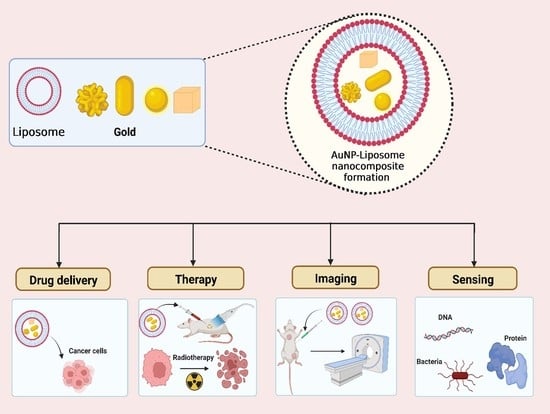
The Golden Liposomes: Preparation and Biomedical Applications of Gold-Liposome Nanocomposites
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- Discuss the outstanding properties of AuNP (the guest) and liposomes (the host) to justify the preparation of AuNP-liposome nanocomposite;
- Discuss and illustrate various chemistries to prepare AuNP-liposome nanocomposites and analytical tools to confirm and describe the prepared nanocomposites;
- Highlight and discuss the reported biomedical applications of AuNP-liposome nanocomposites and future directions.
2. Gold Nanoparticles: The Guest
3. Liposome Nanoparticles: The Host
4. AuNP-Liposome Nanocomposites: Rationale of Preparation
5. AuNP-liposome Nanocomposites: Architectures, Chemistry of Preparation and Analytical Characterization
5.1. Unveiling the Architectures of AuNP-Liposome Nanocomposites
5.2. Chemistries to Prepare AuNP-Liposome Nanocomposite
| AuNP Characteristics | Nanocomposite Preparation Chemistry | Nanocomposite Characteristics | Outcomes and Remarks | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
| [139] |
|
|
|
| [140] |
|
|
|
| [159] |
|
|
|
| [160] |
|
|
|
| [161] |
|
|
|
| [162] |
|
|
|
| [163] |
|
|
|
| [122] |
|
|
|
| [164] |
|
|
|
| [165] |
5.3. Analytical Characterization of AuNP-Liposome Nanocomposites
6. Biomedical Applications of the AuNP-Liposome Nanocomposites
6.1. Imaging
6.2. Sensing
6.3. Phototherapy and Laser-Triggered Drug Delivery
7. Biodistribution and Pharmacokinetics of AuNP-Liposome Nanocomposites

8. Outlook and Remarks
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bayda, S.; Adeel, M.; Tuccinardi, T.; Cordani, M.; Rizzolio, F. The History of Nanoscience and Nanotechnology: From Chemical–Physical Applications to Nanomedicine. Molecules 2020, 25, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dreaden, E.C.; Alkilany, A.M.; Huang, X.; Murphy, C.J.; El-Sayed, M.A. The golden age: Gold nanoparticles for biomedicine. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 2740–2779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mosleh-Shirazi, S.; Abbasi, M.; Moaddeli, M.R.; Vaez, A.; Shafiee, M.; Kasaee, S.R.; Amani, A.M.; Hatam, S. Nanotechnology Advances in the Detection and Treatment of Cancer: An Overview. Nanotheranostics 2022, 6, 400–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salvador-Morales, C.; Grodzinski, P. Nanotechnology Tools Enabling Biological Discovery. ACS Nano 2022, 16, 5062–5084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandra, S.; Hu, T. From Prevention to Therapy: A Roadmap of Nanotechnologies to Stay Ahead of Future Pandemics. ACS Nano 2022, 16, 9985–9993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patra, J.K.; Das, G.; Fraceto, L.F.; Campos, E.V.R.; del Pilar Rodriguez-Torres, M.; Acosta-Torres, L.S.; Diaz-Torres, L.A.; Grillo, R.; Swamy, M.K.; Sharma, S.; et al. Nano based drug delivery systems: Recent developments and future prospects. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2018, 16, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dutta, D.; Das, B.M. Scope of green nanotechnology towards amalgamation of green chemistry for cleaner environment: A review on synthesis and applications of green nanoparticles. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2020, 15, 100418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seaberg, J.; Montazerian, H.; Hossen, M.N.; Bhattacharya, R.; Khademhosseini, A.; Mukherjee, P. Hybrid Nanosystems for Biomedical Applications. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 2099–2142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meesaragandla, B.; Komaragiri, Y.; Schlüter, R.; Otto, O.; Delcea, M. The impact of cell culture media on the interaction of biopolymer-functionalized gold nanoparticles with cells: Mechanical and toxicological properties. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 16643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.; Wang, Y.; Song, Z.; Feng, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, D.; Lin, F. The Basic Properties of Gold Nanoparticles and their Applications in Tumor Diagnosis and Treatment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goddard, Z.R.; Marín, M.J.; Russell, D.A.; Searcey, M. Active targeting of gold nanoparticles as cancer therapeutics. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2020, 49, 8774–8789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokammel, M.A.; Islam, M.J.; Hasanuzzaman, M.; Hashmi, S. Nanoscale Materials for Self-Cleaning and Antibacterial Applications; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; El-Sayed, M.A. Gold nanoparticles: Optical properties and implementations in cancer diagnosis and photothermal therapy. J. Adv. Res. 2010, 1, 13–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alkilany, A.M.; Lohse, S.E.; Murphy, C.J. The Gold Standard: Gold Nanoparticle Libraries To Understand the Nano–Bio Interface. Accounts Chem. Res. 2012, 46, 650–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carnovale, C.; Bryant, G.; Shukla, R.; Bansal, V. Identifying Trends in Gold Nanoparticle Toxicity and Uptake: Size, Shape, Capping Ligand, and Biological Corona. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 242–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stetsenko, M.O.; Rudenko, S.P.; Maksimenko, L.; Serdega, B.K.; Pluchery, O.; Snegir, S.V. Optical Properties of Gold Nanoparticle Assemblies on a Glass Surface. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2017, 12, 348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sulaiman, G.M.; Waheeb, H.M.; Jabir, M.S.; Khazaal, S.H.; Dewir, Y.H.; Naidoo, Y. Hesperidin Loaded on Gold Nanoparticles as a Drug Delivery System for a Successful Biocompatible, Anti-Cancer, Anti-Inflammatory and Phagocytosis Inducer Model. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 9362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.-P.; Ma, B.-Y.; Wei, X.-W.; Qian, Z.-Y. The in vitro and in vivo toxicity of gold nanoparticles. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2017, 28, 691–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Perry, H.L.; Wilton-Ely, J.D.E.T. Strategies for the functionalisation of gold nanorods to reduce toxicity and aid clinical translation. Nanotheranostics 2021, 5, 155–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eustis, S.; El-Sayed, M.A. Why gold nanoparticles are more precious than pretty gold: Noble metal surface plasmon resonance and its enhancement of the radiative and nonradiative properties of nanocrystals of different shapes. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2005, 35, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; O’Connor, R.; Kwizera, E.A. Gold Nanoparticle Based Platforms for Circulating Cancer Marker Detection. Nanotheranostics 2017, 1, 80–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreiuk, B.; Nicolson, F.; Clark, L.M.; Panikkanvalappil, S.R.; Rashidian, M.; Harmsen, S.; Kircher, M.F. Design and synthesis of gold nanostars-based SERS nanotags for bioimaging applications. Nanotheranostics 2022, 6, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grzelczak, M.; Pérez-Juste, J.; Mulvaney, P.; Liz-Marzán, L.M. Shape control in gold nanoparticle synthesis. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2008, 37, 1783–1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmati, S.; Doherty, W.; Babadi, A.A.; Mansor, M.A.C.; Julkapli, N.; Hessel, V.; Ostrikov, K. Gold–Carbon Nanocomposites for Environmental Contaminant Sensing. Micromachines 2021, 12, 719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, P.; Xue, R.; Wei, Y.; Lei, X.; Ai, J.; Wang, T.; Shi, Z.; Wang, X.; Wang, Q.; Soliman, F.M.; et al. Gold nanoparticles/tetraaminophenyl porphyrin functionalized multiwalled carbon nanotubes nanocomposites modified glassy carbon electrode for the simultaneous determination of p-acetaminophen and p-aminophenol. Arab. J. Chem. 2020, 13, 1040–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, G.H.; Kim, K.; Nam, H.; Shin, K.; Choi, W.; Shin, J.H.; Lim, G. CNT-Au nanocomposite deposition on gold microelectrodes for improved neural recordings. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 252, 152–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.-C.; Sun, D.; Zhang, R.; Lin, W.-F.; Macias-Montero, M.; Patel, J.; Askari, S.; McDonald, C.; Mariotti, D.; Maguire, P. Gold nanoparticle-polymer nanocomposites synthesized by room temperature atmospheric pressure plasma and their potential for fuel cell electrocatalytic application. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 46682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Afzali, M.; Mostafavi, A.; Shamspur, T. Developing a novel sensor based on ionic liquid molecularly imprinted polymer/gold nanoparticles/graphene oxide for the selective determination of an anti-cancer drug imiquimod. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 143, 111620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Si, J.; Yan, L.; Li, M.; Hou, X. Enhanced nonlinear absorption and ultrafast carrier dynamics in graphene/gold nanoparticles nanocomposites. Carbon 2019, 148, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Miao, Z.; Ma, M.; Du, X.; Lin, J.; Han, B.; Takahashi, S.; Anzai, J.-I.; Chen, Q. Dual-function amperometric sensors based on poly(diallydimethylammoniun chloride)-functionalized reduced graphene oxide/manganese dioxide/gold nanoparticles nanocomposite. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 222, 663–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolaños, K.; Kogan, M.J.; Araya, E. Capping gold nanoparticles with albumin to improve their biomedical properties. Int. J. Nanomed. 2019, 14, 6387–6406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, T.; Wang, Y.; Wang, M.; Zheng, L.; Dai, W.; Jiao, C.; Song, Z.; Ma, Y.; Ding, Y.; Zhang, Z.; et al. Impact of Albumin Pre-Coating on Gold Nanoparticles Uptake at Single-Cell Level. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanzhakov, M.; Kudinov, V.; Baskaev, K.; Morozevich, G.; Stepanova, D.; Torkhovskaya, T.; Tereshkina, Y.A.; Korotkevich, E.; Tikhonova, E. Composite phospholipid-gold nanoparticles with targeted fragment for tumor imaging. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 142, 111985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pornpattananangkul, D.; Zhang, L.; Olson, S.; Aryal, S.; Obonyo, M.; Vecchio, K.; Huang, C.-M.; Zhang, L. Bacterial Toxin-Triggered Drug Release from Gold Nanoparticle-Stabilized Liposomes for the Treatment of Bacterial Infection. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 4132–4139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Alkilany, A.M.; Rachid, O.; Alkawareek, M.Y.; Billa, N.; Daou, A.; Murphy, C.J. PLGA-Gold Nanocomposite: Preparation and Biomedical Applications. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkilany, A.M.; Abulateefeh, S.R.; Murphy, C.J. Facile Functionalization of Gold Nanoparticles with PLGA Polymer Brushes and Efficient Encapsulation into PLGA Nanoparticles: Toward Spatially Precise Bioimaging of Polymeric Nanoparticles. Part. Part. Syst. Charact. 2018, 36, 1800414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veeren, A.; Ogunyankin, M.O.; Shin, J.E.; Zasadzinski, J.A. Liposome-Tethered Gold Nanoparticles Triggered by Pulsed NIR Light for Rapid Liposome Contents Release and Endosome Escape. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, G.; Mikhailovsky, A.; Khant, H.A.; Zasadzinski, J.A. Synthesis, Characterization, and Optical Response of Gold Nanoshells Used to Trigger Release from Liposomes. Methods Enzymol. 2009, 464, 279–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kojima, C.; Hirano, Y.; Kono, K. Preparation of Complexes of Liposomes with Gold Nanoparticles. Methods Enzymol. 2009, 464, 131–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, P.P.; Thomas, J.M. Gold in a Metallic Divided State—From Faraday to Present-Day Nanoscience. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 5480–5486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dieringer, J.A.; McFarland, A.M.; Shah, N.C.; Stuart, D.A.; Whitney, A.V.; Yonzon, C.R.; Young, M.A.; Zhang, X.; Duyne, R.P.V. Introductory Lecture: Surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy: New materials, concepts, characterization tools, and applications. Faraday Discuss. 2006, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rastinehad, A.R.; Anastos, H.; Wajswol, E.; Winoker, J.S.; Sfakianos, J.P.; Doppalapudi, S.K.; Carrick, M.R.; Knauer, C.J.; Taouli, B.; Lewis, S.C.; et al. Gold nanoshell-localized photothermal ablation of prostate tumors in a clinical pilot device study. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 18590–18596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Amina, S.J.; Guo, B. A Review on the Synthesis and Functionalization of Gold Nanoparticles as a Drug Delivery Vehicle. Int. J. Nanomed. 2020, 15, 9823–9857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amendola, V.; Polizzi, S.; Meneghetti, M. Laser Ablation Synthesis of Gold Nanoparticles in Organic Solvents. J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 7232–7237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raliya, R.; Saha, D.; Chadha, T.S.; Raman, B.; Biswas, P. Non-invasive aerosol delivery and transport of gold nanoparticles to the brain. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, srep44718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hainfeld, J.F.; O’Connor, M.J.; Lin, P.; Qian, L.; Slatkin, D.N.; Smilowitz, H.M. Infrared-Transparent Gold Nanoparticles Converted by Tumors to Infrared Absorbers Cure Tumors in Mice by Photothermal Therapy. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e88414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hatakeyama, Y.; Onishi, K.; Nishikawa, K. Effects of sputtering conditions on formation of gold nanoparticles in sputter deposition technique. RSC Adv. 2011, 1, 1815–1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hühn, J.; Carrillo-Carrion, C.; Soliman, M.G.; Pfeiffer, C.; Valdeperez, D.; Masood, A.; Chakraborty, I.; Zhu, L.; Gallego, M.; Yue, Z.; et al. Selected Standard Protocols for the Synthesis, Phase Transfer, and Characterization of Inorganic Colloidal Nanoparticles. Chem. Mater. 2016, 29, 399–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, H.; Xiahou, Y.; Zhang, P.; Ding, W.; Wang, D. Revitalizing the Frens Method To Synthesize Uniform, Quasi-Spherical Gold Nanoparticles with Deliberately Regulated Sizes from 2 to 330 nm. Langmuir 2016, 32, 5870–5880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frens, G. Controlled Nucleation for the Regulation of the Particle Size in Monodisperse Gold Suspensions. Nat. Phys. Sci. 1973, 241, 20–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brust, M.; Walker, M.; Bethell, D.; Schiffrin, D.J.; Whyman, R. Synthesis of thiol-derivatised gold nanoparticles in a two-phase Liquid–Liquid system. J. Chem. Soc. Chem. Commun. 1994, 1994, 801–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Iglesias, A.; Winckelmans, N.; Altantzis, T.; Bals, S.; Grzelczak, M.; Liz-Marzán, L.M. High-Yield Seeded Growth of Monodisperse Pentatwinned Gold Nanoparticles through Thermally Induced Seed Twinning. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 139, 107–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikoobakht, B.; El-Sayed, M.A. Preparation and Growth Mechanism of Gold Nanorods (NRs) Using Seed-Mediated Growth Method. Chem. Mater. 2003, 15, 1957–1962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.-H.; Murphy, C.J. Mini Gold Nanorods with Tunable Plasmonic Peaks beyond 1000 nm. Chem. Mater. 2018, 30, 1427–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, X.; Gao, Y.; Chen, J.; Reifsnyder, D.C.; Zheng, C.; Murray, C.B. Seeded Growth of Monodisperse Gold Nanorods Using Bromide-Free Surfactant Mixtures. Nano Lett. 2013, 13, 2163–2171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Xia, Y. Shape-Controlled Synthesis of Gold and Silver Nanoparticles. Science 2002, 298, 2176–2179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, C.; Shuford, K.L.; Chen, M.; Lee, E.J.; Cho, S.O. A Facile Polyol Route to Uniform Gold Octahedra with Tailorable Size and Their Optical Properties. ACS Nano 2008, 2, 1760–1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.X.; Shameli, K.; Miyake, M.; Kuwano, N.; Khairudin, N.B.B.A.; Mohamad, S.E.B.; Yew, Y.P. Green Synthesis of Gold Nanoparticles Using Aqueous Extract of Garcinia mangostana Fruit Peels. J. Nanomater. 2016, 2016, 8489094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ramakrishna, M.; Babu, D.R.; Gengan, R.M.; Chandra, S.; Rao, G.N. Green synthesis of gold nanoparticles using marine algae and evaluation of their catalytic activity. J. Nanostruct. Chem. 2015, 6, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Iranmanesh, S.; Bonjar, G.H.S.; Baghizadeh, A. Study of the biosynthesis of gold nanoparticles by using several saprophytic fungi. SN Appl. Sci. 2020, 2, 1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Guo, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Wang, J.; Gu, N. Biosynthesis of gold nanoparticles using the bacteria Rhodopseudomonas capsulata. Mater. Lett. 2007, 61, 3984–3987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bansal, S.A.; Kumar, V.; Karimi, J.; Singh, A.P.; Kumar, S. Role of gold nanoparticles in advanced biomedical applications. Nanoscale Adv. 2020, 2, 3764–3787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milan, J.; Niemczyk, K.; Kus-Liśkiewicz, M. Treasure on the Earth—Gold Nanoparticles and Their Biomedical Applications. Materials 2022, 15, 3355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chuang, Y.-C.; Lee, H.-L.; Chiou, J.-F.; Lo, L.-W. Recent Advances in Gold Nanomaterials for Photothermal Therapy. J. Nanotheranostics 2022, 3, 117–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Das, N.; Rayavarapu, R.G. Role of Tunable Gold Nanostructures in Cancer Nanotheranostics: Implications on Synthesis, Toxicity, Clinical Applications and Their Associated Opportunities and Challenges. J. Nanotheranostics 2023, 4, 1–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, E. Gold Nanoparticle-Based Plasmonic Biosensors. Biosensors 2023, 13, 411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.-C.; Chen, C.-P.; Wu, T.-H.; Yang, C.-H.; Lin, C.-W.; Chen, C.-Y. Gold Nanoparticle-Based Colorimetric Strategies for Chemical and Biological Sensing Applications. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kumar, D.; Saini, N.; Jain, N.; Sareen, R.; Pandit, V. Gold nanoparticles: An era in bionanotechnology. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2013, 10, 397–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weigel, A.; Sebesta, A.; Kukura, P. Dark Field Microspectroscopy with Single Molecule Fluorescence Sensitivity. ACS Photonics 2014, 1, 848–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boby, N.; Ali, S.A.; Preena, P.; Kaur, G.; Kumar, S.; Chaudhuri, P. Detection of multiple organisms based on the distance-dependent optical properties of gold nanoparticle and dark-field microscopy. Talanta 2018, 188, 325–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Acunto, M. Detection of Intracellular Gold Nanoparticles: An Overview. Materials 2018, 11, 882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- SoRelle, E.D.; Liba, O.; Campbell, J.L.; Dalal, R.; Zavaleta, C.L.; de la Zerda, A. A hyperspectral method to assay the microphysiological fates of nanomaterials in histological samples. Elife 2016, 5, e16352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aldosari, F.M.M. Characterization of Labeled Gold Nanoparticles for Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering. Molecules 2022, 27, 892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Peng, Y.; Duan, X.; Yang, L.; Lan, J.; Wang, F. Homologous Gold Nanoparticles and Nanoclusters Composites with Enhanced Surface Raman Scattering and Metal Fluorescence for Cancer Imaging. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Z.; Yang, P.; Xu, H.; Zheng, H. Surface enhanced fluorescence and Raman scattering by gold nanoparticle dimers and trimers. J. Appl. Phys. 2013, 113, 033102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cao, Y.; Qian, R.-C.; Li, D.-W.; Long, Y.-T. Raman/fluorescence dual-sensing and imaging of intracellular pH distribution. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 17584–17587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iosin, M.; Toderas, F.; Baldeck, P.; Astilean, S. Study of protein–gold nanoparticle conjugates by fluorescence and surface-enhanced Raman scattering. J. Mol. Struct. 2009, 924–926, 196–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venditti, I.; Cartoni, A.; Cerra, S.; Fioravanti, R.; Salamone, T.A.; Sciubba, F.; Tabocchini, M.A.; Dini, V.; Battocchio, C.; Iucci, G.; et al. Hydrophilic Gold Nanoparticles as Anti-PD-L1 Antibody Carriers: Synthesis and Interface Properties. Part. Part. Syst. Charact. 2022, 39, 2100282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sayed, I.H.; Huang, X.; El-Sayed, M.A. Selective laser photo-thermal therapy of epithelial carcinoma using anti-EGFR antibody conjugated gold nanoparticles. Cancer Lett. 2006, 239, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; El-Sayed, I.H.; Qian, W.; El-Sayed, M.A. Cancer Cell Imaging and Photothermal Therapy in the Near-Infrared Region by Using Gold Nanorods. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 2115–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirsch, L.R.; Stafford, R.J.; Bankson, J.A.; Sershen, S.R.; Rivera, B.; Price, R.E.; Hazle, J.D.; Halas, N.J.; West, J.L. Nanoshell-mediated near-infrared thermal therapy of tumors under magnetic resonance guidance. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 13549–13554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rodzik-Czałka, Ł.; Lewandowska-Łańcucka, J.; Gatta, V.; Venditti, I.; Fratoddi, I.; Szuwarzyński, M.; Romek, M.; Nowakowska, M. Nucleobases functionalized quantum dots and gold nanoparticles bioconjugates as a fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET) system—Synthesis, characterization and potential applications. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 514, 479–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Liang, H.; Ma, S.; Wang, D.; Huang, J. Gold nanoparticle based photothermal therapy: Development and application for effective cancer treatment. Sustain. Mater. Technol. 2019, 22, e00109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; Liu, F.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, W.; Hu, J.; Liu, J.; Dai, Z.; Wang, K.; Wei, Y.; Bai, J.; et al. Salt-induced aggregation of gold nanoparticles for photoacoustic imaging and photothermal therapy of cancer. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 4452–4457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, H.S.; Lee, D.Y. Near-Infrared-Responsive Cancer Photothermal and Photodynamic Therapy Using Gold Nanoparticles. Polymers 2018, 10, 961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, M.; Peng, D.; Hao, H.; Hu, J.; Wang, D.; Wang, K.; Liu, J.; Guo, X.; Wei, Y.; Gao, W. Thermally Triggered in Situ Assembly of Gold Nanoparticles for Cancer Multimodal Imaging and Photothermal Therapy. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 10453–10460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.R.K.; Wu, Y.; El-Sayed, M.A. Gold-Nanoparticle-Assisted Plasmonic Photothermal Therapy Advances Toward Clinical Application. J. Phys. Chem. C 2019, 123, 15375–15393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manrique-Bedoya, S.; Abdul-Moqueet, M.; Lopez, P.; Gray, T.; Disiena, M.; Locker, A.; Kwee, S.; Tang, L.; Hood, R.L.; Feng, Y.; et al. Multiphysics Modeling of Plasmonic Photothermal Heating Effects in Gold Nanoparticles and Nanoparticle Arrays. J. Phys. Chem. C 2020, 124, 17172–17182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Wang, D.; Zhang, C.; Liu, H.; Hao, M.; Kan, S.; Liu, D.; Liu, W. The Applications of Gold Nanoparticles in the Diagnosis and Treatment of Gastrointestinal Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2022, 11, 819329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurizi, L.; Forte, J.; Ammendolia, M.G.; Hanieh, P.N.; Conte, A.L.; Relucenti, M.; Donfrancesco, O.; Ricci, C.; Rinaldi, F.; Marianecci, C.; et al. Effect of Ciprofloxacin-Loaded Niosomes on Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus Biofilm Formation. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 2662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musielak, E.; Feliczak-Guzik, A.; Nowak, I. Synthesis and Potential Applications of Lipid Nanoparticles in Medicine. Materials 2022, 15, 682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bangham, A.D.; Hill, M.W.; Miller, N.G.A. Preparation and Use of Liposomes as Models of Biological Membranes. In Methods in Membrane Biology; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1974; pp. 1–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozzuto, G.; Molinari, A. Liposomes as nanomedical devices. Int. J. Nanomed. 2015, 10, 975–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lombardo, D.; Kiselev, M.A. Methods of Liposomes Preparation: Formation and Control Factors of Versatile Nanocarriers for Biomedical and Nanomedicine Application. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šturm, L.; Ulrih, N.P. Basic Methods for Preparation of Liposomes and Studying Their Interactions with Different Compounds, with the Emphasis on Polyphenols. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dua, J.S.; Rana, A.C.; Bhandari, A.K. Liposome: Methods of preparation and applications. Int. J. Pharm. Stud. Res. 2012, 3, 14–20. [Google Scholar]
- William, B.; Noémie, P.; Brigitte, E.; Géraldine, P. Supercritical fluid methods: An alternative to conventional methods to prepare liposomes. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 383, 123106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Rooijen, N.; Sanders, A. Liposome mediated depletion of macrophages: Mechanism of action, preparation of liposomes and applications. J. Immunol. Methods 1994, 174, 83–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Wang, X.; Liu, Y.; Yang, G.; Falconer, R.J.; Zhao, C.-X. Lipid Nanoparticles for Drug Delivery. Adv. NanoBiomed Res. 2021, 2, 2100109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunha, S.; Amaral, M.H.; Lobo, J.M.S.; Silva, A.C. Lipid Nanoparticles for Nasal/Intranasal Drug Delivery. Crit. Rev. Ther. Drug Carr. Syst. 2017, 34, 257–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirchandani, Y.; Patravale, V.B.; Brijesh, S. Solid lipid nanoparticles for hydrophilic drugs. J. Control Release 2021, 335, 457–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- da Silva, G.H.R.; de Moura, L.D.; de Carvalho, F.V.; Geronimo, G.; Mendonça, T.C.; de Lima, F.F.; de Paula, E. Antineoplastics Encapsulated in Nanostructured Lipid Carriers. Molecules 2021, 26, 6929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Saqr, A.; Wani, S.U.D.; Gangadharappa, H.V.; Aldawsari, M.F.; Khafagy, E.-S.; Abu Lila, A.S. Enhanced Cytotoxic Activity of Docetaxel-Loaded Silk Fibroin Nanoparticles against Breast Cancer Cells. Polymers 2021, 13, 1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, G.; Liu, D.; Guo, W.; Wang, M.; Wu, C.; Guo, M.; Ai, X.; Wang, Y.; He, Z. Docetaxel prodrug liposomes for tumor therapy: Characterization, in vitro and in vivo evaluation. Drug Deliv. 2016, 23, 1272–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Batist, G.; Barton, J.; Chaikin, P.; Swenson, C.; Welles, L. Myocet (liposome-encapsulated doxorubicin citrate): A new approach in breast cancer therapy. Expert Opin. Pharmacother. 2002, 3, 1739–1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bulbake, U.; Doppalapudi, S.; Kommineni, N.; Khan, W. Liposomal Formulations in Clinical Use: An Updated Review. Pharmaceutics 2017, 9, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adler-Moore, J.; Proffitt, R.T. AmBisome: Liposomal formulation, structure, mechanism of action and pre-clinical experience. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2002, 49, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barenholz, Y. Doxil®—The first FDA-approved nano-drug: Lessons learned. J. Control Release 2012, 160, 117–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Chen, G.; Zhang, J. A Review of Liposomes as a Drug Delivery System: Current Status of Approved Products, Regulatory Environments, and Future Perspectives. Molecules 2022, 27, 1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, K.S.; Liu, S.; Mao, J.; Zhang, J.; Qiu, L. Dual-Functional Peptide Driven Liposome Codelivery System for Efficient Treatment of Doxorubicin-Resistant Breast Cancer. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2021, 15, 3223–3239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; He, X.; Deng, B.; Shi, C.; Lin, L.; Liu, P.; Yang, Z.; Yang, S.; Xu, Z. Sorafenib and indocyanine green co-loaded in photothermally sensitive liposomes for diagnosis and treatment of advanced Hepatocellular carcinoma Qianyuan. J. Mater. Chem. B 2018, 6, 5823–5834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, M.H.Y.; Harmatys, K.M.; Charron, D.M.; Chen, J.; Zheng, G. Stable J-Aggregation of an aza-BODIPY-Lipid in a Liposome for Optical Cancer Imaging. Angew. Chem. 2019, 131, 13528–13533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, H.; He, Y.; Liang, J.; Cheng, Z.; Zhang, M.; Zhu, Y.; Hong, C.; Qin, J.; Xu, X.; Wang, J. Role of Liposome Size, Surface Charge, and PEGylation on Rheumatoid Arthritis Targeting Therapy. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 20304–20315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganesan, P.; Narayanasamy, D. Lipid nanoparticles: Different preparation techniques, characterization, hurdles, and strategies for the production of solid lipid nanoparticles and nanostructured lipid carriers for oral drug delivery. Sustain. Chem. Pharm. 2017, 6, 37–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargas, K.M.; Shon, Y.-S. Hybrid lipid–nanoparticle complexes for biomedical applications. J. Mater. Chem. B 2019, 7, 695–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thostenson, E.; Li, C.; Chou, T. Nanocomposites in context. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2005, 65, 491–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, D.; Kar, T.; Das, P.K. Gel-nanocomposites: Materials with promising applications. Soft Matter 2011, 8, 2348–2365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elgohary, M.M.; Helmy, M.W.; Mortada, S.M.; Elzoghby, A.O. Dual-targeted nano-in-nano albumin carriers enhance the efficacy of combined chemo / herbal therapy of lung cancer. Nanomedicine 2018, 13, 2221–2224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Z.; Lou, S.; Hu, Y.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, C. A Nano-in-Nano Polymer–Dendrimer Nanoparticle-Based Nanosystem for Controlled Multidrug Delivery. Mol. Pharm. 2017, 14, 2697–2710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dichello, G.A.; Fukuda, T.; Maekawa, T.; Whitby, R.L.; Mikhalovsky, S.V.; Alavijeh, M.; Pannala, A.S.; Sarker, D.K. Preparation of liposomes containing small gold nanoparticles using electrostatic interactions. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 105, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pornpattananangkul, D.; Olson, S.; Aryal, S.; Sartor, M.; Huang, C.-M.; Vecchio, K.; Zhang, L. Stimuli-Responsive Liposome Fusion Mediated by Gold Nanoparticles. ACS Nano 2010, 4, 1935–1942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rengan, A.K.; Bukhari, A.B.; Pradhan, A.; Malhotra, R.; Banerjee, R.; Srivastava, R.; De, A. In Vivo Analysis of Biodegradable Liposome Gold Nanoparticles as Efficient Agents for Photothermal Therapy of Cancer. Nano Lett. 2015, 15, 842–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathiyazhakan, M.; Wiraja, C.; Xu, C. A Concise Review of Gold Nanoparticles-Based Photo-Responsive Liposomes for Controlled Drug Delivery. Nano-Micro Lett. 2017, 10, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Musielak, M.; Potoczny, J.; Boś-Liedke, A.; Kozak, M. The Combination of Liposomes and Metallic Nanoparticles as Multifunctional Nanostructures in the Therapy and Medical Imaging—A Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arvizo, R.; Bhattacharya, R.; Mukherjee, P. Gold nanoparticles: Opportunities and challenges in nanomedicine. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2010, 7, 753–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Taguchi, K.; Okamoto, Y.; Matsumoto, K.; Otagiri, M.; Chuang, V.T.G. When Albumin Meets Liposomes: A Feasible Drug Carrier for Biomedical Applications. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, M.-W.; Park, T.-E. Recent advances with liposomes as drug carriers for treatment of neurodegenerative diseases. Biomed. Eng. Lett. 2021, 11, 211–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adler-Moore, J.P.; Proffitt, R.T. Development, Characterization, Efficacy and Mode of Action of Ambisome, A Unilamellar Liposomal Formulation of Amphotericin B. J. Liposome Res. 1993, 3, 429–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, K.; Friend, D.S.; Glabe, C.G.; Papahadjopoulos, D. Liposomes containing colloidal gold are a useful probe of liposome-cell interactions. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1983, 732, 320–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.P.; Alvi, S.B.; Pemmaraju, D.B.; Singh, A.D.; Manda, S.V.; Srivastava, R.; Rengan, A.K. NIR triggered liposome gold nanoparticles entrapping curcumin as in situ adjuvant for photothermal treatment of skin cancer. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 110, 375–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, D.S.; Prasad, R.; Devrukhkar, J.; Selvaraj, K.; Srivastava, R. Disintegrable NIR Light Triggered Gold Nanorods Supported Liposomal Nanohybrids for Cancer Theranostics. Bioconj. Chem. 2017, 29, 1510–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Hao, S.; Zuo, J.; Guo, H.; Liu, M.; Zhu, H.; Sun, H. NIR-Activated Thermosensitive Liposome–Gold Nanorod Hybrids for Enhanced Drug Delivery and Stimulus Sensitivity. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2022, 9, 340–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goh, E.T.H.; Cheung, P.C.F.; Akira, S.; Centre, B.; Defense, H. Doxorubicin/gold nanoparticles coated with liposomes for chemo- photothermal synergetic antitumor therapy. Nanotechnology 2018, 29, 405101. [Google Scholar]
- Luchini, A.; D’errico, G.; Leone, S.; Vaezi, Z.; Bortolotti, A.; Stella, L.; Vitiello, G.; Paduano, L. Structural organization of lipid-functionalized-Au nanoparticles. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2018, 168, 2–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tao, Y.; Han, J.; Ye, C.; Thomas, T.; Dou, H. Reduction-responsive gold-nanoparticle-conjugated Pluronic micelles: An effective anti-cancer drug delivery system. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 18864–18871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Granick, S. How to Stabilize Phospholipid Liposomes (Using Nanoparticles). Nano Lett. 2006, 6, 694–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugikawa, K.; Matsuo, K.; Ikeda, A. Suppression of Gold Nanoparticle Aggregation on Lipid Membranes Using Nanosized Liposomes To Increase Steric Hindrance. Langmuir 2018, 35, 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, H.; Niidome, Y.; Niidome, T.; Kaneko, K.; Kawasaki, H.; Yamada, S. Modification of Gold Nanorods Using Phosphatidylcholine to Reduce Cytotoxicity. Langmuir 2005, 22, 2–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-H.; Shin, Y.; Lee, W.; Whang, K.; Kim, D.; Lee, L.P.; Choi, J.-W.; Kang, T. General and programmable synthesis of hybrid liposome/metal nanoparticles. Sci. Adv. 2016, 2, e1601838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barroso, M.F.; Luna, M.A.; Tabares, J.S.F.; Delerue-Matos, C.; Correa, N.M.; Moyano, F.; Molina, P.G. Gold nanoparticles covalently assembled onto vesicle structures as possible biosensing platform. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2016, 7, 655–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paasonen, L.; Sipilä, T.; Subrizi, A.; Laurinmäki, P.; Butcher, S.J.; Rappolt, M.; Yaghmur, A.; Urtti, A.; Yliperttula, M. Gold-embedded photosensitive liposomes for drug delivery: Triggering mechanism and intracellular release. J. Control Release 2010, 147, 136–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.-H.; Oh, S.-G.; Mun, J.-Y.; Han, S.-S. Loading of gold nanoparticles inside the DPPC bilayers of liposome and their effects on membrane fluidities. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2006, 48, 112–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regan, D.; Williams, J.B.; Borri, P.; Langbein, W. Lipid Bilayer Thickness Measured by Quantitative DIC Reveals Phase Transitions and Effects of Substrate Hydrophilicity. Langmuir 2019, 35, 13805–13814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Szoka, F.; Papahadjopoulos, D. Comparative Properties and Methods of Preparation of Lipid Vesicles (Liposomes). Annu. Rev. Biophys. Bioeng. 1980, 9, 467–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olson, F.; Hunt, C.; Szoka, F.; Vail, W.; Papahadjopoulos, D. Preparation of liposomes of defined size distribution by extrusion through polycarbonate membranes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)—Biomembr. 1979, 557, 9–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kojima, C.; Hirano, Y.; Yuba, E.; Harada, A.; Kono, K. Preparation and characterization of complexes of liposomes with gold nanoparticles. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2008, 66, 246–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-López, V.; Fernández-Romero, J.; Gómez-Hens, A. Evaluation of liposome populations using a sucrose density gradient centrifugation approach coupled to a continuous flow system. Anal. Chim. Acta 2009, 645, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.-Y.; Shin, S.H.R.; Abezgauz, L.L.; Lewis, S.A.; Chirsan, A.M.; Danino, D.D.; Bishop, K.J.M. Integration of Gold Nanoparticles into Bilayer Structures via Adaptive Surface Chemistry. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 5950–5953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Von White, I.G.; Chen, Y.; Roder-Hanna, J.; Bothun, G.D.; Kitchens, C.L. Structural and Thermal Analysis of Lipid Vesicles Encapsulating Hydrophobic Gold Nanoparticles. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 4678–4685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nsairat, H.; Khater, D.; Sayed, U.; Odeh, F.; Al Bawab, A.; Alshaer, W. Liposomes: Structure, composition, types, and clinical applications. Heliyon 2022, 8, e09394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Piano, R.; Caccavo, D.; Lamberti, G.; Remaut, K.; Seynaeve, H.; Barba, A.A. A New Productive Approach and Formulative Optimization for Curcumin Nanoliposomal Delivery Systems. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudhakar, K.; Fuloria, S.; Subramaniyan, V.; Sathasivam, K.V.; Azad, A.K.; Swain, S.S.; Sekar, M.; Karupiah, S.; Porwal, O.; Sahoo, A.; et al. Ultraflexible Liposome Nanocargo as a Dermal and Transdermal Drug Delivery System. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 2557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sztandera, K.; Gorzkiewicz, M.; Klajnert-Maculewicz, B. Gold Nanoparticles in Cancer Treatment. Mol. Pharm. 2019, 16, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonkar, R.; Sonali; Jha, A.; Viswanadh, M.K.; Burande, A.S.; Narendra; Pawde, D.M.; Patel, K.K.; Singh, M.; Koch, B.; et al. Gold liposomes for brain-targeted drug delivery: Formulation and brain distribution kinetics. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2020, 120, 111652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohout, C.; Santi, C.; Polito, L. Anisotropic Gold Nanoparticles in Biomedical Applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Alkilany, A.M.; Nagaria, P.K.; Hexel, C.R.; Shaw, T.J.; Murphy, C.J.; Wyatt, M.D. Cellular Uptake and Cytotoxicity of Gold Nanorods: Molecular Origin of Cytotoxicity and Surface Effects. Small 2009, 5, 701–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alkilany, A.; Shatanawi, A.; Kurtz, T.; Caldwell, R. Toxicity and Cellular Uptake of Gold Nanorods in Vascular Endothelium and Smooth Muscles of Isolated Rat Blood Vessel: Importance of Surface Modification. Small 2012, 8, 1270–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gudlur, S.; Goyal, G.; Pradhan, A.; Ho, J.C.S.; Srivastava, R.; Liedberg, B. Cationic Liposomes Enable Shape Control in Surfactant-Free Synthesis of Biocompatible Gold Nanorods. Chem. Mater. 2021, 33, 4558–4567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Știufiuc, G.F.; Nițică, S.; Toma, V.; Iacoviță, C.; Zahn, D.; Tetean, R.; Burzo, E.; Lucaciu, C.M.; Știufiuc, R.I. Synergistical Use of Electrostatic and Hydrophobic Interactions for the Synthesis of a New Class of Multifunctional Nanohybrids: Plasmonic Magneto-Liposomes. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zarchi, A.A.K.; Amini, S.M.; Salimi, A.; Kharazi, S. Synthesis and characterisation of liposomal doxorubicin with loaded gold nanoparticles. IET Nanobiotechnol. 2018, 12, 846–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, K.; Bao, M.; Xin, C.; Wang, L.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, H.; Wang, Z. Green synthesis of gold nanoparticles coated doxorubicin liposomes using procyanidins for light–controlled drug release. Adv. Powder Technol. 2020, 31, 3640–3649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.; Wang, Z.; Zong, S.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, C.; Zhang, R.; Yun, B.; Cui, Y. Investigating the Intracellular Behaviors of Liposomal Nanohybrids via SERS: Insights into the Influence of Metal Nanoparticles. Theranostics 2018, 8, 941–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugikawa, K.; Kadota, T.; Yasuhara, K.; Ikeda, A. Anisotropic Self-Assembly of Citrate-Coated Gold Nanoparticles on Fluidic Liposomes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 4059–4063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunjiappan, S.; Panneerselvam, T.; Somasundaram, B.; Arunachalam, S.; Sankaranarayanan, M.; Parasuraman, P. Preparation of liposomes encapsulated Epirubicin-gold nanoparticles for Tumor specific delivery and release. Biomed. Phys. Eng. Express 2018, 4, 045027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvi, S.B.; Rajalakshmi, P.S.; Jogdand, A.; Sanjay, A.Y.; Veeresh, B.; John, R.; Rengan, A.K. Iontophoresis mediated localized delivery of liposomal gold nanoparticles for photothermal and photodynamic therapy of acne. Biomater. Sci. 2021, 9, 1421–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baxa, U. Imaging of Liposomes by Transmission Electron Microscopy. Charact. Nanoparticles Intend. Drug Deliv. 2017, 1682, 73–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sitaula, S.; Mackiewicz, M.R.; Reed, S.M. Gold nanoparticles become stable to cyanide etch when coated with hybrid lipid bilayers. Chem. Commun. 2008, 26, 3013–3015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charest, G.; Tippayamontri, T.; Shi, M.; Wehbe, M.; Anantha, M.; Bally, M.; Sanche, L. Concomitant Chemoradiation Therapy with Gold Nanoparticles and Platinum Drugs Co-Encapsulated in Liposomes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jhun, J.; Moon, J.; Ryu, J.; Shin, Y.; Lee, S.; Cho, K.-H.; Kang, T.; Cho, M.-L.; Park, S.-H. Liposome/gold hybrid nanoparticle encoded with CoQ10 (LGNP-CoQ10) suppressed rheumatoid arthritis via STAT3/Th17 targeting. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0241080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hachenberger, Y.U.; Rosenkranz, D.; Kriegel, F.L.; Krause, B.; Matschaß, R.; Reichardt, P.; Tentschert, J.; Laux, P.; Jakubowski, N.; Panne, U.; et al. Tackling Complex Analytical Tasks: An ISO/TS-Based Validation Approach for Hydrodynamic Chromatography Single Particle Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry. Materials 2020, 13, 1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schulz, M.; Olubummo, A.; Binder, W.H. Beyond the lipid-bilayer: Interaction of polymers and nanoparticles with membranes. Soft Matter 2012, 8, 4849–4864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Bihan, O.; Bonnafous, P.; Marak, L.; Bickel, T.; Trépout, S.; Mornet, S.; De Haas, F.; Talbot, H.; Taveau, J.-C.; Lambert, O. Cryo-electron tomography of nanoparticle transmigration into liposome. J. Struct. Biol. 2009, 168, 419–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rengan, A.K.; Jagtap, M.; De, A.; Banerjee, R.; Srivastava, R. Multifunctional gold coated thermo-sensitive liposomes for multimodal imaging and photo-thermal therapy of breast cancer cells. Nanoscale 2013, 6, 916–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozano, N.; Al-Jamal, W.T.; Taruttis, A.; Beziere, N.; Burton, N.C.; Bossche, J.V.D.; Mazza, M.; Herzog, E.; Ntziachristos, V.; Kostarelos, K. Liposome–Gold Nanorod Hybrids for High-Resolution Visualization Deep in Tissues. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 13256–13258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Appidi, T.; Rajalakshmi, P.S.; Chinchulkar, S.A.; Pradhan, A.; Begum, H.; Shetty, V.; Srivastava, R.; Ganesan, P.; Rengan, A.K. A plasmon-enhanced fluorescent gold coated novel lipo-polymeric hybrid nanosystem: Synthesis, characterization and application for imaging and photothermal therapy of breast cancer. Nanoscale 2022, 14, 9112–9123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Liu, Q.; Jing, C.; Li, Y.; Li, D.; Luo, W.; Wen, Y.; He, Y.; Huang, Q.; Long, Y.-T.; et al. Catalytic Gold Nanoparticles for Nanoplasmonic Detection of DNA Hybridization. Angew. Chem. 2011, 123, 12200–12204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedighi, A.; Li, P.C.H.; Pekcevik, I.C.; Gates, B.D. A Proposed Mechanism of the Influence of Gold Nanoparticles on DNA Hybridization. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 6765–6777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lo, K.-M.; Lai, C.-Y.; Chan, H.-M.; Ma, D.-L.; Li, H.-W. Monitoring of DNA–protein interaction with single gold nanoparticles by localized scattering plasmon resonance spectroscopy. Methods 2013, 64, 331–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, C.-S.; Yu, T.-B.; Chen, C.-T. Gold nanoparticle-based competitive colorimetric assay for detection of protein–protein interactions. Chem. Commun. 2005, 34, 4273–4275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandhu, K.K.; McIntosh, C.M.; Simard, J.M.; Smith, S.W.; Rotello, V.M. Gold Nanoparticle-Mediated Transfection of Mammalian Cells. Bioconj. Chem. 2001, 13, 3–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crew, E.; Rahman, S.; Razzak-Jaffar, A.; Mott, D.; Kamundi, M.; Yu, G.; Tchah, N.; Lee, J.; Bellavia, M.; Zhong, C.-J. MicroRNA Conjugated Gold Nanoparticles and Cell Transfection. Anal. Chem. 2011, 84, 26–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazur, F.; Tran, H.; Kuchel, R.P.; Chandrawati, R. Rapid Detection of Listeriolysin O Toxin Based on a Nanoscale Liposome–Gold Nanoparticle Platform. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2020, 3, 7270–7280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Moon, B.-S.; Hwang, E.; Shaban, S.; Lee, W.; Pyun, D.-G.; Lee, D.H.; Kim, D.-H. Solid-state colorimetric polydiacetylene liposome biosensor sensitized by gold nanoparticles. Analyst 2021, 146, 1682–1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Malinick, A.S.; Yang, T.; Cheng, W.; Cheng, Q. Gold nanoparticle-coupled liposomes for enhanced plasmonic biosensing. Sensors Actuators Rep. 2020, 2, 100023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Sheng, A.; Hu, Y.; Mao, D.; Ning, L.; Zhang, J. Modularization of three-dimensional gold nanoparticles/ferrocene/liposome cluster for electrochemical biosensor. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 124–125, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubio-Camacho, M.; Martínez-Tomé, M.J.; Cuestas-Ayllón, C.; de la Fuente, J.M.; Esquembre, R.; Mateo, C.R. Tailoring the plasmonic properties of gold-liposome nanohybrids as a potential powerful tool for light-mediated therapies. Colloid Interface Sci. Commun. 2023, 52, 100690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, M.; Taghavi, S.; Abnous, K.; Taghdisi, S.M.; Ramezani, M.; Alibolandi, M. Hybrid Vesicular Drug Delivery Systems for Cancer Therapeutics. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1802136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradhan, A.; Kumari, A.; Srivastava, R.; Panda, D. Quercetin Encapsulated Biodegradable Plasmonic Nanoparticles for Photothermal Therapy of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2019, 2, 5727–5738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Mikhailovsky, A.; Khant, H.A.; Fu, C.; Chiu, W.; Zasadzinski, J.A. Remotely Triggered Liposome Release by Near-Infrared Light Absorption via Hollow Gold Nanoshells. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 8175–8177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Agarwal, A.; Mackey, M.A.; El-Sayed, M.A.; Bellamkonda, R.V. Remote Triggered Release of Doxorubicin in Tumors by Synergistic Application of Thermosensitive Liposomes and Gold Nanorods. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 4919–4926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lajunen, T.; Viitala, L.; Kontturi, L.-S.; Laaksonen, T.; Liang, H.; Vuorimaa-Laukkanen, E.; Viitala, T.; Le Guével, X.; Yliperttula, M.; Murtomäki, L.; et al. Light induced cytosolic drug delivery from liposomes with gold nanoparticles. J. Control Release 2015, 203, 85–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Liu, Y.; Luo, L.; Li, L.; Xing, S.; Yin, T.; Bian, K.; Zhu, R.; Gao, D. A chemo-photothermal synergetic antitumor drug delivery system: Gold nanoshell coated wedelolactone liposome. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 101, 505–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takakura, Y.; Takahashi, Y. Strategies for persistent retention of macromolecules and nanoparticles in the blood circulation. J. Control Release 2022, 350, 486–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papini, E.; Tavano, R.; Mancin, F. Opsonins and Dysopsonins of Nanoparticles: Facts, Concepts, and Methodological Guidelines. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 567365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Wang, X.; Li, J.; Nie, Y.; Liao, G.; Yu, Y.; Li, C. Overcoming the Reticuloendothelial System Barrier to Drug Delivery with a “don’t-Eat-Us” Strategy. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 13015–13026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Chen, H.; Liu, A.-Y.; Shen, J.-J.; Shah, V.; Zhang, C.; Hong, J.; Ding, Y. Gold conjugate-based liposomes with hybrid cluster bomb structure for liver cancer therapy. Biomaterials 2016, 74, 280–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.S.; Liu, W.; Misra, P.; Tanaka, E.; Zimmer, J.P.; Ipe, B.I.; Bawendi, M.G.; Frangioni, J.V. Renal clearance of quantum dots. Nat. Biotechnol. 2007, 25, 1165–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Al-Jamal, W.T.; Kostarelos, K. Liposomes: From a Clinically Established Drug Delivery System to a Nanoparticle Platform for Theranostic Nanomedicine. Acc. Chem. Res. 2011, 44, 1094–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haraldsson, B.; Nyström, J.; Deen, W.M. Properties of the Glomerular Barrier and Mechanisms of Proteinuria. Physiol. Rev. 2008, 88, 451–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mitchell, M.J.; Billingsley, M.M.; Haley, R.M.; Wechsler, M.E.; Peppas, N.A.; Langer, R. Engineering precision nanoparticles for drug delivery. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2020, 20, 101–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García, K.P.; Zarschler, K.; Barbaro, L.; Barreto, J.A.; O’Malley, W.; Spiccia, L.; Stephan, H.; Graham, B. Zwitterionic-Coated “Stealth” Nanoparticles for Biomedical Applications: Recent Advances in Countering Biomolecular Corona Formation and Uptake by the Mononuclear Phagocyte System. Small 2014, 10, 2516–2529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zalba, S.; Hagen, T.L.T.; Burgui, C.; Garrido, M.J. Stealth nanoparticles in oncology: Facing the PEG dilemma. J. Control Release 2022, 351, 22–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, J.; Ha, Y.S.; Hwang, S.; Lee, W.; Song, J.; Yoo, J.; Kim, S. pH-responsive gold nanoparticles-in-liposome hybrid nanostructures for enhanced systemic tumor delivery. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 10175–10178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bariana, M.; Zhang, B.; Sun, J.; Wang, W.; Wang, J.; Cassella, E.; Myint, F.; Anuncio, S.A.; Ouk, S.; Liou, H.-C.; et al. Targeted Lymphoma Therapy Using a Gold Nanoframework-Based Drug Delivery System. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 15, 6312–6325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morishita, M.; Takahashi, Y.; Nishikawa, M.; Sano, K.; Kato, K.; Yamashita, T.; Imai, T.; Saji, H.; Takakura, Y. Quantitative Analysis of Tissue Distribution of the B16BL6-Derived Exosomes Using a Streptavidin-Lactadherin Fusion Protein and Iodine-125-Labeled Biotin Derivative After Intravenous Injection in Mice. J. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 104, 705–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kooijmans, S.A.A.; Fliervoet, L.A.L.; van der Meel, R.; Fens, M.H.A.M.; Heijnen, H.F.G.; van Bergen En Henegouwen, P.M.P.; Vader, P.; Schiffelers, R.M. PEGylated and targeted extracellular vesicles display enhanced cell specificity and circulation time. J. Control Release 2016, 224, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.; Hu, Q.; Song, Y.K. Liposome clearance from blood: Different animal species have different mechanisms. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1995, 1240, 277–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Litzinger, D.C.; Buiting, A.M.; van Rooijen, N.; Huang, L. Effect of liposome size on the circulation time and intraorgan distribution of amphipathic poly(ethylene glycol)-containing liposomes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)—Biomembr. 1994, 1190, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, C.H.J.; Zuckerman, J.E.; Webster, P.; Davis, M.E. Targeting kidney mesangium by nanoparticles of defined size. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 6656–6661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]











Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Idoudi, S.; Ismail, R.; Rachid, O.; Elhissi, A.; Alkilany, A.M. The Golden Liposomes: Preparation and Biomedical Applications of Gold-Liposome Nanocomposites. J. Nanotheranostics 2023, 4, 201-227. https://doi.org/10.3390/jnt4030010
Idoudi S, Ismail R, Rachid O, Elhissi A, Alkilany AM. The Golden Liposomes: Preparation and Biomedical Applications of Gold-Liposome Nanocomposites. Journal of Nanotheranostics. 2023; 4(3):201-227. https://doi.org/10.3390/jnt4030010
Chicago/Turabian StyleIdoudi, Sourour, Roua Ismail, Ousama Rachid, Abdelbary Elhissi, and Alaaldin M. Alkilany. 2023. "The Golden Liposomes: Preparation and Biomedical Applications of Gold-Liposome Nanocomposites" Journal of Nanotheranostics 4, no. 3: 201-227. https://doi.org/10.3390/jnt4030010
APA StyleIdoudi, S., Ismail, R., Rachid, O., Elhissi, A., & Alkilany, A. M. (2023). The Golden Liposomes: Preparation and Biomedical Applications of Gold-Liposome Nanocomposites. Journal of Nanotheranostics, 4(3), 201-227. https://doi.org/10.3390/jnt4030010