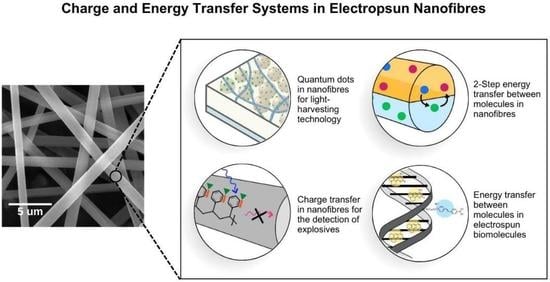
Light-Driven Energy and Charge Transfer Processes between Additives within Electrospun Nanofibres
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Electrospinning: How It Works
2.1. Factors That Affect Fibre Formation
2.1.1. Polymer Molecular Weight and Concentration
2.1.2. Viscosity
2.1.3. Applied Voltage and Tip-to-Collector Distance
2.1.4. Conductivity
2.1.5. Flow Rate
2.1.6. Solvent
2.1.7. Environmental Factors
2.2. Light-Harvesting Materials in Electrospun Nanofibres
3. Energy Transfer Systems within Electrospun Nanofibres
3.1. Förster Resonance Energy Transfer (FRET) in Electrospun Nanofibres
3.1.1. Molecules
3.1.2. Quantum Dots
3.2. Metal-Enhanced Fluorescence
3.3. Upconversion
4. Charge Transfer Systems in Electrospun Nanofibres: Photoinduced Electron Transfer (PET)
4.1. Acceptors: Naphthalimide and Quinoline
4.2. Donors: Carbazole
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Halicka, K.; Cabaj, J. Electrospun Nanofibers for Sensing and Biosensing Applications—A Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haghighat Bayan, M.A.; Afshar Taromi, F.; Lanzi, M.; Pierini, F. Enhanced Efficiency in Hollow Core Electrospun Nanofiber-Based Organic Solar Cells. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 21144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres-Martinez, E.J.; Cornejo Bravo, J.M.; Serrano Medina, A.; Pérez González, G.L.; Villarreal Gómez, L.J. A Summary of Electrospun Nanofibers as Drug Delivery System: Drugs Loaded and Biopolymers Used as Matrices. Curr. Drug. Deliv. 2018, 15, 1360–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gagaoua, M.; Pinto, V.Z.; Göksen, G.; Alessandroni, L.; Lamri, M.; Dib, A.L.; Boukid, F. Electrospinning as a Promising Process to Preserve the Quality and Safety of Meat and Meat Products. Coatings 2022, 12, 644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nhlapo, N.; Dzogbewu, T.C.; de Smidt, O. Nanofiber Polymers for Coating Titanium-Based Biomedical Implants. Fibers 2022, 10, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, S.; Si, Y.; Han, Y.; Wu, T.; Iqbal, M.I.; Fei, B.; Li, R.K.Y.; Hu, J.; Qu, J. Recent Progress in Protective Membranes Fabricated via Electrospinning: Advanced Materials, Biomimetic Structures, and Functional Applications. Adv. Mater. 2022, 34, 2107938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, T.; Zhang, J.; Gao, X.; Yuan, D.; Gu, Z.; Xu, Y. Electrospun Nanofibers for Bone Regeneration: From Biomimetic Composition, Structure to Function. J. Mater. Chem. B 2022, 10, 6078–6106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fennel, F.; Lochbrunner, S. Long Distance Energy Transfer in a Polymer Matrix Doped with a Perylene Dye. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2011, 13, 3527–3533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.S.; Yakunin, S.; Avaro, J.; Kang, X.; Bodnarchuk, M.I.; Liebi, M.; Sun, X.; Rossi, R.M.; Kovalenko, M.V.; Boesel, L.F. Amphiphilic Polymer Co-Network: A Versatile Matrix for Tailoring the Photonic Energy Transfer in Wearable Energy Harvesting Devices. Adv. Energy Mater. 2022, 12, 2200441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tailor, S.; Vashistha, N.; Modi, A.; Modi, S.C. One-Step Fabrication of Thermal Sprayed Polymer Coating on Metals. Mater. Res. Express 2020, 7, 016425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaliyaraj Selva Kumar, A.; Zhang, Y.; Li, D.; Compton, R.G. A Mini-Review: How Reliable Is the Drop Casting Technique? Electrochem. Commun 2020, 121, 106867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norrman, K.; Ghanbari-Siahkali, A.; Larsen, N.B. 6 Studies of Spin-Coated Polymer Films. Annu. Rep. Sect. “C” (Phys. Chem.) 2005, 101, 174–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmati, M.; Mills, D.K.; Urbanska, A.M.; Saeb, M.R.; Reddy Venugopal, J.; Ramakrishna, S.; Mozafari, M. Electrospinning for Tissue Engineering Applications. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2020, 117, 100721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirjalili, M.; Zohoori, S. Review for Application of Electrospinning and Electrospun Nanofibers Technology in Textile Industry. J. Nanostructure Chem. 2016, 6, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Almuhamed, S.; Bonne, M.; Khenoussi, N.; Brendle, J.; Schacher, L.; Lebeau, B.; Adolphe, D.C. Electrospinning Composite Nanofibers of Polyacrylonitrile/Synthetic Na-Montmorillonite. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2016, 35, 146–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sambaer, W.; Zatloukal, M.; Kimmer, D. 3D Modeling of Filtration Process via Polyurethane Nanofiber Based Nonwoven Filters Prepared by Electrospinning Process. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2011, 66, 613–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sill, T.J.; von Recum, H.A. Electrospinning: Applications in Drug Delivery and Tissue Engineering. Biomaterials 2008, 29, 1989–2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.Y.; Chiu, Y.C.; Shih, C.C.; Wu, W.C.; Chen, W.C. Electrospun Nanofibers with Dual Plasmonic-Enhanced Luminescent Solar Concentrator Effects for High-Performance Organic Photovoltaic Cells. J. Mater. Chem. A Mater. 2015, 3, 15039–15048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sznitko, L.; Romano, L.; Camposeo, A.; Wawrzynczyk, D.; Cyprych, K.; Mysliwiec, J.; Pisignano, D. Interplay of Stimulated Emission and Fluorescence Resonance Energy Transfer in Electrospun Light-Emitting Fibers. J. Phys. Chem. C 2018, 122, 762–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, M.; Ge, M.; Wang, J.; Tang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Mi, J.; Cai, W.; Lai, Y.; et al. Rational Design of Electrospun Nanofibers for Gas Purification: Principles, Opportunities, and Challenges. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 446, 137099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadil, F.; Affandi, N.D.N.; Misnon, M.I.; Bonnia, N.N.; Harun, A.M.; Alam, M.K. Review on Electrospun Nanofiber-Applied Products. Polymers 2021, 13, 2087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frenot, A.; Chronakis, I.S. Polymer Nanofibers Assembled by Electrospinning. Curr. Opin. Colloid. Interface Sci. 2003, 8, 64–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, T.; Ying, S.; Titov, K.; Dolbnya, I.P.; Tan, J.C.; Korsunsky, A.M. Operando Observation of the Taylor Cone during Electrospinning by Multiple Synchrotron X-Ray Techniques. Mater. Des. 2016, 110, 933–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaseashta, A. Controlled Formation of Multiple Taylor Cones in Electrospinning Process. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2007, 90, 093115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haider, A.; Haider, S.; Kang, I.K. A Comprehensive Review Summarizing the Effect of Electrospinning Parameters and Potential Applications of Nanofibers in Biomedical and Biotechnology. Arab. J. Chem. 2018, 11, 1165–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes, C.G.; Lagerwall, J.P.F. Disruption of Electrospinning Due to Water Condensation into the Taylor Cone. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 26566–26576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suresh, S.; Becker, A.; Glasmacher, B. Polymers Impact of Apparatus Orientation and Gravity in Electrospinning-A Review of Empirical Evidence. Polymers 2020, 12, 2448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, T.D.; Dalton, P.D.; Hutmacher, D.W. Direct Writing by Way of Melt Electrospinning. Adv. Mater. 2011, 23, 5651–5657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, J.; Mohtaram, N.K.; Ahmed, F.; Montgomery, A.; Carlson, M.; Lee, P.C.D.; Willerth, S.M.; Jun, M.B.G. Fabrication of Poly (ϵ-Caprolactone) Microfiber Scaffolds with Varying Topography and Mechanical Properties for Stem Cell-Based Tissue Engineering Applications. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2013, 25, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Han, D.; Steckl, A. Coaxial Electrospinning Formation of Complex Polymer Fibers and Their Applications. Chempluschem 2019, 84, 1453–1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Rutledge, G.C. Electrical Conductivity of Electrospun Polyaniline and Polyaniline-Blend Fibers and Mats. Macromolecules 2012, 45, 4238–4246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, X.; Liu, Y.; Gao, Y.; Liu, P. Electrospun Coaxial Fibers to Optimize the Release of Poorly Water-Soluble Drug. Polymers 2022, 14, 469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, S.; Liao, I.C.; Adler, A.; Leong, K.W. Electrohydrodynamics: A Facile Technique to Fabricate Drug Delivery Systems. Adv. Drug. Deliv. Rev. 2009, 61, 1043–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ji, W.; Yang, F.; Van Den Beucken, J.J.J.P.; Bian, Z.; Fan, M.; Chen, Z.; Jansen, J.A. Fibrous Scaffolds Loaded with Protein Prepared by Blend or Coaxial Electrospinning. Acta Biomater. 2010, 6, 4199–4207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abarzúa-Illanes, P.N.; Padilla, C.; Ramos, A.; Isaacs, M.; Ramos-Grez, J.; Olguín, H.C.; Valenzuela, L.M. Improving Myoblast Differentiation on Electrospun Poly(ε-Caprolactone) Scaffolds. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2017, 105, 2241–2251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, C.Y.; Inai, R.; Kotaki, M.; Ramakrishna, S. Aligned Biodegradable Nanofibrous Structure: A Potential Scaffold for Blood Vessel Engineering. Biomaterials 2004, 25, 877–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fennessey, S.F.; Farris, R.J. Fabrication of Aligned and Molecularly Oriented Electrospun Polyacrylonitrile Nanofibers and the Mechanical Behavior of Their Twisted Yarns. Polymer 2004, 45, 4217–4225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundaray, B.; Subramanian, V.; Natarajan, T.S.; Xiang, R.Z.; Chang, C.C.; Fann, W.S. Electrospinning of Continuous Aligned Polymer Fibers. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2004, 84, 1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katta, P.; Alessandro, M.; Ramsier, R.D.; Chase, G.G. Continuous Electrospinning of Aligned Polymer Nanofibers onto a Wire Drum Collector. Nano Lett. 2004, 4, 2215–2218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Murugan, R.; Wang, S.; Ramakrishna, S. Electrospinning of Nano/Micro Scale Poly(l-Lactic Acid) Aligned Fibers and Their Potential in Neural Tissue Engineering. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 2603–2610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theron, S.A.; Zussman, E.; Yarin, A.L. Experimental Investigation of the Governing Parameters in the Electrospinning of Polymer Solutions. Polymer 2004, 45, 2017–2030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.S.; Ang, B.C.; Andriyana, A.; Afifi, A.M. A Review on Fabrication of Nanofibers via Electrospinning and Their Applications. SN Appl. Sci. 2019, 1, 1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jacobs, V.; Anandjiwala, R.D.; Maaza, M. The Influence of Electrospinning Parameters on the Structural Morphology and Diameter of Electrospun Nanofibers. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2010, 115, 3130–3136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shenoy, S.L.; Bates, W.D.; Frisch, H.L.; Wnek, G.E. Role of Chain Entanglements on Fiber Formation during Electrospinning of Polymer Solutions: Good Solvent, Non-Specific Polymer–Polymer Interaction Limit. Polymer 2005, 46, 3372–3384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demir, M.M.; Yilgor, I.; Yilgor, E.; Erman, B. Electrospinning of Polyurethane Fibers. Polymer 2002, 43, 3303–3309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koski, A.; Yim, K.; Shivkumar, S. Effect of Molecular Weight on Fibrous PVA Produced by Electrospinning. Mater. Lett. 2004, 58, 493–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, H.M.; Lee, H.W.; Karim, M.R.; Cheong, I.W.; Bae, E.A.; Kim, T.H.; Islam, M.S.; Ji, B.C.; Yeum, J.H. Electrospinning and Characterization of Medium-Molecular-Weight Poly(Vinyl Alcohol)/High-Molecular-Weight Poly(Vinyl Alcohol)/Montmorillonite Nanofibers. Colloid. Polym. Sci. 2009, 287, 751–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inai, R.; Kotaki, M.; Ramakrishna, S. Structure and Properties of Electrospun PLLA Single Nanofibres. Nanotechnology 2005, 16, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nezarati, R.M.; Eifert, M.B.; Cosgriff-Hernandez, E. Effects of Humidity and Solution Viscosity on Electrospun Fiber Morphology. Tissue Eng. Part. C Methods 2013, 19, 810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tiwari, S.K.; Venkatraman, S.S. Importance of Viscosity Parameters in Electrospinning: Of Monolithic and Core–Shell Fibers. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2012, 32, 1037–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Tan, G.Z.; Zhou, Y. Effects of Viscosities and Solution Composition on Core-Sheath Electrospun Polycaprolactone(PCL) Nanoporous Microtubes. Polymers 2021, 13, 3650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, L.; Ziegler, G.R. Quantitative Relationship between Electrospinning Parameters and Starch Fiber Diameter. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 92, 1416–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, C.J.; Chase, G.G.; Yarin, A.L.; Reneker, D.H. Effects of Parameters on Nanofiber Diameter Determined from Electrospinning Model. Polymer 2007, 48, 6913–6922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nugraha, A.S.; Chou, C.C.; Yu, P.H.; Lin, K.L. Effects of Applied Voltage on the Morphology and Phases of Electrospun Poly(Vinylidene Difluoride) Nanofibers. Polym. Int. 2022, 71, 1176–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samatham, R.; Kim, K.J. Electric Current as a Control Variable in the Electrospinning Process. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2006, 46, 954–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fallahi, D.; Rafizadeh, M.; Mohammadi, N.; Vahidi, B. Effect of Applied Voltage on Surface and Volume Charge Density of the Jet in Electrospinning of Polyacrylonitrile Solutions. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2010, 50, 1372–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atabey, E.; Wei, S.; Zhang, X.; Gu, H.; Yan, X.; Huang, Y.; Shao, L.; He, Q.; Zhu, J.; Sun, L.; et al. Fluorescent Electrospun Polyvinyl Alcohol/CdSe@ZnS Nanocomposite Fibers. J. Compos. Mater. 2013, 47, 3175–3185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajeev, U.S.; Anand, K.A.; Menon, D.; Nair, S. Control of Nanostructures in PVA, PVA/Chitosan Blends and PCL through Electrospinning. Bull. Mater. Sci. 2008, 31, 343–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ignatova, M.; Starbova, K.; Markova, N.; Manolova, N.; Rashkov, I. Electrospun Nano-Fibre Mats with Antibacterial Properties from Quaternised Chitosan and Poly(Vinyl Alcohol). Carbohydr. Res. 2006, 341, 2098–2107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syed Bakar, S.S.; Foong, K.M.; Abdul Halif, N.; Yahud, S. Effect of Solution Concentration and Applied Voltage on Electrospun Polyacrylonitrile Fibers. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 701, 012018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Yuan, X.; Wu, L.; Han, Y.; Sheng, J. Study on Morphology of Electrospun Poly(Vinyl Alcohol) Mats. Eur. Polym. J. 2005, 41, 423–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Ju, K.; Wang, Z.; Li, W.; Ke, H.; He, J. Electrospun Jets Number and Nanofiber Morphology Effected by Voltage Value: Numerical Simulation and Experimental Verification. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2019, 14, 310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mit-Uppatham, C.; Nithitanakul, M.; Supaphol, P. Ultrafine Electrospun Polyamide-6 Fibers: Effect of Solution Conditions on Morphology and Average Fiber Diameter. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2004, 205, 2327–2338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topuz, F.; Satilmis, B.; Uyar, T. Electrospinning of Uniform Nanofibers of Polymers of Intrinsic Microporosity (PIM-1): The Influence of Solution Conductivity and Relative Humidity. Polymer 2019, 178, 121610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uyar, T.; Besenbacher, F. Electrospinning of Uniform Polystyrene Fibers: The Effect of Solvent Conductivity. Polymer 2008, 49, 5336–5343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, W.K.; Youk, J.H.; Lee, T.S.; Park, W.H. The Effects of Solution Properties and Polyelectrolyte on Electrospinning of Ultrafine Poly(Ethylene Oxide) Fibers. Polymer 2004, 45, 2959–2966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, S.H.; Inai, R.; Kotaki, M.; Ramakrishna, S. Systematic Parameter Study for Ultra-Fine Fiber Fabrication via Electrospinning Process. Polymer 2005, 46, 6128–6134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acik, G.; Cansoy, C.E.; Kamaci, M. Effect of Flow Rate on Wetting and Optical Properties of Electrospun Poly(Vinyl Acetate) Micro-Fibers. Colloid. Polym. Sci. 2018, 297, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zargham, S.; Bazgir, S.; Tavakoli, A.; Rashidi, A.S.; Damerchely, R. The Effect of Flow Rate on Morphology and Deposition Area of Electrospun Nylon 6 Nanofiber. J. Eng. Fibers Fab. 2012, 7, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jabur, A.R.; Najim, M.A.; Al-Rahman, S.A.A. Study the Effect of Flow Rate on Some Physical Properties of Different Polymeric Solutions. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2018, 1003, 012069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuangchote, S.; Sagawa, T.; Yoshikawa, S. Electrospinning of Poly(Vinyl Pyrrolidone): Effects of Solvents on Electrospinnability for the Fabrication of Poly(p-Phenylene Vinylene) and TiO2 Nanofibers. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2009, 114, 2777–2791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Zhenyu, L.I.; Hong, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Qiu, S.; Wang, C.E.; Wei, Y. Influence of Solvents on the Formation of Ultrathin Uniform Poly(Vinyl Pyrrolidone) Nanofibers with Electrospinning. J. Polym. Sci. B. Polym. Phys. 2004, 42, 3721–3726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fong, H.; Reneker, D.H. Elastomeric Nanofibers of Styrene-Butadiene-Styrene Triblock Copolymer. J. Polym. Sci. B Polym. Phys. 1999, 37, 3488–3493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fong, H.; Chun, I.; Reneker, D.H. Beaded Nanofibers Formed during Electrospinning. Polymer 1999, 40, 4585–4592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelipenko, J.; Kocbek, P.; Govedarica, B.; Rošic, R.; Baumgartner, S.; Kristl, J. The Topography of Electrospun Nanofibers and Its Impact on the Growth and Mobility of Keratinocytes. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2013, 84, 401–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripatanasuwan, S.; Zhong, Z.; Reneker, D.H. Effect of Evaporation and Solidification of the Charged Jet in Electrospinning of Poly(Ethylene Oxide) Aqueous Solution. Polymer 2007, 48, 5742–5746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghorbani, M.; Nezhad-Mokhtari, P.; Sohrabi, H.; Roshangar, L. Electrospun Chitosan/Nanocrystalline Cellulose-Graft-Poly(N-Vinylcaprolactam) Nanofibers as the Reinforced Scaffold for Tissue Engineering. J. Mater. Sci. 2020, 55, 2176–2185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vrieze, S.; Van Camp, T.; Nelvig, A.; Hagström, B.; Westbroek, P.; De Clerck, K. The Effect of Temperature and Humidity on Electrospinning. J. Mater. Sci. 2009, 44, 1357–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Chien, H.S.; Hsu, C.H.; Wang, Y.C.; Wang, C.T.; Lu, H.A. Electrospinning of Polyacrylonitrile Solutions at Elevated Temperatures. Macromolecules 2007, 40, 7973–7983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramazani, S.; Karimi, M. Investigating the Influence of Temperature on Electrospinning of Polycaprolactone Solutions. E-polymers 2014, 14, 323–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ippel, B.D.; Van Haaften, E.E.; Bouten, C.V.C.; Dankers, P.Y.W. Impact of Additives on Mechanical Properties of Supramolecular Electrospun Scaffolds. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2020, 2, 3742–3748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, H.; Liu, J.; O’Connor, H.M.; Gunnlaugsson, T.; James, T.D.; Zhang, H. Photoinduced Electron Transfer (PeT) Based Fluorescent Probes for Cellular Imaging and Disease Therapy. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2023, 52, 2322–2357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.H.; Ha, T.; Shin, M.; Lee, S.N.; Choi, J.W. Nanomaterial-Based Fluorescence Resonance Energy Transfer (FRET) and Metal-Enhanced Fluorescence (MEF) to Detect Nucleic Acid in Cancer Diagnosis. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehrler, B.; Yanai, N.; Nienhaus, L. Up- and down-Conversion in Molecules and Materials. J. Chem. Phys. 2021, 154, 070401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singha, S.; Kim, D.; Seo, H.; Cho, S.W.; Ahn, K.H. Fluorescence Sensing Systems for Gold and Silver Species. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 4367–4399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Huy, B.; Thangadurai, D.T.; Sharipov, M.; Ngoc Nghia, N.; Van Cuong, N.; Lee, Y.I. Recent Advances in Turn Off-on Fluorescence Sensing Strategies for Sensitive Biochemical Analysis—A Mechanistic Approach. Microchem. J. 2022, 179, 107511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ner, Y.; Grote, J.G.; Stuart, J.A.; Sotzing, G.A. White Luminescence from Multiple-Dye-Doped Electrospun DNA Nanofibers by Fluorescence Resonance Energy Transfer. Angew. Chem. 2009, 121, 5236–5240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liberale, F.; Fiore, M.; Ruffo, R.; Bernasconi, R.; Shiratori, S.; Magagnin, L. Red Phosphorus Decorated Electrospun Carbon Anodes for High Efficiency Lithium Ion Batteries. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 13233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triyana, K.; Rianjanu, A.; Nugroho, D.B.; As’ari, A.H.; Kusumaatmaja, A.; Roto, R.; Suryana, R.; Wasisto, H.S. A Highly Sensitive Safrole Sensor Based on Polyvinyl Acetate (PVAc) Nanofiber-Coated QCM. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 15407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thamer, B.M.; Aldalbahi, A.; Meera Moydeen, A.; Rahaman, M.; El-Newehy, M.H. Modified Electrospun Polymeric Nanofibers and Their Nanocomposites as Nanoadsorbents for Toxic Dye Removal from Contaminated Waters: A Review. Polymers 2021, 13, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, A.; Kaur, P.; Ahuja, S. Förster Resonance Energy Transfer (FRET) and Applications Thereof. Anal. Methods 2020, 12, 5532–5550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Huang, C.; Emery, B.P.; Sedgwick, A.C.; Bull, S.D.; He, X.P.; Tian, H.; Yoon, J.; Sessler, J.L.; James, T.D. Förster Resonance Energy Transfer (FRET)-Based Small-Molecule Sensors and Imaging Agents. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2020, 49, 5110–5139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tonsomboon, K.; Noppakuadrittidej, P.; Sutikulsombat, S.; Petdum, A.; Panchan, W.; Wanichacheva, N.; Sooksimuang, T.; Karoonuthaisiri, N. Turn-On Fluorescence Resonance Energy Transfer (FRET)-Based Electrospun Fibrous Membranes: Rapid and Ultrasensitive Test Strips for on-Site Detection of Mercury (II) Ion. Sens. Actuators B. Chem. 2021, 344, 130212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaerkitcha, N.; Sagawa, T. Highly Efficient Fluorescence Resonance Energy Transfer in Electrospun Nanofibers Containing Pyrene and Porphyrin. Chem. Lett. 2018, 47, 794–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Z.; Wang, Q.; Wang, C.; Xu, D.; Ma, G.; Pan, K. Electrospun Janus Nanofibers for White-Light Emission through Efficient Spatial Isolation to Control Two-Step Energy Transfer. J. Mater. Chem. C. Mater. 2019, 7, 1065–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vohra, V.; Calzaferri, G.; Destri, S.; Pasini, M.; Porzio, W.; Botta, C. Toward White Light Emission through Efficient Two-Step Energy Transfer in Hybrid Nanofibers. ACS Nano 2010, 4, 1409–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmood, R.; Castillo-Rodriguez, J.; Grandy, R.A.; Koivisto, B.D. Energy Transfer between Molecules from Core to Shell in One-Dimensional Coaxial Electrospun Nanofibres. Mater. Chem. Front. 2023, 7, 1120–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deerinck, T.J. The Application of Fluorescent Quantum Dots to Confocal, Multiphoton, and Electron Microscopic Imaging. Toxicol. Pathol. 2008, 36, 112–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Devi, S.; Kumar, M.; Tiwari, A.; Tiwari, V.; Kaushik, D.; Verma, R.; Bhatt, S.; Sahoo, B.M.; Bhattacharya, T.; Alshehri, S.; et al. Quantum Dots: An Emerging Approach for Cancer Therapy. Front. Mater. 2022, 8, 798440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, E.M.; Kroupa, D.M.; Zhang, J.; Schulz, P.; Marshall, A.R.; Kahn, A.; Lany, S.; Luther, J.M.; Beard, M.C.; Perkins, C.L.; et al. Revisiting the Valence and Conduction Band Size Dependence of PbS Quantum Dot Thin Films. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 3302–3311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wegner, K.D.; Hildebrandt, N. Quantum Dots: Bright and Versatile in Vitro and in Vivo Fluorescence Imaging Biosensors. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 4792–4834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kargozar, S.; Hoseini, S.J.; Milan, P.B.; Hooshmand, S.; Kim, H.W.; Mozafari, M. Quantum Dots: A Review from Concept to Clinic. Biotechnol. J. 2020, 15, 2000117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dos Santos, M.C.; Algar, W.R.; Medintz, I.L.; Hildebrandt, N. Quantum Dots for Förster Resonance Energy Transfer (FRET). TrAC—Trends Anal. Chem. 2020, 125, 115819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altintas, Y.; Kiremitler, N.B.; Genc, S.; Onses, M.S.; Mutlugün, E. FRET Enabled Light Harvesting within Quantum Dot Loaded Nanofibers. J. Phys. D. Appl. Phys. 2018, 51, 065111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.J.; Hwang, D.; Chung, H.; Kim, D.Y.; Kim, D. Controlling the Spatial Distribution of Quantum Dots in Nanofiber for Light-Harvesting Devices. NPG Asia Mater. 2015, 7, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Huang, J.; Cai, J.; Zhu, J.; Yang, X.; Shen, J.; Li, C. Perovskite Quantum Dots Encapsulated in Electrospun Fiber Membranes as Multifunctional Supersensitive Sensors for Biomolecules, Metal Ions and PH. Nanoscale Horiz. 2017, 2, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeoung, E.; Yeh, Y.-C.; Nelson, T.; Kushida, T.; Wang, L.-S.; Mout, R.; Li, X.; Saha, K.; Gupta, A.; Tonga, G.Y.; et al. Fabrication of Functional Nanofibers Through Post-Nanoparticle Functionalization. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2015, 36, 678–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fu, Y.; Chen, X.; Mou, X.; Ren, Z.; Li, X.; Han, G. A Dual-Color Luminescent Localized Drug Delivery System with Ratiometric-Monitored Doxorubicin Release Functionalities. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2016, 2, 652–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, Y.; Kook, Y.M.; Lee, K.; Koh, W.G. Metal Enhanced Fluorescence (MEF) for Biosensors: General Approaches and a Review of Recent Developments. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 111, 102–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodgson, G.K.; Dogantzis, N.P.; Impellizzeri, S. Single Molecule Techniques Can Distinguish the Photophysical Processes Governing Metal-Enhanced Fluorescence. J. Phys. Chem. C. 2020, 124, 28298–28305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawar, S.; Bhattacharya, A.; Nag, A. Metal-Enhanced Fluorescence Study in Aqueous Medium by Coupling Gold Nanoparticles and Fluorophores Using a Bilayer Vesicle Platform. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 5983–5990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.Y.; Wu, H.C.; Chiu, Y.C.; Chen, W.C. Plasmon-Enhanced Polymer Photovoltaic Device Performance Using Different Patterned Ag/PVP Electrospun Nanofibers. Adv. Energy Mater. 2014, 4, 1301665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Cao, M.; Wu, W.; Xu, H.; Cheng, S.; Fan, L.J. Polyacrylonitrile/Noble Metal/SiO2 Nanofibers as Substrates for the Amplified Detection of Picomolar Amounts of Metal Ions through Plasmon-Enhanced Fluorescence. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 1374–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burris, A.J.; Cheng, Q. Plasmon-Enhanced Fluorescence in Electrospun Nanofibers of Polydiacetylenes Infused with Silver Nanoparticles. Langmuir 2021, 37, 14920–14929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, B.J.; Kwon, J.E.; Lee, K.; Koh, W.G. Highly Sensitive Metal-Enhanced Fluorescence Biosensor Prepared on Electrospun Fibers Decorated with Silica-Coated Silver Nanoparticles. Sens. Actuators B. Chem. 2019, 284, 140–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Ågren, H.; Chen, G. Near Infrared Harvesting Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells Enabled by Rare-Earth Upconversion Materials. Dalton Trans. 2018, 47, 8526–8537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Q.; Huang, P.; Zheng, W.; You, W.; Li, R.; Tu, D.; Xu, J.; Chen, X. Cooperative and Non-Cooperative Sensitization Upconversion in Lanthanide-Doped LiYbF4 Nanoparticles. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 6521–6528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Joubert, M.-F. Photon avalanche upconversion in rare earth laser materials. Opt. Mater. 1999, 11, 181–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de la Mora, M.B.; Amelines-Sarria, O.; Monroy, B.M.; Hernández-Pérez, C.D.; Lugo, J.E. Materials for Downconversion in Solar Cells: Perspectives and Challenges. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2017, 165, 59–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Li, X.; Chi, D.; Zhang, H.; Liu, X. Lanthanide-Doped Upconversion Materials: Emerging Applications for Photovoltaics and Photocatalysis. Nanotechnology 2014, 25, 482001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkinson, K.; Ekstrand-Hammarström, B.; Ahlinder, L.; Guldevall, K.; Pazik, R.; Keopiński, L.; Kvashnina, K.O.; Butorin, S.M.; Brismar, H.; Önfelt, B.; et al. Visualization of Custom-Tailored Iron Oxide Nanoparticles Chemistry, Uptake, and Toxicity. Nanoscale 2012, 4, 7383–7393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Z.; Li, C.; Ma, P.; Li, G.; Cheng, Z.; Peng, C.; Yang, D.; Yang, P.; Lin, J. Electrospinning Preparation and Drug-Delivery Properties of an Up-Conversion Luminescent Porous NaYF4:Yb3+, Er 3+@silica Fiber Nanocomposite. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2011, 21, 2356–2365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auzel, F. Upconversion and Anti-Stokes Processes with f and d Ions in Solids. Chem. Rev. 2004, 104, 139–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Jia, H.; Ye, H.; Dai, T.; Yin, X.; He, J.; Chen, R.; Wang, Y.; Pang, X. Facile Fabrication of Transparent and Upconversion Photoluminescent Nanofiber Mats with Tunable Optical Properties. ACS Omega 2018, 3, 8220–8225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yu, H.; Jiang, P.; Chen, B.; Sun, J.; Cheng, L.; Li, X.; Zhang, J.; Xu, S. Electrospinning Preparation and Upconversion Luminescence of Y2Ti2O7:Tm/Yb Nanofibers. Appl. Phys. A Mater. Sci. Process. 2020, 126, 690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, W.; Xu, M.; Shi, J.; Zhu, J.; Li, Y. Highly Temperature-Sensitive and Blue Upconversion Luminescence Properties of Bi2Ti2O7:Tm3+/Yb3+ Nanofibers by Electrospinning. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 391, 123546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doose, S.; Neuweiler, H.; Sauer, M. Fluorescence Quenching by Photoinduced Electron Transfer: A Reporter for Conformational Dynamics of Macromolecules. ChemPhysChem 2009, 10, 1389–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magri, D.C. Logical Sensing with Fluorescent Molecular Logic Gates Based on Photoinduced Electron Transfer. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2021, 426, 213598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veale, E.B.; Frlmannsson, D.O.; Lawler, M.; Gunnlaugsson, T. 4-Amino-1,8-Naphthalimide-Based Tröger’s Bases as High Affinity DNA Targeting Fluorescent Supramolecular Scaffolds. Org. Lett. 2009, 11, 4040–4043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamal, A.; Bolla, N.R.; Srikanth, P.S.; Srivastava, A.K. Naphthalimide Derivatives with Therapeutic Characteristics: A Patent Review. Expert. Opin. Ther. Pat. 2013, 23, 299–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bojinov, V.B.; Georgiev, N.I. Design, Synthesis and Sensor Activity of a Highly Photostable Blue Emitting 1,8-Naphthalimide. J. Lumin. 2012, 132, 2235–2241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tigoianu, R.; Airinei, A.; Georgescu, E.; Nicolescu, A.; Georgescu, F.; Isac, D.L.; Deleanu, C.; Oancea, F. Synthesis and Solvent Dependent Fluorescence of Some Piperidine-Substituted Naphthalimide Derivatives and Consequences for Water Sensing. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 2760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonardi, A.-H.; Zahouily, S.; Dietlin, C.; Graff, B.; Morlet-Savary, F.; Ibrahim-Ouali, M.; Gigmes, D.; Hoffmann, N.; Dumur, F.; Lalevee, J.; et al. New 1,8-Naphthalimide Derivatives as Photoinitiators for Free-Radical Polymerization Upon Visible Light. Catalysts 2019, 9, 637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gale, P.; Gunnlaugsson, T.; Duke, R.M.; Veale, E.B.; Pfeffer, F.M.; Kruger, P.E. Supramolecular Chemistry of Anionic Species Themed Issue Colorimetric and Fluorescent Anion Sensors: An Overview of Recent Developments in the Use of 1,8-Naphthalimide-Based Chemosensors. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2010, 39, 3936–3953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pablos, J.L.; Hernández, E.; Catalina, F.; Corrales, T. Solid Fluorescence PH Sensors Based on 1,8-Naphthalimide Copolymers Synthesized by UV Curing. Chemosensors 2022, 10, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Wang, S.; Zhu, M. Quinoline-Based Fluorescence Sensors. In Molecular Photochemistry—Various Aspects; InTech: London, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qin, J.C.; Yang, Z.Y. Selective Fluorescent Sensor for Al3+ Using a Novel Quinoline Derivative in Aqueous Solution. Synth. Met. 2015, 209, 570–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Ye, X.; Liu, G.; Lv, Y.; Zhang, X.; Chen, S.; Lam, J.W.Y.; Kwok, H.S.; Tao, X.; Tang, B.Z. Structural Features and Optical Properties of a Carbazole-Containing Ethene as a Highly Emissive Organic Solid. J. Mater. Chem. C Mater. 2014, 2, 1004–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekkar, F.; Bettahar, F.; Moreno, I.; Meghabar, R.; Hamadouche, M.; Hernáez, E.; Vilas-Vilela, J.L.; Ruiz-Rubio, L. Polycarbazole and Its Derivatives: Synthesis and Applications: A Review of the Last 10 Years. Polymers 2020, 12, 2227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Shi, N.; Zhang, J.; Wu, X.; Wang, T.; Yang, L.; Yang, R.; Ou, C.; Xue, W.; Feng, X.; et al. Electrospun Fluorescent Sensors for the Selective Detection of Nitro Explosive Vapors and Trace Water. J. Mater. Chem. A Mater. 2018, 6, 18543–18550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



























| Structure | Name | Absorbance Maxima | Emission Maxima | Solvent | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | 1,8-napthalimide | 360 nm | 440 nm | DMF | [131] |
 | 2-(4-Methyl-5-oxo-2,5-dihydrofuran-2-yloxy)-6-(4-methylpiperidin-1-yl)- benzo[de]isoquinoline-1,3-dione | 402 | 508 | dioxane | [132] |
| 416 | 521 | acetonitrile | [132] | ||
| 420 | 528 | methanol | [132] | ||
 | 2-(2-methoxyethyl)-6-((2-morpholinoethyl)amino)-1H-benzo[de]isoquinoline1,3(2H)-dione | 430 | 520 | acetonitrile | [133] |
 | 4-amino-1,8-napthalimide | 450 nm | 550 nm | water | [134] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mahmood, R.; Mananquil, T.; Scenna, R.; Dennis, E.S.; Castillo-Rodriguez, J.; Koivisto, B.D. Light-Driven Energy and Charge Transfer Processes between Additives within Electrospun Nanofibres. Molecules 2023, 28, 4857. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28124857
Mahmood R, Mananquil T, Scenna R, Dennis ES, Castillo-Rodriguez J, Koivisto BD. Light-Driven Energy and Charge Transfer Processes between Additives within Electrospun Nanofibres. Molecules. 2023; 28(12):4857. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28124857
Chicago/Turabian StyleMahmood, Reeda, Tristan Mananquil, Rebecca Scenna, Emma S. Dennis, Judith Castillo-Rodriguez, and Bryan D. Koivisto. 2023. "Light-Driven Energy and Charge Transfer Processes between Additives within Electrospun Nanofibres" Molecules 28, no. 12: 4857. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28124857
APA StyleMahmood, R., Mananquil, T., Scenna, R., Dennis, E. S., Castillo-Rodriguez, J., & Koivisto, B. D. (2023). Light-Driven Energy and Charge Transfer Processes between Additives within Electrospun Nanofibres. Molecules, 28(12), 4857. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28124857