, Y., Wang, X., Yong, Z., Liu, F., & Wang, Z. (2023). Low Vanadium Permeability Membranes Based on Flexible Hydrophilic Side Chain Grafted Polybenzimidazole/Polymeric Ionic Liquid for VRFBs. Batteries, 9(2), 141. https://doi.org/10.3390/batteries9020141