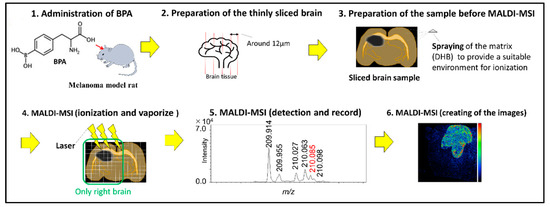
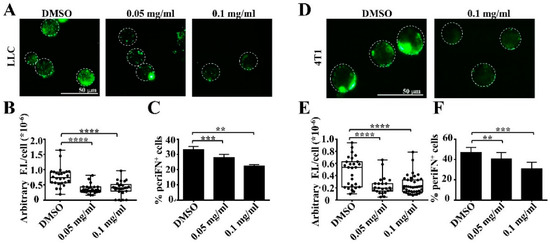
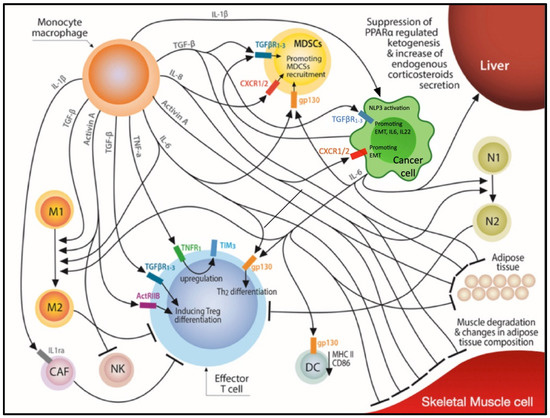
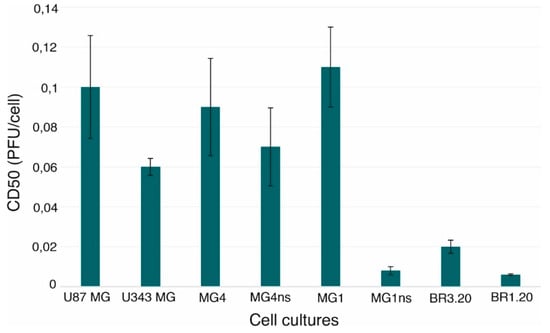
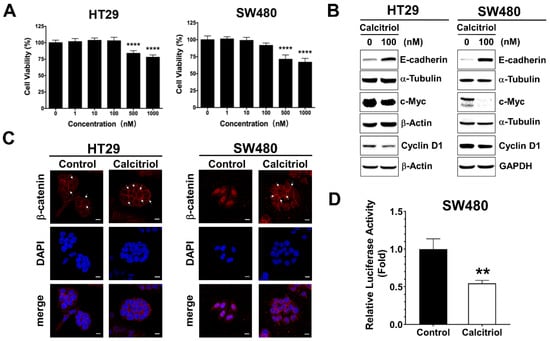
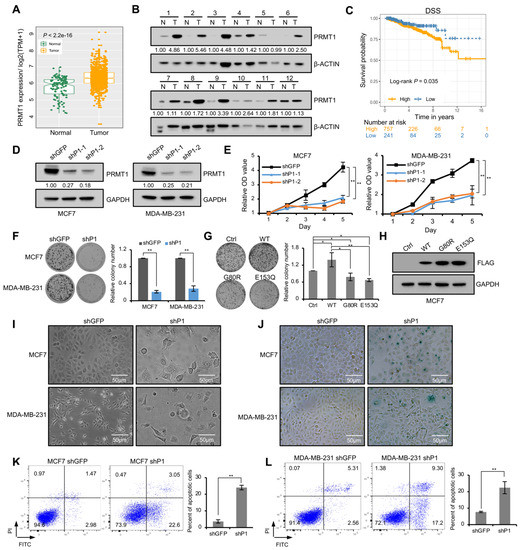
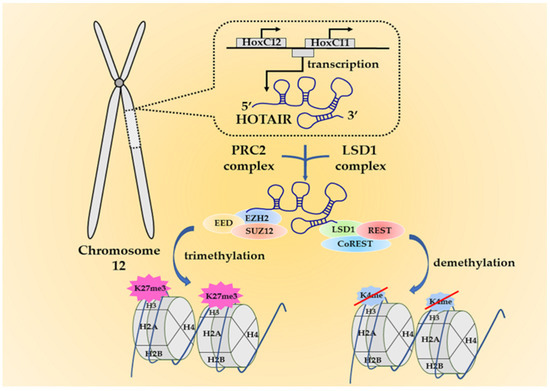
Tumor Progression, Microenvironments, and Therapeutics
A topical collection in Life (ISSN 2075-1729). This collection belongs to the section "Physiology and Pathology".
Viewed by 50657
Editors
Interests: fibronectin in cancer metastasis; extracellular matrix; circulating tumor cells; cell-cell adhesion; anti-metastatic strategies; tumor microenvironments; immunosurveillance against cancer metastasis; dipeptidyl peptidase IV (CD26)
Interests: anti-tumor mechanism of natural compounds; chemoprevention; ferroptosis; autophagy; apoptosis; oncogene; cell cycle; signaling transduction; nutrition
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
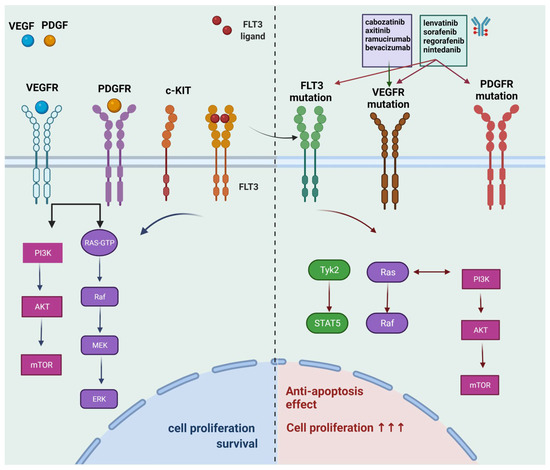
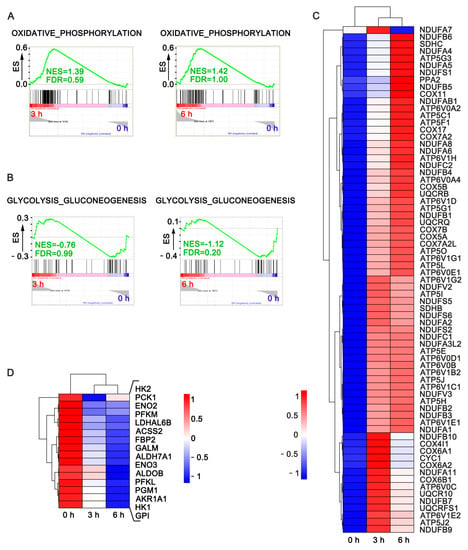
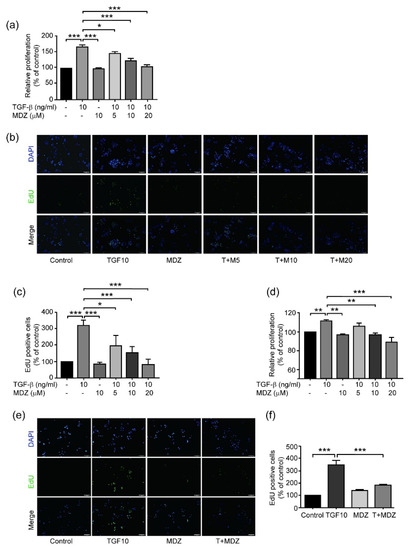
Tumor progression starts from transformation, followed by early progression within the microenvironments of primary tumor tissues, blood-borne to become circulating tumor cells (CTCs), colonization into distant organs in which a pre-metastatic niche has been built, and outgrowth as secondary tumor tissues that lead to cancer death. Although innumerous efforts, i.e., chemo-, radiation-, and target-therapies, have been made to kill tumor cells, the outcome of these therapeutic strategies, mainly exerting pro-apoptotic effects on cancer cells, often leads to distant relapse and increased mortality due to drug resistance and cancer metastasis. Therefore, alternative, adjuvant, or combinatory therapeutic strategies employing less cytotoxic drugs that may target various steps of tumor progression and/or primary or distant tumor microenvironments and circumvent unwanted adverse effects caused by those pro-apoptotic cancer drugs, are urgently needed.
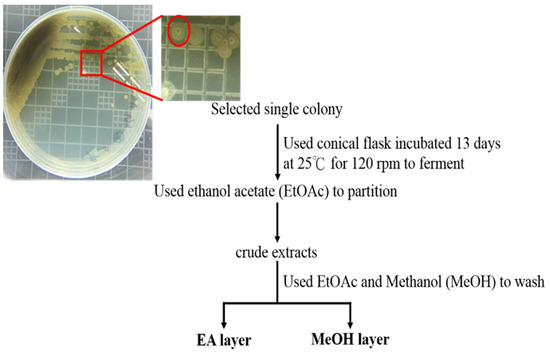
In this Topical Collection, advances in molecular mechanisms underlying tumor progression and therapeutic approaches, either targeting tumor cells or tumor microenvironments to fight against cancer will be presented in identifying less cytotoxic drugs, including, but not limited to, repurposed drugs, phytochemical agents, synthetic compounds or small molecules, nutrients in foods, siRNA, miRNAs, lncRNAs, antibodies, and other protein drugs, to serve as an alternative, adjuvant, or combinatory cancer therapeutics and understanding the underlying molecular mechanisms.
We welcome full communications, full reviews, perspectives, case reports (for very rare diseases) and original research articles.
Prof. Dr. Hung-Chi Cheng
Prof. Dr. Chun-Li Su
Prof. Dr. Ming-Fen Lee
Collection Editors
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Life is an international peer-reviewed open access monthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2600 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- tumor progression
- tumor microenvironments
- circulating tumor cells
- premetastatic niche
- cancer metastasis
- drug repurposing
- phytochemicals
- synthetic small molecules
- nutrients in foods
- alternative, adjuvant, or combinatory therapeutics