Advanced Methodologies for Sustainability Assessment: Theory and Practice
A topical collection in Sustainability (ISSN 2071-1050).
Viewed by 259392Editor
Interests: multi-criteria; fuzzy set; soft computing; renewable energy; sustainability; circular economy; technology assessment; hypersoft sets; sustainable development goals
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
In recent years, the concept of sustainability has been revised and new models have become increasingly pervasive. Appraising sustainability is complex and uncertain because sustainability encompasses environmental, technical, economic, and social dimensions. The scientific procedure of assessment has a vital role because it can supply the right tools for understanding the real meaning of sustainability. Indeed, many researchers have contributed new approaches or models for measuring sustainability. A very important line of research concerns the applications of multi-criteria and soft computing models that address the complexity of the value of sustainability.
This Topical Collection aims to collect original contributions, subject to a rigorous peer review, concerning the main advancements and innovations in evaluation methods and theories for estimating sustainability values, as applied in practice in various sectors (e.g., those areas concerning water, soil, air, waste management, supply chains, materials, renewable energy, etc.).
Topics of interest include current research about applications of sustainability measurement in the following area:
- Multi-criteria, analytic network process;
- Fuzzy set, Fuzzy inference, Fuzzy multicriteria;
- Soft computing: Neuro-fuzzy, Neural net, Algorithm genetics, evolution algorithms particle swarm optimization (PSO), chaos theory;
- Artificial Intelligence (AI)
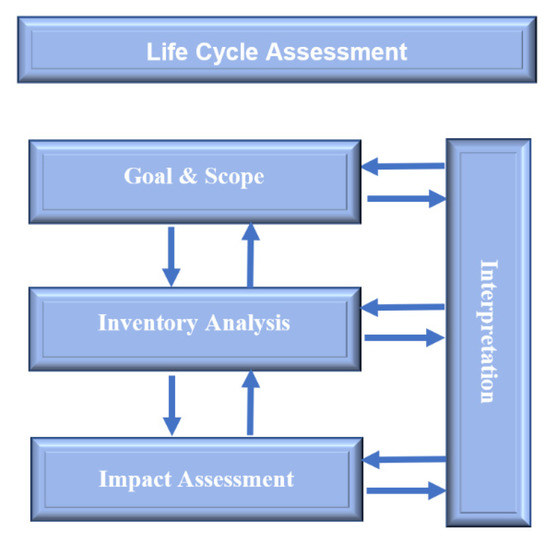
- Hybrid models: LCA+multi-criteria, LCA+Fuzzy-sets, LCA+Algoritm genetics, Footprint+fuzzy inference, Carbon footprint+ fuzzy-sets, others hybrids models;
- Dynamic Systems;
- Montecarlo analysis, mathematical programming and goal programming;
- Other advanced modeling of environmental sustainability
Prof. Dr. Fausto Cavallaro
Collection Editor
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Sustainability is an international peer-reviewed open access semimonthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2400 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- Sustainability assessment
- Sustainabilty management
- Multi-criteria
- Fuzzy set and inference
- Soft computing