Teaching Innovation in Higher Education: Areas of Knowledge
Share This Topical Collection
Editors
 Dr. José Jesús Gázquez Linares
Dr. José Jesús Gázquez Linares
 Dr. José Jesús Gázquez Linares
Dr. José Jesús Gázquez Linares
E-Mail
Website
Collection Editor
1. Department of Psychology, Universidad de Almería, Calle Universidad de Almería, 04120 Almería, Spain
2. Universidad Autónoma de Chile, Av. Pedro de Valdivia 425, Providencia, Región Metropolitana, Chile
Interests: psychology of sustainability; engagement work; occupational health; psychosocial; organizational environments; personality; aggressive behavior; emotional intelligence; burnout; public health
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
 Dr. María del Carmen Pérez-Fuentes
Dr. María del Carmen Pérez-Fuentes
 Dr. María del Carmen Pérez-Fuentes
Dr. María del Carmen Pérez-Fuentes
E-Mail
Website
Collection Editor
Department of Psychology, Universidad de Almería, Almería, Andalucía, Spain
Interests: psychology of sustainability; engagement work; occupational health; psychosocial; organizational environments; personality; aggressive behavior; emotional intelligence; burnout; alcohol; tobacco; multilevel analysis; emotions; public health
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
Teaching and learning has undergone, and is undergoing, changes motivated by technological advances, which are making new teaching tools and environments possible, as well as changes in teaching paradigms. For decades, innovation and improving quality in teaching have been part of the educational policies of higher education. The construction of an innovative teaching culture in higher education that facilitates or ensures better-quality education is an essential part of today’s universities.
Several innovation types may be differentiated, depending on the depth of the transformation proposed: technical and reflexive and/or critical innovations. The proposal for this Special Issue is framed within this context, in the various areas of knowledge in the university.
Dr. José Jesús Gázquez Linares
Dr. María del Carmen Pérez-Fuentes
Dr. María del Mar Simón Márquez
Collection Editors
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. European Journal of Investigation in Health, Psychology and Education is an international peer-reviewed open access monthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript.
The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 1400 CHF (Swiss Francs).
Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's
English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- teaching
- innovation
- higher education
- areas of knowledge
Published Papers (12 papers)
Open AccessArticle
Instructional Videos for Students in Dental Medicine: Rules of Design and Correlations with Their Habits as Internet Consumers
by
Cristina Gena Dascalu, Claudiu Topoliceanu and Magda Ecaterina Antohe
Cited by 1 | Viewed by 1077
Abstract
Multimedia resources, such as instructional videos, are currently enjoying a certain popularity in the training programs for medical and dental students. The major challenge is to create such resources with quality content that is approved by students. In order to answer this challenge,
[...] Read more.
Multimedia resources, such as instructional videos, are currently enjoying a certain popularity in the training programs for medical and dental students. The major challenge is to create such resources with quality content that is approved by students. In order to answer this challenge, it is imperative to find out which features of instructional videos are considered to be necessary and useful by students, thus being able to excite them, to hold their attention, and to stimulate them in learning with pleasure. Aim: We investigated the opinions of a sample of 551 students from four medical universities in Romania, in order to identify the students’ preferred characteristics in instructional videos, both globally and comparatively on genders and age groups and also according to their general preferences for using internet services. Material and methods: We used univariate (hypothesis testing) and multivariate (two-step clustering) data analysis techniques and revealed three clusters of students, primarily determined by their perceptions of the visual appearance of the instructional videos. Results: The structure of the clusters by gender and age group was relatively similar, but we recorded differences associated with the students’ expressed preferences for certain internet services compared to others. The first identified cluster (35.4% of the cases) contains students who prefer instructional videos to contain images used only for aesthetic purposes and to fill the gaps; they use internet services mainly for communication. The second cluster of students (34.8%) prefers videos designed as practical lessons, using explanatory drawings and diagrams drawn at the same time as the explanations; they also use internet services mainly for communication. The last cluster of students (29.8%) prefer videos designed as PowerPoint presentations, with animated pictures, diagrams, and drawings; they are slightly younger than the others and use internet services mainly for information and communication, but also for domestic facilities. Conclusions: The students’ preferences for certain features of instructional videos depend not only on gender and age but are also related to their developmental background and general opinions about modern technologies.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Using the DREAM Methodology for Course Assessment in the Field of ICT-Enabled Education for Sustainability
by
Vassilios Makrakis
Cited by 6 | Viewed by 1995
Abstract
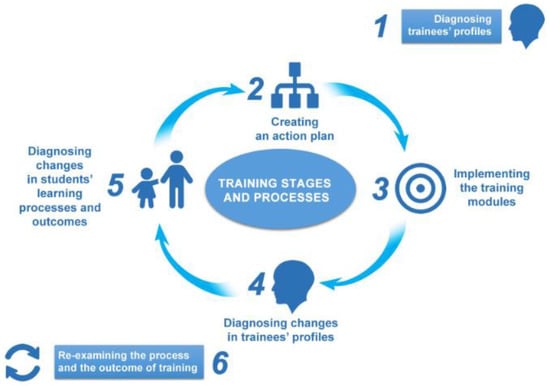
This study explores the application of the DREAM methodology for course assessment in three South East Asian universities aiming to embed sustainability and sustainable development goals (SDGs) in multiple academic disciplines enabled by information and communication technologies (ICTs). A mixing of content and
[...] Read more.
This study explores the application of the DREAM methodology for course assessment in three South East Asian universities aiming to embed sustainability and sustainable development goals (SDGs) in multiple academic disciplines enabled by information and communication technologies (ICTs). A mixing of content and thematic analysis was used, which aligns with the underpinning philosophy of the Diagnosing, Reviewing/Reflecting, Explaining, Assessing, Managing (DREAM) methodology. The DREAM methodology integrates five processes, starting from diagnosing, to reviewing/reflecting, explaining, assessing, and, finally, managing. Results show that merging semantic and latent themes has contributed to uncovering what messages students’ narratives convey and provided a space for focusing both on the surface and explicit meanings of the data as well as on theory building and policy making. They also show the effectiveness of the DREAM methodology in constructing new knowledge and generating meaningful interpretations and suggestions to teacher educators and other academic teaching staff, as well as higher education institutions’ policymakers and planners.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
The Therapist’s Intuition and Responsiveness: What Makes the Difference between Expert and in Training Gestalt Psychotherapists
by
Margherita Spagnuolo Lobb, Federica Sciacca, Serena Iacono Isidoro and Santo Di Nuovo
Cited by 7 | Viewed by 3998
Abstract
This study aims to investigate the presence of intuition and responsiveness in early students and in experienced students and psychotherapists, which is understood as the ability to integrate bodily sensitivity and cognition of what is experienced with the patient (aesthetic relational knowing—ARK). The
[...] Read more.
This study aims to investigate the presence of intuition and responsiveness in early students and in experienced students and psychotherapists, which is understood as the ability to integrate bodily sensitivity and cognition of what is experienced with the patient (aesthetic relational knowing—ARK). The study compares how the therapist’s felt sense of the phenomenological intersubjective field and aesthetic relational competence differs between a group of experienced students and psychotherapists and a group of beginners. The sample consisted of 128 participants (20 M; 108 F), finally divided into two groups: “experienced students and psychotherapists” and “beginners”. The Aesthetic Relational Knowledge Scale (ARKS), a questionnaire consisting of 58 items targeting three factors (empathy, body awareness, and resonance), was administered. Statistical analyses were conducted to assess (i) differences between the two groups (through Student’s t and Cohen’s d for effect sizes), (ii) the influence of the level of training for each ARK factor using analyses of covariance for testing the possible influence of demographic variables, and (iii) logistic regressions to compare the influence of the three factors of the ARK model on the group variable with groups as a categorical variable. Significant differences between the two groups were found in body awareness and resonance. Body awareness was found to be the variable best discriminating between the beginners and the experienced students and psychotherapists. Despite being non-significant, there is a tendency suggesting that empathy appears more relevant at the beginning of training. The study shows the importance of training for the development of the therapist’s intuition and responsiveness, especially in the factors of body awareness and resonance. The results indicate the importance of assessing and supporting the aesthetic and field resonance of therapists in training, increasing quality and depth of the therapist’s responsiveness. This study is limited by a correlational design using self-report and on a limited sample, but it shows that the ARKS can monitor the effectiveness of training related to Gestalt therapeutic competencies.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
Pharmacy Students’ Mental Health and Resilience in COVID-19: An Assessment after One Year of Online Education
by
Dalal Hammoudi Halat, Samar Younes, Jihan Safwan, Zeina Akiki, Marwan Akel and Mohamad Rahal
Cited by 18 | Viewed by 3229
Abstract
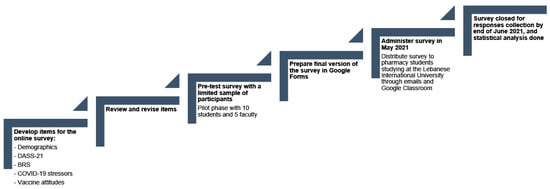
COVID-19 has impacted mental health and affected education due to the shift to remote learning. The purpose of the current study was to assess the mental health of pharmacy students one year following the onset of the pandemic. A descriptive cross-sectional questionnaire was
[...] Read more.
COVID-19 has impacted mental health and affected education due to the shift to remote learning. The purpose of the current study was to assess the mental health of pharmacy students one year following the onset of the pandemic. A descriptive cross-sectional questionnaire was distributed to pharmacy students. The severity of depression, anxiety, and stress was assessed by the Depression Anxiety Stress Scale (DASS-21), and resilience was assessed by the Brief Resilience Scale (BRS). COVID-19-related economic, educational, and health stressors, and students’ vaccine attitudes were surveyed. Descriptive, bivariate, and multivariable analysis were used, and a
p-value of <0.05 was considered significant. A total of 561 students participated; 37% had mild-to-moderate depression, 37% had severe-to-extremely-severe anxiety, and 52% demonstrated normal stress levels. Severe depression, anxiety, and stress were associated with smoking and feeling isolated due to COVID-19. Around 40% of students had low resilience, associated with smoking, being in the third or fourth year of pharmacy study, and the consumption of caffeinated beverages. The mean score of satisfaction with online learning was 60.3 ± 21.3%. Only 5% of participants were vaccinated, of which 87% trusted the benefits of vaccines and their role in controlling the pandemic. One year after the onset of COVID-19, depression, anxiety, stress, and low resilience were observed among pharmacy students; the investigation of the long-term mental effects of the pandemic on university students is warranted.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Programs of Access to Pedagogy: Diagnostic of Its Design in Chilean Private Universities
by
Karen Núñez-Valdés, Neliot Villena Olivares, Cristian Villegas Dianta, Marisol López Núñez and Antonio Castillo-Paredes
Cited by 2 | Viewed by 2975
Abstract
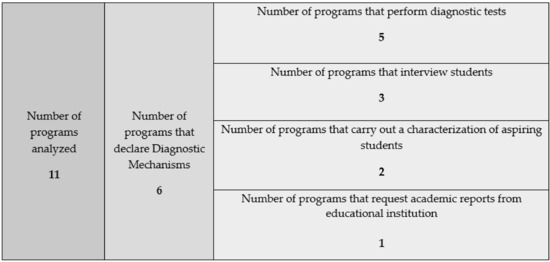
The objective of this study is to describe and analyze comparatively the Programs of Access to Pedagogies (PAP) of Chilean private universities, in order to know how this policy has been developed in this type of institution. After an exhaustive and meticulous treatment
[...] Read more.
The objective of this study is to describe and analyze comparatively the Programs of Access to Pedagogies (PAP) of Chilean private universities, in order to know how this policy has been developed in this type of institution. After an exhaustive and meticulous treatment of the information contained in the 11 private university programs in Chile, categories were created for later analysis, based on the criteria contained in the programs. The results were analyzed based on pre-established analytical criteria, within which three to seven categories were found that allow the description and analysis of the PAPs. Among these, categories related to “Development of skills”, “Pedagogical vocation”, “Promotion of equity”, “Academic performance”, “Transversal skills” and “Academic support” stand out, being found in eight programs of the 11 analyzed. Although the Programs of Access to Pedagogy careers, established objectives, eligibility criteria, permanence criteria, camping, among others, follow the law, these programs have limitations, due to their heterogeneous construction, which translates into the interpretation of the laws, for which a series of challenges emerge, all of them associated with the search for strategies to strengthen the attraction and training of future good teachers.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Linguistic–Cultural Mediation in Asylum and Refugee Settings and Its Emotional Impact on Arabic–Spanish Interpreters
by
Bachir Mahyub-Rayaa and Moulay-Lahssan Baya-Essayahi
Cited by 3 | Viewed by 2415
Abstract
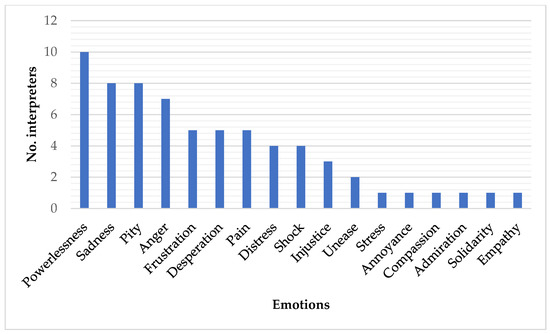
Emotional factors in linguistic–cultural mediation have attracted the attention of prior literature for a number of decades, both regarding the cognitive processes involved in language interpreting and the impact of stress and emotion on the performance of interpreters. However, research has not yet
[...] Read more.
Emotional factors in linguistic–cultural mediation have attracted the attention of prior literature for a number of decades, both regarding the cognitive processes involved in language interpreting and the impact of stress and emotion on the performance of interpreters. However, research has not yet been replicated in the Arabic–Spanish pair, despite it being one of the combinations most requested by public services in Spain and Europe. Methodology: An exploratory study conducted by an anonymous online 17-item survey was carried out in order to discover the perception of Arabic–Spanish interpreters in asylum and refugee settings about the emotional impact of their job. Out of 30 contacted, 23 active interpreters completed the survey. Results: The answers showed that all of the interpreters had been exposed to situations that had emotionally impacted them. Triggering situations and a list of negative emotions were collected. Discussion: Direct and indirect implications of the referred emotional episodes and their consequences on the performance of the interpreters were analysed and discussed. Conclusions: Linguistic–cultural mediation in these settings exposes interpreters to harsh stories that trigger mostly negative emotions. These professionals lack psychological support; thus, they are forced to deal individually with each situation, without taking into account the possible consequences on their work and their physical and mental health.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Effectiveness of a Program to Improve Attention towards Affective-Sexual, Bodily and Gender Diversity in University Students
by
Francisco Manuel Morales-Rodríguez
Cited by 3 | Viewed by 2415
Abstract
It is necessary for the university environment to contribute to the improvement of the attention paid to affective-sexual, bodily, and gender diversity. This research deals with how, by means of a teaching innovation program, competences for affective-sexual diversity were developed. Specifically, negative attitudes
[...] Read more.
It is necessary for the university environment to contribute to the improvement of the attention paid to affective-sexual, bodily, and gender diversity. This research deals with how, by means of a teaching innovation program, competences for affective-sexual diversity were developed. Specifically, negative attitudes towards diversity, knowledge, and degree of empathy on these issues before and after the implementation of the program are compared. The degree of satisfaction, perceived usefulness, and fulfillment of the objectives proposed in the program were also evaluated. An ex post facto design was used. The participants in this study were 129 students belonging to Educational Sciences and Psychology, out of 2400 who benefited from the innovation program. The results showed an increase in competences related to the attention to diversity, with the improvement of attitudes and knowledge about affective-sexual diversity after the application of the program. It is concluded that this type of innovation program, with quality training, contributes to the improvement of coexistence and the prevention of gender violence in university classrooms, eliminating stereotypes and negative attitudes towards diversity.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
Physical Spaces in Higher Education as Scenarios of Learning Innovation: Compositional and Formative Synergies among Architecture, Music, and Fashion
by
Pablo Campos, Laura Luceño and Carlos Aguirre
Cited by 2 | Viewed by 2421
Abstract
Learning innovation is a positive approach on the contemporary higher education international stage. This article stresses the need to devise physical spaces that are also innovative. For that purpose, using a qualitative methodology, we investigated recent trends based on the synergies between certain
[...] Read more.
Learning innovation is a positive approach on the contemporary higher education international stage. This article stresses the need to devise physical spaces that are also innovative. For that purpose, using a qualitative methodology, we investigated recent trends based on the synergies between certain creative disciplines: architecture, music, and fashion. The comparison was based on compositional features and formative dimension. Using a qualitative methodological comprehensive approach, a set of case studies was analysed. The findings show the usefulness of activating these synergies as effective strategies when enriching educational processes in different ways. Six cases of excellence wherein university physical spaces reached levels of innovation were studied, representing relevant transfers among the three disciplines. The text presents examples that show the educational consequences in the establishment of those synergies, in terms of both composition (music–architecture) and the activation of heritage sites in the city as venues of learning innovation (fashion–architecture). The basic conclusions were based on the fact that the increase in teaching and spatial creativity that emanates from said synergies among the three disciplines can be potentially extrapolated to other areas of knowledge.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Perceptions and Degree of Satisfaction with the Health Sciences University Educational Community Regarding the Measures Adopted for the Prevention of COVID-19 in the Academic Year 2020/2021
by
Óscar Rodríguez-Nogueira, Raquel Leirós-Rodríguez, Enedina Quiroga-Sánchez, Mª José Álvarez-Álvarez and Lorena Álvarez-Barrio
Cited by 6 | Viewed by 2765
Abstract
The COVID-19 pandemic caused the start of the academic year 2020/2021 to be conditioned by health and safety regulations. The present research was defined with the aim of analyzing the degree of satisfaction and perceptions on the establishment of bubble groups and pairs
[...] Read more.
The COVID-19 pandemic caused the start of the academic year 2020/2021 to be conditioned by health and safety regulations. The present research was defined with the aim of analyzing the degree of satisfaction and perceptions on the establishment of bubble groups and pairs and on the use of audiovisual platforms for the development of theoretical and practical university teaching in three degrees of health sciences. A cross-sectional descriptive study was carried out on a representative sample of students and teachers of health sciences in Ponferrada (
n = 285). Specific questionnaires designed for this study were completed virtually during April and May 2021. The results indicate that that satisfaction was moderate–high. The perception of the influence of bubble pairs on the quality of teaching can be interpreted as very low. These results increase with the age and academic and professional experience of students and faculty members, respectively. However, the participants belonging to physiotherapy considered that the quality of teaching had worsened much more compared to their counterparts in nursing and podiatry.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Multivariate Analysis of Attitudes, Knowledge and Use of ICT in Students Involved in Virtual Research Seedbeds
by
Magda Alejandra Martinez-Daza, Alfredo Guzmán Rincón, Jader Alexis Castaño Rico, Nuria Segovia-García and Harvey Yesid Montilla Buitrago
Cited by 10 | Viewed by 4238
Abstract
The incorporation of information and communication technologies (ICTs) in higher education has been carried out in a transversal manner within the curriculum, and the processes of formative research in both face-to-face and virtual programmes are not an exception to this process. In this
[...] Read more.
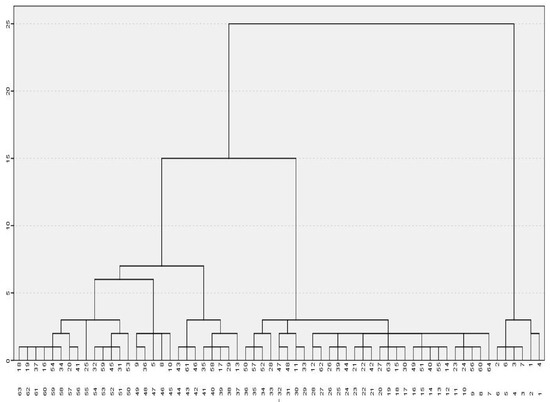
The incorporation of information and communication technologies (ICTs) in higher education has been carried out in a transversal manner within the curriculum, and the processes of formative research in both face-to-face and virtual programmes are not an exception to this process. In this context, it is recognised that students’ perceptions of the inclusion of technologies in the classroom can influence their teaching and learning process; however, they have not been widely addressed in multiple settings including research seedbeds. Thus, this paper aims to identify such perceptions represented in the attitudes, knowledge and uses of ICTs in students ascribed to the research seedbed in a virtual business administration programme of an Institution of Higher Education located in Colombia. For its fulfillment, the ACUTIC scale was applied to a sample of 65 students in order to identify these perceptions through a hierarchical cluster analysis, a single factor analysis of variance (ANOVA) test, a post hoc Tukey method and a factor analysis. The main result is that attitudes, knowledge and use of ICTs are varied and they can be represented in three clusters. In general, the attitude towards the incorporation of technologies in the research seedbed is positive; however, there is a gap in terms of knowledge and use, especially of those tools oriented to the disciplinary field and research.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessReview
Projection of E-Learning in Higher Education: A Study of Its Scientific Production in Web of Science
by
Jesús López-Belmonte, Adrián Segura-Robles, Antonio-José Moreno-Guerrero and María-Elena Parra-González
Cited by 29 | Viewed by 5039
Abstract
E-learning is conceived as a purely virtual training approach. Different learning styles have been proliferated in recent years, especially now, due to the impact of COVID-19 in the educational field. The aim of this study is to discover the evolution of e-learning in
[...] Read more.
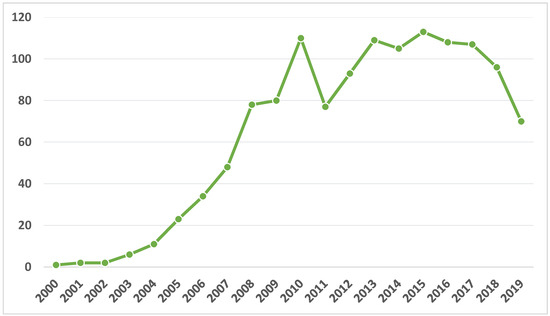
E-learning is conceived as a purely virtual training approach. Different learning styles have been proliferated in recent years, especially now, due to the impact of COVID-19 in the educational field. The aim of this study is to discover the evolution of e-learning in higher education (ELHI) in scientific literature indexed on the Web of Science. Co-word analysis and bibliometric analysis was performed. A total matrix of 1261 documents was analyzed through SciMAT software. The results revealed that studies on ELHI are written in English and presented by conference papers. The main source of publication for the conferences is EDULEARN proceedings, while the journal source is
Procedia-
Social and Behavioral Sciences. Spain is the country with the highest volume of production. It is concluded that research on ELHI use does not have an established line of research, due to its recent creation and the lack of related research. The bibliometric analysis specifies that the research is oriented towards knowing the level of acceptance and application of the pedagogical method in the teaching and learning processes.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Reading Motivation, Alcohol and Drug Use in Future Teachers in Preschool and Primary School
by
María de la Rocha Díaz, Inmaculada Méndez and Cecilia Ruiz-Esteban
Viewed by 2568
Abstract
Future teachers will have to develop the reading habit in their students, as this is an essential factor in schoolchildren. The lack of reading motivation among young people and the need to have it in order to transmit it has been evidenced. Young
[...] Read more.
Future teachers will have to develop the reading habit in their students, as this is an essential factor in schoolchildren. The lack of reading motivation among young people and the need to have it in order to transmit it has been evidenced. Young people often prefer to spend their leisure time using alcohol and other drugs rather than reading books for pleasure. The factors that influence reading motivation are varied, but the objective of this research work focuses on establishing the relationship between reading motivation and the problematic use of alcohol and other drugs in future teachers of Preschool and Primary Education. A total of 178 subjects among university students were recruited (56.6% girls). The ages ranged from 18 to 34 (
M = 21.59,
SD = 3.52). The first scale used was the MULTICAGE CAD-4 for behavioral addiction together with a Scale for Characterizing Motivation for Academic Reading (EMLA). The results of the study indicate that those young people who were more involved in the consumption of alcohol and drugs had a lower reading habit. Likewise, the study also reveals significant mean differences in reading motivation based on gender and age. This shows the need to enact healthy habits from the university related to increasing reading motivation and promoting the reading habit in future teachers.
Full article