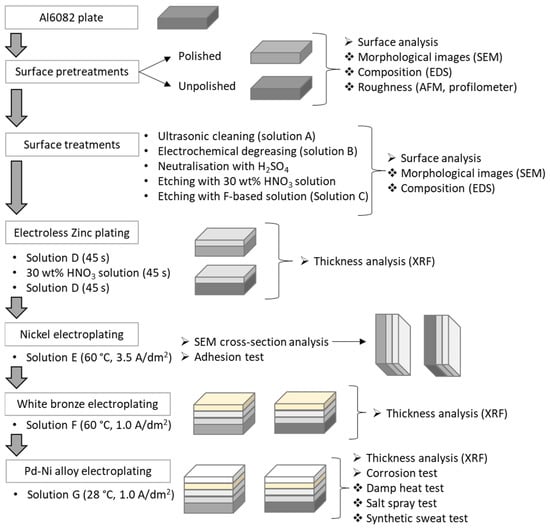
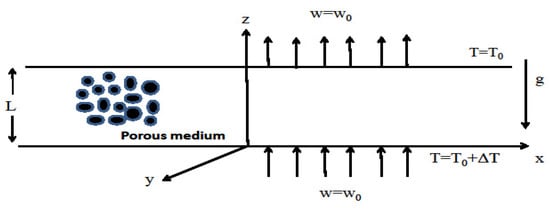
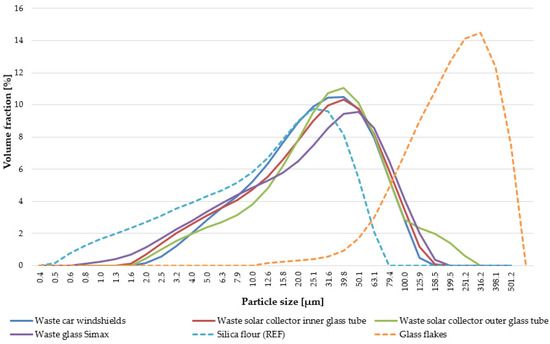
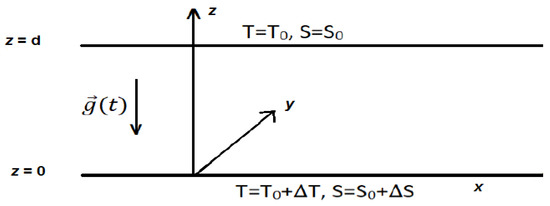
Feature Paper Collection for Topic Editors and Invited Scholars in Coatings
A topical collection in Coatings (ISSN 2079-6412). This collection belongs to the section "Corrosion, Wear and Erosion".
Viewed by 24131Editor
Interests: heat and mass transfer; fluid mechanics; modeling and simulation; convection; nanofluids; porous media; thermal radiation; electronics cooling
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
This Feature Paper Collection for Topic Editors and Invited Scholars in Coatings for Topic Editors from the Coatings journal (ISSN 2079-6412) is dedicated to the publication and discussion of research articles, letters, reviews, and communications on all aspects of science and engineering of coatings, thin and thick films, surfaces, and interfaces.
We welcome the submission of reviews and outstanding articles to this Feature Paper Collection to improve current knowledge of coatings, thin and thick films, surfaces, and interfaces. Manuscripts for this important Feature Paper Collection of Coatings will be accepted by the editorial office, the Topic Editor, and Editorial Board Members by invitation only.
- Thin and thick films;
- Processes for coating deposition and modification;
- Characterization techniques;
- Functional, protective, and decorative coatings;
- Dyes, pigments, and their intermediates;
- Wear, corrosion, erosion;
- Coatings for high temperature;
- Film materials for packaging;
- Applied surface science;
- Adsorption, adhesion, functionalization;
- Fundamental and functional properties of surface and interfaces;
- Theoretical and computational modeling of surfaces and interfaces;
- High surface area systems: colloids, nanoparticles, large interfaces.
Prof. Dr. Mikhail Sheremet
Collection Editor
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Coatings is an international peer-reviewed open access monthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2600 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.