Topic Menu
► Topic MenuTopic Editors



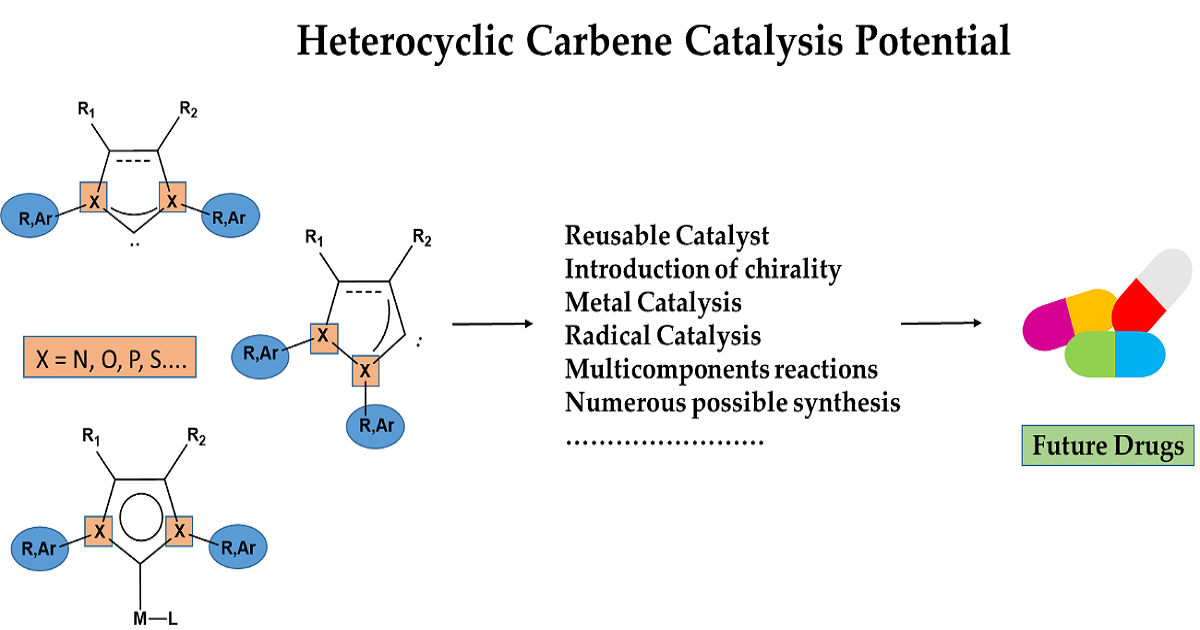
Heterocyclic Carbene Catalysis
Topic Information
Dear Colleagues,
Heterocyclic carbene catalysis is a powerful process that has experienced rapid development. In particular, N-heterocycle carbenes (NHC), which have been applied in wide areas of organic synthesis. Their use in catalysis for the formation of new bonds via umpolung or non-umpolung mechanisms has developed in the last decade, involving several intermediates and allowing a fairly wide use of this type of catalysis. Recent applications have been reported in total natural synthesis with stereo and regioselectivity. We believe that the use of these intermediates or ligands will increase.
This Topic aims to review new methods and recent developments for the synthesis of complexes with heterocyclic carbene ligands and their use for the synthesis of various molecules of interest.
Prof. Dr. Sabine Berteina-Raboin
Prof. Dr. Thierry Besson
Prof. Dr. Patrick Rollin
Topic Editors
Keywords
- catalysis
- natural products
- total synthesis
- heterocyclic carbenes
- ligands
- coordination chemistry
- transition metal catalysis and organocatalysis
- heterocyclic chemistry
Participating Journals
| Journal Name | Impact Factor | CiteScore | Launched Year | First Decision (median) | APC | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

Catalysts
|
3.8 | 6.8 | 2011 | 12.9 Days | CHF 2200 | Submit |
Chemistry
|
2.4 | 3.2 | 2019 | 13.4 Days | CHF 1800 | Submit |
Inorganics
|
3.1 | 2.8 | 2013 | 14.7 Days | CHF 2700 | Submit |

Molbank
|
0.6 | 0.7 | 1997 | 13.9 Days | CHF 500 | Submit |

Molecules
|
4.2 | 7.4 | 1996 | 15.1 Days | CHF 2700 | Submit |

Polymers
|
4.7 | 8.0 | 2009 | 14.5 Days | CHF 2700 | Submit |

MDPI Topics is cooperating with Preprints.org and has built a direct connection between MDPI journals and Preprints.org. Authors are encouraged to enjoy the benefits by posting a preprint at Preprints.org prior to publication:
- Immediately share your ideas ahead of publication and establish your research priority;
- Protect your idea from being stolen with this time-stamped preprint article;
- Enhance the exposure and impact of your research;
- Receive feedback from your peers in advance;
- Have it indexed in Web of Science (Preprint Citation Index), Google Scholar, Crossref, SHARE, PrePubMed, Scilit and Europe PMC.

