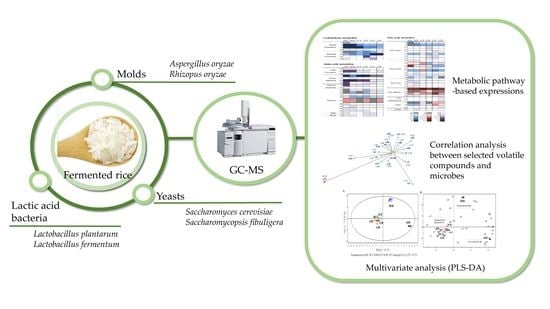
Distinctive Formation of Volatile Compounds in Fermented Rice Inoculated by Different Molds, Yeasts, and Lactic Acid Bacteria
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. PLS-DA for Volatile Metabolite Profiles in Fermented Rice
2.2. Volatile Compounds Based on Metabolic Pathways in Fermented Rice According to Each Microbe
2.3. Microbe-Specific Volatile Compounds in Fermented Rice
3. Material and Methods
3.1. Chemicals and Reagents
3.2. Sample Preparation
3.3. Volatile Compounds Analysis
3.4. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lee, S.-W.; Yoon, S.-R.; Kim, G.-R.; Woo, S.-M.; Jeong, Y.-J.; Yeo, S.-H.; Kim, K.-S.; Kwon, J.-H. Effect of nuruk and fermentation method on organic acid and volatile compounds in brown rice vinegar. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2012, 21, 453–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blandino, A.; Al-Aseeri, M.E.; Pandiella, S.S.; Cantero, D.; Webb, C. Cereal-based fermented foods and beverages. Food Res. Int. 2003, 36, 527–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kum, S.J.; Yang, S.O.; Lee, S.M.; Chang, P.S.; Choi, Y.H.; Lee, J.J.; Hurh, B.S.; Kim, Y. Effects of Aspergillus species inoculation and their enzymatic activities on the formation of volatile components in fermented soybean paste (doenjang). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 1401–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, M.K.; Cho, I.H.; Lee, S.; Choi, H.-K.; Kwon, D.-Y.; Kim, Y.-S. Metabolite profiling of cheonggukjang, a fermented soybeanpaste, during fermentation by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry and principal component analysis. Food Chem. 2010, 122, 1313–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Z.; Dai, S.; Niu, Y.; Yu, H.; Zhu, J.; Tian, H.; Gu, Y. Discrimination of Chinese vinegars based on headspace solid-phase microextraction-gas chromatography mass spectrometry of volatile compounds and multivariate analysis. J. Food Sci. 2011, 76, C1125–C1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, E.Y.; Lee, S.M.; Kim, M.J.; Seo, J.A.; Kim, Y.-S. Comparison of volatile and non-volatile metabolites in rice wine fermented by Koji inoculated with Saccharomycopsis fibuligera and Aspergillus oryzae. Food Res. Int. 2018, 109, 596–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, M.K.; Choi, H.-S.; Kim, Y.-S.; Cho, I.H. Change in profiles of volatile compounds from two types of Fagopyrum Esculentum (buckwheat) soksungjang during fermentation. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2017, 26, 871–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, J.-H.; Kim, Y.-H.; Kim, J.H.; Choi, S.; Lee, J.-S.; Kim, H.-K. Comparison of microbial diversity of Korean commercial makgeolli showing high β-glucan content and high antihypertensive activity, respectively. Mycobiology 2012, 40, 138–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haruta, S.; Ueno, S.; Egawa, I.; Hashiguchi, K.; Fujii, A.; Nagano, M.; Ishii, M.; Igarashi, Y. Succession of bacterial and fungal communities during a traditional pot fermentation of rice vinegar assessed by PCR-mediated denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2006, 109, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stark, D.; Münch, T.; Sonnleitner, B.; Marison, I.W.; von Stockar, U. Extractive bioconversion of 2-phenylethanol from l-phenylalanine by Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biotechnol. Prog. 2002, 18, 514–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Sharma, N.S.; Saharan, M.R.; Singh, R. Extracellular acid protease from Rhizopus oryzae: Purification and characterization. Process Biochem. 2005, 40, 1701–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazelwood, L.A.; Daran, J.M.; van Maris, A.J.; Pronk, J.T.; Dickinson, J.R. The Ehrlich pathway for fusel alcohol production: A century of research on Saccharomyces cerevisiae metabolism. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 74, 2259–2266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leroy, F.; De Vuyst, L. Lactic acid bacteria as functional starter cultures for the food fermentation industry. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2004, 15, 67–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, H.; Hwang, H.; Lee, J.E.; Kim, H.R. Quantitative analysis of volatile flavor components in Korean alcoholic beverage and Japanese sake using SPME-GC/MS. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2016, 25, 979–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, D.E.; Lee, S.M.; Jang, E.S.; Shin, H.W.; Moon, B.S.; Lee, C.H. Metabolomic profiles of Aspergillus oryzae and Bacillus amyloliquefaciens during rice koji fermentation. Molecules 2016, 21, 773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, H.S.; Lee, S.M.; Singh, D.; Park, M.K.; Kim, Y.-S.; Shin, H.W.; Cho, S.A.; Lee, C.H. Evaluating the headspace volatolome, primary metabolites, and aroma characteristics of koji fermented with Bacillus amyloliquefaciens and Aspergillus oryzae. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 28, 1260–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boumba, V.A.; Ziavrou, K.S.; Vougiouklakis, T. Biochemical pathways generating post-mortem volatile compounds co-detected during forensic ethanol analyses. Forensic Sci. Int. 2008, 174, 133–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, F.; Ludovico, P.; Leão, C. Sugar metabolism in yeasts: An overview of aerobic and anaerobic glucose catabolism. In Biodiversity and Ecophysiology of Yeasts; Péter, G., Rosa, C., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2006; pp. 101–121. [Google Scholar]
- Vivijs, B.; Moons, P.; Geeraerd, A.H.; Aertsen, A.; Michiels, C.W. 2,3-Butanediol fermentation promotes growth of Serratia Plymuthica at low pH but not survival of extreme acid challenge. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2014, 175, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pogačić, T.; Maillard, M.-B.; Leclerc, A.; Hervé, C.; Chuat, V.; Valence, F.; Thierry, A. Lactobacillus and Leuconostoc volatilomes in cheese conditions. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 100, 2335–2346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonda, I.; Bar, E.B.; Portnoy, V.; Lev, S.; Burger, J.; Schaffer, A.A.; Tadmor, Y.; Gepstein, S.; Giovannoni, J.J.; Lewinsohn, N.K.E. Branched-chain and aromatic amino acid catabolism into aroma volatiles in Cucumis melo L. Fruit. J. Exp. Bot. 2010, 61, 1111–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landaud, S.; Helinck, S.; Bonnarme, P. Formation of volatile sulfur compounds and metabolism of methionine and other sulfur compounds in fermented food. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2008, 77, 1191–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.-M.; Shin, K.-J.; Lee, S.-J. Exploring nuruk aroma; identification of volatile compounds in commercial fermentation starters. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2016, 25, 393–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masuo, S.; Osada, L.; Zhou, S.; Fujita, T.; Takaya, N. Aspergillus oryzae pathways that convert phenylalanine into the flavor volatile 2-phenylethanol. Fungal Genet. Biol. 2015, 77, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirata, H.; Ohnishi, T.; Watanabe, N. Biosynthesis of floral scent 2-phenylethanol in rose flowers. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2016, 80, 1865–1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zeng, Z.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, T.; Tamogami, S.; Chen, J.Y. Analysis of flavor volatiles of glutinous rice during cooking by combined gas chromatography–mass spectrometry with modified headspace solid-phase microextraction Method. J. Food Composit. Anal. 2009, 22, 347–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šućur, S.; ČADEŽ, N.; KOŠMERL, T. Volatile phenols in wine: Control measures of Brettanomyces/Dekkera Yeasts. Acta Agric. Slov. 2016, 107, 453–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.-E.; Kim, C.-W.; Yeo, S.-H.; Jeong, S.-T.; Kim, Y.-S.; Choi, H.-S. Effect of heat-treated Nuruk on the quality characteristics of aged Yakju. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2018, 27, 715–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, A.-Q.; Juwono, N.K.P.; Leong, S.S.J.; Chang, M.W. Production of fatty acid-derived valuable chemicals in synthetic microbes. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2014, 2, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romero-Guido, C.; Belo, I.; Ta, T.M.N.; Cao-Hoang, L.; Alchihab, M.; Gomes, N.; Thonart, P.; Teixeira, J.A.; Destain, J.; Waché, Y. Biochemistry of lactone formation in yeast and fungi and its utilisation for the production of flavour and fragrance compounds. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2011, 89, 535–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mo, X.; Fan, W.; Xu, Y. Changes in volatile compounds of Chinese rice wine wheat Qu during fermentation and storage. J. Inst. Brewing 2009, 115, 300–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, J.; Nam, P.-W.; Lee, S.-J.; Lee, K.-G. Volatile compounds isolated from rice beers brewed with three medicinal plants. J. Inst. Brewing 2013, 119, 271–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacvonkralj, M.; Jug, T.; Komel, E.; Fajt, N.; JARNI, K.; Zivkovic, J.; Mujic, I.; Trutic, N. Effects of ripening degree and sample preparation on peach aroma profile characterization by headspace solid-phase microextraction. Turk. J. Agric. For. 2014, 38, 676–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, S.; Choi, S.J.; Kwak, J.; Kim, K.; Seo, M.; Moon, T.W.; Lee, Y.-W. Aspergillus oeyzae strains isolated from traditional Korean nuruk: Fermentation properties and influence on rice wine quality. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2013, 22, 425–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalaivani, M.; Sabitha, R.; Kalaiselvan, V.; Rajasekaran, A. Health benefits and clinical impact of major nutrient, red yeast rice: A review. Food Bioproc. Tech. 2009, 3, 333–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhadana, B.; Chauhan, M. Bioethanol production using Saccharomyces cerevisiae with different perspectives: Substrates, growth variables, inhibitor reduction and immobilization. Ferment. Technol. 2016, 5, 3–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steele, J.; Broadbent, J.; Kok, J. Perspectives on the contribution of lactic acid bacteria to cheese flavor development. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2013, 24, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pires, E.J.; Teixeira, J.A.; Brányik, T.; Vicente, A.A. Yeast: The soul of beer’s aroma—A review of flavour-active esters and higher alcohols produced by the brewing yeast. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 98, 1937–1949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are not available from the authors. |


| No. 1 | Volatile Compound | Sample 2 |
|---|---|---|
| v6 | 2-Methylbutanal | AOR |
| v7 | 3-Methylbutanal | |
| v9 | Ethyl propanoate | |
| v16 | Ethyl 2-methylbutanoate | |
| v46 | 2-Methylpropanoic acid | |
| v48 | 2-Phenylacetaldehyde | |
| v21 | 3-Methylbutyl acetate | ROR |
| v51 | 5-Ethyloxolan-2-one | |
| v36 | 3-Ethoxypropan-1-ol | |
| v55 | Ethyl tetradecanoate | |
| v49 | 1-Phenylethanone | |
| v54 | 2-Phenylethanol | |
| v12 | 3-Methylpentan-2-one | RICE/SCR/SPR/LFR/LPR |
| v18 | Hexanal | |
| v23 | 5-Methylhexan-2-one | |
| v24 | Butan-1-ol | |
| v27 | 3-Hydroxy-3-methylbutan-2-one | |
| v30 | 3-Hydroxybutan-2-one | |
| v41 | Furan-2-carbaldehyde | |
| v45 | Butane-2,3-diol | |
| v53 | Hexanoic acid |
| No. 1 | Volatile Compound | RI 2 | Relative Peak Area (Mean ± SD) 3 | ID 4 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RICE 5 | AOR | ROR | SCR | SFR | LFR | LPR | ||||
| Carbohydrate metabolism | ||||||||||
| Ethanol fermentation | ||||||||||
| v1 | Acetaldehyde | <800 | ND 6a 7 | 0.723 ± 0.009c | 0.300 ± 0.006b | NDa | NDa | NDa | NDa | B |
| v4 | Ethyl acetate | 885 | 0.013 ± 0.002a | 0.438 ± 0.014f | 0.337 ± 0.007e | 0.092 ± 0.006d | 0.025 ± 0.003ab | 0.052 ± 0.005c | 0.031 ± 0.002b | A |
| v8 | Ethanol | 931 | 0.080 ± 0.007a | 19.811 ± 0.558b | 31.903 ± 0.914c | 33.447 ± 1.427d | 0.466 ± 0.021a | 0.700 ± 0.021a | 0.167 ± 0.003a | A |
| v40 | Acetic acid | 1454 | NDa | 0.058 ± 0.002c | 0.152 ± 0.005e | 0.038 ± 0.002b | 0.096 ± 0.006d | NDa | 0.485 ± 0.014f | A |
| Butanediol fermentation | ||||||||||
| v11 | Butane-2,3-dione | 971 | 0.187 ± 0.010b | NDa | NDa | 0.487 ± 0.017c | 1.259 ± 0.055e | 0.719 ± 0.022d | 0.165 ± 0.003b | A |
| v30 | 3-Hydroxybutan-2-one | 1279 | 0.037 ± 0.002a | 0.069 ± 0.002ab | 0.270 ± 0.002b | 0.107 ± 0.004ab | 0.265 ± 0.012b | 12.172 ± 0.310d | 0.781 ± 0.024c | A |
| v45 | Butane-2,3-diol | 1542 | NDa | NDa | NDa | NDa | 1.657 ± 0.073c | 0.163 ± 0.008b | NDa | A |
| v47 | Butane-1,3-diol | 1579 | NDa | 0.257 ± 0.005c | NDa | NDa | 0.195 ± 0.010b | 0.507 ± 0.016d | NDa | A |
| Amino acid metabolism | ||||||||||
| Valine degradation | ||||||||||
| v6 | 2-Methylbutanal | 909 | NDa | 1.485 ± 0.040c | 0.014 ± 0.003a | 0.070 ± 0.006b | 0.011 ± 0.000a | NDa | NDa | A |
| v16 | Ethyl 2-methylbutanoate | 1050 | NDa | 0.110 ± 0.002b | NDa | NDa | NDa | NDa | NDa | A |
| Leucine degradation | ||||||||||
| v7 | 3-Methylbutanal | 913 | 0.011 ± 0.002a | 3.824 ± 0.106d | 0.108 ± 0.001b | 0.237 ± 0.008c | 0.125 ± 0.007b | NDa | NDa | A |
| v21 | 3-Methylbutyl acetate | 1119 | NDa | NDa | 0.042 ± 0.002b | NDa | NDa | NDa | NDa | A |
| v25 | 3-Methylbutan-1-ol | 1211 | NDa | 14.935 ± 0.420c | 39.594 ± 1.129d | 1.298 ± 0.055b | 1.03 ± 0.045b | 0.036 ± 0.005a | 0.080 ± 0.001a | A |
| v50 | 3-Methylbutanoic acid | 1683 | NDa | 1.314 ± 0.035d | NDa | NDa | 0.324 ± 0.015c | 0.191 ± 0.008b | NDa | A |
| Isoleucine degradation | ||||||||||
| v10 | Ethyl 2-methylpropanoate | 959 | NDa | 0.462 ± 0.011c | 0.204 ± 0.004b | NDa | NDa | NDa | NDa | A |
| v19 | 2-Methylpropan-1-ol | 1100 | NDa | 2.439 ± 0.067d | 2.359 ± 0.059c | 0.216 ± 0.009b | 0.032 ± 0.004a | NDa | 0.026 ± 0.002a | A |
| v46 | 2-Methylpropanoic acid | 1575 | NDa | 0.368 ± 0.008b | NDa | NDa | NDa | NDa | NDa | A |
| Benzenes | ||||||||||
| v13 | Toluene | 1033 | 0.102 ± 0.019c | NDa | 0.146 ± 0.005d | 0.082 ± 0.003b | 0.260 ± 0.012e | 0.082 ± 0.006b | 0.110 ± 0.001c | A |
| v20 | Ethylbenzene | 1115 | 0.027 ± 0.002bc | NDa | 0.064 ± 0.007d | NDa | 0.071 ± 0.005d | 0.024 ± 0.004b | 0.032 ± 0.002c | A |
| v22 | 1,4-Xylene | 1130 | NDa | NDa | 0.046 ± 0.002b | NDa | 0.053 ± 0.005c | NDa | NDa | A |
| v28 | Styrene | 1250 | 0.074 ± 0.004a | 0.068 ± 0.002a | 0.190 ± 0.004f | 0.145 ± 0.006e | 0.136 ± 0.007d | 0.088 ± 0.006b | 0.106 ± 0.001c | A |
| v44 | Benzaldehyde | 1517 | 0.178 ± 0.010e | 0.083 ± 0.001c | 0.048 ± 0.008b | NDa | 0.107 ± 0.006d | NDa | 0.110 ± 0.001d | A |
| v48 | 2-Phenylacetaldehyde | 1637 | NDa | 0.222 ± 0.004b | NDa | NDa | NDa | NDa | NDa | A |
| v49 | 1-Phenylethanone | 1645 | NDa | NDa | 0.039 ± 0.008b | NDa | NDa | NDa | NDa | A |
| v52 | Ethyl 2-phenylacetate | 1785 | NDa | 0.117 ± 0.002c | 0.035 ± 0.002b | NDa | NDa | NDa | NDa | A |
| v54 | 2-Phenylethanol | >1900 | NDa | 0.020 ± 0.002b | 0.455 ± 0.004e | 0.131 ± 0.005d | 0.038 ± 0.004c | NDa | NDa | B |
| Sulfur-containing volatile compounds | ||||||||||
| v17 | (methyldisulfanyl)Methane | 1065 | NDa | 0.114 ± 0.002d | NDa | NDa | 0.024 ± 0.004b | 0.023 ± 0.004b | 0.030 ± 0.002c | A |
| Phenol | ||||||||||
| v56 | 4-Ethenyl-2-methoxyphenol | >1900 | NDa | 0.021 ± 0.002b | 0.020 ± 0.003b | NDa | 0.048 ± 0.005c | 0.069 ± 0.005d | NDa | B |
| Fatty acid metabolism | ||||||||||
| Fatty Ketones | ||||||||||
| v2 | Propan-2-one | 812 | 0.227 ± 0.014b | 1.040 ± 0.010f | 0.103 ± 0.001a | 0.270 ± 0.009c | 0.337 ± 0.015e | 0.316 ± 0.012d | 0.218 ± 0.005b | A |
| v5 | Butan-2-one | 901 | 0.044 ± 0.002b | NDa | 0.372 ± 0.008f | 0.109 ± 0.006e | 0.106 ± 0.006e | 0.085 ± 0.006d | 0.068 ± 0.001c | A |
| v12 | 3-Methylpentan-2-one | 1012 | NDa | NDa | NDa | NDa | 0.175 ± 0.009b | NDa | NDa | A |
| v23 | 5-Methylhexan-2-one | 1136 | NDa | NDa | NDa | NDa | 0.02 ± 0.003b | NDa | NDa | A |
| v27 | 3-Hydroxy-3-methylbutan-2-one | 1239 | NDa | NDa | NDa | NDa | NDa | 0.078 ± 0.006b | NDa | C |
| v33 | 6-Methylhept-5-en-2-one | 1334 | 0.033 ± 0.002a | 0.094 ± 0.001e | 0.051 ± 0.008bc | 0.045 ± 0.002b | 0.063 ± 0.005d | 0.037 ± 0.005a | 0.055 ± 0.001c | A |
| v34 | 3-Hydroxypentan-2-one | 1337 | NDa | NDa | NDa | NDa | 0.060 ± 0.005b | 0.079 ± 0.006c | NDa | C |
| v37 | Nonan-2-one | 1386 | NDa | NDa | NDa | NDa | 0.043 ± 0.004c | 0.012 ± 0.000b | NDa | A |
| Fatty alcohols | ||||||||||
| v15 | Propan-1-ol | 1041 | NDa | 0.447 ± 0.01c | 0.085 ± 0.007b | NDa | NDa | NDa | NDa | A |
| v24 | Butan-1-ol | 1150 | 0.081 ± 0.007c | 0.081 ± 0.001c | 0.069 ± 0.007b | 0.030 ± 0.002a | 0.159 ± 0.008e | 0.069 ± 0.005b | 0.121 ± 0.001d | A |
| v29 | Pentan-1-ol | 1254 | 0.147 ± 0.009cd | 0.040 ± 0.002a | 0.151 ± 0.005d | 0.118 ± 0.005b | 0.138 ± 0.007c | 0.240 ± 0.010e | 0.246 ± 0.006e | A |
| v32 | 3-Methylbut-2-en-1-ol | 1323 | NDa | NDa | NDa | NDa | 0.030 ± 0.004b | 0.027 ± 0.004b | NDa | C |
| v35 | Hexan-1-ol | 1357 | 0.102 ± 0.011b | 0.321 ± 0.007e | 0.311 ± 0.002e | 0.069 ± 0.003a | 0.218 ± 0.011c | 0.501 ± 0.016f | 0.294 ± 0.007d | A |
| v36 | 3-Ethoxypropan-1-ol | 1377 | NDa | NDa | 0.055 ± 0.008b | NDa | NDa | NDa | NDa | A |
| v39 | Oct-1-en-3-ol | 1454 | 0.029 ± 0.002b | 0.050 ± 0.002d | 0.035 ± 0.002c | 0.040 ± 0.002c | 0.058 ± 0.005e | 0.030 ± 0.004b | NDa | A |
| v42 | 2-Ethylhexan-1-ol | 1493 | NDa | 0.044 ± 0.002cd | 0.056 ± 0.008e | 0.046 ± 0.002d | 0.099 ± 0.006f | 0.031 ± 0.004b | 0.038 ± 0.002bc | A |
| Fatty esters | ||||||||||
| v9 | Ethyl propanoate | 950 | NDa | 0.240 ± 0.005b | NDa | NDa | NDa | NDa | NDa | A |
| v14 | Ethyl butanoate | 1034 | NDa | 0.271 ± 0.005c | 0.251 ± 0.003b | NDa | NDa | NDa | NDa | A |
| v55 | Ethyl tetradecanoate | >1900 | NDa | NDa | 0.051 ± 0.008b | NDa | NDa | NDa | NDa | B |
| v57 | Ethyl hexadecanoate | >1900 | NDa | 0.098 ± 0.001b | 0.321 ± 0.002c | NDa | NDa | NDa | NDa | B |
| Fatty aldehydes | ||||||||||
| v18 | Hexanal | 1076 | 1.305 ± 0.086d | 0.190 ± 0.003b | 0.242 ± 0.003b | 0.105 ± 0.004a | 0.249 ± 0.012b | 0.071 ± 0.005a | 0.201 ± 0.004b | A |
| v31 | Octanal | 1284 | 0.026 ± 0.002c | NDa | NDa | 0.018 ± 0.001b | 0.029 ± 0.004d | NDa | NDa | A |
| v38 | Nonanal | 1390 | 0.265 ± 0.017e | 0.182 ± 0.003c | 0.215 ± 0.003d | 0.192 ± 0.008c | 0.193 ± 0.01c | 0.051 ± 0.005a | 0.080 ± 0.001b | A |
| v43 | Decanal | 1496 | NDa | 0.069 ± 0.002d | 0.040 ± 0.008c | NDa | NDa | 0.028 ± 0.004b | 0.025 ± 0.002b | A |
| Fatty carboxylic acid | ||||||||||
| v53 | Hexanoic acid | 1865 | NDa | NDa | NDa | NDa | NDa | NDa | 0.075 ± 0.001b | A |
| Furans | ||||||||||
| v3 | Oxolane | 855 | 0.137 ± 0.008d | NDa | NDa | 0.189 ± 0.007e | NDa | 0.037 ± 0.005b | 0.068 ± 0.001c | A |
| v26 | 2-Pentylfuran | 1227 | 0.045 ± 0.002c | 0.089 ± 0.001f | 0.071 ± 0.007e | 0.036 ± 0.002ab | 0.062 ± 0.005d | 0.029 ± 0.004a | 0.040 ± 0.002bc | A |
| v41 | Furan-2-carbaldehyde | 1459 | 0.021 ± 0.002b | NDa | NDa | NDa | NDa | NDa | NDa | A |
| Lactone | ||||||||||
| v51 | 5-Ethyloxolan-2-one | 1694 | NDa | NDa | 0.094 ± 0.007b | NDa | NDa | NDa | NDa | A |
| AOR 3 | ROR | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No.1 | r-Value 2 | Volatile Compound | No. | r-Value | Volatile Compound |
| v16 | 1.00 | Ethyl 2-methylbutanoate | v21 | 1.00 | 3-Methylbutyl acetate |
| v48 | 1.00 | 2-Phenylacetaldehyde | v51 | 1.00 | 5-Ethyloxolan-2-one |
| v9 | 1.00 | Ethyl propanoate | v36 | 0.99 | 3-Ethoxypropan-1-ol |
| v46 | 1.00 | 2-Methylpropanoic acid | v55 | 0.99 | Ethyl tetradecanoate |
| v6 | 1.00 | 2-Methylbutanal | v49 | 0.98 | 1-Phenylethanone |
| v7 | 1.00 | 3-Methylbutanal | v54 | 0.96 | 2-Phenylethanol |
| v15 | 0.98 | Propan-1-ol | v57 | 0.95 | Ethyl hexadecanoate |
| v2 | 0.97 | Propan-2-one | v5 | 0.95 | Butan-2-one |
| v50 | 0.97 | 3-Methylbutanoic acid | v25 | 0.93 | 3-Methylbutan-1-ol |
| v52 | 0.95 | Ethyl 2-phenylacetate | v28 | 0.75 | Styrene |
| v17 | 0.95 | (methyldisulfanyl)Methane | |||
| v1 | 0.91 | Acetaldehyde | |||
| v10 | 0.90 | Ethyl 2-methylpropanoate | |||
| v33 | 0.88 | 6-Methylhept-5-en-2-one | |||
| v43 | 0.78 | Decanal | |||
| v4 | 0.75 | Ethyl acetate | |||
| v29 | −0.72 | Pentan-1-ol | |||
| SPR | SCR | ||||
| v12 | 1.00 | 3-Methylpentan-2-one | v3 | 0.93 | Oxolane |
| v45 | 0.99 | Butane-2,3-diol | |||
| v23 | 0.99 | 5-Methylhexan-2-one | |||
| v37 | 0.96 | Nonan-2-one | |||
| v42 | 0.93 | 2-Ethylhexan-1-ol | |||
| v13 | 0.83 | Toluene | |||
| v31 | 0.82 | Octanal | |||
| v11 | 0.82 | Butane-2,3-dione | |||
| v24 | 0.76 | Butan-1-ol | |||
| v22 | 0.70 | 1,4-Xylene | |||
| LFR | LPR | ||||
| v30 | 1.00 | 3-Hydroxybutan-2-one | v53 | 1.00 | Hexanoic acid |
| v27 | 1.00 | 3-Hydroxy-3-methylbutan-2-one | v40 | 0.96 | Acetic acid |
| v47 | 0.83 | Butane-1,3-diol | |||
| v56 | 0.76 | 4-Ethenyl-2-methoxyphenol | |||
| v34 | 0.75 | 3-Hydroxypentan-2-one | |||
| v35 | 0.74 | Hexan-1-ol | |||
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Park, M.K.; Kim, Y.-S. Distinctive Formation of Volatile Compounds in Fermented Rice Inoculated by Different Molds, Yeasts, and Lactic Acid Bacteria. Molecules 2019, 24, 2123. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24112123
Park MK, Kim Y-S. Distinctive Formation of Volatile Compounds in Fermented Rice Inoculated by Different Molds, Yeasts, and Lactic Acid Bacteria. Molecules. 2019; 24(11):2123. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24112123
Chicago/Turabian StylePark, Min Kyung, and Young-Suk Kim. 2019. "Distinctive Formation of Volatile Compounds in Fermented Rice Inoculated by Different Molds, Yeasts, and Lactic Acid Bacteria" Molecules 24, no. 11: 2123. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24112123
APA StylePark, M. K., & Kim, Y. -S. (2019). Distinctive Formation of Volatile Compounds in Fermented Rice Inoculated by Different Molds, Yeasts, and Lactic Acid Bacteria. Molecules, 24(11), 2123. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24112123