Journal Description
Journal of Otorhinolaryngology, Hearing and Balance Medicine
Journal of Otorhinolaryngology, Hearing and Balance Medicine
is an international, scientific, peer-reviewed, open access journal of otorhinolaryngology, hearing and balance medical studies, published semiannually online by MDPI.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 36.2 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 3.8 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the second half of 2024).
- Recognition of Reviewers: reviewers who provide timely, thorough peer-review reports receive vouchers entitling them to a discount on the APC of their next publication in any MDPI journal, in appreciation of the work done.
Latest Articles
GLI1-Altered Mesenchymal Tumours in the Head and Neck: A Case Report and Literature Review
J. Otorhinolaryngol. Hear. Balance Med. 2025, 6(1), 2; https://doi.org/10.3390/ohbm6010002 - 31 Jan 2025
Abstract
►
Show Figures
Background and Clinical Significance: GLI1 gene alterations have recently been identified as a pathological phenomenon associated with a distinct novel entity of mesenchymal neoplasms. They have been reported to occur in any soft tissue of the body, with a specific affinity for the
[...] Read more.
Background and Clinical Significance: GLI1 gene alterations have recently been identified as a pathological phenomenon associated with a distinct novel entity of mesenchymal neoplasms. They have been reported to occur in any soft tissue of the body, with a specific affinity for the head and neck region. The aim of this article is to increase awareness of this entity and provide a detailed summary of the modes of presentation and diagnostic and therapeutic issues surrounding these tumours occurring in the head and neck region. Case Presentation: We report the case of a 39-year-old male patient with ACTB::GLI1 fusion-related mesenchymal tongue tumour who was successfully treated by surgery. Conclusions: GLI1-altered mesenchymal tumours in the head and neck may harbour various clinical presentations. Larger series are needed to better define the clinicopathological range of this novel entity. We suggest a follow-up period of at least 2 years with imaging, followed by a clinical follow-up of 3 years. Certain clinicopathological features may warrant further and more extensive follow-up.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
Effects of Integrated Virtual Reality and Galvanic Vestibular Stimulation on Standing Balance
by
Gaurav N. Pradhan, Sarah E. Kingsbury, Jan Stepanek and Michael J. Cevette
J. Otorhinolaryngol. Hear. Balance Med. 2025, 6(1), 1; https://doi.org/10.3390/ohbm6010001 - 27 Dec 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background/Objectives: Galvanic vestibular stimulation (GVS) integrated into virtual reality (VR) environments enhances immersion and mitigates cybersickness. It is well known that GVS can affect standing balance. Most studies have investigated the effects of GVS in VR in seated conditions. The purpose of this
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Galvanic vestibular stimulation (GVS) integrated into virtual reality (VR) environments enhances immersion and mitigates cybersickness. It is well known that GVS can affect standing balance. Most studies have investigated the effects of GVS in VR in seated conditions. The purpose of this study was to evaluate the impact of joint GVS and VR with moving visual stimulus on standing balance. Methods: Using a repeated measures counter-balanced design, motion sickness, postural sway, and velocity utilizing the center of pressure (COP) along the mediolateral (ML) and anteroposterior (AP) axes were obtained in 18 subjects during optokinetic (OPK) stimulus (black and white vertical bars moving from left to the right) in VR across three interventions: GVS in the same direction of visual stimulus—left to right ear (Positive GVS), GVS in the opposite direction of visual stimulus—right to left ear (Negative GVS), and without GVS (Null GVS). Motion sickness symptom scoring was obtained using the Pensacola Diagnostic Index. Results: The PDI score was increased significantly in the Negative GVS. The root mean square and sway range of COP along ML was greater during the Positive GVS and Negative GVS than the Null GVS, while, along AP, it was only greater during Negative GVS. During Positive GVS, mean positive and negative peak velocities, only in ML, were increased and decreased, respectively. During Negative GVS, only negative peak velocities in both ML and AP directions were decreased. Conclusions: This research highlights the importance of testing combined VR and GVS to assess standing balance while mitigating cybersickness.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessTechnical Note
Approach to Epistaxis
by
Raisa Chowdhury, Sena Turkdogan, Jennifer A. Silver, Jessica Hier, Stuart Bursey, Danah Quttaineh, Mark Khoury and Lamiae Himdi
J. Otorhinolaryngol. Hear. Balance Med. 2024, 5(2), 21; https://doi.org/10.3390/ohbm5020021 - 23 Dec 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Epistaxis, commonly referred to as nosebleeds, is a frequent clinical presentation with etiologies spanning from localized trauma to systemic conditions and medication effects. Despite its high prevalence, management approaches vary significantly depending on the cause and severity. To provide a comprehensive review of
[...] Read more.
Epistaxis, commonly referred to as nosebleeds, is a frequent clinical presentation with etiologies spanning from localized trauma to systemic conditions and medication effects. Despite its high prevalence, management approaches vary significantly depending on the cause and severity. To provide a comprehensive review of current management strategies for epistaxis, focusing on initial interventions, evaluation techniques, and preventive measures. A structured review of the literature was conducted to identify effective strategies for the initial management, evaluation, and prevention of epistaxis. Emphasis was placed on practical applications for clinicians in both emergency and outpatient settings. Initial Management: Direct pressure and topical vasoconstrictors remain the first-line interventions. Persistent cases may require nasal packing or cautery. Evaluation: Identification of underlying causes such as hypertension, coagulopathies, and structural nasal abnormalities is crucial, particularly in recurrent or severe cases. Laboratory tests and imaging may aid in diagnosis and management planning. Prevention: Patient education on nasal hygiene, avoidance of nasal trauma, and maintenance of a humidified environment are critical in reducing recurrence. Integrating effective initial management with thorough evaluation and preventive strategies significantly improves patient outcomes.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessTechnical Note
Approach to Hyperthyroidism
by
Raisa Chowdhury, Sena Turkdogan, Jennifer A. Silver, Jessica Hier, Stuart Bursey, Danah Quttaineh, Mark Khoury and Lamiae Himdi
J. Otorhinolaryngol. Hear. Balance Med. 2024, 5(2), 20; https://doi.org/10.3390/ohbm5020020 - 10 Dec 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background: Hyperthyroidism, characterized by excessive thyroid hormone production, presents in diverse clinical forms, including overt and subclinical disease. Accurate and timely diagnosis is critical to prevent complications such as cardiac dysfunction, osteoporosis, and thyroid storm. Objective: To provide a comprehensive review of the
[...] Read more.
Background: Hyperthyroidism, characterized by excessive thyroid hormone production, presents in diverse clinical forms, including overt and subclinical disease. Accurate and timely diagnosis is critical to prevent complications such as cardiac dysfunction, osteoporosis, and thyroid storm. Objective: To provide a comprehensive review of the clinical presentation, diagnostic methods, and management strategies for hyperthyroidism, focusing on current practices, advancements, and challenges in treatment. Methods: This review synthesizes findings from peer-reviewed literature on the diagnosis and management of hyperthyroidism. Results: Thyroid function tests (TFTs) are the cornerstone of hyperthyroidism diagnosis, with suppressed TSH levels and elevated T3 and/or T4 levels confirming overt disease. Thyroid receptor antibodies (TRAb) are critical for diagnosing autoimmune hyperthyroidism and predicting relapse risk. Iodine scintigraphy is utilized in specific cases, such as suspected toxic adenoma or multinodular goiter. Management strategies include beta-blockers for symptomatic relief, though side effects such as bradycardia and fatigue may occur. Antithyroid medications, including methimazole and propylthiouracil, inhibit hormone synthesis, with remission more likely in patients with low TRAb levels and small goiters. Definitive treatments include radioactive iodine therapy (RAI), which effectively reduces thyroid activity but often results in hypothyroidism, and thyroidectomy, a surgical option for large goiters or malignancy, with potential complications like hypocalcemia and recurrent laryngeal nerve injury. Conclusions: The management of hyperthyroidism necessitates a personalized approach integrating diagnostic precision, emerging innovations, and patient-centered care.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessGuidelines
A Practical Guideline to Capturing and Documenting the Real-Time Consequences of Fluctuating Hearing Loss in School-Age Children
by
Cassandra Cowan, Kathleen Jones, Amberley V. Ostevik, Sara Al Souqi, William Hodgetts and Jacqueline Cummine
J. Otorhinolaryngol. Hear. Balance Med. 2024, 5(2), 19; https://doi.org/10.3390/ohbm5020019 - 5 Dec 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background: Fluctuating conductive hearing loss resulting from middle ear conditions, such as otitis media, is the most common cause of hearing loss in children, with Indigenous Peoples experiencing otitis media at a rate three times higher than non-Indigenous populations. Children with chronic hearing
[...] Read more.
Background: Fluctuating conductive hearing loss resulting from middle ear conditions, such as otitis media, is the most common cause of hearing loss in children, with Indigenous Peoples experiencing otitis media at a rate three times higher than non-Indigenous populations. Children with chronic hearing loss face increased educational, social, and economic challenges. However, treating and documenting fluctuating hearing loss remains difficult due to its sporadic and invisible nature, frequently leading to delayed or missed identification and inconsistent management. Methods: A comprehensive literature search was completed with a librarian, but few resources were located for this condition and population. Results: This practical guideline aims to improve the documentation and subsequent management of otitis media in school-aged children, with a focus on rural and Indigenous communities in Canada, where access to healthcare professionals may be limited. Conclusions: Despite efforts to raise awareness about otitis media in rural and Indigenous communities, there are still few accessible tools for caregivers to track the severity of fluctuating hearing loss. This guideline aims to help fill this gap.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Spatial Release from Masking for Small Spatial Separations Using Simulated Cochlear Implant Speech
by
Nirmal Srinivasan, SaraGrace McCannon and Chhayakant Patro
J. Otorhinolaryngol. Hear. Balance Med. 2024, 5(2), 18; https://doi.org/10.3390/ohbm5020018 - 27 Nov 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background: Spatial release from masking (SRM) is the improvement in speech intelligibility when the masking signals are spatially separated from the target signal. Young, normal- hearing listeners have a robust auditory sys-tem that is capable of using the binaural cues even with a
[...] Read more.
Background: Spatial release from masking (SRM) is the improvement in speech intelligibility when the masking signals are spatially separated from the target signal. Young, normal- hearing listeners have a robust auditory sys-tem that is capable of using the binaural cues even with a very small spatial separation between the target and the maskers. Prior studies exploring SRM through simulated cochlear implant (CI) speech have been completed using substantial spatial separations, exceeding 45° between the target signal and masking signals. Nevertheless, in re-al-world conversational scenarios, the spatial separation between the target and the maskers may be considerably less than what has been previously investigated. This study presents SRM data utilizing simulated CI speech with young, normal-hearing listeners, focusing on smaller but realistic spatial separations between the target and the maskers. Methods: Twenty-five young, normal-hearing listeners participated in this study. Speech identification thresholds, the target-to-masker ratio required to accurately identify 50% of the target words, were measured for both natural speech and simulated CI speech. Results: The results revealed that young, normal-hearing listeners had significantly higher speech identification thresholds when presented with simulated CI speech in comparison to natural speech. Furthermore, the amount of SRM was found to be greater for natural speech than for the simulated CI speech. Conclusions: The data suggests that young normal-hearing individuals are capable of utilizing the interaural level difference cues in the simulated cochlear implant signal to achieve masking release at reduced spatial separations between the target and the maskers, highlighting the auditory system’s capability to extract these interaural cues even in the presence of degraded speech signals.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessTechnical Note
Comprehensive Diagnostic Approach to Head and Neck Masses
by
Raisa Chowdhury, Sena Turkdogan, Raihanah Alsayegh, Hamad Almhanedi, Dana Al Majid, Gabriella Le Blanc, George Gerardis and Lamiae Himdi
J. Otorhinolaryngol. Hear. Balance Med. 2024, 5(2), 17; https://doi.org/10.3390/ohbm5020017 - 19 Nov 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Head and neck masses are a significant diagnostic challenge and differential diagnoses range from inflammatory, infectious, and neoplastic conditions. Timely, accurate evaluation is essential for optimal patient outcomes. This review highlights a systematic approach to diagnosing head and neck masses through comprehensive history,
[...] Read more.
Head and neck masses are a significant diagnostic challenge and differential diagnoses range from inflammatory, infectious, and neoplastic conditions. Timely, accurate evaluation is essential for optimal patient outcomes. This review highlights a systematic approach to diagnosing head and neck masses through comprehensive history, physical examination, and a variety of diagnostic tools. Imaging modalities such as computed tomography (CT), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), and ultrasound are integral in diagnosis. Fine-needle aspiration (FNA) biopsy is a minimally invasive option for a preliminary diagnosis. However, in cases where it may be inconclusive or when extensive tissue sampling is needed to confirm a diagnosis, open tissue biopsy is considered. Collaboration among a multidisciplinary team (surgeons, radiologists, and pathologists) is vital in developing an effective individualized treatment plan. Early detection and accurate diagnosis of head and neck masses are critical for achieving favorable clinical outcomes.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Diagnosis and Management of Obstructive Sleep Apnea: Updates and Review
by
Shan Luong, Liz Lezama and Safia Khan
J. Otorhinolaryngol. Hear. Balance Med. 2024, 5(2), 16; https://doi.org/10.3390/ohbm5020016 - 29 Oct 2024
Abstract
Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) is a heterogenous disease process that cannot be adequately categorized by AHI alone. There is a significant prevalence of OSA in the general population with ongoing efforts to evaluate the risk factors contributing to OSA and its associated clinical
[...] Read more.
Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) is a heterogenous disease process that cannot be adequately categorized by AHI alone. There is a significant prevalence of OSA in the general population with ongoing efforts to evaluate the risk factors contributing to OSA and its associated clinical implications. Only by improving our understanding of OSA can we advance our methods in the diagnosis and treatment of OSA. For this article, the authors reviewed keywords of obstructive sleep apnea diagnosis and therapy in the databases of Embase, Medline, and Medline ePub over the past 3 years, excluding any articles that only addressed sleep apnea in children under age 17 years. This review article is divided into three main sections. First, we will investigate the use of novel screening tools, biomarkers, anthropometric measurements, and novel wearable technologies that show promise in improving the diagnosis of OSA. There is mention of comorbid conditions seen in OSA patients since certain disease combinations can significantly worsen health and should raise our awareness to diagnose and manage those concomitant disorders. The second section will look at the current and developing treatment options for OSA. These include positive airway therapy (PAP), mandibular advancement device (MAD), exciting new findings in certain medications, orofacial myofunctional therapy (OMT), hypoglossal nerve stimulation therapy (HGNS), and other surgical options. We will conclude with a section reviewing the current Clinical Practice Guidelines for Diagnostic Testing in Adults with Obstructive Sleep Apnea from 2017, which strongly advises polysomnography (PSG) or home sleep apnea testing (HSAT), along with comprehensive sleep evaluation for uncomplicated patients with a clinical presentation of OSA.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
Navigating the Health Care System with Chronic Dizziness: A Qualitative Study
by
Elizabeth Cornforth and Katherine Schramm
J. Otorhinolaryngol. Hear. Balance Med. 2024, 5(2), 15; https://doi.org/10.3390/ohbm5020015 - 17 Oct 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Introduction: The purpose of this study was to qualitatively explore the experiences of chronic dizziness diagnosis and management within the health care system. Methods: This qualitative phenomenological study used focus groups to interview a convenience sample of individuals with chronic dizziness (n
[...] Read more.
Introduction: The purpose of this study was to qualitatively explore the experiences of chronic dizziness diagnosis and management within the health care system. Methods: This qualitative phenomenological study used focus groups to interview a convenience sample of individuals with chronic dizziness (n = 13) and vestibular physical therapists (n = 15). Focus group data were systematically analyzed using a descriptive coding process. Results: Two major themes emerged from interviews with individuals with dizziness: (1.) complexities navigating the health system and (2.) loss of self-identity. Three major themes emerged from interviews with vestibular physical therapists: (1.) patients have a complex, multi-factorial presentation, (2.) importance of the multidisciplinary care team, and (3.) behavior influences outcomes. Individuals with chronic dizziness identified many challenges in effectively navigating the health system and receiving an effective diagnosis and management, including the patient–provider relationship, with negative impacts on quality of life. Vestibular physical therapist data concurred and validated these experiences. Conclusion: Given the complex, multi-factorial nature of dizziness, increased use of the biopsychosocial model in a multidisciplinary dizziness clinic may inform a more holistic approach for this patient population and improve future outcomes for individuals with chronic dizziness.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Nasal Septal Deviation Classifications Associated with Revision Septoplasty
by
Karina Bayer, Johannes Brady-Praun, Gerold Besser, Faris F. Brkic, Markus Haas, Christian A. Mueller and David T. Liu
J. Otorhinolaryngol. Hear. Balance Med. 2024, 5(2), 14; https://doi.org/10.3390/ohbm5020014 - 27 Sep 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background: This study aimed to identify clinical characteristics and classifications of nasal septal deviations associated with revision septoplasty. Methods: The cross-sectional study design included 652 patients undergoing septoplasty at a tertiary referral center. We classified patients according to Baumann’s validated septal deviation classification
[...] Read more.
Background: This study aimed to identify clinical characteristics and classifications of nasal septal deviations associated with revision septoplasty. Methods: The cross-sectional study design included 652 patients undergoing septoplasty at a tertiary referral center. We classified patients according to Baumann’s validated septal deviation classification and assessed similarities and differences regarding septal pathologies and types of nasal septal deviations in both groups. Results: The sample comprised 600 primary surgery cases and 52 revision cases. In primary surgeries, type 1 septal deviations were most common (60.3%), followed by type 5 (10.5%) and type 3 (10.0%). In revision surgeries, type 1 deviations (36.5%) were most common, followed by type 3 (25.0%) and type 2 (17.3%). Group comparisons revealed that type 2 and type 3 septal deviations, high septal deviations, and septal perforations were significantly more frequent in revision cases. Common septal pathologies included an oblique septum (98.0%), ipsilateral septal crest (76.4%), contralateral turbinal hyperplasia (42.5%), and vomeral spur (39.9%). Conclusions: This study suggests that using validated classification systems for septal deviations, which combine various pathologies, can provide a more clinically relevant assessment and improve patient counseling and treatment.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Cerebrovascular Burden and Its Association with Ménière’s Disease: A Case-Control Study
by
Francisco Alves de Sousa, João Tarrio, Bruno Moreira, Ana Nóbrega Pinto, Luís Meireles and Ângela Reis Rego
J. Otorhinolaryngol. Hear. Balance Med. 2024, 5(2), 13; https://doi.org/10.3390/ohbm5020013 - 24 Sep 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background: Ménière’s disease (MD) lacks a universally accepted pathogenesis model. Recent research has revisited the vascular hypothesis. This study aims to compare the cerebrovascular burden in patients with MD and age-matched controls, investigating the potential role of cerebrovascular dysfunction in MD. Methods
[...] Read more.
Background: Ménière’s disease (MD) lacks a universally accepted pathogenesis model. Recent research has revisited the vascular hypothesis. This study aims to compare the cerebrovascular burden in patients with MD and age-matched controls, investigating the potential role of cerebrovascular dysfunction in MD. Methods: A total of 145 patients (70 MD, 75 controls) underwent magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) assessment for small-vessel disease (SVD) markers (including Fazekas and EPVS scores), cortical strokes, and baseline comorbidities. Statistical analyses were performed to compare the cerebrovascular burden between the groups, adjusting for potential confounders. Results: The MD group exhibited significantly higher mean SVD scores across various measures compared to controls (p < 0.05). This association persisted even after adjusting for age, sex, and comorbidities (ORs ranging from 1.746 to 2.495, p < 0.05). Neither the presence of cortical strokes nor comorbidities significantly differed between groups. Conclusions: This study is the first to compare cerebrovascular burden between MD patients and controls. The findings suggest that cerebrovascular dysfunction may contribute to MD incidence. Further research is needed to elucidate the relationship between cerebrovascular disease and MD, potentially leading to novel therapeutic avenues.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
The Emerging Role of Pharmacotherapy in Obstructive Sleep Apnea
by
Nikhil Jaganathan, Younghoon Kwon, William J. Healy and Varsha Taskar
J. Otorhinolaryngol. Hear. Balance Med. 2024, 5(2), 12; https://doi.org/10.3390/ohbm5020012 - 7 Sep 2024
Abstract
Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) is a prevalent pathology with current modalities of treatment including continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP), surgery, weight loss, hypoglossal nerve stimulation, and pharmacotherapy. While CPAP is the current standard treatment for OSA, lack of tolerance and side effects necessitate
[...] Read more.
Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) is a prevalent pathology with current modalities of treatment including continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP), surgery, weight loss, hypoglossal nerve stimulation, and pharmacotherapy. While CPAP is the current standard treatment for OSA, lack of tolerance and side effects necessitate alternative modalities of treatment. Various pharmacologic agents exist with mechanisms that may target OSA. Early trials have demonstrated efficacy of noradrenergic-antimuscarinic combinations to stimulate the airway, promote pharyngeal muscle tone, and prevent airway collapse. These agents, which we discuss in detail, have demonstrated significant reductions in apnea-hypopnea index (AHI) and lowest oxygen saturations based on preliminary studies. Glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists (GLP-1RA), which stimulate endogenous insulin, reducing glucagon release, and decreasing gastric emptying, have shown positive results for OSA patients through weight loss with reductions in AHI. In this narrative review article, we highlight the mechanisms, current data, and future potential for multiple drug classes, including respiratory stimulants and GLP-1RAs.
Full article
Open AccessCase Report
Case Report and Literature Review on Tongue Schwannoma
by
Michelangelo Pierri, Antonio Moffa, Lorenzo Sabatino, Francesco Iafrati, Simone Di Giovanni, Luigi De Benedetto and Manuele Casale
J. Otorhinolaryngol. Hear. Balance Med. 2024, 5(2), 11; https://doi.org/10.3390/ohbm5020011 - 12 Aug 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Schwannoma is a neoplasm originating from cells surrounding and insulating axons in peripheral nerves. It usually presents benign behaviour with slow growth. A significant portion of cases occur in the head and neck region but rarely in the oral cavity, where the tongue
[...] Read more.
Schwannoma is a neoplasm originating from cells surrounding and insulating axons in peripheral nerves. It usually presents benign behaviour with slow growth. A significant portion of cases occur in the head and neck region but rarely in the oral cavity, where the tongue is the most frequently affected organ. This article describes the case of a man presenting an asymptomatic mass on the dorsal aspect of the tongue that sought attention at the Integrated Therapies in Otorhinolaryngology Department of the Policlinico Campus Bio-Medico Foundation in Rome. After clinical and radiological examinations, the patient underwent surgical treatment under local anaesthesia. A literature search was conducted on PubMed and Google Scholar. Only complete case reports published in English from 1923 to 2023 were selected. A total of 183 cases were considered after the selection of relevant articles and the elimination of duplicates. The resulting data confirm that the most common presentation of this pathology consists of a painless mass in the oral tongue; usually, this lesion is removed surgically via a transoral approach, but different variations were described depending on the dimensions and position of the lesion.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Cardiovascular Risk Profile in Ménière’s Disease and Posterior Circulation Infarction: A Comparative Study
by
Francisco Alves de Sousa, João Tarrio, Rita Rodrigues, Clara Serdoura Alves, Mariline Santos, Ana Nóbrega Pinto, Luís Meireles and Ângela Reis Rego
J. Otorhinolaryngol. Hear. Balance Med. 2024, 5(2), 10; https://doi.org/10.3390/ohbm5020010 - 15 Jul 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Ménière’s disease (MD) has an unclear cause. The microvascular dysregulation of the inner ear has been increasingly pointed out as a potential contributor. This study investigates the prevalence of cardiovascular risk factors (CVRFs) in MD patients compared to those with posterior circulation cerebral
[...] Read more.
Ménière’s disease (MD) has an unclear cause. The microvascular dysregulation of the inner ear has been increasingly pointed out as a potential contributor. This study investigates the prevalence of cardiovascular risk factors (CVRFs) in MD patients compared to those with posterior circulation cerebral infarction (POCI). CVRFs like hypertension, diabetes, dyslipidemia, obesity, coronary heart disease, and smoking were assessed in both MD and POCI patients. Brain MRI identified POCI etiology as “small vessel occlusion” (SVO) or “other etiology” (OE). This study included 64 MD and 84 POCI patients. Compared to MD, POCI OE showed a higher prevalence of CVRFs across various age groups, including hypertension, diabetes, dyslipidemia, and smoking. Notably, the odds of having POCI OE were significantly higher for individuals with hypertension and smoking. On the other hand, POCI SVO showed a similar prevalence of CVRFs compared to MD. This study revealed no significant differences in CVRF prevalence between MD and smaller vessel POCI. However, a clear distinction emerged when comparing MD to POCI with the involvement of larger blood vessels. Further research is needed to confirm these findings and explore potential shared risk factors between POCI (SVO) and MD.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessSystematic Review
Effect of Continuous Positive Airway Pressure after Pulmonary Vein Isolation in Obstructive Sleep Apnea Patients with Atrial Fibrillation: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
by
Angkawipa Trongtorsak, Omar Khalil, Hussein Krayem, Mathurin Suwanwalaikorn, Kimberly R. Ding, Natchaya Polpichai, Ronpichai Chokesuwattanaskul and Narut Prasitlumkum
J. Otorhinolaryngol. Hear. Balance Med. 2024, 5(2), 9; https://doi.org/10.3390/ohbm5020009 - 4 Jul 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background: Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) was associated with atrial fibrillation (AF) as well as the recurrence of AF after rhythm control strategy. However, the data on continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) and recurrent AF after catheter ablation with pulmonary vein isolation (PVI) remain
[...] Read more.
Background: Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) was associated with atrial fibrillation (AF) as well as the recurrence of AF after rhythm control strategy. However, the data on continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) and recurrent AF after catheter ablation with pulmonary vein isolation (PVI) remain unclear. We conducted this systematic review and meta-analysis to evaluate the effect of CPAP treatment in OSA patients after atrial fibrillation ablation. Methods: We searched MEDLINE and Embase databases from inception to September 2023 to identify studies that assess the effect of CPAP in OSA patients on the recurrence of AF after PVI. Data from each study were combined using the random effects model. Results: Eight studies (one randomized controlled trial and seven cohort studies) with 1487 OSA patients (660 in the CPAP group and 827 in the control group) were included. The use of CPAP in OSA patients was associated with significantly lower AF recurrence after PVI (odds ratio (OR) = 0.36, 95% conference interval (CI) 0.25–0.53, p < 0.001). The results of sensitivity analysis remain the same as the main analysis. Conclusions: Our meta-analysis demonstrated that CPAP treatment was associated with lower rates of AF recurrence after PVI.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessTechnical Note
Orthopedic Surgery Position Enhances Safety in Adults with Cervical Rigidity during Cochlear Implantation
by
Chiara Lazzarin and Antonio Frisina
J. Otorhinolaryngol. Hear. Balance Med. 2024, 5(1), 8; https://doi.org/10.3390/ohbm5010008 - 12 Jun 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Cochlear implantation is the therapy used for patients with severe to profound sensorineural hearing loss. For the success of the surgery, it is important that each surgical step is performed with meticulous precision, starting from the correct patient position on the operating table.
[...] Read more.
Cochlear implantation is the therapy used for patients with severe to profound sensorineural hearing loss. For the success of the surgery, it is important that each surgical step is performed with meticulous precision, starting from the correct patient position on the operating table. In elderly or obese patients, this can be difficult to achieve due to cervical rigidity. With this technical note, we want to describe a new position from orthopedic surgery to perform a posterior tympanotomy accurately, ensuring a safe procedure and avoiding unpleasant complications.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessSystematic Review
Exploring the Prevalence of Psychiatric Disorders in Otosclerosis Patients: A Systematic Review
by
Soroush Farsi, Alexa N. Pearce, Emily Goodman, Siddharth Patel, Deanne King, John Dornhoffer and Robert Saadi
J. Otorhinolaryngol. Hear. Balance Med. 2024, 5(1), 7; https://doi.org/10.3390/ohbm5010007 - 27 May 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Objective: The primary objective of this research is to conduct a systematic review of the available studies and evidence to determine if there is a significant relationship between otosclerosis and psychiatric disorders. By critically evaluating the existing data, this study aims to provide
[...] Read more.
Objective: The primary objective of this research is to conduct a systematic review of the available studies and evidence to determine if there is a significant relationship between otosclerosis and psychiatric disorders. By critically evaluating the existing data, this study aims to provide insights into the potential interplay between these medical conditions. Data Sources: PubMed, Embase, Ebsco, Proquest, and Web of Science Review Methods: PubMed, Embase, Ebsco, Proquest, and Web of Science databases were queried for original English articles from 1950 to 2023. This review was conducted in accordance with the 2020 PRISMA guidelines. The publications were screened by two independent viewers. The Newcastle–Ottawa Scale quality instrument was used to assess the quality of studies. Results: Initially, 153 abstracts were screened for eligibility. After a rigorous selection process, five studies met the criteria, collectively encompassing 262 patients diagnosed with otosclerosis. The reported mean ages ranged from 25 to 52 years. A combined assessment of psychiatric disorder rates among otosclerosis patients revealed a rate of 36%. Depression, anxiety, and schizophrenia were the most common mental illnesses reported in all six studies. One of the studies specifically examined psychiatric disorder rates before and after stapedectomy, revealing a statistically significant decrease in depressive and anxiety-related symptoms following the surgical intervention. Conclusions: This systematic review emphasizes the emerging evidence connecting otosclerosis with psychiatric disorders and underscores the importance of adopting a multidisciplinary approach to assess and manage otosclerosis patients.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Towards Comprehensive Newborn Hearing and Genetic Screening in Russia: Perspectives of Implementation
by
Svetlana Chibisova, Tatiana Markova, Evgenia Tsigankova and George Tavartkiladze
J. Otorhinolaryngol. Hear. Balance Med. 2024, 5(1), 6; https://doi.org/10.3390/ohbm5010006 - 15 May 2024
Cited by 1
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The universal newborn hearing screening (NHS) program was implemented in Russia in 2008 to replace the high-risk newborn hearing screening. More than 95% coverage and significant improvement in early detection and intervention is achieved. Meanwhile, it was shown that current OAE-based hearing screening
[...] Read more.
The universal newborn hearing screening (NHS) program was implemented in Russia in 2008 to replace the high-risk newborn hearing screening. More than 95% coverage and significant improvement in early detection and intervention is achieved. Meanwhile, it was shown that current OAE-based hearing screening missed 13% of newborns with genetically ascertained hereditary sensorineural hearing loss (SNHL). The aim of the study is to assess the results of genetic investigation and NHS in a large cohort of Russian children with bilateral SNHL and to study the feasibility of implementation of combined hearing and genetic screening in Russia. Genetic, audiological and NHS data of 1292 pediatric patients with bilateral SNHL born in 2008–2021 were analyzed. GJB2 sequencing was performed for all subjects, 644 patients had pathological GJB2 genotype, 406 of them were homozygous for c.35delG variant. The group of 155 GJB2-negative patients were searched for other SNHL genes, The pathological genotypes were identified at 87 patients. The most frequent genes were STRC (21.8%), USH2A (16.1%), OTOF (8%) and SLC26A4 (6.9%). Children with confirmed genetic etiology passed NHS in 21% of cases. The perspectives of implementation of national comprehensive newborn hearing and genetic screening including whole exome sequencing technologies are discussed.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
The Intelligibility Benefits of Modern Computer-Synthesized Speech for Normal-Hearing and Hearing-Impaired Listeners in Non-Ideal Listening Conditions
by
Yizhen Ma and Yan Tang
J. Otorhinolaryngol. Hear. Balance Med. 2024, 5(1), 5; https://doi.org/10.3390/ohbm5010005 - 18 Apr 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Speech intelligibility is a concern for public health, especially in non-ideal listening conditions where listeners often listen to the target speech in the presence of background noise. With advances in technology, synthetic speech has been increasingly used in lieu of actual human voices
[...] Read more.
Speech intelligibility is a concern for public health, especially in non-ideal listening conditions where listeners often listen to the target speech in the presence of background noise. With advances in technology, synthetic speech has been increasingly used in lieu of actual human voices in human–machine interfaces, such as public announcement systems, answering machines, virtual personal assistants, and GPS, to interact with users. However, previous studies showed that speech generated by computer speech synthesizers was often intrinsically less natural and intelligible than natural speech produced by human speakers. In terms of noise, listening to synthetic speech is challenging for listeners with normal hearing (NH), not to mention for hearing-impaired (HI) listeners. Recent developments in speech synthesis have significantly improved the naturalness of synthetic speech. In this study, the intelligibility of speech generated by commercial synthesizers from Google, Amazon, and Microsoft was evaluated by both NH and HI listeners in different noise conditions. Compared to a natural female voice as the baseline, listeners’ listening performance suggested that some of the synthetic speech was significantly more intelligible even at rather adverse listening conditions for the NH cohort. Further acoustical analyses revealed that elongated vowel sounds and reduced spectral tilt were primarily responsible for improved intelligibility for NH, but not for HI due to their impairment at high frequencies and possible cognitive decline associated with aging.
Full article
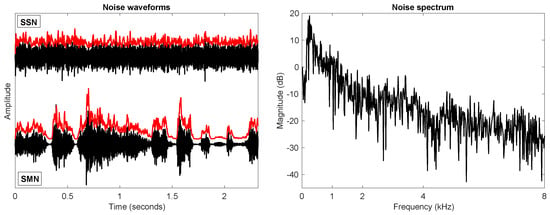
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Comparison of Halmágyi–Curthoys Head Impulse (Thrust) Test with Romberg’s Test in Detection of Vestibular Hypofunctioning in Vertigo Patients
by
Santhosh Kumar Rajamani, Radha Srinivasan Iyer and Anusha Venkatraman
J. Otorhinolaryngol. Hear. Balance Med. 2024, 5(1), 4; https://doi.org/10.3390/ohbm5010004 - 4 Mar 2024
Cited by 1
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
This study aimed to compare the diagnostic efficacy of the Halmágyi–Curthoys head impulse (thrust) test and Romberg’s test in detecting vestibular hypofunctioning among two groups of 50 vertigo patients each; the two groups were randomly assigned. The assessment utilized the visual analog scale
[...] Read more.
This study aimed to compare the diagnostic efficacy of the Halmágyi–Curthoys head impulse (thrust) test and Romberg’s test in detecting vestibular hypofunctioning among two groups of 50 vertigo patients each; the two groups were randomly assigned. The assessment utilized the visual analog scale (VAS) to quantify subjective experiences of vertigo. The results revealed distinctive patterns in the detection of vestibular hypofunctioning, highlighting the strengths and limitations of each test. The Halmágyi–Curthoys head impulse test demonstrated utility in identifying vestibular hypofunctioning and its effect on vestibulo–ocular reflexes, particularly in cases with sudden head movements. Romberg’s test was useful in assessing postural instability in vestibular hypofunctioning due to defects in vestibulospinal reflexes. The integration of VAS scores provided valuable subjective insights into the patient experience. This comparative analysis contributes to a nuanced understanding of diagnostic tools for vestibular hypofunctioning in vertigo patients, offering clinicians valuable information for tailored assessments and interventions.
Full article
Figure 1
Highly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics

Conferences
Special Issues
Special Issue in
JOHBM
Etiology, Diagnosis, and Treatment of Congenital Hearing Loss
Guest Editor: Yu SunDeadline: 30 September 2025





