Xenobiotics in Developmental Neurotoxicity (Closed)
A topical collection in Toxics (ISSN 2305-6304). This collection belongs to the section "Reproductive and Developmental Toxicity".
Viewed by 42746Editor
Interests: pancreatic cancer; environmental toxicants; mitochondrial toxicity; apoptosis; cellular regulation; tryptophan-kynurenine pathway; indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
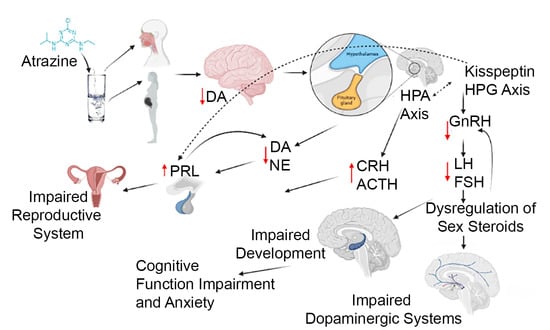
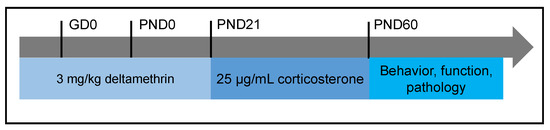
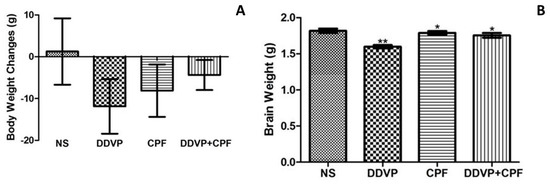
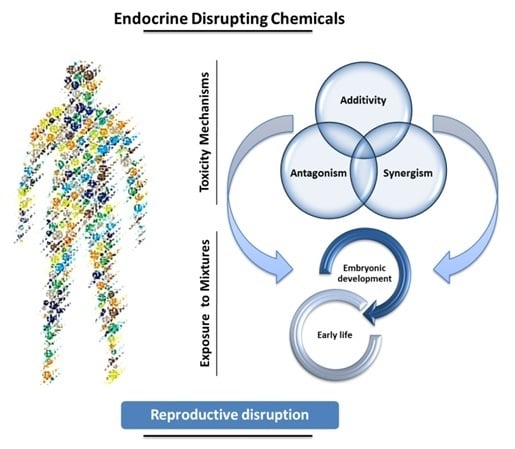
The role of xenobiotics in the development of the brain is a rapidly expanding field. A xenobiotic agent is a foreign substance found in a biological organism that would not be normally found in that organism, or found at much higher concentrations than expected. These agents can cover chemical pollutants, drugs, or other biological agents, such as viral particles. There have been significant advances in neuroscience research over the last two decades. The developing brain is extremely sensitive to insult from exogenous xenobiotics. This sensitivity is not confined to in utero exposure, but also throughout infant, toddler, and pre-teen adolescent neurodevelopment. Work in developmental neurotoxicology (DNT) has lagged. Reasons for this delay include; (1) difficulty in finding appropriate model systems, (2) lack of existing toxicology data on many of the chemicals that are commercially available, and (3) relative lack of information regarding mixtures of various chemicals that are commercially available. Most xenobiotics can be categorized based on their physiological/chemical agent. These categories include antioxidants, carcinogens, drugs (prescription/over-the-counter/illegal), environmental pollutants, food additives, hydrocarbons, and pesticides. Of the tens of thousands of compounds, only about 100 compounds have minimal or incomplete evidence of DNT, which includes some pesticides (organophosphates), prescription drugs and a variety of other chemicals. It is clear that additional research is needed to identify appropriate model systems to study DNT effects that will improve the translation from alternative to human model systems. Also, additional work is needed to identify and develop accurate biomarkers that will signal exposure to DNT compounds early in the exposure period, facilitating medical intervention. The purpose of this Topical Collection is to provide a forum to develop a compendium of work spanning a variety of topics to further our understanding of DNT.
Prof. David R. Wallace
Collection Editor
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Toxics is an international peer-reviewed open access monthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2600 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- xenobiotics
- biomarkers
- animal models
- in vitro testing
- neurodevelopment
- risk assessment