Firm Size and Sustainable Innovation Management (Closed)
A topical collection in Sustainability (ISSN 2071-1050).
Viewed by 96614Editors
Interests: innovation management; alliances and networks; technology strategy; patenting, technology transfer; university-industry collaborations; search and recombination
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Interests: innovation; technology management; strategy
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
The interest in the relationship between firm size and innovation management dates back to the pioneering studies by Schumpeter. So far, a wealth of research has been conducted on this topic. However, in-depth discussion about the influence of firm size on sustainable innovation management has been neglected, hence requiring further debates as highlighted by Messeni Petruzzelli and Ardito [1].
That is, in the context of sustainable innovation management, there has been the tendency to rely on the “conventional” theories regarding the role of firm size. However, such theories may be not completely valid in this context because of the specific peculiarities differentiating sustainable innovations from conventional ones (e.g., regulations, types of firms - e.g., family vs. non-family - ultimate goals, openness, ethics, and more complex innovation outcomes). Therefore, in the realm of sustainable innovation, a reassessment/repositioning of the role of firm size can be reasonable.
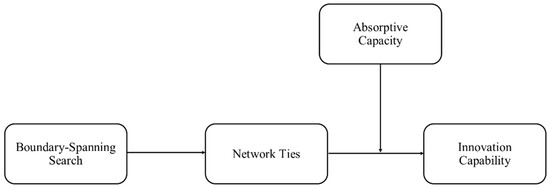
Specifically, it has been proven that firm size may directly affect innovation performance or how firms shape their strategic orientations, organizational structure, knowledge management system, etc. to innovate. Yet, whether these direct influences of firm size remain the same in the context of sustainable innovation management is still an open area of research. Furthermore, it has been shown that, in some cases, the direct effect of firm size is moderated/mediated by other factors (e.g., absorptive capacity) or, conversely, firm size acts as a moderating/mediating factor in explaining innovation performance [2].
This implies that the direct effects that firm size has on sustainable innovation management may be subject to some of its specificities. Likewise, the effects of factors already proved to influence sustainable innovation practices, processes, and outcomes, especially if they are contradictory, can be reassessed by distinguishing firms by their size.
All in all, we contend that there are many open issues in the literature regarding firm size and sustainable innovation management. In line with the above debate, we invite original contributions that increase our comprehension on this topic. We look for papers with theoretical insights, empirical data analysis, case studies or other suitable methods to shed new light on a variety of lines of inquiry, such as:
- repositioning/reconceptualizing the role of firm size in the context of sustainable innovation management;
- assessing which aspects of sustainable innovation management (strategic orientations, organizational structure, business models, firms’ openness, etc.) are mainly influenced by firm size;
- assessing which are the specificities characterizing sustainable innovation practices, processes, and outcomes that may help to revisit the role of firm size;
- reassessing the influence of factors affecting practices, processes, and outcomes related to sustainable innovations in light of the potential moderating influence of firm size;
- evaluating the moderating/mediating factors of the relationship between firm size and sustainable innovation management practices, processes, and outcomes.
References
Messeni Petruzzelli, A., and L. Ardito. (2019). Firm Size and Sustainable Innovation Management. Sustainability 11(21), 6072, https://doi.org/10.3390/su11216072
Messeni Petruzzelli, A., L. Ardito, and T. Savino. (2018). Maturity of knowledge inputs and innovation value: Journal of Business Research 86, 190-201, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2018.02.009
Prof. Dr. Antonio Messeni Petruzzelli
Dr. Lorenzo Ardito
Collection Editors
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Sustainability is an international peer-reviewed open access semimonthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2400 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- firm size
- sustainable innovation management
- sustainable innovation practices, processes, and outcomes
- innovation performance
- strategic management