Biomedical Applications of Blow-Spun Coatings, Mats, and Scaffolds—A Mini-Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
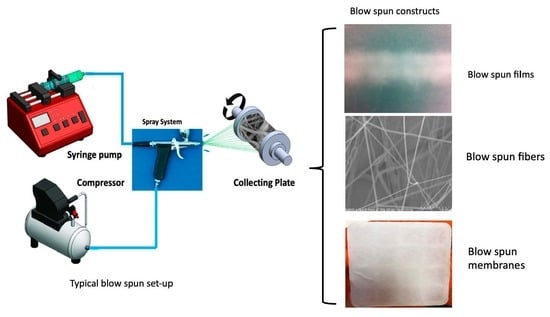
2. Solution Blow Spinning
3. Blow-Spun Nanocomposites
3.1. Nanoparticles
3.2. Nanoclay
4. Blow-Spun Applications
4.1. Antimicrobial
4.2. Drug Delivery
4.3. Textiles Used in Medicine
Trauma
4.4. Tissue Regeneration
4.4.1. Skin Tissue Regeneration
4.4.2. Bone Tissue Regeneration
5. Commercial Applications
6. Limitations of Blow Spinning
7. Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Luk, B.T.; Zhang, L. Current advances in polymer-based nanotheranostics for cancer treatment and diagnosis. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 21859–21873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nayl, A.A.; Abd-Elhamid, A.I.; Awwad, N.S.; Abdelgawad, M.A.; Wu, J.; Mo, X.; Gomha, S.M.; Aly, A.A.; Bräse, S. Recent progress and potential biomedical applications of electrospun nanofibers in regeneration of tissues and organs. Polymers 2022, 14, 1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cosson, S.; Otte, E.A.; Hezaveh, H.; Cooper-White, J.J. Cooper-White, Concise Review: Tailoring bioengineered scaffolds for stem cell applications in tissue engineering and regenerative medicine. Stem Cells Trans. Med. 2015, 4, 156–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakraborty, C.; Pal, S.; Doss, G.P.C.; Wen, Z.-H.; Lin, C.-S. Nanoparticles as ‘smart’ pharmaceutical delivery. Front. Biosci. 2013, 18, 1030–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayanan, K.B.; Park, G.T.; Han, S.S. Electrospun poly (vinyl alcohol)/reduced graphene oxide nanofibrous scaffolds for skin tissue engineering. Colloids Surfaces B Biointerfaces 2020, 191, 110994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, Y.; Stuelten, C.H.; Kilts, T.; Wadhwa, S.; Iozzo, R.V.; Robey, P.G.; Chen, X.-D.; Young, M.F. Extracellular matrix proteoglycans control the fate of bone marrow stromal cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 30481–30489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pham, Q.P.; Kasper, F.K.; Baggett, L.S.; Raphael, R.M.; Jansen, J.A.; Mikos, A.G. The influence of an in vitro generated bone-like extracellular matrix on osteoblastic gene expression of marrow stromal cells. Biomaterials 2008, 29, 2729–2739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozario, T.; DeSimone, D.W. The extracellular matrix in development and morphogenesis: A dynamic view. Dev. Biol. 2010, 341, 126–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Geckil, H.; Xu, F.; Zhang, X.; Moon, S.; Demirci, U. Engineering hydrogels as extracellular matrix mimics. Nanomedicine 2010, 5, 469–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kyburz, K.A.; Anseth, K.S. Synthetic mimics of the extracellular matrix: How simple is complex enough? Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2015, 43, 489–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yao, T.; Chen, H.; Samal, P.; Giselbrecht, S.; Baker, M.B.; Moroni, L. Self-assembly of electrospun nanofibers into gradient honeycomb structures. Mater. Des. 2019, 168, 107614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valdoz, J.C.; Johnson, B.C.; Jacobs, D.J.; Franks, N.A.; Dodson, E.L.; Sanders, C.; Cribbs, C.G.; Van Ry, P.M. The ECM: To scaffold, or not to scaffold, that Is the question. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joyce, K.; Fabra, G.T.; Bozkurt, Y.; Pandit, A. Bioactive potential of natural biomaterials: Identification, retention and assessment of biological properties. Sig. Transduct. Target Ther. 2021, 6, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Yuan, Q.; Yin, T.; You, J.; Gu, Z.; Xiong, S.; Hu, Y. Self-assembly of collagen-based biomaterials: Preparation, characterizations and biomedical applications. J. Mater. Chem. B 2018, 6, 2650–2676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolas, J.; Magli, S.; Rabbachin, L.; Sampaolesi, S.; Nicotra, F.; Russo, L. 3D extracellular matrix mimics: Fundamental concepts and role of materials chemistry to influence stem cell fate. Biomacromolecules 2020, 21, 1968–1994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvatore, L.; Gallo, N.; Natali, M.L.; Terzi, A.; Sannino, A.; Madaghiele, M. Mimicking the hierarchical organization of natural collagen: Toward the development of ideal scaffolding material for tissue regeneration. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2021, 9, 644595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moysidou, C.-M.; Barberio, C.; Owens, R.M. Advances in engineering human tissue models. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2012, 8, 620962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahedi, P.; Rezaeian, I.; Ranaei-Siadat, S.-O.; Jafari, S.H.; Supaphol, P. A review on wound dressings with an emphasis on electrospun nanofibrous polymeric bandages. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2010, 21, 77–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Gu, H.; Mi, H.; Rao, C.; Fu, J.; Turng, L.-S. Fabrication of scaffolds in tissue engineering: A review. Front. Mech. Eng. 2018, 13, 107–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jun, I.; Han, H.-S.; Edwards, J.R.; Jeon, H. Electrospun fibrous scaffolds for tissue engineering: Viewpoints on architecture and fabrication. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Akbari, M.; Tamayol, A.; Bagherifard, S.; Serex, L.; Mostafalu, P.; Faramarzi, N.; Mohammadi, M.H.; Khademhosseini, A. Textile technologies and tissue engineering: A path toward organ weaving. Adv. Healthcare Mater. 2016, 5, 751–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vasita, R.; Katti, D.S. Nanofibers and their applications in tissue engineering. Int. J. Nanomed. 2006, 1, 2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helfman, T.; Ovington, L.; Falanga, V. Occlusive dressings and wound healing. Clin. Dermatol. 1994, 12, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sripriya, R.; Kumar, M.S.; Ahmed, M.R.; Sehgal, P.K. Collagen bilayer dressing with ciprofloxacin, an effective system for infected wound healing. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2007, 18, 335–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demina, T.S.; Bolbasov, E.N.; Peshkova, M.A.; Efremov, Y.M.; Bikmulina, P.Y.; Birdibekova, A.V.; Popyrina, T.N.; Kosheleva, N.V.; Tverdokhlebov, S.I.; Timashev, P.S.; et al. Electrospinning vs. electro-assisted solution blow spinning for fabrication of fibrous scaffolds for tissue engineering. Polymers 2022, 14, 5254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, X.; Chen, H.-L.; Guo, C. Polymeric nanofibers for drug delivery applications: A recent review. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2022, 33, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teo, W.E.; Ramakrishna, S. A review on electrospinning design and nanofibre assemblies. Nanotechnology 2006, 17, R89–R106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Midha, V.K.; Dakuri, A. Spun bonding technology and fabric properties: A review. J. Text. Eng. Fash. Technol. 2017, 1, 126–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, W.; Chen, M.; Qu, T.; Li, J.; Man, Y. Three-dimensional electrospun nanofibrous scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B Appl. Biomater. 2020, 108, 1311–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anjum, S.; Rahman, F.; Pandey, P.; Arya, D.K.; Alam, M.; Rajinikanth, P.S.; Ao, Q. Electrospun biomimetic nanofibrous scaffolds: A promising prospect for pone tissue engineering and regenerative medicine. Intern. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 9206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behrens, A.M.; Casey, B.J.; Sikorski, M.J.; Wu, K.L.; Tutak, W.; Sandler, A.D.; Kofinas, P. In situ deposition of PLGA nanofibers via solution blow spinning. ACS Macro Lett. 2014, 3, 249–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Lim, C.T.; Ramakrishna, S.; Huang, Z.-M. Recent development of polymer nanofibers for biomedical and biotechnological applications. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2005, 16, 933–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsiao, H.-Y.; Huang, C.-M.; Liu, Y.-Y.; Kuo, Y.-C.; Chen, H. Effect of air blowing on the morphology and nanofiber properties of blowing-assisted electrospun polycarbonates. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2011, 116, 2658–2667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daristotle, J.L.; Behrens, A.M.; Sandler, A.D.; Kofi, P. A review of the fundamental principles and applications of solution blow spinning. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 34951–34963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ho, D.H.; Cheon, S.; Hong, P.; Park, J.H.; Suk, J.W.; Kim, D.H.; Han, J.T.; Cho, J.H. Multifunctional smart textronics with blow-spun nonwoven fabrics. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1900025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, M.A.; Oliveira, J.E.; Medeiros, E.S.; Glenn, G.M.; Mattoso, L.H.C. Controlled release of linalool using nanofibrous membranes of poly(lactic acid) obtained by electrospinning and solution blow spinning: A comparative study. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2015, 15, 5628–5636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, J.E.; Medeiros, E.S.; Cardozo, L.; Voll, F.; Madurera, E.H.; Mattoso, L.H.C.; Assis, O.B.G. Development of poly (lactic acid) nanostructured membranes for the controlled delivery of progesterone to livestock animals. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2013, 33, 844–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasan, S.; Chhatre, S.S.; Mabry, J.M.; Cohen, R.E.; McKinley, G.H. Solution spraying of poly(methyl methacrylate) blends to fabricate microtextured, superoleophobic surfaces. Polymer 2011, 52, 3209–3218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Souza, M.A.; Sakamoto, K.Y.; Mattoso, L.H.C. Release of the diclofenac sodium by nanofibers of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate- co -3-hydroxyvalerate) obtained from electrospinning and solution blow spinning. J. Nanomater. 2014, 2014, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lorente, M.A.; Corral, A.; González-Benito, J. PCL/collagen blends prepared by solution blow spinning as potential materials for skin regeneration. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2021, 138, 50493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tutak, W.; Sarkar, S.; Lin-Gibson, S.; Farooque, T.M.; Jyotsnendu, G.; Wang, D.; Kohn, J.; Bolikal, D.; Simon, C.G. The support of bone marrow stromal cell differentiation by airbrushed nanofiber scaffolds. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 2389–2398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Benito, J.; Teno, J.; González-Gaitano, G.; Xu, S.; Chiang, M. PVDF/TiO2 nanocomposites prepared by solution blow spinning: Surface properties and their relationship with S. mutans adhesion. Polym. Test. 2016, 59, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dias, Y.J.; Gimenes, T.C.; Torres, S.A.P.V.; Malmonge, J.A.; Gualdi, A.J.; de Paula, F.R. PVDF/Ni fibers synthesis by solution blow spinning technique. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2018, 29, 514–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Costa, R.G.F.; Brichi, G.S.; Ribeiro, C.; Mattoso, L.H.C. Nanocomposite fibers of poly(lactic acid)/titanium dioxide prepared by solution blow spinning. Polym. Bull. 2016, 73, 2973–2985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasireddi, R.; Kruse, J.; Vakili, M.; Kulkarni, S.; Keller, T.F.; Monteiro, D.C.F.; Trebbin, M. Solution blow spinning of polymer/nanocomposite micro-/nanofibers with tunable diameters and morphologies using a gas dynamic virtual nozzle. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 14297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tsinas, Z.; Tao, R.; Forster, A.L. Solution blow spinning of polymeric nano-composite fibers for personal protective equipment. J. Vis. Exp. 2021, 169, e62283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katouah, H.A.; El-Sayed, R.; El-Metwaly, N.M. Solution blowing spinning technology and plasma-assisted oxidation-reduction process toward green development of electrically conductive cellulose nanofibers. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2021, 28, 56363–56375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhullar, S.K.; Rana, D.; Ozsel, B.K.; Orhan, M.; Jun, M.B.G.; Buttar, H.S.; Ostrovidov, S.; Ramalingam, M. Development of silver-based bactericidal composite nanofibers by airbrushing. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2018, 18, 2951–2955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saba, N.; Jawaid, M.; Asim, M. Recent advances in nanoclay/natural fibers hybrid composites. In Nanoclay Reinforced Polymer Composites; Engineering Materials; Jawaid, M., Qaiss, A., Bouhfid, R., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Zhang, J.; Su, Y.; Wang, H.; Wang, X.-X.; Huang, L.-P.; Yu, M.; Ramakrishna, S.; Long, Y.-Z. Recent progress and challenges in solution blow spinning. Mater. Horiz. 2021, 8, 426–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, I.J.; Yu, J.; Yang, Y.; Zbi, J.; Hu, Z. Intercalated montmorillonite reinforced polyimide separator prepared by solution blow spinning for lithium-ion batteries. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2020, 59, 12879–12888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joussein, E.; Petit, S.; Churchman, J.; Theng, B.; Righi, D.; Delvaux, B. Halloysite clay minerals—A review. Clay Min. 2005, 40, 383–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syamaladevi, R.M.; Tang, J.; Villa-Rojas, R.; Sablani, S.; Carter, B.; Campbell, G. Therapeutic applications of halloysite. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massaro, M.; Cavallaro, G.; Colletti, C.G.; Lazzara, G.; Milioto, S.; Noto, R.; Riela, S. Chemical modification of halloysite nanotubes for controlled loading and release. J. Mater. Chem. B 2018, 6, 3415–3433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullayev, E.; Lvov, Y. Halloysite clay nanotubes as a ceramic ‘skeleton’ for functional biopolymer composites with sustained drug release. J. Mater. Chem. B 2013, 1, 2894–2903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavallaro, G.; Lazzara, G.; Milioto, S.; Parisi, F.; Evtugyn, V.G.; Rozhina, E.; Fakhrullin, R.F. Nanohydrogel formation within the halloysite lumen for triggered and sustained release. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 8265–8273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.; Abdullayev, E.; Hollister, A.; Mills, D.; Lvov, Y.M. Clay nanotube/poly (methyl methacrylate) bone cement composites with a sustained antibiotic release. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2012, 297, 645–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Humayun, A.; Mills, D.K. Surface modification of 3D printed PLA/zinc/halloysite composite scaffolds with antibacterial and osteogenic capabilities. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 3971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leporatti, S. Halloysite clay nanotubes as nano-bazookas for drug delivery. Polym. Int. 2017, 66, 1111–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atif, R.; Khaliq, J.; Combrinck, M.; Hassanin, A.H.; Shehata, N.; Elnabawy, E.; Shyha, I. Hassasin Solution blow spinning of polyvinylidene fluoride-based fibers for energy harvesting applications: A review. Polymers 2020, 12, 1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Huang, H. Incorporation of halloysite nanotubes into PVDF matrix: Nucleation of electroactive phase accompany with significant reinforcement and dimensional stability improvement. Compos. Part A 2014, 66, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. The Burden of Health Care−Associated Infection Worldwide. 2010. Available online: http://www.who.int/gpsc/country_work/burden_hcai/en/ (accessed on 8 March 2021).
- Cao, Y.; Shen, C.; Yang, Z.; Cai, Z.; Deng, Z.; Wu, D. Polycaprolactone/polyvinyl pyrrolidone nanofibers developed by solution blow spinning for encapsulation of chlorogenic acid. Food Qual. Saf. 2022, 6, fyac014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Sanz, M.; Bilbao-Sáinz, C.C.; Du, W.-X.; Chiou, B.-S.; Williams, T.G.; Wood, D.F.; Iman, S.H.; Orts, W.J.; Lopez-Rubio, A.; Lagaron, J.M. Antimicrobial poly(lactic acid)-based nanofibres developed by solution blow spinning. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2015, 15, 616–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McFarland, A.W., Jr.; Elumalai, A.; Miller, C.C.; Humayun, A.; Mills, D.K. Effectiveness and applications of a metal-coated HNT/polylactic acid antimicrobial filtration system. Polymers 2022, 14, 1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelgawad, A.M.; Hudson, S.M.; Rojas, O.J. Antimicrobial wound dressing nanofiber mats from multicomponent (chitosan/silver-NPs/polyvinyl alcohol) systems. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 100, 166–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langer, R. Polymeric delivery systems for controlled drug release. Chem. Eng. Commun. 1980, 6, 1–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonan, R.F.; Bonan, P.R.F.; Batista, A.U.D.; Sampaio, F.C.; Albuquerque, A.J.R.; Moraes, M.C.B.; Mattoso, L.H.C.; Glenn, G.M.; Medeiros, E.S.; Oliveira, J.E. In vitro antimicrobial activity of solution blow spun poly (lactic acid)/polyvinylpyrrolidone nanofibers loaded with Copaiba (Copaifera sp.) oil. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2015, 48, 372–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, I.M.F.; Rocha, I.M.; Pires, E.G.; Muniz, I.d.A.F.; Maciel, P.P.; de Lima, J.M.; Santos, I.M.G.D.; Batista, R.B.D.; de Medeiros, E.L.G.; de Medeiros, E.S.; et al. Effectiveness of core-shell nanofibers incorporating Amphotericin B by solution blow spinning against Leishmania and Candida species. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 8, 571821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleem, H.; Zaidi, S.J. Sustainable use of nanomaterials in textiles and their environmental impact. Materials 2020, 13, 5134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, S.; Hui, P.C.-L.; Kan, C.-W. Thermoresponsive hydrogels and their biomedical applications: Special insight into their applications in textile based transdermal therapy. Polymers 2015, 10, 480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kramer, A.; Guggenbichler, P.; Heldt, P.; Jünger, M.; Ladwig, A.; Thierbach, H.; Weber, U.; Daeschlein, G. Hygienic relevance and risk assessment of antimicrobial-impregnated textiles. Curr. Probl. Dermatol. 2006, 33, 78–109. [Google Scholar]
- Dadol, G.C.; Kilic, A.; Tijing, L.D.; Lim, K.J.A.; Cabatingan, L.K.; Tan, N.P.B.; Stojanovska, E.; Polat, Y. Solution blow spinning (SBS) and SBS-spun nanofibers: Materials, methods, and applications. Mater. Today Commun. 2020, 25, 101656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butruk-Raszeja, B.A.; Kuźmińska, A.; Wojasiński, M.; Piotrowska, Z. Physicochemical and mechanical properties of blow spun nanofibrous prostheses modified with acrylic acid and REDV peptide. Coatings 2020, 10, 1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S. Developing UV-protective textiles based on electrospun zinc oxide nanocomposite fibers. Fibers Polym. 2009, 10, 295–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, T.; Li, X.; Shi, Q.; Wang, H.; Huang, Q.; Fukuda, T. Microfluidic spun alginate hydrogel microfibers and their application in tissue engineering. Gels 2018, 4, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paschoalina, R.T.; Traldia, B.; Aydinc, G.; Oliveirad, G.J.; Rutten, S.; Mattoso, L.H.C.; Zenke, M.; Sechi, A. Solution blow spinning fibres: New immunologically inert substrates for the analysis of cell adhesion and motility. Acta Biomater. 2017, 51, 161–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Borojeni, I.A.; Gajewski, G.; Riahi, R.A. Application of electrospun nonwoven fibers in air filters. Fibers 2022, 10, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalid, B.; Bai, X.; Wei, H.; Huang, Y.; Wu, H.; Cui, Y. Direct blow-spinning of nanofibers on a window screen for highly efficient PM removal. Nano Lett. 2017, 17, 1140–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Wang, K.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, C.; Wang, B. Application of textile technology in tissue engineering: A review. Acta Biomater. 2021, 128, 60–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaishya, R.; Agarwal, A.K.; Tiwari, M.; Vaish, A.; Vijay, V.; Nigam, Y. Medical textiles in orthopedics: An overview. J. Clin. Orthop. Trauma 2018, 9 (Suppl. S1), S26–S33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamal, Z.; Yadav, N.; Rani, S.P. Medical Textiles: State of Art. Inter. J. Home Sci. 2018, 4, 275–280. [Google Scholar]
- Claro, P.; Cunha, I.; Paschoalin, R.; Gaspar, D.; Miranda, K.; Oliveira, O.N., Jr.; Martins, R.; Pereira, L.; Marconcini, J.M.; Fortunato, E.; et al. Ionic conductive cellulose cats by solution blow spinning as substrate and a dielectric interstate layer for flexible electronics. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 26237–26246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, R.; Xu, X.; Zhuang, X.; Cheng, B. Solution blowing of chitosan/PVA hydrogel nanofiber mats. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 101, 1116–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Cheng, F.; Gao, J.; Wang, L. Antibacterial wound dressing from chitosan/polyethylene oxide nanofibers mats embedded with silver nanoparticles. J. Biomater. Appl. 2014, 29, 1086–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- dos Santos, D.M.; Correa, D.S.; Medeiros, E.S.; Oliveira, J.E.; Mattoso, L.H.C. Advances in functional polymer nanofibers: From spinning fabrication techniques to recent biomedical applications. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 45673–45701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rampichová, M.; Buzgo, M.; Míčková, A.; Vocetková, K.; Sovková, V.; Lukášová, V.; Filová, E.; Rustichelli, F.; Amler, E. Platelet-functionalized three-dimensional poly-ε-caprolactone fibrous scaffold prepared using centrifugal spinning for delivery of growth factors. Int. J. Nanomed. 2017, 12, 347–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kern, N.G.; Behrens, A.M.; Srinivasan, P.; Rossi, C.T.; Daristotle, J.L.; Kofinas, P.; Sandler, A.D. Solution blow spun polymer: A novel preclinical surgical sealant for bowel anastomoses. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2017, 52, 1308–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Zhang, J.; Cheng, N.; Liu, Z.; Wu, Y.-B.; Zhou, Q.-Q.; Li, C.-Y.; Yu, M.; Ramakrishna, S.; Wang, R.; et al. A non-surgical suturing strategy for rapid cardiac hemostasis. Nano Res. 2022, 16, 810–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habibovic, P. Strategic directions in osteoinduction and biomimetics. Tissue Eng. Part A 2017, 23, 1295–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pape, H.C.; Evans, A.; Kobbe, P. Autologous bone graft: Properties and techniques. J. Orthop. Trauma 2010, 24 (Suppl. S1), S36–S40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, F.; Jokisch, S.; Bargel, H.; Scheibel, T. Centrifugal electrospinning enables the production of meshes of ultrathin polymer fibers. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2020, 2, 4360–4367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, S.; Ma, J.-X.; Xu, L.; Gu, X.-S.; Ma, X.-L. Biodegradable materials for bone defect repair. Mil. Med. Res. 2020, 7, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popkov, A.V.; Kulbakin, D.E.; Popkov, D.A.; Gorbach, E.N.; Kononovich, N.A.; Danilenko, N.V.; Stankevich, K.S.; Choynzonov, E.L.; Zheravin, A.A.; Khlusov, I.A.; et al. Solution blow spinning of PLLA/hydroxyapatite composite scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. Biomed. Mater. 2021, 16, 0550052021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahalingam, S.; Bayram, C.; Gultekinoglu, M.; Ulubayram, K.; Homer-Vanniasinkam, S.; Edirisinghe, M. Co-axial gyro-spinning of PCL/PVA/HA core-sheath fibrous scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. Macromol. Biosci. 2021, 21, 2100177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyer, C.; Karnik, S.; Ambrose, J.; Mills, D.K. Airbrushed polymer films and nanofibers embedded with clay nanotubes for tissue engineering and drug delivery applications. Tissue Eng. Part A 2015, 21 (Suppl. S1), S333. [Google Scholar]
- Biomedical Textiles Market by Fiber Type. Available online: https://www.marketsandmarkets.com/Market-Reports/biomedical-textile-market-231997196.html (accessed on 12 May 2022).
- Biomedical Textiles Market Insights by Latest Trends, Future Growth, Top Companies, Revenue Forecast, Demand Forecast to 2022. Available online: https://www.marketwatch.com/press-release/biomedical-textiles-market-insights-by-latest-trends-future-growth-top-companies-revenue-forecast-demand-forecast-to-2022-2021-09-17?tesla=y (accessed on 15 June 2022).
- Nanofibers Market Size Is Projected to Reach USD 3.35 Billion by 2030, Growing at a CAGR of 18%: Straits Research. Available online: https://www.globenewswire.com/news-release/2022/06/27/2469823/0/en/Nanofibers-Market-Size-is-projected-to-reach-USD-3-35-Billion-by-2030-growing-at-a-CAGR-of-18-Straits-Research.html (accessed on 31 May 2022).
- Global Nanofibers Market–Industry Trends and Forecast to 2029. Available online: https://www.databridgemarketresearch.com/reports/global-nanofibers-market (accessed on 9 June 2022).
- Avossa, J.; Herwig, G.; Toncelli, C.; Itel, F.; Rossi, R.M. Electrospinning based on benign solvents: Current definitions, implications and strategies. Green Chem. 2022, 24, 2347–2375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parize, D.D.D.S.; de Oliveira, J.E.; Foschini, M.M.; Marconcini, J.M.; Mattoso, L.H.C. Poly(lactic acid) fibers obtained by solution blow spinning: Effect of a greener solvent on the fiber diameter. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2016, 133, 43379. [Google Scholar]
- Dias, A.M.G.C.; Cena, C.; Lutz-Bueno, V.; Mezzenga, R.; Marques, A.; Ferreira, I.; Roque, A.C.A. Solvent modulation in peptide sub-microfibers obtained by solution blow spinning. Front. Chem. 2022, 10, 1054347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magaz, A.; Roberts, A.D.; Faraji, S.; Nascimento, T.R.L.; Medeiros, E.S.; Zhang, W.; Greenhalgh, R.D.; Mautner, A.; Li, X.; Blaker, J.J. Porous, aligned, and biomimetic fibers of regenerated silk fibroin produced by solution blow spinning. Biomacromolecules 2018, 19, 4542–4553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Corduas, F.; Lamprou, D.A.; Mancuso, E. Next-generation surgical meshes for drug delivery and tissue engineering applications: Materials, design and emerging manufacturing technologies. Bio-Des. Manuf. 2021, 4, 278–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, M.; Gómez-Gil, V.; Pérez-Köhler, B.; Pascual, G.; Bellón, J. Polymer hernia repair materials: Adapting to patient needs and surgical techniques. Materials 2021, 14, 2790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turrentine, F.; Denlinger, C.; Simpson, V.B.; Garwood, R.A.; Guerlain, S.; Agrawal, A.; Friel, C.M.; LaPar, D.J.; Stukenborg, G.J.; Jones, R.S. Morbidity, mortality, cost, and survival estimates of gastrointestinal anastomotic leaks. J. Am. Coll. Surg. 2015, 220, 195–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabbi, M.; Hagens, E.R.C.; Henegouwen, M.I.V.B.; Gisbertz, S.S. Anastomotic leakage after esophagectomy for esophageal cancer: Definitions, diagnostics, and treatment. Dis. Esophagus 2021, 34, doaa039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.K.R.; Hassan, M.N. Solution Blow Spinning (SBS): A promising spinning system for submicron/nanofibre production. Text. Leather Rev. 2021, 4, 181–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giuntoli, G.; Muzio, G.; Actis, C.; Ganora, A.; Calzone, S.; Bruno, M.; Ciardelli, G.; Carmagnola, I.; Tonda-Turo, C. In-vitro characterization of a hernia mesh featuring a nanostructured coating. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2021, 8, 589223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Gao, G.; Wang, P.; Ye, J.; Huang, Y.; Wu, H. The effect of PLGA-collagen I patch on inguinal hernia. Farmacia 2012, 66, 839–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noor Sanbhal, N.; Saitaer, X.; Peerzada, M.; Habboush, A.; Wang, F.; Wang, L. One-step surface functionalized hydrophilic polypropylene meshes for hernia repair using bio-inspired polydopamine. Fibers 2019, 7, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Daristotle, J.L.; Zaki, S.T.; Lau, L.W.; Torres, L.; Zografos, A.; Srinivasan, P.; Ayyub, O.B.; Sandler, A.D.; Kofinas, P. Improving the adhesion, flexibility, and hemostatic efficacy of a sprayable polymer blend surgical sealant by incorporating silica particles. Acta Biomater. 2019, 90, 205–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mobaraki, M.; Liu, M.; Masoud, A.-R.; Mills, D.K. Biomedical Applications of Blow-Spun Coatings, Mats, and Scaffolds—A Mini-Review. J. Compos. Sci. 2023, 7, 86. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs7020086
Mobaraki M, Liu M, Masoud A-R, Mills DK. Biomedical Applications of Blow-Spun Coatings, Mats, and Scaffolds—A Mini-Review. Journal of Composites Science. 2023; 7(2):86. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs7020086
Chicago/Turabian StyleMobaraki, Mohammadmahdi, Meichen Liu, Abdul-Razak Masoud, and David K. Mills. 2023. "Biomedical Applications of Blow-Spun Coatings, Mats, and Scaffolds—A Mini-Review" Journal of Composites Science 7, no. 2: 86. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs7020086
APA StyleMobaraki, M., Liu, M., Masoud, A. -R., & Mills, D. K. (2023). Biomedical Applications of Blow-Spun Coatings, Mats, and Scaffolds—A Mini-Review. Journal of Composites Science, 7(2), 86. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs7020086