Natural Killer Cells, the Terminator of Aggressive Tumors: Development, Function Source and Effective Therapeutics
A special issue of Cells (ISSN 2073-4409). This special issue belongs to the section "Cellular Immunology".
Deadline for manuscript submissions: closed (15 May 2023) | Viewed by 5255
Special Issue Editors
2. Division of Advanced Prosthodontics and Weintraub Center for Reconstructive Biotechnology, UCLA School of Dentistry, Los Angeles, CA 90095, USA
3. The Jonsson Comprehensive Cancer Center, UCLA School of Dentistry and Medicine, Los Angeles, CA 90095, USA
Interests: natural killer cells; differentiation; cancer stem cells; cell death; NK therapeutics
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Interests: natural killer cells; oral cancer; pancreatic cancer; cancer immunotherapy; humanized-BLT mice; osteoclasts; cell expansion; T cells; osteonecrosis of jaw; probiotic bacteria; chemotherapy; bisphosphonates; monocytes; dendritic cells; clinical trials; NAC
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Special Issue Information
Dear Colleagues,
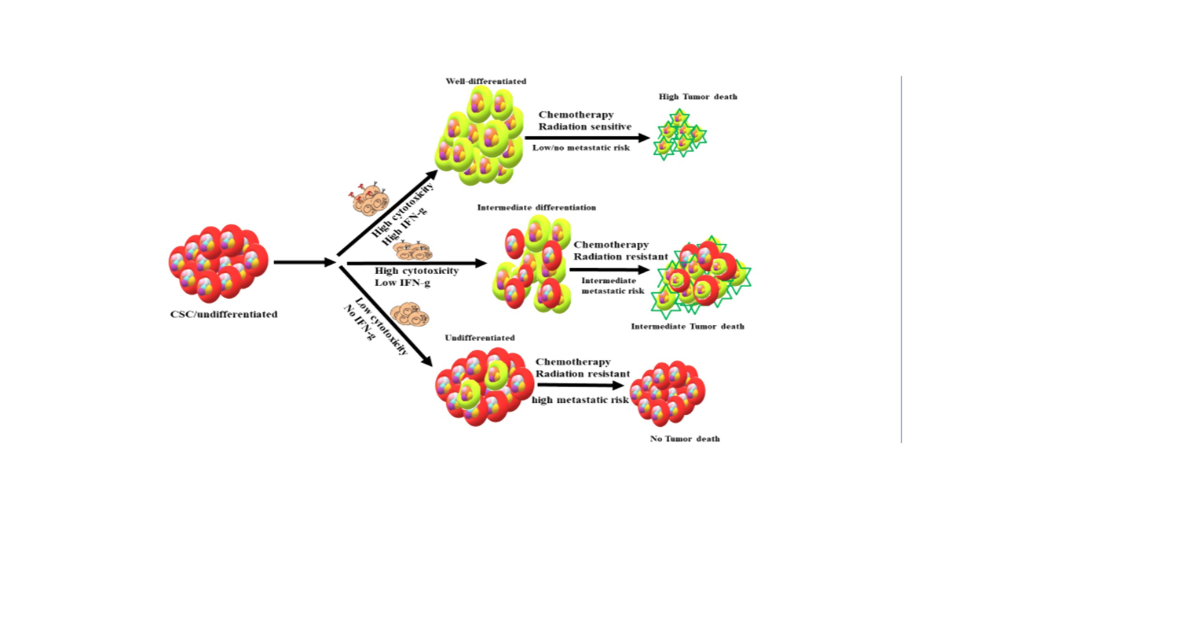
We have long known about the important roles of NK cells in cancer therapy; however, only recently have we started to appreciate the scope of the significance of these cells in tumor therapy. Identification of cancer stem cells or poorly differentiated tumors as prime targets of NK cells has finally shown the indispensable role of these cells in cancer therapy. In addition, successful cancer therapy will require restoration of both NK and T cell functions in cancer patients, since each are likely designed to target different subsets of tumor cells with opposing degrees of cellular differentiation with differing expression of MHC class I. NK cells mediate successful control of the tumor cells by their direct cytolytic effect and/or through antibody-mediated ADCC or indirectly through differentiation of tumor cells by IFN-g, which increases the efficacy of chemotherapeutic and radiotherapeutic targeting strategies (Fig. 1). Moreover, strategies should be designed to allow maintenance of good NK expansion and function in cancer patients, since not only are they capable of expanding cancer suppressing CD8+ T cells, but they are also key in limiting the expansion of immune suppressive cells such as TAMs, Tregs, MDSCs, MSCs, and fibroblasts. Mature allogeneic activated NK cells can be combined with other immunotherapeutic strategies such as oncolytic viruses, ADCC-inducing antibodies, check point inhibitors, CAR-T, CAR-NK, and chemotherapeutic and radiotherapeutic strategies for the ultimate goal of tumor eradication.
Dr. Anahid Jewett
Dr. Kawaljit Kaur
Guest Editors
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the special issue website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Cells is an international peer-reviewed open access semimonthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2700 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- cancer stem cells/poorly differentiated tumors
- MHC class I
- activating NK receptors
- ADCC
- development
- NK function
Benefits of Publishing in a Special Issue
- Ease of navigation: Grouping papers by topic helps scholars navigate broad scope journals more efficiently.
- Greater discoverability: Special Issues support the reach and impact of scientific research. Articles in Special Issues are more discoverable and cited more frequently.
- Expansion of research network: Special Issues facilitate connections among authors, fostering scientific collaborations.
- External promotion: Articles in Special Issues are often promoted through the journal's social media, increasing their visibility.
- e-Book format: Special Issues with more than 10 articles can be published as dedicated e-books, ensuring wide and rapid dissemination.
Further information on MDPI's Special Issue polices can be found here.







