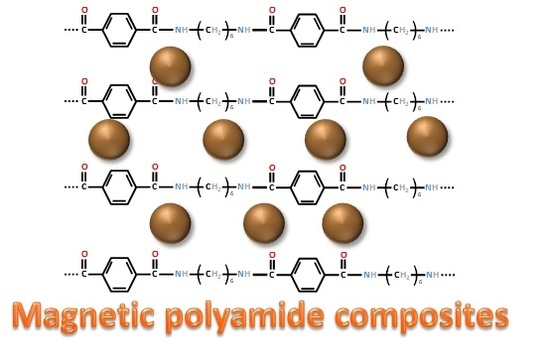
Magnetic Polyamide Nanocomposites for the Microextraction of Benzophenones from Water Samples
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Optimization of the Extraction Procedure
2.2. Analytical Parameters of the Method, Accuracy, and Real Sample Analysis
3. Material and Methods
3.1. Reagents
3.2. Preparation of the Magnetic Polyamide Nanocomposites (MNPs)
3.2.1. Synthesis of the Magnetic Core (Fe2CoO4 MNPs)
3.2.2. Synthesis of Isophthaloyl and Terephthaloyl Polyamides
3.2.3. Synthesis of the Magnetic Polyamide Nanocomposites (MNPs)
3.3. Characterization of the Magnetic Polyamide Nanocomposites (MNPs)
3.4. Extraction Procedure
3.5. UPLC (Ultra-Performance Liquid Chromatography) Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Reyes-Gallardo, E.M.; Lucena, R.; Cárdenas, S.; Valcárcel, M. Polymer-nanoparticles composites in bioanalytical sample preparation. Bioanalysis 2015, 7, 1723–1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayazi, Z. Application of nanocomposite-based sorbents in microextraction techniques: A review. Analyst 2017, 142, 721–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nika, C.E.; Yiantzi, E.; Psillakis, E. Plastic pellets sorptive extraction: Low-cost, rapid and efficient extraction of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons from environmental waters. Anal. Chim. Acta 2016, 922, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagheri, H.; Banihashemi, S.; Zandian, F.K. Microextraction of antidepressant drugs into syringes packed with a nanocomposite consisting of polydopamine, silver nanoparticles and polypyrrole. Microchim. Acta 2016, 183, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.J.; Zhou, X.; Tong, S.S.; Jia, Q. Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide-co-N,N′-methylene bisacrylamide) monolithic column embedded with γ-alumina nanoparticles microextraction coupled with high-performance liquid chromatography for the determination of synthetic food dyes in soft drink samples. Talanta 2013, 105, 386–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fresco-Cala, B.; Cárdenas, S.; Herrero-Martínez, J.M. Preparation of porous methacrylate monoliths with oxidized single-walled carbon nanohorns for the extraction of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs from urine samples. Microchim. Acta 2017, 184, 1863–1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asgharinezhad, A.A.; Ebrahimzadeh, H.; Mirbabaei, F.; Mollazadeh, N.; Shekari, N. Dispersive micro-solid-phase extraction of benzodiazepines from biological fluids based on polyaniline/magnetic nanoparticles composite. Anal. Chim. Acta 2014, 844, 80–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ríos-Gómez, J.; Ferrer-Monteagudo, B.; López-Lorente, Á.I.; Lucena, R.; Luque, R.; Cárdenas, S. Efficient combined sorption/photobleaching of dyes promoted by cellulose/titania-based nanocomposite films. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 194, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes-Gallardo, E.M.; Lasarte-Aragonés, G.; Lucena, R.; Cárdenas, S.; Valcárcel, M. Hybridization of commercial polymeric microparticles and magnetic nanoparticles for the dispersive micro-solid phase extraction of nitroaromatic hydrocarbons from water. J. Chromatogr. A 2013, 1271, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagheri, H.; Manouchehri, M.; Allahdadlalouni, M. A magnetic multifunctional dendrimeric coating on a steel fiber for solid phase microextraction of chlorophenols. Microchim. Acta 2017, 184, 2201–2209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Ma, X.; Zhang, X.; Wang, R.; Chen, Y.; Li, Z. Magnetic molecularly imprinted polymer nanoparticles-based solid-phase extraction coupled with gas chromatography–mass spectrometry for selective determination of trace di-(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate in water samples. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2016, 408, 7857–7864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, X.M.; Zhu, G.T.; Yin, J.; Zhao, Q.; Yuan, B.F.; Feng, Y.Q. Electrospun polystyrene/oxidized carbon nanotubes film as both sorbent for thin film microextraction and matrix for matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2014, 1351, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Deng, H.; Song, D.; Xu, H. Electrospun polystyrene/graphene nanofiber film as a novel adsorbent of thin film microextraction for extraction of aldehydes in human exhaled breath condensates. Anal. Chim. Acta 2015, 878, 102–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Miao, Y.E.; Ji, S.; Tjiu, W.W.; Liu, T. Electrospun carbon nanofibers decorated with Ag-Pt bimetallic nanoparticles for selective detection of dopamine. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 12449–12456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reyes-Gallardo, E.M.; Lucena, R.; Cárdenas, S.; Valcárcel, M. Magnetic nanoparticles-nylon 6 composite for the dispersive micro solid phase extraction of selected polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons from water samples. J. Chromatogr. A 2014, 1345, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reyes-Gallardo, E.M.; Lucena, R.; Cárdenas, S. Silica nanoparticles-nylon 6 composites: Synthesis, characterization and potential use as sorbent. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 2308–2314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes-Gallardo, E.M.; Lucena, R.; Cárdenas, S.; Valcárcel, M. Dispersive micro-solid phase extraction of bisphenol A from milk using magnetic nylon 6 composite and its final determination by HPLC-UV. Microchem. J. 2016, 124, 751–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benedé, J.L.; Chisvert, A.; Giokas, D.L.; Salvador, A. Stir bar sorptive-dispersive microextraction mediated by magnetic nanoparticles-nylon 6 composite for the extraction of hydrophilic organic compounds in aqueous media. Anal. Chim. Acta 2016, 926, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghambari, H.; Reyes-Gallardo, E.M.; Lucena, R.; Saraji, M.; Cárdenas, S. Recycling polymer residues to synthesize magnetic nanocomposites for dispersive micro-solid phase extraction. Talanta 2017, 170, 451–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, Y.; Kojima, H.; Takeuchi, S.; Uramaru, N.; Sanoh, S.; Sugihara, K.; Kitamura, S.; Ohta, S. Metabolism of UV-filter benzophenone-3 by rat and human liver microsomes and its effect on endocrine-disrupting activity. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2015, 282, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreurs, R.H.M.M.; Sonneveld, E.; Jansen, J.H.J.; Seinen, W.; van der Burg, B. Interaction of polycyclic musks and UV filters with the estrogen receptor (ER), androgen receptor (AR), and progesterone receptor (PR) in reporter gene bioassays. Toxicol. Sci. 2005, 83, 264–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, N.; Zhu, Q.; Yang, Y.; Huang, J.; Dang, X.; Chen, H. A novel dispersive solid-phase extraction method using metal-organic framework MIL-101 as the adsorbent for the analysis of benzophenones in toner. Talanta 2015, 132, 713–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casado-Carmona, F.A.; del CarmenAlcudia-León, M.; Lucena, R.; Cárdenas, S.; Valcárcel, M. Magnetic nanoparticles coated with ionic liquid for the extraction of endocrine disrupting compounds from waters. Microchem. J. 2016, 128, 347–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, C.; Stepkowska, A.; Alegre, A.; Nogueira, J.M.F. Determination of trace levels of benzophenone-type ultra-violet filters in real matrices by bar adsorptive micro-extraction using selective sorbent phases. J. Chromatogr. A 2013, 1311, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.; Guo, J.F.; Bai, L.; Shi, Z.G.; Qi, L.M. Retrieval of the extraction solvent by magnetic particles for dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction of UV filters. J. Liq. Chromatogr. Relat. Technol. 2015, 38, 104–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, D.; Lee, H.K. Ionic liquid based hollow fiber supported liquid phase microextraction of ultraviolet filters. J. Chromatogr. A 2012, 1229, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, L.; Liu, J.; Yang, X.; Peng, Y.; Xu, L. Orthogonal array design for the optimization of ionic liquid-based dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction of benzophenone-type UV filters. J. Sep. Sci. 2011, 34, 700–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Hu, L.; Liu, X.; Yin, S.; Lu, R.; Zhang, S.; Zhou, W.; Gao, H. Deep eutectic solvent-based ultrasound-assisted dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction coupled with high-performance liquid chromatography for the determination of ultraviolet filters in water samples. J. Chromatogr. A 2017, 1516, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chisvert, A.; Cárdenas, S.; Lucena, R. Dispersive micro-solid phase extraction. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 112, 226–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballesteros-Esteban, T.; Reyes-Gallardo, E.M.; Lucena, R.; Cárdenas, S.; Valcárcel, M. Determination of propranolol and carvedilol in urine samples using a magnetic polyamide composite and LC-MS/MS. Bioanalysis 2016, 8, 2115–2123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Yin, X.; Wu, S.; Wang, M.; Wen, Z.; Gu, Z. Determination of phthalate esters in water samples using Nylon6 nanofibers mat-based solid-phase extraction coupled to liquid chromatography. Microchim. Acta 2010, 168, 267–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Valverde, M.T.; Rosende, M.; Lucena, R.; Cárdenas, S.; Miró, M. Lab-on-a-Valve Mesofluidic Platform for On-Chip Handling of Carbon-Coated Titanium Dioxide Nanotubes in a Disposable Microsolid Phase-Extraction Mode. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 4783–4791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walfish, S. A statistical perspective on the ICH Q2A and Q2B guidelines for validation of analytical methods. BioPharm Int. 2006, 19, 28–36. [Google Scholar]
Sample Availability: Samples of the composites are available from the authors. |






| Variable | Initial Value | Interval Studied | Optimum Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Elution solvent | Methanol | Several solvents | Mixture of 1-propanol and 0.01 M NaOH solution (50:50, v/v) |
| Elution temperature (°C) | RT 1 | RT 1/60 | RT 1 |
| Sample volume (mL) | 10 | 5–40 | 40 |
| Extraction time (min) | 30 | 15–120 | 15 |
| pH | 7.4 | 3–9 | 3 |
| Analyte | Linear Range (ng/mL) | Determination Coefficient (R2) | LOD a (ng/mL) | AER b (%) | EF c | Intra-Day RSD % (n = 6) d | Inter-Day RSD % (n = 3) d |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BP-2 | 14.3–5000 | 0.997 | 4.3 | 7.6 | 6.1 | 5.6 | 8.0 |
| 4-OH-BP | 2.0–1000 | 0.997 | 0.6 | 20.6 | 16.5 | 1.9 | 3.8 |
| BP-1 | 1.6–1000 | 0.998 | 0.5 | 28.8 | 23.0 | 1.5 | 4.6 |
| BP-8 | 7.2–2500 | 0.999 | 2.2 | 8.9 | 7.1 | 1.7 | 7.7 |
| BP-6 | 10–2500 | 0.998 | 3.0 | 9.0 | 7.2 | 4.9 | 5.3 |
| BP-3 | 1.7–1000 | 0.997 | 0.5 | 30.1 | 24.1 | 3.0 | 8.4 |
| Analyte | Creek (RR ± SD) a | Tap (RR ± SD) a | River (RR ± SD) a |
|---|---|---|---|
| BP-2 | 84 ± 3 | 87 ± 3 | 105 ± 4 |
| 4-OH-BP | 96 ± 3 | 98 ± 2 | 86 ± 3 |
| BP-1 | 100 ± 2 | 100 ± 3 | 96 ± 1 |
| BP-8 | 96 ± 5 | 104 ± 5 | 102 ± 3 |
| BP-6 | 90 ± 2 | 103 ± 4 | 104 ± 4 |
| BP-3 | 98 ± 3 | 97 ± 2 | 97 ± 2 |
| Method | Analyte | LOD (ng/mL) | LDR (ng/mL) | Intra-Day RSD % | EF | RR % | Synthesis Time (hours:mins) | Extraction Time (mins) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Magnetic D-µ-SPE-UPLC-DAD | BP-2 | 4.3 | 14.3–5000 | 5.6 | 6.1 | 84–105 | 4:45 | 15 | Present method |
| 4-OH-BP | 0.6 | 2–1000 | 1.9 | 16.5 | 86–98 | ||||
| BP-1 | 0.5 | 1.6–1000 | 1.5 | 23 | 96–100 | ||||
| BP-8 | 2.2 | 7.2–2500 | 1.7 | 7.1 | 96–104 | ||||
| BP-6 | 3.0 | 10–2500 | 4.9 | 7.2 | 90–104 | ||||
| BP-3 | 0.5 | 1.7–1000 | 3.0 | 24.1 | 97–98 | ||||
| D-µ-SPE-HPLC-DAD | BP-1 | 1.2 | 4–3500 | 1.5 | - | - | 37:00 | 55 | [22] |
| BP-3 | 0.9 | 4–3500 | 2.3 | - | - | ||||
| Magnetic D-µ-SPE-HPLC-MS/MS | BP-2 | 0.81 | 2.7–500 | 5.2 | 21.4 | 92–96 | 132:30 | 27 | [23] |
| 4-OH-BP | 0.62 | 2.07–500 | 4.2 | 29.3 | 90–93 | ||||
| BP-1 | 1.21 | 4.03–500 | 7.1 | 17.3 | 89–92 | ||||
| BP-8 | 0.84 | 2.80–500 | 5.1 | 34.1 | 87–96 | ||||
| BP-6 | 1.11 | 3.70–500 | 8.3 | 18.4 | 92–98 | ||||
| BP-3 | 0.16 | 0.87–500 | 7.3 | 49.2 | 89–96 | ||||
| BAµE-HPLC-DAD | 4-OH-BP | Sorbent 1: 0.3 | 1–24 | 5.6 | - | - | - | Sorbent 1: 255 Sorbent 2: 990 | [24] |
| Sorbent 2: 0.4 | 2–24 | 3.4 | - | - | |||||
| BP-1 | Sorbent 1: 0.3 | 1–24 | 5.0 | - | - | ||||
| Sorbent 2: 0.4 | 2–24 | 1.5 | - | - | |||||
| BP-3 | Sorbent 1: 0.3 | 1–24 | 2.6 | - | - | ||||
| Sorbent 2: 0.4 | 2–24 | 8.5 | - | - | |||||
| MR-DLLME-HPLC-DAD | 4-OH-BP | 0.7 | 70–7000 | 4.1 | 93 | - | 28:40 | 5 | [25] |
| BP-1 | 1.8 | 70–7000 | 3.7 | 110 | - | ||||
| BP-3 | 12.3 | 70–7000 | 4.4 | 107 | - | ||||
| IL-HF-LPME-HPLC-UV | BP-1 | 0.5 | 10–1000 | 8.2 | 25 | 101.9–102.7 | - | 50 | [26] |
| BP-3 | 0.2 | 5–1000 | 1.1 | 216 | 98.1–104.9 | ||||
| IL-DLLME-HPLC-UV | 4-OH-BP | 2.4 | 10–1000 | 6.3 | 21.7 | - | - | 14 | [27] |
| BP-1 | 6.4 | 20–1000 | 4.1 | 18.9 | - | ||||
| BP-3 | 3.3 | 10–1000 | 8.0 | 20.3 | - | ||||
| USA-DLLME HPLC-UV | BP | 0.15 | 0.5–500 | 4.0–5.9 | 76 | 92–102 | - | 9 | [28] |
| BP-1 | 0.15 | 0.5–500 | 2.4–4.2 | 67 | 90–103 | ||||
| BP-3 | 0.30 | 1–500 | 3.7–5.1 | 74 | 94–100 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ghambari, H.; Reyes-Gallardo, E.M.; Lucena, R.; Saraji, M.; Cárdenas, S. Magnetic Polyamide Nanocomposites for the Microextraction of Benzophenones from Water Samples. Molecules 2019, 24, 953. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24050953
Ghambari H, Reyes-Gallardo EM, Lucena R, Saraji M, Cárdenas S. Magnetic Polyamide Nanocomposites for the Microextraction of Benzophenones from Water Samples. Molecules. 2019; 24(5):953. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24050953
Chicago/Turabian StyleGhambari, Hoda, Emilia M. Reyes-Gallardo, Rafael Lucena, Mohammad Saraji, and Soledad Cárdenas. 2019. "Magnetic Polyamide Nanocomposites for the Microextraction of Benzophenones from Water Samples" Molecules 24, no. 5: 953. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24050953
APA StyleGhambari, H., Reyes-Gallardo, E. M., Lucena, R., Saraji, M., & Cárdenas, S. (2019). Magnetic Polyamide Nanocomposites for the Microextraction of Benzophenones from Water Samples. Molecules, 24(5), 953. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24050953