Journal Description
Journal of Nanotheranostics
Journal of Nanotheranostics
is an international, peer-reviewed, open access journal on nanotheranostics published quarterly online by MDPI.
- Open Access—free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 18.2 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 3.3 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the second half of 2024).
- Recognition of Reviewers: APC discount vouchers, optional signed peer-review and reviewer names published annually in the journal.
Latest Articles
Nanozyme-Based Cancer Nanotheranostics: Emerging Applications and Challenges in Brain Cancer Therapeutics
J. Nanotheranostics 2025, 6(1), 4; https://doi.org/10.3390/jnt6010004 - 31 Jan 2025
Abstract
Regrettably, despite undeniable advances in cancer diagnosis and therapy, primary brain cancer (or brain cancer) remains one of the deadliest forms of malignant tumors, where glioblastoma (GBM) is known as the most malignant diffuse glioma of astrocytic lineage. Fortunately, to improve this scenario,
[...] Read more.
Regrettably, despite undeniable advances in cancer diagnosis and therapy, primary brain cancer (or brain cancer) remains one of the deadliest forms of malignant tumors, where glioblastoma (GBM) is known as the most malignant diffuse glioma of astrocytic lineage. Fortunately, to improve this scenario, remarkable progress in nanotechnology has brought new promise and raised expectations in cancer treatment. Nanomedicine, principally an area amalgamating nanotechnology with biology and medicine, has demonstrated a pivotal role, starting with the earliest detection and diagnosis while also offering novel multimodal cancer therapy alternatives. In the vast realm of nanotechnology, nanozymes, a type of nanomaterial with intrinsic enzyme-like activities and characteristics connecting the fields of nanocatalysts, enzymology, and biology, have emerged as powerful nanotools for cancer theranostics. Hence, this fascinating field of research has experienced exponential growth in recent years. As it is virtually impossible to cover all the literature on this broad domain of science in one paper, this review focuses on presenting a multidisciplinary approach, with its content extending from fundamental knowledge of nanozymes and enzyme-mimicking catalysis to the most recent advances in nanozymes for therapy targeting brain cancers. Although we are at the very early stages of research, it can be envisioned that the strategic development of nanozymes in brain cancer theranostics will positively offer disruptive nanoplatforms for future nano-oncology.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Nanozymes: New Advances in the Next Generation of Enzyme-Like Nanosystems)
►
Show Figures
Open AccessOpinion
From Traditional Nanoparticles to Cluster-Triggered Emission Polymers for the Generation of Smart Nanotheranostics in Cancer Treatment
by
Cristina Blasco-Navarro, Carlos Alonso-Moreno and Iván Bravo
J. Nanotheranostics 2025, 6(1), 3; https://doi.org/10.3390/jnt6010003 - 22 Jan 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Nanotheranostics integrates diagnostic and therapeutic functionalities using nanoscale materials, advancing personalized medicine by enhancing treatment precision and reducing adverse effects. Key materials for nanotheranostics include metallic nanoparticles, quantum dots, carbon dots, lipid nanoparticles and polymer-based nanocarriers, each offering unique benefits alongside specific challenges.
[...] Read more.
Nanotheranostics integrates diagnostic and therapeutic functionalities using nanoscale materials, advancing personalized medicine by enhancing treatment precision and reducing adverse effects. Key materials for nanotheranostics include metallic nanoparticles, quantum dots, carbon dots, lipid nanoparticles and polymer-based nanocarriers, each offering unique benefits alongside specific challenges. Polymer-based nanocarriers, including hybrid and superparamagnetic nanoparticles, improve stability and functionality but are complex to manufacture. Polymeric nanoparticles with aggregation-induced emission (AIE) present promising theranostic potential for cancer detection and treatment. However, challenges such as translating the AIE concept to living systems, addressing toxicity concerns, overcoming deep-tissue imaging limitations, or ensuring biocompatibility remain to be resolved. Recently, cluster-triggered emission (CTE) polymers have emerged as innovative materials in nanotheranostics, offering enhanced fluorescence and biocompatibility. These polymers exhibit increased fluorescence intensity upon aggregation, making them highly sensitive for imaging and therapeutic applications. CTE nanoparticles, crafted from biodegradable polymers, represent a safer alternative to traditional nanotheranostics that rely on embedding conventional fluorophores or metal-based agents. This advancement significantly reduces potential toxicity while enhancing biocompatibility. The intrinsic fluorescence allows real-time monitoring of drug distribution and activity, optimizing therapeutic efficacy. Despite their potential, these systems face challenges such as maintaining stability under physiological conditions and addressing the need for comprehensive safety and efficacy studies to meet clinical and regulatory standards. Nevertheless, their unique properties position CTE nanoparticles as promising candidates for advancing theranostic strategies in personalized medicine, bridging diagnostic and therapeutic functionalities in innovative ways.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
PTT-Mediated Inhibition of Cancer Proliferation and Tumor Progression by DARPin-Coated Gold Nanoparticles
by
Galina M. Proshkina, Elena I. Shramova, Ekaterina V. Serova, Egor A. Myachev, Aziz B. Mirkasymov, Sergey M. Deyev and Alexander B. Kotlyar
J. Nanotheranostics 2025, 6(1), 2; https://doi.org/10.3390/jnt6010002 - 4 Jan 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Targeting HER2-positive cancer cells with precision therapies is a critical challenge in oncology. Here, we present a study on gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) conjugated with DARPin_9-29, a designed ankyrin repeat protein with high specificity and affinity for HER2 receptors. In this study, we investigate
[...] Read more.
Targeting HER2-positive cancer cells with precision therapies is a critical challenge in oncology. Here, we present a study on gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) conjugated with DARPin_9-29, a designed ankyrin repeat protein with high specificity and affinity for HER2 receptors. In this study, we investigate the therapeutic potential of AuNP-DARPin_9-29 conjugates, which was synthesized and characterized by us earlier, for photothermal therapy (PTT). By combining AuNP-DARPin treatment with visible light illumination, we show selective inhibition of HER2-positive cancer cell proliferation and tumor progression in a murine model. The results highlight the effectiveness of AuNP-DARPin in disrupting cancer cell viability and reducing tumor growth, providing a cost-effective and targeted approach for combating HER2-positive cancers.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Carbon Dots: New Rising Stars in the Carbon Family for Diagnosis and Biomedical Applications
by
Muneeb Ullah, Uzma Azeem Awan, Haider Ali, Abdul Wahab, Shahid Ullah Khan, Muhammad Naeem, Muhammad Ruslin, Apon Zaenal Mustopa and Nurhasni Hasan
J. Nanotheranostics 2025, 6(1), 1; https://doi.org/10.3390/jnt6010001 - 28 Dec 2024
Abstract
Carbon dots (CDs) are a class of carbon-based nanomaterials undergoing rapid development with broad potential applications across diverse biomedical fields. These materials are highly attractive for diagnostics, therapeutics, and nanomedicine due to their remarkable optical and physicochemical properties, including photoluminescence, biocompatibility, and aqueous
[...] Read more.
Carbon dots (CDs) are a class of carbon-based nanomaterials undergoing rapid development with broad potential applications across diverse biomedical fields. These materials are highly attractive for diagnostics, therapeutics, and nanomedicine due to their remarkable optical and physicochemical properties, including photoluminescence, biocompatibility, and aqueous dispersibility. CDs can be synthesized using various techniques, ranging from top-down to bottom-up approaches. Among these, biogenic synthesis, utilizing natural sources and waste materials, presents an eco-friendly and sustainable alternative. CDs have exhibited considerable promise in diagnostics, especially with bioimaging and biosensing, providing both high sensitivity and precise identification. CDs are presently being investigated in the pharmaceutical sector for their potential applications in cancer and infection treatment, as well as in photodynamic and thermal therapies. The advancement of CD composites, through enhanced functionality and broader application, facilitates novel research in nanomedicine. This article highlights the advantages of CDs, focusing on their structural properties, classification, and versatility in synthesis methods. Furthermore, the safety and toxicity profiles of CDs are critically analyzed. In conclusion, the innocuity, adaptability, and multifunctionality of CDs position them as a cornerstone in the advancement of nanotechnology and biomedical applications. With their broad applicability and promising potential, CDs stand poised to drive significant innovation across diagnostics, therapeutics, and other domains, heralding a new era in nanomedicine and sustainable material development.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Carbon Nanomaterials as Nano-Theranostic Tools in Disease Treatment)
►▼
Show Figures

Graphical abstract
Open AccessReview
Application of Metal Oxide Nanoparticles in Different Carcinomas
by
Nutan Rani, Yousuf Khan, Sapna Yadav, Kalawati Saini and Dipak Maity
J. Nanotheranostics 2024, 5(4), 253-272; https://doi.org/10.3390/jnt5040015 - 20 Dec 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Metal oxide nanoparticles (MONPs) have recently attracted much attention from researchers due to their use in cancer chemotherapy, targeted drug delivery, and diagnosis/MRI imaging. Various studies have demonstrated that different metal oxide NPs show cytotoxic effects by inducing apoptosis in cancerous cells and
[...] Read more.
Metal oxide nanoparticles (MONPs) have recently attracted much attention from researchers due to their use in cancer chemotherapy, targeted drug delivery, and diagnosis/MRI imaging. Various studies have demonstrated that different metal oxide NPs show cytotoxic effects by inducing apoptosis in cancerous cells and do not have any toxic impact on normal cells. The mechanism of cytotoxicity is shown through reactive oxygen species (ROS) generated by (MONPs) in the cancerous cell. In vitro and in vivo studies reveal that in some cases metal oxide NPs are used alone and somewhere these NPs are used in combination with other therapies such as photodynamic therapy and with anticancer nanomedicines as drug carriers or drug conjugates. The phenomenon of enhanced permeability and retention (EPR) effect has been the basis of targeted drug delivery to cancerous tumors. Finally, we also provide a simple and comparative analysis of the major apoptosis pathways proposed to increase beginner understanding of anti-cancer nanomaterials. Herein, we have reviewed the most important antitumor results obtained with different metal oxide nanoparticles such as ZnO, Fe2O3/Fe3O4, CuO/Cu2O, TiO2, CeO2, and HfO2, respectively. These NPs can be applied to treat cancer by either passive or active processes. A passive process uses the enhanced permeability and retention (EPR) effect. Superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (SPIONs), due to their unique magnetic and physiochemical properties have been used in magnetic fluid hyperthermia (MFH) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) in vitro as well as in vivo. Now, the research has reached the stage of clinical trials for the treatment of various types of cancer. ZnO NPs have been used very vastly in cytotoxic as well as in targeted drug delivery. These NPs are also used for loading anticancer drugs such as doxorubicin. Herein, in this review, we have examined current advances in utilizing MONPs and their analogs as cancer therapeutic, diagnostic, and drug-delivery agents.
Full article

Graphical abstract
Open AccessReview
Advances in Photothermal and Photodynamic Nanotheranostics for Precision Cancer Treatment
by
Hossein Omidian and Sumana Dey Chowdhury
J. Nanotheranostics 2024, 5(4), 228-252; https://doi.org/10.3390/jnt5040014 - 13 Dec 2024
Abstract
Nanotheranostics, combining photothermal therapy (PTT) and photodynamic therapy (PDT), can transform precision cancer treatment by integrating diagnosis and therapy into a single platform. This review highlights recent advances in nanomaterials, drug delivery systems, and stimuli-responsive mechanisms for effective PTT and PDT. Multifunctional nanoparticles
[...] Read more.
Nanotheranostics, combining photothermal therapy (PTT) and photodynamic therapy (PDT), can transform precision cancer treatment by integrating diagnosis and therapy into a single platform. This review highlights recent advances in nanomaterials, drug delivery systems, and stimuli-responsive mechanisms for effective PTT and PDT. Multifunctional nanoparticles enable targeted delivery, multimodal imaging, and controlled drug release, overcoming the challenges posed by tumor microenvironments. Emerging approaches such as hybrid therapies and immune activation further enhance therapeutic efficacy. This paper discusses the limitations of nanotheranostics, including synthesis complexity and limited tissue penetration, and explores future directions toward biocompatible, scalable, and clinically translatable solutions.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Topic Application of Nanomaterials and Nanobiotechnology in Cancer)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessFeature PaperArticle
Exploring the Role of Fibroblasts in Promoting Neuroblastoma Cell Migration and Invasion
by
Diana Corallo, Cristina Nardelli, Marcella Pantile, Sara Menegazzo, Alessandra Biffi and Sanja Aveic
J. Nanotheranostics 2024, 5(4), 212-227; https://doi.org/10.3390/jnt5040013 - 8 Dec 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Neuroblastoma, the most common pediatric extracranial solid tumor, arises from the malignant transformation of neural crest progenitors in the peripheral nervous system. Its clinical and genetic heterogeneity poses significant challenges, especially in high-risk patients with metastatic disease. Two plastic neuroblastoma cell phenotypes, adrenergic
[...] Read more.
Neuroblastoma, the most common pediatric extracranial solid tumor, arises from the malignant transformation of neural crest progenitors in the peripheral nervous system. Its clinical and genetic heterogeneity poses significant challenges, especially in high-risk patients with metastatic disease. Two plastic neuroblastoma cell phenotypes, adrenergic (ADR) and mesenchymal (MES), have been identified. Notably, MES neuroblastoma cells exhibit increased migration and chemoresistance. Cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs) in the tumor microenvironment further promote tumor aggressiveness by enhancing cancer cell proliferation, extracellular matrix remodeling, angiogenesis and metastasis. This study explored the role of non-activated fibroblasts in ADR and MES neuroblastoma cell proliferation, migration and invasion in vitro and in vivo. Results showed that MES and ADR neuroblastoma cells influenced fibroblast activation into CAFs differently, with MES cells promoting a more invasive environment leading to tumor spread. These findings enhance our understanding of how ADR and MES phenotypes contribute to the formation of a pro-metastatic niche by activating fibroblasts in CAFs. This insight could inform new therapeutic strategies targeting the tumor microenvironment to prevent neuroblastoma metastasis.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Characteristics and Preparation of Solid Lipid Nanoparticles and Nanostructured Lipid Carriers
by
Marjorie de Carvalho Vieira Queiroz and Luís Alexandre Muehlmann
J. Nanotheranostics 2024, 5(4), 188-211; https://doi.org/10.3390/jnt5040012 - 25 Nov 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Solid lipid nanoparticles (SLNs) and nanostructured lipid carriers (NLCs) have emerged as promising systems for delivering active ingredients. They are derived from physiological, biodegradable, and biocompatible lipids, offering benefits such as sustained release promotion and increased drug stability. These systems are apt for
[...] Read more.
Solid lipid nanoparticles (SLNs) and nanostructured lipid carriers (NLCs) have emerged as promising systems for delivering active ingredients. They are derived from physiological, biodegradable, and biocompatible lipids, offering benefits such as sustained release promotion and increased drug stability. These systems are apt for the efficient transport of therapeutic drugs to target tissues while also providing advantages such as facilitating large-scale industrial production, bioavailability, and protection against degradation. The preparation of these nanoparticles involves utilizing diverse types of lipids, surfactants, and solvents. Common lipid varieties encompass triglycerides, steroids, and fatty acids, selected based on the active ingredient for stabilization within the lipid matrix. Preparation methods can be categorized into high-energy and low-energy approaches. This study investigated the differences between the main methodologies used, comparing SLN and NLC systems, and scrutinizing their respective advantages, disadvantages, and applications.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Nanotechnology-Enhanced Orthopaedic Surgery
by
Alexander Shao-Rong Pang, Zi Qiang Glen Liau, Jacob Yoong-Leong Oh and Dinesh Kumar Srinivasan
J. Nanotheranostics 2024, 5(4), 167-187; https://doi.org/10.3390/jnt5040011 - 13 Nov 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Nanomaterials hold significant promise for the future of orthopaedic implants due to their ability to mimic the nanoscale components of the bone, such as collagen fibrils and hydroxyapatite. Nanomaterials can regulate cell behaviour while offering mechanical strength and biocompatibility, making them ideal for
[...] Read more.
Nanomaterials hold significant promise for the future of orthopaedic implants due to their ability to mimic the nanoscale components of the bone, such as collagen fibrils and hydroxyapatite. Nanomaterials can regulate cell behaviour while offering mechanical strength and biocompatibility, making them ideal for bone repair and tissue regeneration. This comprehensive review explores the key existing and potential applications of nanotechnology in orthopaedics, including bone tissue engineering, drug delivery systems, systems combatting implant-related infections, and the surface preparation of implants to enhance osseointegration. These innovations are poised to revolutionise orthopaedic care by improving implant durability, reducing infection risks, and promoting bone regeneration to deliver personalised treatment and create better patient outcomes.
Full article

Graphical abstract
Open AccessReview
Drug Delivery Systems for Infectious Eye Diseases: Advancements and Prospects
by
Binapani Mahaling, Namrata Baruah and Aumreetam Dinabandhu
J. Nanotheranostics 2024, 5(4), 133-166; https://doi.org/10.3390/jnt5040010 - 6 Oct 2024
Cited by 1
Abstract
Infectious ocular diseases like keratitis, conjunctivitis, and endophthalmitis pose significant clinical challenges due to the complexities of delivering drugs to the eye. Recent advancements in drug delivery systems offer promising improvements for treating these conditions. Key strategies include targeted delivery through physicochemical modifications,
[...] Read more.
Infectious ocular diseases like keratitis, conjunctivitis, and endophthalmitis pose significant clinical challenges due to the complexities of delivering drugs to the eye. Recent advancements in drug delivery systems offer promising improvements for treating these conditions. Key strategies include targeted delivery through physicochemical modifications, magnetic nanoparticles, and ligand-receptor interactions. This review explores the safety and biocompatibility of ocular drug delivery systems through in vivo ocular toxicity studies, in vitro cytotoxicity assays, hemocompatibility studies, ocular tolerance tests, and genotoxicity assays. It also examines combination therapies and stimuli-responsive delivery systems for their potential to enhance therapeutic efficacy. Furthermore, we discuss tailored and optimized drug delivery approaches for infectious ocular diseases, outlining current challenges and future directions for developing effective ocular drug delivery systems.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Nanoengineered Solutions: Advancements in Targeted Drug Delivery and Theranostics)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessBrief Report
How Reproducible Is Feraheme® (Ferumoxytol Injection)? Comparison of Size, Zeta Potential, and Complement Activation of Different Batches over 15 Years
by
Utibeabasi Ettah, Sarah Jacques and Dmitri Simberg
J. Nanotheranostics 2024, 5(3), 128-132; https://doi.org/10.3390/jnt5030009 - 3 Sep 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Ferumoxytol injection, also known as Feraheme®, is an approved IV injectable iron supplement and an experimental MRI contrast agent. Initially, it was approved as an IV bolus agent, but its use was later limited to a slow infusion drip due to
[...] Read more.
Ferumoxytol injection, also known as Feraheme®, is an approved IV injectable iron supplement and an experimental MRI contrast agent. Initially, it was approved as an IV bolus agent, but its use was later limited to a slow infusion drip due to high levels of infusion reactions. We collected various batches of ferumoxytol with expiration dates ranging from 2010 to 2025 and compared their size and zeta potential. Since nanoparticle surface properties can affect infusion reactions, we conducted a dot blot immunoassay to measure complement C3 opsonization with ferumoxytol preparations. We observed differences in nanoparticle size and zeta potential between batches and a 2.5-fold variation in complement activation. Interestingly, older batches from 2010 showed more uniform size distribution and lower complement activation than some of the newer batches. This finding may be valuable to the nanomedicine community and regulatory authorities.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Advanced Characterization and Sample Preparation Strategies for Nanoformulations
by
Akanksha Nadkarni, Dhwani Rana, Nimeet Desai, Derajram Benival, Vishvesh Joshi, Sagar Salave and Dignesh Khunt
J. Nanotheranostics 2024, 5(3), 104-127; https://doi.org/10.3390/jnt5030008 - 14 Aug 2024
Cited by 1
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The escalating impact and remarkable progress of nanotechnology have shifted the paradigms of medicine and the healthcare system. Nanosystems have emerged, extensively holding the potential to advance disease diagnosis and treatment specificity. The extraordinary attributes imparted by nano-systems have helped in overcoming the
[...] Read more.
The escalating impact and remarkable progress of nanotechnology have shifted the paradigms of medicine and the healthcare system. Nanosystems have emerged, extensively holding the potential to advance disease diagnosis and treatment specificity. The extraordinary attributes imparted by nano-systems have helped in overcoming the limitations of conventional interventions to an extent and led to targeted therapy, to name one. The role of nanotechnology in diagnosis is another breakthrough in its appellation. This article aims to address the current characterization and sample preparation techniques for the analysis of nanosystems and provide insights into novel methodologies and in situ instrumentation that have eased sampling procedures.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessOpinion
Anti-Poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG) Antibodies: From Where Are We Coming and Where Are We Going
by
Dmitri Simberg and S. Moein Moghimi
J. Nanotheranostics 2024, 5(3), 99-103; https://doi.org/10.3390/jnt5030007 - 29 Jul 2024
Abstract
PEGylation technology confers stability and modulates the biological performance of a broad range of preclinical and clinical nanopharmaceuticals. However, the emerging PEG immunogenicity in the general population is thought to impact the efficacy and safety of PEGylated medicines. Despite this, the clinical significance
[...] Read more.
PEGylation technology confers stability and modulates the biological performance of a broad range of preclinical and clinical nanopharmaceuticals. However, the emerging PEG immunogenicity in the general population is thought to impact the efficacy and safety of PEGylated medicines. Despite this, the clinical significance of PEG immunogenicity is still not clear and remains debatable. By considering the strategic importance of the PEGylation technology in nanopharmaceutical engineering, we raise a number of critical questions and briefly discuss gaps in the knowledge of PEG immunogenicity and its clinical significance.
Full article
Open AccessReview
Paradoxical Roles of Carbon Nanotubes in Cancer Therapy and Carcinogenesis
by
Bohan Xu, Shunjie Wu, Yiyang Wang, Yuhe Ji, Shufeng Liang, Chunyan Wang and Xin Tian
J. Nanotheranostics 2024, 5(3), 84-98; https://doi.org/10.3390/jnt5030006 - 8 Jul 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Carbon nanotubes (CNTs), members of the nanomaterial family, are increasingly being used in consumer products and extensively studied for various biomedical applications. Due to their benign elemental composition, large surface area, and chemical and biological activities, CNTs demonstrate great potential in cancer therapy,
[...] Read more.
Carbon nanotubes (CNTs), members of the nanomaterial family, are increasingly being used in consumer products and extensively studied for various biomedical applications. Due to their benign elemental composition, large surface area, and chemical and biological activities, CNTs demonstrate great potential in cancer therapy, including drug delivery, imaging analysis, photothermal therapy, photodynamic therapy, and radiotherapy. However, there is still a major knowledge gap when it comes to transitioning from research to clinical applications. One of the important issues is that the biological toxicity of CNTs, especially in terms of carcinogenesis, and the underlying mechanisms are not fully understood. Therefore, a thorough evaluation of toxicity and the underlying mechanisms of carcinogenesis is essential to enable the wide application of CNTs. In this review, we summarize the recent progress of CNTs as multifunctional therapeutics in cancer therapy. Furthermore, a detailed discussion is provided on the carcinogenesis and potential mechanisms of CNTs. Finally, the review ends with further challenges and prospects for CNTs with the expectation of facilitating their broader utilization.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Nano-Enabled Colorimetric Assay for the Detection of Paracoccidioides lutzii: Advancing Diagnostics with Nanotechnology
by
Olavo O. Comparato Filho, Marcela A. Cândido, Aveline Ventura, Flavia V. Morais and Leandro Raniero
J. Nanotheranostics 2024, 5(3), 75-83; https://doi.org/10.3390/jnt5030005 - 26 Jun 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Deforestation is a common occurrence driven by agricultural expansion, urbanization, and infrastructure development. These activities often lead to increased human interaction with ecosystems, potentially exposing individuals to Paracoccidioides spores (P. brasiliensis and P. lutzii) found in the soil, resulting in Paracoccidioidomycosis
[...] Read more.
Deforestation is a common occurrence driven by agricultural expansion, urbanization, and infrastructure development. These activities often lead to increased human interaction with ecosystems, potentially exposing individuals to Paracoccidioides spores (P. brasiliensis and P. lutzii) found in the soil, resulting in Paracoccidioidomycosis (PCM). This fungal infection is endemic to specific regions in Latin America, such as Brazil, Colombia, Venezuela, and Argentina. Diagnosis typically involves a combination of clinical assessment, imaging techniques, and laboratory examinations. P. lutzii lacks the glycoprotein Gp43, a key antigenic protein utilized in serological tests for PCM diagnosis. In this study, a colorimetric test employing gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) and label-free methodology was employed for P. lutzii detection. The effectiveness of the label-free colorimetric test was assessed using a total of 100 samples. This detection was achieved through the amplification of the gp43 gene and the use of a specific probe (5′CAGGGGTGCG3′) in conjunction with AuNPs. The receiver operating characteristic curve was employed to assess the test, revealing that the method can accurately detect P. lutzii with a sensitivity of 100% and a specificity of 100%. The findings indicate a substantial impact on remote endemic regions attributable to the implementation of cost-effective diagnostic methodologies.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Titanium Dioxide-Based Nanoparticles to Enhance Radiation Therapy for Cancer: A Literature Review
by
Masao Nakayama, Hiroaki Akasaka, Ryohei Sasaki and Moshi Geso
J. Nanotheranostics 2024, 5(2), 60-74; https://doi.org/10.3390/jnt5020004 - 31 May 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Titanium dioxide nanoparticles (TiO2 NPs) have been investigated as one of the potential dose enhancement agents for radiation therapy. The role of TiO2 NPs as a photodynamic sensitiser has been well documented, but its sensitisation with X-rays is not highlighted. Unlike
[...] Read more.
Titanium dioxide nanoparticles (TiO2 NPs) have been investigated as one of the potential dose enhancement agents for radiation therapy. The role of TiO2 NPs as a photodynamic sensitiser has been well documented, but its sensitisation with X-rays is not highlighted. Unlike other metal NPs, such as gold NPs, the main challenge for TiO2 NPs as radiosensitisers is their low atomic number, resulting in a small cross-section for X-rays. This review summarises the results of current research in this area to explore the dose enhancement inflicted by TiO2 NPs, which could potentially be of great value in improving radiation therapy efficiency.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Unlocking the Potential of Gold as Nanomedicine in Cancer Immunotherapy
by
Panangattukara Prabhakaran Praveen Kumar, Maggie Lee and Taeho Kim
J. Nanotheranostics 2024, 5(2), 29-59; https://doi.org/10.3390/jnt5020003 - 30 Apr 2024
Cited by 1
Abstract
Nanotechnology advancements have resulted in many sensors and devices for biomedical applications. Among the various nanomaterials, gold nanoparticles (AuNPs), due to their size, shape, biocompatibility, and unique plasmonic property, are an excellent candidate for many biomedical applications. AuNPs, known for their easy surface
[...] Read more.
Nanotechnology advancements have resulted in many sensors and devices for biomedical applications. Among the various nanomaterials, gold nanoparticles (AuNPs), due to their size, shape, biocompatibility, and unique plasmonic property, are an excellent candidate for many biomedical applications. AuNPs, known for their easy surface modifications, robust nature, and photothermal activities, find application in drug delivery and cancer treatment studies. In this review, we are highlighting the recent trends in using AuNPs as nanomedicine for cancer immunotherapy. Cancer immunotherapy not only eliminates the primary tumors but also allows for the treatment of metastasis along with the recurrence of the tumor. AuNPs possess tissue-specific delivery functions that depend on the tunability in size and surface functionalization of AuNPs. AuNPs can be used to activate the tumor’s immune defense ability, or they can be used to enhance the anti-tumor immune response. Understanding the interaction of the tumor environment and nanobiomedicine is very important. In the present review, we give an idea of the mode of action of AuNPs and various combinations of therapies for cancer immunotherapy.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Interventional Nanotheranostics for Translational Nano-Immunotherapy)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Graphene Oxide Chemical Refining Screening to Improve Blood Compatibility of Graphene-Based Nanomaterials
by
Fabio Pieretti, Alessandro Moretto, Emanuele Papini and Regina Tavano
J. Nanotheranostics 2024, 5(1), 13-28; https://doi.org/10.3390/jnt5010002 - 20 Feb 2024
Abstract
Graphene oxide (GO) nanoparticles, due to their favorable water solubility, compared to graphene (GA), are a hot research topic in biomedical and pharmaceutical research. However, GO clinical translation may be complicated by its high surface/volume ratio enhancing the interaction with human blood components.
[...] Read more.
Graphene oxide (GO) nanoparticles, due to their favorable water solubility, compared to graphene (GA), are a hot research topic in biomedical and pharmaceutical research. However, GO clinical translation may be complicated by its high surface/volume ratio enhancing the interaction with human blood components. In fact, GO’s bi-dimensional nature and strong negative charge may lead to severe biological effects, such as thrombogenicity and immune cell activation. This study explores the impact of further GO surface chemical modulation on major adverse effects: blood plasma coagulation and hemolysis. To this aim, we refined GO nanoparticles by fine-tuned reduction chemistry, esterification and introduction of negative or positive charges. With this approach, we were able to mitigate plasma coagulation and hemolysis at variable degrees and to identify GO derivatives with improved biocompatibility. This opens the door to the progress of graphene-based nanotheranostic applications.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Carbon Nanomaterials as Nano-Theranostic Tools in Disease Treatment)
►▼
Show Figures
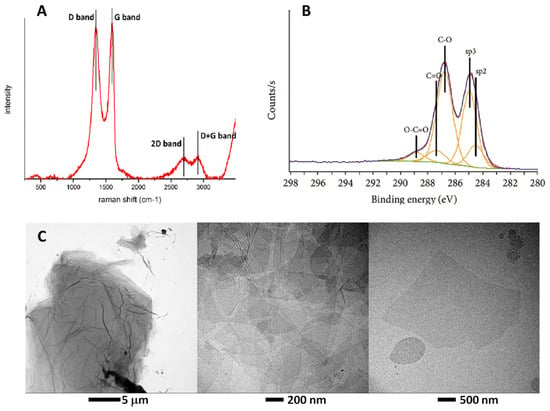
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
The Role of Fullerenes in Neurodegenerative Disorders
by
Daisy L. Wilson, Jyoti Ahlawat and Mahesh Narayan
J. Nanotheranostics 2024, 5(1), 1-12; https://doi.org/10.3390/jnt5010001 - 16 Jan 2024
Cited by 1
Abstract
The use of carbon nanomaterials including fullerenes, carbon nanotubes, carbon nano-onions, carbon dots and carbon quantum dots for environmental applications has increased substantially. These nanoparticles are now used in the development of sensors and switches, in agriculture as smart fertilizers and in the
[...] Read more.
The use of carbon nanomaterials including fullerenes, carbon nanotubes, carbon nano-onions, carbon dots and carbon quantum dots for environmental applications has increased substantially. These nanoparticles are now used in the development of sensors and switches, in agriculture as smart fertilizers and in the biomedical realm for cancer therapy intervention, as antioxidants, in gene delivery and as theranostics. Here, we review the role of fullerenes as neuroprotectants. Their sp2 hybridized architectures and ability to intervene in the soluble-to-toxic transformation of amyloidogenic trajectories is highlighted here, along with other physico–chemical properties that impact interventional efficacy. Also highlighted are drawbacks that need to be overcome and future prospects.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Advances and Innovations in Theranostic Nanobiomaterials)
►▼
Show Figures
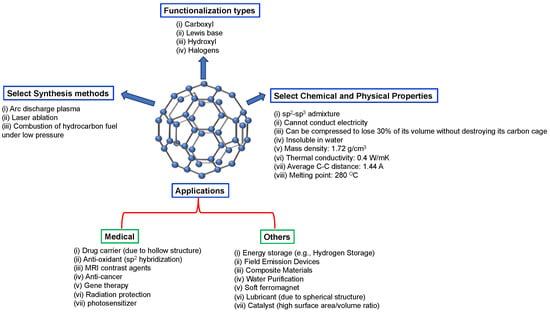
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Efficacy of 15 nm Gold Nanoparticles for Image-Guided Gliosarcoma Radiotherapy
by
Elette Engels, Michael Lerch, Stéphanie Corde and Moeava Tehei
J. Nanotheranostics 2023, 4(4), 480-495; https://doi.org/10.3390/jnt4040021 - 26 Oct 2023
Cited by 2
Abstract
Targeted brain cancer treatments are sorely needed to improve long-term prognosis, particularly for gliosarcoma and glioblastoma patients. Gold nanoparticles (GNPs) have unique properties including high atomic number, biocompatibility, and small size for cancer cell internalization. GNPs are consequently an ideal candidate for improved
[...] Read more.
Targeted brain cancer treatments are sorely needed to improve long-term prognosis, particularly for gliosarcoma and glioblastoma patients. Gold nanoparticles (GNPs) have unique properties including high atomic number, biocompatibility, and small size for cancer cell internalization. GNPs are consequently an ideal candidate for improved cancer targeting using image-guided radiotherapy. This work investigated 15 nm AuroVistTM GNPs for image-guided gliosarcoma radiotherapy and identified optimum GNP concentrations. The GNPs were found to be 15–20 nm using optical surface plasmon resonance absorption, with a (41.3 ± 0.3) nm hydrodynamic diameter. Confocal imaging showed that 50–500 µg/mL of the GNPs was well-internalized into the 9L cells within 24–48 h. γ-H2AX assays showed that 50–500 µg/mL of the GNPs radiosensitized the 9L cells irradiated with 125 and 150 kVp X-rays. However, only 500 µg/mL of the GNPs produced significant long-term dose enhancement with 150 kVp X-rays (with a sensitization enhancement ratio at 10% survival of 1.43, and 1.13 with 50 µg/mL) using clonogenic assay. CT imaging of the GNPs in the 9L tumors in Fischer rats further showed that GNP concentrations above 500 µg/mL were required to distinguish the tumor from the brain, and the GNPs were detected 48 h after injection. These promising results indicate that the GNPs can be used for selective gliosarcoma treatment with image-guided X-ray radiotherapy at concentrations above 500 µg/mL.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Emerging Strategies in Nanomedicine)
►▼
Show Figures
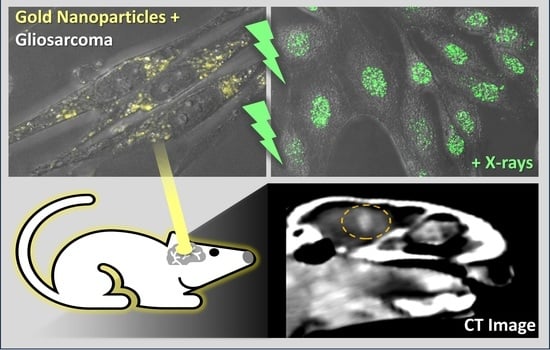
Graphical abstract
Highly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Topic in
Biomedicines, JNT, Pharmaceutics, Polymers, Nanomaterials, Pharmaceuticals, Biophysica
Applications of Polymers and Polymer Nanomaterials in Drug Delivery and Nanomedicine
Topic Editors: Stanislav Rangelov, Emi HaladjovaDeadline: 31 May 2025
Topic in
Biomedicines, Cancers, JCM, Nanomaterials, Pharmaceutics, JNT
Application of Nanomaterials and Nanobiotechnology in Cancer
Topic Editors: Ayan Kumar Barui, Susheel Kumar NethiDeadline: 31 May 2026

Conferences
Special Issues
Special Issue in
JNT
Nanozymes: New Advances in the Next Generation of Enzyme-Like Nanosystems
Guest Editors: Herman Sander Mansur, Alexandra Ancelmo Piscitelli MansurDeadline: 28 February 2025
Special Issue in
JNT
Nanoengineered Solutions: Advancements in Targeted Drug Delivery and Theranostics
Guest Editor: Tamer ElbayoumiDeadline: 31 May 2025








