Topic Editors


Advanced Electrical Machines and Drives Technologies, 2nd Volume
Topic Information
Dear Colleagues,
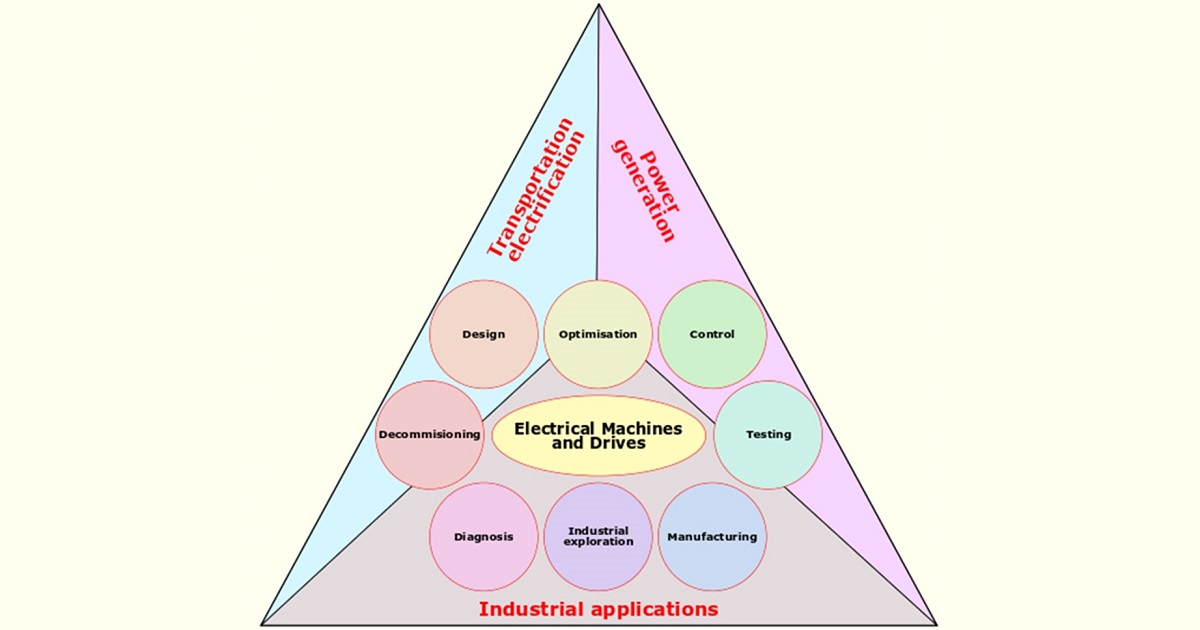
This Topic is a continuation of the previous successful Topic “Advanced Electrical Machines and Drives Technologies”. Electrical machines and drives are among the most important components used in a wide application range, such as industry, transportation, power systems, etc. Also, nowadays, their development is a real challenge, as it is concentrated on efficiency improvements, together with material and manufacturing cost reductions. The literature on such devices is huge, covering a lot of working principles and topologies. Worldwide, a great number of specialists are involved in these fields, who are seeking both the latest technical advancements and publishing possibilities to reach a greater audience.
This topic intends to collect papers from the fields of electrical machines and drives which focus on their design, optimization, modeling, experimental testing, and fabrication, as well on their application fields. Multidisciplinary approaches are welcomed.
Prof. Dr. Loránd Szabó
Dr. Marcin Wardach
Topic Editors
Keywords
- bearingless electrical machines
- brushless DC motors
- claw-pole generators
- double salient permanent magnet machines
- electrical machine vibrations and noises
- fault-tolerant electrical machines and Induction machines
- flux reversal machines and Flux-switching machines
- hybrid excitation machines and steppers
- linear motors and memory motors
- permanent-magnet-assisted variable reluctance machines
- permanent magnet synchronous machines and Switched reluctance machines
- multiphase, high-speed, high-power, low-cost motors and drives
- high-performance AC motors and servo drives
- advanced control algorithms for AC motor drives
- fault diagnosis and fault tolerance in AC motors and drives
Participating Journals
| Journal Name | Impact Factor | CiteScore | Launched Year | First Decision (median) | APC | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

Applied Sciences
|
2.5 | 5.3 | 2011 | 17.8 Days | CHF 2400 | Submit |
Designs
|
- | 3.9 | 2017 | 15.2 Days | CHF 1600 | Submit |

Energies
|
3.0 | 6.2 | 2008 | 17.5 Days | CHF 2600 | Submit |
Machines
|
2.1 | 3.0 | 2013 | 15.6 Days | CHF 2400 | Submit |

Vehicles
|
2.4 | 4.1 | 2019 | 24.7 Days | CHF 1600 | Submit |

MDPI Topics is cooperating with Preprints.org and has built a direct connection between MDPI journals and Preprints.org. Authors are encouraged to enjoy the benefits by posting a preprint at Preprints.org prior to publication:
- Immediately share your ideas ahead of publication and establish your research priority;
- Protect your idea from being stolen with this time-stamped preprint article;
- Enhance the exposure and impact of your research;
- Receive feedback from your peers in advance;
- Have it indexed in Web of Science (Preprint Citation Index), Google Scholar, Crossref, SHARE, PrePubMed, Scilit and Europe PMC.
Related Topic
- Advanced Electrical Machines and Drives Technologies (54 articles)

