Cities and Infrastructure
A topical collection in Buildings (ISSN 2075-5309). This collection belongs to the section "Construction Management, and Computers & Digitization".
Viewed by 63857Editors
Interests: sensing technologies; AI; machine learning; advanced GIS; BIM; digital twins; city analytics methods; digital construction; smart cities; smart construction
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Interests: transport planning; travel behaviour; smart transport; machine learning applications
Interests: BIM; ICT applications in construction industry; digital twins; construction sustainability; women in construction; construction health and safety
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
This Topical Collection is interdisciplinary and intends to cover a wide range of issues related to our cities and infrastructure. Rapid urbanisation and the advancement of digital technologies provide opportunities to transform cities into smarter, more sustainable and resilient environments. Sustainable development goals (SDGs) provide directions for making cities “inclusive, safe, resilient and sustainable” (SDG No. 11) and building “resilient infrastructure, [that] promote[s] inclusive and sustainable industrialization and foster innovation” (SDG No. 9).
This Topical Collection seeks papers, reports, and review articles that present novel tools, advanced methodologies, or case studies devoted to bridging the gaps between the theory and practices in cities and infrastructure development and SDGs.
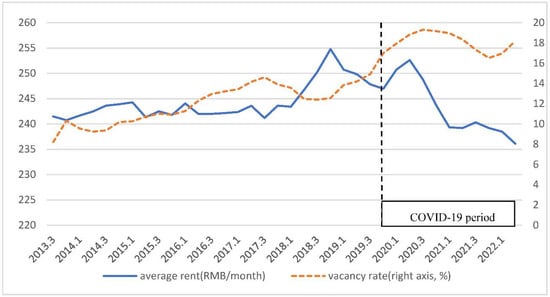
COVID-19 has presented significant changes and challenges in the ways we live, communicate, carry out tasks in cities, and develop our infrastructure projects. In this Topical Collection, we are also keen to share the lessons learnt from adopting digital technologies in managing and planning cities and infrastructure, and the applied analytics on city and infrastructure data before and during the pandemic, which provide better insights on the changes of patterns and activities during this extraordinary period.
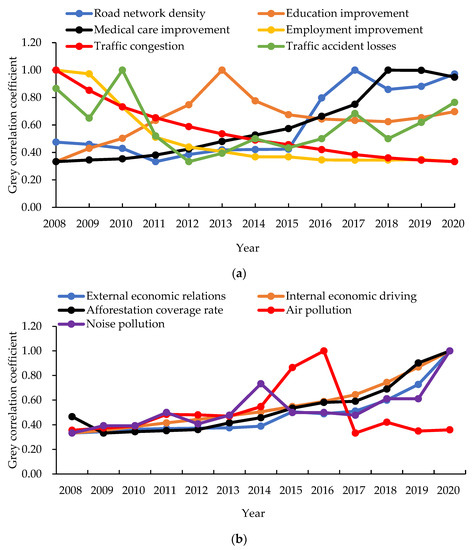
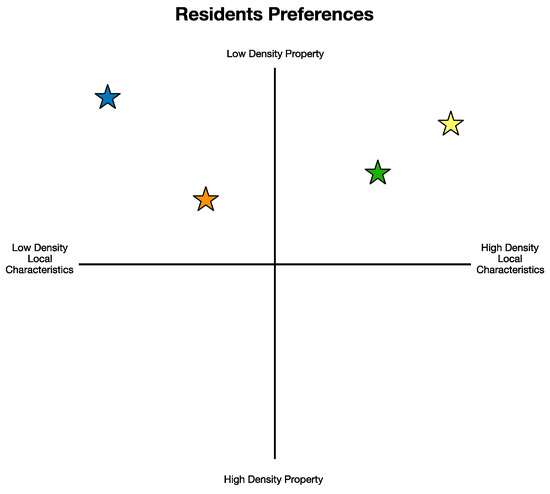
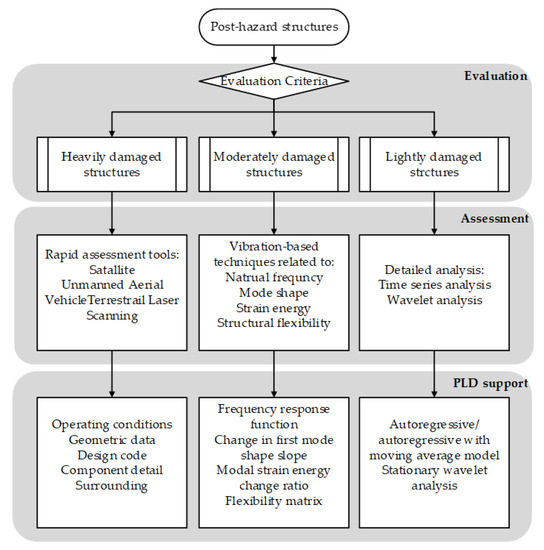
Potential topics for this Topical Collection include but are not limited to cities, transport, construction challenges, application of digital technologies and information systems such as GIS, BIM, digital twin, visualisation methods, machine learning, computer vision, sensing technologies, big geospatial data management for improving smart cities, and other management topics related to cities and infrastructure and the spatiotemporal changes of cities during COVID-19.
Dr. Sara Shirowzhan
Dr. Brian Lee
Dr. Cynthia Changxin Wang
Collection Editors
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Buildings is an international peer-reviewed open access monthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2600 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- BIM and GIS applications
- sustainable development goals
- construction management
- infrastructure management
- city planning
- transport planning
- city and building analytics
- advances in digital technologies for the built environment
- machine learning applications
- digital twins and Internet of Things
- built environment—challenges and trends
- spatiotemporal changes and analysis
- COVID-19—disruptions and effects