Waste Utilization and Resource Recovery
A topical collection in Sustainability (ISSN 2071-1050). This collection belongs to the section "Resources and Sustainable Utilization".
Viewed by 102159Editors
Interests: solid waste composting and digestion; waste utilization and resource recovery; advanced physiochemical and biological treatment; contaminant transport in multiphase; environmental risk assessment and management; synchrotron-assisted environmental process analysis; surface water and groundwater quality; environmental sustainability
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Interests: water and wastewater treatment; membrane filtration technologies; environmental applications of nanotechnologies; synchrotron-based environmental analysis; planning and optimization of environmental systems
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
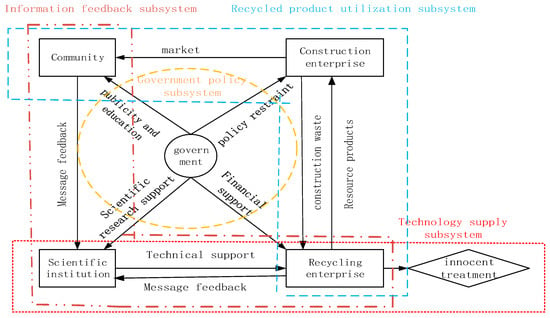
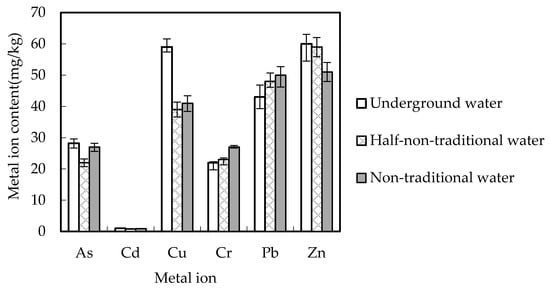
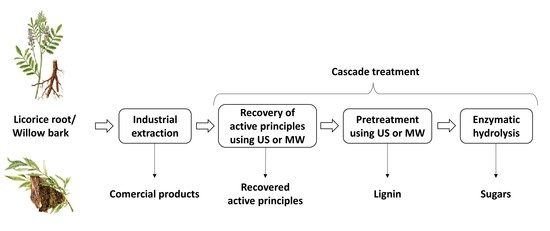
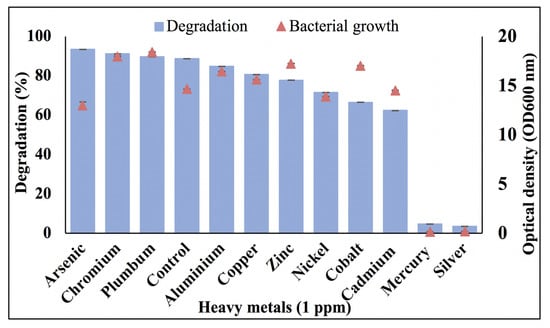
With the rapid development of the economy and population growth, a large amount of solid waste has been generated from domestic, industrial, and agricultural activities over the last few decades. Improper treatment and disposal of solid waste have adverse impacts on the ecosystem and human health. Improving our fundamental understanding of various waste disposal processes will help alleviate environmental pollution and establish efficient waste management. In particular, there has been an increasing interest in the use of waste as a resource for energy and nutrient recovery, value-added product generation, and pollution mitigation. Such resource recovery is an effective way to reduce waste and improve sustainability in operation. In waste utilization, it is also necessary to make systematic considerations for a number of critical environmental and technical factors, as well as their interrelationships and the related policy implications. Although many efforts have been made, some challenges to waste utilization and resource recovery remain to be overcome. Dealing with these problems through sustainable approaches has become an urgent issue for both government and academia. This Special Issue is dedicated to the perception of waste utilization and resource recovery based on the integration of environmental, economic, and social considerations. It will provide a summary of recent progress in the development of operational strategies for sustainable waste utilization. The Special Issue calls for original research, and mini and full reviews, including perspectives in the field of the current standing of waste utilization and resource recovery.
Prof. Dr. Chunjiang An
Dr. Xiujuan Chen
Collection Editors
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Sustainability is an international peer-reviewed open access semimonthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2400 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- waste management
- waste disposal
- waste utilization
- resource recovery
- waste minimization
- fate of contaminant from waste
- systems analysis
- waste characterization
- economic analysis
- sustainability