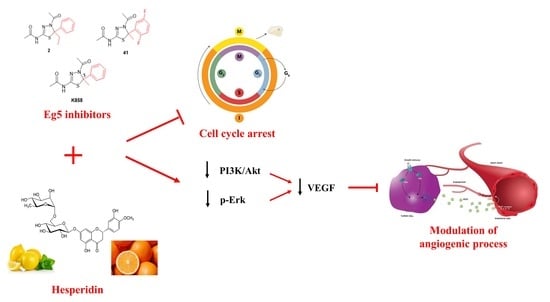
Negative Modulation of the Angiogenic Cascade Induced by Allosteric Kinesin Eg5 Inhibitors in a Gastric Adenocarcinoma In Vitro Model
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Docking Simulation Studies
2.2. Effect of HSD and Eg5 Inhibitors on AGS Cell Proliferation
2.3. Cell Cycle Modulation by Eg5 Inhibitors Alone and in Combination with HSD
2.4. Effect of Eg5 Inhibitors in Monotherapy and Combination with HSD on VEGF Activity and PI3K/Akt Pathway
2.5. Effect of Eg5 Inhibitors and HSD on Erk 1/2 Activation
2.6. Modulation of ANGPT2 Gene Expression after Treatment with Eg5 Inhibitors Alone and in Combination with HSD
2.7. Effect of 2 in Combination with HSD on AGS Cells Migration
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemistry
4.2. In Silico Experiments
4.3. Cell Culture
4.4. MTT Assay
4.5. Cell Cycle Analysis
4.6. Protein Extraction and Western Blot Analysis
4.7. ELISA Analysis of VEGF Secretion
4.8. RNA Extraction
4.9. Reverse Transcription (RT) and Real-Time RT-Polymerase Chain Reaction (Real-Time RT-PCR)
4.10. Wound Healing
4.11. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, Y.-C.; Fang, W.-L.; Wang, R.-F.; Liu, C.-A.; Yang, M.-H.; Lo, S.-S.; Wu, C.-W.; Li, A.-F.; Shyr, Y.-M.; Huang, K.-H. Clinicopathological Variation of Lauren Classification in Gastric Cancer. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 2016, 22, 197–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plummer, M.; Franceschi, S.; Vignat, J.; Forman, D.; de Martel, C. Global burden of gastric cancer attributable to Helicobacter pylori. Int. J. Cancer 2015, 136, 487–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sexton, R.E.; Al Hallak, M.N.; Diab, M.; Azmi, A.S. Gastric cancer: A comprehensive review of current and future treatment strategies. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2020, 39, 1179–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yusefi, A.R.; Lankarani, K.B.; Bastani, P.; Radinmanesh, M.; Kavosi, Z. Risk Factors for Gastric Cancer: A Systematic Review. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2018, 19, 591–603. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Johnston, F.M.; Beckman, M. Updates on Management of Gastric Cancer. Curr. Oncol. Rep. 2019, 21, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Machlowska, J.; Baj, J.; Sitarz, M.; Maciejewski, R.; Sitarz, R. Gastric Cancer: Epidemiology, Risk Factors, Classification, Genomic Characteristics and Treatment Strategies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woehlke, G.; Schliwa, M. Walking on two heads: The many talents of kinesin. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2000, 1, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rath, O.; Kozielski, F. Kinesins and cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2012, 12, 527–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, B.; Allingham, J.S. These motors were made for walking. Protein Sci. 2020, 29, 1707–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konjikusic, M.J.; Gray, R.S.; Wallingford, J.B. The developmental biology of kinesins. Dev. Biol. 2021, 469, 26–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Gong, H.; Huang, K. Oncogenic role of kinesin proteins and targeting kinesin therapy. Cancer Sci. 2013, 104, 651–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, X.; Shu, K.; Wang, Z.; Ding, D. Prognostic significance of KIF2A and KIF20A expression in human cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Medicine 2019, 98, e18040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucanus, A.J.; Yip, G.W. Kinesin superfamily: Roles in breast cancer, patient prognosis and therapeutics. Oncogene 2018, 37, 833–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Song, T.; Xue, X.; Cao, G.; Huang, P. Kinesin superfamily proteins: Roles in osteosarcoma. Front. Biosci. 2021, 26, 370–378. [Google Scholar]
- Huo, D.; Yang, H.; Huang, J.-D.; Cai, J.-P.; Cui, J. Roles of kinesin superfamily proteins in colorectal cancer carcinogenesis (Review). Oncol. Rep. 2021, 46, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imai, T.; Oue, N.; Nishioka, M.; Mukai, S.; Oshima, T.; Sakamoto, N.; Sentani, K.; Matsusaki, K.; Yoshida, K.; Yasui, W. Overexpression of KIF11 in Gastric Cancer with Intestinal Mucin Phenotype. Pathobiology 2017, 84, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Chen, W.R.; Yang, L.C.; Wang, J.; Sun, J.Y.; Zhang, W.W.; He, Z.Y.; Wu, S.G. KIF11 Functions as an Oncogene and Is Associated with Poor Outcomes from Breast Cancer. Cancer Res. Treat. 2019, 51, 1207–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Wang, X.; Yang, Y.; Li, D.; Ren, H.; Zhu, Q.; Chen, Q.; Han, S.; Hao, J.; Zhou, J. Ectopic expression of the microtubule-dependent motor protein Eg5 promotes pancreatic tumourigenesis. J. Pathol. 2010, 221, 221–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piao, X.-M.; Byun, Y.J.; Jeong, P.; Ha, Y.-S.; Yoo, E.S.; Yun, S.J.; Kim, W.-J. Kinesin Family Member 11 mRNA Expression Predicts Prostate Cancer Aggressiveness. Clin. Genitourin. Cancer 2017, 15, 450–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Lu, J.; Niu, Z.; Ding, K.; Bi, D.; Liu, S.; Li, J.; Wu, F.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, Z.; et al. A Potent Chemotherapeutic Strategy with Eg5 Inhibitor against Gemcitabine Resistant Bladder Cancer. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0144484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Venere, M.; Horbinski, C.; Crish, J.F.; Jin, X.; Vasanji, A.; Major, J.; Burrows, A.C.; Chang, C.; Prokop, J.; Wu, Q.; et al. The mitotic kinesin KIF11 is a driver of invasion, proliferation, and self-renewal in glioblastoma. Sci. Transl. Med. 2015, 7, 304ra143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- El-Nassan, H.B. Advances in the discovery of kinesin spindle protein (Eg5) inhibitors as antitumor agents. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 62, 614–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Saez, I.; Skoufias, D.A. Eg5 targeting agents: From new anti-mitotic based inhibitor discovery to cancer therapy and resistance. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2021, 184, 114364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakai, R.; Iida, S.; Takahashi, T.; Tsujita, T.; Okamoto, S.; Takada, C.; Akasaka, K.; Ichikawa, S.; Ishida, H.; Kusaka, H.; et al. K858, a novel inhibitor of mitotic kinesin Eg5 and antitumor agent, induces cell death in cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 3901–3909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guglielmi, P.; Secci, D.; Rotondi, G.; Carradori, S. An Update on Eg5 Kinesin Inhibitors for the Treatment of Cancer. In Advances in Medicinal Chemistry Research; Ferreira da Silva Júnior, E., Ed.; Nova Science Publishers: Hauppauge, NY, USA, 2019; pp. 283–329. ISBN 978-1-53616-368-1. [Google Scholar]
- Kapoor, T.M.; Mayer, T.U.; Coughlin, M.L.; Mitchison, T.J. Probing spindle assembly mechanisms with monastrol, a small molecule inhibitor of the mitotic kinesin, Eg5. J. Cell Biol. 2000, 150, 975–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tawfik, H.O.; El-Hamamsy, M.H.; Sharafeldin, N.A.; El-Moselhy, T.F. Design, synthesis, and bioactivity of dihydropyrimidine derivatives as kinesin spindle protein inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2019, 27, 115126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, J.R.; Gilmartin, A.G.; Dhanak, D.; Knight, S.D.; Parrish, C.A.; Luo, L.; Sutton, D.; Caulder, E.; Diamond, M.A.; Giardiniere, M.; et al. A second generation KSP inhibitor, SB-743921, is a highly potent and active therapeutic in preclinical models of cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2006, 12, B11. [Google Scholar]
- Sheth, P.R.; Shipps, G.W.; Seghezzi, W.; Smith, C.K.; Chuang, C.C.; Sanden, D.; Basso, A.D.; Vilenchik, L.; Gray, K.; Annis, D.A.; et al. Novel Benzimidazole Inhibitors Bind to a Unique Site in the Kinesin Spindle Protein Motor Domain. Biochemistry 2010, 49, 8350–8358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, I.; Hameed, S.; Al-Masoudi, N.A.; Abdul-Reda, N.A.; Simpson, J. New triazolothiadiazole and triazolothiadiazine derivatives as kinesin Eg5 and HIV inhibitors: Synthesis, QSAR and modeling studies. Z. Naturforsch.-Sect. B. 2015, 70, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhn, M.; von Mering, C.; Campillos, M.; Jensen, L.J.; Bork, P. STITCH: Interaction networks of chemicals and proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008, 36, D684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talapatra, S.K.; Tham, C.L.; Guglielmi, P.; Cirilli, R.; Chandrasekaran, B.; Karpoormath, R.; Carradori, S.; Kozielski, F. Crystal structure of the Eg5-K858 complex and implications for structure-based design of thiadiazole-containing inhibitors. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 156, 641–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adasme, M.F.; Linnemann, K.L.; Bolz, S.N.; Kaiser, F.; Salentin, S.; Haupt, V.J.; Schroeder, M. PLIP 2021: Expanding the scope of the protein-ligand interaction profiler to DNA and RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, W530–W534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delano, W.L. PyMOL: An Open-Source Molecular Graphics Tool. CCP4 Newsl. Protein Crystallogr. 2002, 40, 82–92. Available online: https://plip-tool.biotec.tu-dresden.de/plip-web/plip/index (accessed on 18 January 2022).
- De Monte, C.; Carradori, S.; Secci, D.; D’Ascenzio, M.; Guglielmi, P.; Mollica, A.; Morrone, S.; Scarpa, S.; Aglianò, A.M.; Giantulli, S.; et al. Synthesis and pharmacological screening of a large library of 1,3,4-thiadiazolines as innovative therapeutic tools for the treatment of prostate cancer and melanoma. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 105, 245–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marconi, G.D.; Carradori, S.; Ricci, A.; Guglielmi, P.; Cataldi, A.; Zara, S. Kinesin Eg5 Targeting Inhibitors as a New Strategy for Gastric Adenocarcinoma Treatment. Molecules 2019, 24, 3948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Szklarczyk, D.; Gable, A.L.; Lyon, D.; Junge, A.; Wyder, S.; Huerta-Cepas, J.; Simonovic, M.; Doncheva, N.T.; Morris, J.H.; Bork, P.; et al. STRING v11: Protein-Protein association networks with increased coverage, supporting functional discovery in genome-wide experimental datasets. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, Y.; Zheng, J.; Li, Y.; Xu, D.-P.; Li, S.; Chen, Y.-M.; Li, H.-B. Natural Polyphenols for Prevention and Treatment of Cancer. Nutrients 2016, 8, 515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira de Oliveira, J.M.P.; Santos, C.; Fernandes, E. Therapeutic potential of hesperidin and its aglycone hesperetin: Cell cycle regulation and apoptosis induction in cancer models. Phytomedicine 2020, 73, 152887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, P.; Khan, F. A mechanistic review of the anticancer potential of hesperidin, a natural flavonoid from citrus fruits. Nutr. Res. 2021, 92, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, V.; Tuli, H.S.; Thakral, F.; Singhal, P.; Aggarwal, D.; Srivastava, S.; Pandey, A.; Sak, K.; Varol, M.; Khan, M.A.; et al. Molecular mechanisms of action of hesperidin in cancer: Recent trends and advancements. Exp. Biol. Med. 2020, 245, 486–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xie, B.; Wang, S.; Jiang, N.; Li, J.J. Cyclin B1/CDK1-regulated mitochondrial bioenergetics in cell cycle progression and tumor resistance. Cancer Lett. 2019, 443, 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cascales, H.S.; Burdova, K.; Middleton, A.; Kuzin, V.; Müllers, E.; Stoy, H.; Baranello, L.; Macurek, L.; Lindqvist, A. Cyclin A2 localises in the cytoplasm at the S/G2 transition to activate PLK1. Life Sci. Alliance 2021, 4, e202000980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carmeliet, P.; Jain, R.K. Angiogenesis in cancer and other diseases. Nature 2000, 407, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Exertier, P.; Javerzat, S.; Wang, B.; Franco, M.; Herbert, J.; Platonova, N.; Winandy, M.; Pujol, N.; Nivelles, O.; Ormenese, S.; et al. Impaired angiogenesis and tumor development by inhibition of the mitotic kinesin Eg5. Oncotarget 2013, 4, 2302–2316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karar, J.; Maity, A. PI3K/AKT/mTOR Pathway in Angiogenesis. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2011, 4, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, X.D.; Chen, H.X.; Guan, R.N.; Lei, Y.P.; Shu, X.; Zhu, Y.; Lv, N.H. Protein kinase B phosphorylation correlates with vascular endothelial growth factor A and microvessel density in gastric adenocarcinoma. J. Int. Med. Res. 2012, 40, 2124–2134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuoka, T.; Yashiro, M.; Nishioka, N.; Hirakawa, K.; Olden, K.; Roberts, J.D. PI3K/Akt signalling is required for the attachment and spreading, and growth in vivo of metastatic scirrhous gastric carcinoma. Br. J. Cancer 2012, 106, 1535–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, G.D. Hesperetin Inhibits Vascular Formation by Suppressing of the PI3K/AKT, ERK, and p38 MAPK Signaling Pathways. Prev. Nutr. Food Sci. 2014, 19, 299–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, S.; Li, C.; Lin, S.; Han, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, L.; Zhou, L.; Kumar, S. Distinct roles of VEGF-A and VEGF-C in tumour metastasis of gastric carcinoma. Oncol. Rep. 2007, 17, 369–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Claesson-Welsh, L.; Welsh, M. VEGFA and tumour angiogenesis. J. Intern. Med. 2013, 273, 114–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melincovici, C.S.; Boşca, A.B.; Şuşman, S.; Mărginean, M.; Mihu, C.; Istrate, M.; Moldovan, I.M.; Roman, A.L.; Mihu, C.M. Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)—Key factor in normal and pathological angiogenesis. Rom. J. Morphol. Embryol. 2018, 59, 455–467. [Google Scholar]
- Villaume, K.; Blanc, M.; Gouysse, G.; Walter, T.; Couderc, C.; Nejjari, M.; Vercherat, C.; Cordier-Bussat, M.; Roche, C.; Scoazec, J.Y. VEGF secretion by neuroendocrine tumor cells is inhibited by octreotide and by inhibitors of the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway. Neuroendocrinology 2010, 91, 268–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, F.; Gao, F.; Xing, L.; Qin, P.; Liang, X.; Zhang, J.; Qiao, X.; Lin, L.; Zhao, Q.; et al. Periostin promotes tumor angiogenesis in pancreatic cancer via Erk/VEGF signaling. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 40148–40159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fei, G.; Cao, M.; Ge, C.; Cui, L. Propofol suppresses hepatocellular carcinoma by inhibiting NET1 through downregulating ERK/VEGF signaling pathway. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 11208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akwii, R.G.; Sajib, M.S.; Zahra, F.T.; Mikelis, C.M. Role of Angiopoietin-2 in Vascular Physiology and Pathophysiology. Cells 2019, 8, 471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Giuppi, M.; La Salvia, A.; Evangelista, J.; Ghidini, M. The Role and Expression of Angiogenesis-Related miRNAs in Gastric Cancer. Biology 2021, 10, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šali, A.; Blundell, T.L. Comparative protein modelling by satisfaction of spatial restraints. J. Mol. Biol. 1993, 234, 779–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettersen, E.F.; Goddard, T.D.; Huang, C.C.; Couch, G.S.; Greenblatt, D.M.; Meng, E.C.; Ferrin, T.E. UCSF Chimera—A visualization system for exploratory research and analysis. J. Comput. Chem. 2004, 25, 1605–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- O’Boyle, N.M.; Banck, M.; James, C.A.; Morley, C.; Vandermeersch, T.; Hutchison, G.R. Open Babel: An Open chemical toolbox. J. Cheminform. 2011, 3, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morris, G.M.; Ruth, H.; Lindstrom, W.; Sanner, M.F.; Belew, R.K.; Goodsell, D.S.; Olson, A.J. AutoDock4 and AutoDockTools4: Automated docking with selective receptor flexibility. J. Comput. Chem. 2009, 30, 2785–2791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Koebel, M.R.; Schmadeke, G.; Posner, R.G.; Sirimulla, S. AutoDock VinaXB: Implementation of XBSF, new empirical halogen bond scoring function, into AutoDock Vina. J. Cheminform. 2016, 8, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fusi, F.; Trezza, A.; Sgaragli, G.; Spiga, O.; Saponara, S.; Bova, S. Ritanserin blocks CaV1.2 channels in rat artery smooth muscles: Electrophysiological, functional, and computational studies. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2020, 41, 1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caciolla, J.; Picone, G.; Farruggia, G.; Valenti, D.; Rampa, A.; Malucelli, E.; Belluti, F.; Trezza, A.; Spiga, O.; Iotti, S.; et al. Multifaceted activity of polyciclic MDR revertant agents in drug-resistant leukemic cells: Role of the spacer. Bioorg. Chem. 2021, 106, 104460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dereeper, A.; Guignon, V.; Blanc, G.; Audic, S.; Buffet, S.; Chevenet, F.; Dufayard, J.F.; Guindon, S.; Lefort, V.; Lescot, M.; Claverie, J.M.; Gascuel, O. Phylogeny.fr: Robust phylogenetic analysis for the non-specialist. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008, 36, W465–W469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemoine, F.; Correia, D.; Lefort, V.; Doppelt-Azeroual, O.; Mareuil, F.; Cohen-Boulakia, S.; Gascuel, O. NGPhylogeny.fr: New generation phylogenetic services for non-specialists. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, W260–W265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Letunic, I.; Bork, P. Interactive Tree Of Life (iTOL) v5: An online tool for phylogenetic tree display and annotation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, W293–W296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, X.; Gong, T.; Yao, D. Examination of the expression and prognostic significance of DLGAPs in gastric cancer using the TCGA database and bioinformatic analysis. Mol. Med. Rep. 2018, 18, 5621–5629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, C.; Hu, C.G.; Ning, Z.K.; Huang, J.; Zhu, Z.M. Identification of key genes controlling cancer stem cell characteristics in gastric cancer. World J. Gastrointest. Surg. 2020, 12, 442–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dar, A.A.; Zaika, A.; Piazuelo, M.B.; Correa, P.; Koyama, T.; Belkhiri, A.; Washington, K.; Castells, A.; Pera, M.; El-Rifai, W. Frequent overexpression of Aurora Kinase A in upper gastrointestinal adenocarcinomas correlates with potent antiapoptotic functions. Cancer 2008, 112, 1688–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, J.; Goel, A.; Zhu, L. Identification of Novel Alternative Splicing Events Associated With Tumorigenesis, Protein Modification, and Immune Microenvironment in Early-Onset Gastric Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 640272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, L.; Li, B.; Yu, X.; Li, Z.; Li, X.; Dang, S.; Lv, Q.; Wei, J.; Sun, H.; Chen, H.; Liu, M.; Li, G. KIF15 facilitates gastric cancer via enhancing proliferation, inhibiting apoptosis, and predict poor prognosis. Cancer Cell Int. 2020, 20, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]












| Gene | Sequence (5′ to 3′) |
|---|---|
| GAPDH-FW | GGGTGTGAACCATGAGAAGTA |
| GAPDH-RW | ACTGTGGTCATGAGTCCTTC |
| ANGPT2-FW | ACCTGTTGAACCAAACAGCG |
| ANGPT2-RW | GTCGAGAGGGAGTGTTCCAAG |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ricci, A.; Gallorini, M.; Del Bufalo, D.; Cataldi, A.; D’Agostino, I.; Carradori, S.; Zara, S. Negative Modulation of the Angiogenic Cascade Induced by Allosteric Kinesin Eg5 Inhibitors in a Gastric Adenocarcinoma In Vitro Model. Molecules 2022, 27, 957. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27030957
Ricci A, Gallorini M, Del Bufalo D, Cataldi A, D’Agostino I, Carradori S, Zara S. Negative Modulation of the Angiogenic Cascade Induced by Allosteric Kinesin Eg5 Inhibitors in a Gastric Adenocarcinoma In Vitro Model. Molecules. 2022; 27(3):957. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27030957
Chicago/Turabian StyleRicci, Alessia, Marialucia Gallorini, Donatella Del Bufalo, Amelia Cataldi, Ilaria D’Agostino, Simone Carradori, and Susi Zara. 2022. "Negative Modulation of the Angiogenic Cascade Induced by Allosteric Kinesin Eg5 Inhibitors in a Gastric Adenocarcinoma In Vitro Model" Molecules 27, no. 3: 957. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27030957
APA StyleRicci, A., Gallorini, M., Del Bufalo, D., Cataldi, A., D’Agostino, I., Carradori, S., & Zara, S. (2022). Negative Modulation of the Angiogenic Cascade Induced by Allosteric Kinesin Eg5 Inhibitors in a Gastric Adenocarcinoma In Vitro Model. Molecules, 27(3), 957. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27030957