Synthetic Peptide Purification via Solid-Phase Extraction with Gradient Elution: A Simple, Economical, Fast, and Efficient Methodology
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
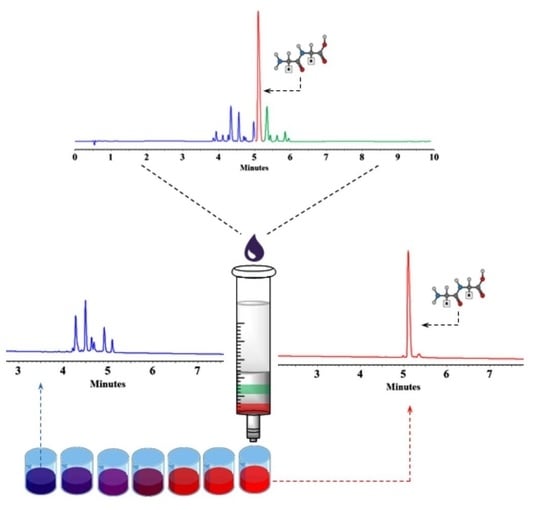
2.1. Purification of Synthetic Peptides via SPE
2.2. Purification of N-Glucosyl Amino Acids via SPE
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Reagents and Materials
3.2. Solid-Phase Peptide Synthesis (SPPS)
3.3. Reverse-Phase High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (RP-HPLC) Analysis
3.4. MALDI-TOF MS
3.5. Purification of molecules via RP-SPE
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ratnaparkhi, M.P.; Pandya, C.S.P. Peptides and proteins in pharmaceuticals. Int. J. Curr. Pharm. Res. 2011, 3, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Craik, D.J.; Fairlie, D.P.; Liras, S.; Price, D. The future of peptide-based drugs. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2013, 81, 136–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schagen, S.K. Topical peptide treatments with effective results. Cosmetics 2017, 4, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez, A.; Vázquez, A. Bioactive peptides: A review. Food Qual. Saf. 2017, 1, 29–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montesino, E.; Bardaji, E. Synthetic Antimicrobial peptides as agricultural pesticides for plant-disease control. Chem. Biodivers. 2008, 5, 1225–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Alessandro, R.; Masarone, D.; Buono, A.; Gravino, R.; Rea, A.; Salerno, G.; Golia, E.; Ammendola, E.; Del Giorno, G.; Santangelo, L.; et al. Natriuretic peptides: Molecular biology, pathophysiology and clinical implications for the cardiologist. Future Cardiol. 2013, 9, 519–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okada, Y.; Asama, H.; Wakamatsu, H.; Chiba, K.; Kamiya, H. Hydrophobic magnetic nanoparticle assisted one-pot liquid-phase peptide synthesis. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2017, 40, 5961–5965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kijewska, M.; Waliczek, M.; Cal, M.; Jaremko, L.; Jaremko, M.; Król, M.; Kołodziej, M.; Lisowski, M.; Stefanowicz, P.; Szewczuk, Z. Solid-phase synthesis of peptides containing aminoadipic semialdehyde moiety and their cyclisations. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 10462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrudu, S.; Simerska, P.; Toth, I. Chemical methods for peptide and protein production. Molecules 2013, 18, 4373–4388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar, M.I. Methods in Molecular Biology, HPLC of Peptides and Proteins, Methods and Protocols; Humana Press Inc.: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, H.L.J.; Zheng, X.Q.; Liu, X.L. Purification and characterization of antioxidant peptide from sunflower protein hydrolysate. Food Technol. Biotechnol. 2010, 48, 519–523. [Google Scholar]
- Cytryniska, M.; Mak, P.; Zdybicka-barabas, A.; Suder, P.; Jakubowicz, T. Purification and characterization of eight peptides from Galleria mellonella immune hemolymph. Peptides 2007, 28, 533–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pingitore, E.V.; Salvucci, E.; Sesma, F.; Nader-Macias, M.E. Different Strategies for Purification of Antimicrobial Peptides from Lactic Acid Bacteria (LAB). In Communicating Current Research and Educational Topics and Trends in Applied Microbiology; Mendez Vilas, A., Ed.; FORMATEX: Badajoz, Spain, 2007; pp. 557–568. [Google Scholar]
- Riding, G.A.; Wang, Y.; Walker, P.J. A Strategy for Purification and Peptide Sequence Analysis of Bovine Ephemeral Fever Virus Structural Proteins. In Bovine Ephemeral Fever and Related Rhabdoviruses; ACIAR Proceedings; St George, T.D., Uren, M.F., Young, P.L., Hoffman, D., Eds.; ACIAR: Canberra, Australia, 1992; Volume 44, pp. 98–102. [Google Scholar]
- Poole, F. New trends in solid-phase extraction. Trends Anal. Chem. 2003, 22, 362–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hennion, M. Solid-phase extraction: Method development, sorbents, and coupling with liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 1999, 856, 3–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poole, F.; Gunatilleka, A.D.; Sethuraman, R. Contributions of theory to method development in solid-phase extraction. J. Chromatogr. A 2000, 885, 17–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herraiz, T.; Casal, V. Evaluation of solid-phase extraction procedures in peptide analysis. J. Chromatogr. A 1995, 708, 209–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmblad, M.; Vogel, J.S. Quantitation of binding, recovery and desalting efficiency of peptides and proteins in solid phase extraction micropipette tips. J. Chromatogr. B 2005, 814, 309–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulczykowska, E. Solid-phase extraction of arginine vasotocin and isotocin in fish samples and subsequent gradient reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatographic separation. J. Chromatogr. B Biomed. Sci. Appl. 1995, 673, 289–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamysz, W.; Okrój, M.; Lempicka, E.; Ossowski, T.; Lukasiak, J. Fast and efficient purification of synthetic peptides by solid-phase extraction. Acta Chromatogr. 2004, 14, 180–186. [Google Scholar]
- Herraiz, T. Sample preparation and reversed phase-high performance chromatography analysis of food-derived peptides. Anal. Chim. Acta 1997, 352, 119–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Causon, R.C.; Mcdowall, R.D. Sample pretreatment techniques for the bioanalysis of peptides. J. Control. Release. 1992, 21, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vergel Galeano, C.F.; Rivera Monroy, Z.J.; Rosas Pérez, J.E.; García Castañeda, J.E. Efficient synthesis of peptides with 4-methylpiperidine as Fmoc removal reagent by solid phase synthesis. J. Mex. Chem. Soc. 2014, 58, 386–392. [Google Scholar]
- Huertas, N.d.J.; Rivera Monroy, Z.J.; Medina, R.F.; García Castañeda, J.E. Antimicrobial activity of truncated and polyvalent peptides derived from the FKCRRQWQWRMKKGLA sequence against Escherichia coli ATCC 25922 and Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 25923. Molecules 2017, 22, 987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuss, H.J. Prediction of Gradients. In The HPLC Expert: Possibilities and Limitations of Modern High Performance Liquid Chromatography, 1st ed.; Kromidas, S., Ed.; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2016; pp. 185–187. [Google Scholar]
- Snyder, L.R.; Kirkland, J.J.; Dolan, J.W. Introduction to the Modern Liquid Chromatography, 3rd ed.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Meyer, V.R. Practical High-Performance Liquid Chromatography, 5th ed.; John Wiley and Sons, Ltd.: Oxford, UK, 2010; pp. 373–385. [Google Scholar]
- Pinzón-Martín, S.M.; Medina, R.F.; Iregui Castro, C.A.; Rivera Monroy, Z.J.; García Castañeda, J.E. Novel synthesis of N-glycosyl amino acids using T3P®: Propylphosphonic acid cyclic anhydride as coupling reagent. Int. J. Pept. Res. Ther. 2017, 24, 291–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo-Aguirre, A.; Rivera-Monroy, Z.; Maldonado, M. Selective o-alkylation of the crown conformer of tetra(4-hydroxyphenyl)calix[4]resorcinarene to the corresponding tetraalkyl ether. Molecules 2017, 22, 1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallo-Molina, C.; Castro-Vargas, H.I.; Garzón-Méndez, W.F.; Martínez-Ramírez, J.A.; Rivera-Monroy, Z.J.; King, J.W.; Parada-Alfonso, F. Extraction, isolation and purification of tetrahydrocannabinol from the Cannabis sativa L. plant using supercritical fluid extraction and solid phase extraction. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2019, 146, 208–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds used in this paper are available from the authors. |



| Fraction N° | Solvent B | Purity b (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| % | μL | ||
| 1 | 0 | 0 | - |
| 2 | 5 | 600 | - |
| 3 | 11 | 1320 | - |
| 4 | 16 | 1920 | - |
| 5 | 17 | 2040 | 66 |
| 6 | 18 | 2160 | 96 |
| 7 | 19 | 2280 | 94 |
| 8 | 20 | 2400 | 92 |
| 9 a | 21 | 2520 | 88 |
| 10 | 22 | 2640 | 77 |
| 11 | 23 | 2760 | 23 |
| 12 | 24 | 2880 | - |
| 13 | 25 | 3000 | - |
| 14 | 50 | 6000 | - |
| 15 | 100 | 12000 | - |
| Peptide Code | Sequence | GRAVY a | %Ha a | Net Charge | tR | Purity b | Purification Yield | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Crude | Purified | |||||||
| 1 | Fc-Ahx-RLLR | N.D. | N.D. | +2 | 6.0 | 65 | 95 | 6 |
| 2 | Fc-Ahx-RLLRRLLR | N.D. | N.D. | +4 | 7.2 | 77 | 90 | 28 |
| 3 | AcOx-Ahx-RLLR | N.D. | N.D. | +2 | 4.4 | 46 | 99 | 10 |
| 4 | KKWQWK | −2.8 | 33 | +3 | 3.7 | 94 | 98 | 48 |
| 5 | IHSMNSTIL | 0.6 | 44 | +1 | 4.3 | 71 | 81 | 71 |
| 6 | PNNNKILVPK | −0.9 | 30 | +2 | 3.0 | 71 | 91 | 60 |
| 7 | LYIKGSGSTANLASSNYFPT | −0.1 | 30 | +1 | 4.9 | 55 | 72 | 16 |
| 8 | VSGLQYRVFR | −1.8 | 40 | +2 | 3.6 | 54 | 92 | 35 |
| 9 | N(Glc(Ac4))-Ahx-RWQWRWQWR | N.D. | N.D. | N.D. | 6.0 | 64 | 76 | 61 |
| 10 | RWQWRWQWR-Ahx-N(Glc(Ac4)) | N.D. | N.D. | N.D. | 6.4 | 60 | 66 | 70 |
| 11 | N(Glc(Ac4))-Ahx-RWQWRWQWR-Ahx-N(Glc(Ac4)) | N.D. | N.D. | N.D. | 6.6 | 66 | 80 | 13 |
| 12 | KKWQWKAKKLG | −1.8 | 36 | +5 | 3.9 | 89 | 99 | 63 |
| 13 | RRWQWRKKKLG | −2.5 | 27 | +6 | 3.8 | 91 | 99 | 66 |
| 14 | (RRWQWRKKKLG)2-K-Ahx | −2.2 | 29 | +13 | 4.4 | 73 | 93 | 27 |
| 15 | Fc-Ahx-RRWQWR | N.D. | N.D. | +3 | 5.8 | 72 | 92 | 13 |
| 16 | AcFer-Ahx-RWQWRWQWR | N.D. | N.D. | +3 | 6.7 | 70 | 89 | 15 |
| 17 | RKKKMKKALQYIKLLKE | −1.2 | 35 | +7 | 4.9 | 61 | 86 | 7 |
| 18 | RYRRKKK | −3.8 | 0 | +6 | 0.7 | 93 | 99 | 41 |
| 19 | KMKKALQY | −1.1 | 37 | +3 | 3.1 | 84 | 98 | 42 |
| 20 | YIKLLKE | −0.1 | 42 | +1 | 4.2 | 99 | 99 | 26 |
| 21 | MKKALQYIKLLKE | −0.3 | 46 | +3 | 5.2 | 86 | 99 | 28 |
| 22 | FYFY | 0.8 | N.D. | 0 | 5.2 | 57 | 83 | 7 |
| 23 | KLLKKLLK | −0.1 | 50 | +4 | 4.0 | 90 | 99 | 55 |
| 24 | KLLK | −0.1 | N.D. | +2 | 1.6 | 89 | 92 | 53 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Insuasty Cepeda, D.S.; Pineda Castañeda, H.M.; Rodríguez Mayor, A.V.; García Castañeda, J.E.; Maldonado Villamil, M.; Fierro Medina, R.; Rivera Monroy, Z.J. Synthetic Peptide Purification via Solid-Phase Extraction with Gradient Elution: A Simple, Economical, Fast, and Efficient Methodology. Molecules 2019, 24, 1215. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24071215
Insuasty Cepeda DS, Pineda Castañeda HM, Rodríguez Mayor AV, García Castañeda JE, Maldonado Villamil M, Fierro Medina R, Rivera Monroy ZJ. Synthetic Peptide Purification via Solid-Phase Extraction with Gradient Elution: A Simple, Economical, Fast, and Efficient Methodology. Molecules. 2019; 24(7):1215. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24071215
Chicago/Turabian StyleInsuasty Cepeda, Diego Sebastián, Héctor Manuel Pineda Castañeda, Andrea Verónica Rodríguez Mayor, Javier Eduardo García Castañeda, Mauricio Maldonado Villamil, Ricardo Fierro Medina, and Zuly Jenny Rivera Monroy. 2019. "Synthetic Peptide Purification via Solid-Phase Extraction with Gradient Elution: A Simple, Economical, Fast, and Efficient Methodology" Molecules 24, no. 7: 1215. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24071215
APA StyleInsuasty Cepeda, D. S., Pineda Castañeda, H. M., Rodríguez Mayor, A. V., García Castañeda, J. E., Maldonado Villamil, M., Fierro Medina, R., & Rivera Monroy, Z. J. (2019). Synthetic Peptide Purification via Solid-Phase Extraction with Gradient Elution: A Simple, Economical, Fast, and Efficient Methodology. Molecules, 24(7), 1215. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24071215