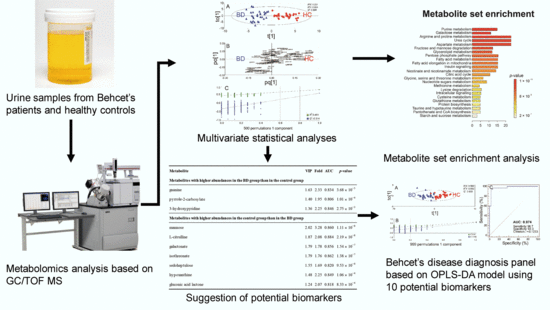
Urinary Metabolomic Profiling to Identify Potential Biomarkers for the Diagnosis of Behcet’s Disease by Gas Chromatography/Time-of-Flight−Mass Spectrometry
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Identification of Metabolites in the Urine Samples of the Discovery Set
2.2. Distinct Metabolomic Profiles in Urine Samples of Behcet’s Disease Patients Using Discovery Set
2.3. Identification of Potential Biomarkers in the Discovery Set
2.4. The Multivariate Statistical Model with the Potential Urinary Biomarkers Selected for Robust Diagnosis of BD
2.5. Metabolic Pathway Analysis of BD
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Samples from Patients
4.2. Metabolite Sample Preparation
4.3. Quality Controls
4.4. Identification of Metabolites and Data Processing
4.5. Gas Chromatography-Time-of-Flight−Mass Spectrometry Data Processing and Statistical Analyses
4.6. Statistical Analyses and Model Validation
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AUC | Area under the receiver operating characteristic curve |
| BD | Behcet’s disease |
| CRP | C-reactive protein |
| GC/TOF−MS | Gas chromatography-time-of-flight–mass spectrometry |
| HC | Healthy control |
| MSEA | Metabolite set enrichment analysis |
| NO | Nitric oxide |
| OPLS-DA | Orthogonal partial least squared-discrimination analysis |
| PCA | Principal component analysis |
| PLS-DA | Partial least squares discriminant analysis |
| PPP | Pentose phosphate pathway |
| RA | Rheumatoid arthritis |
| ROC | Receiver operating characteristic |
| VIP | Variable importance on projection |
| XO | Xanthine oxidase |
| AUC | Area under the receiver operating characteristic curve |
References
- Ambrose, N.L.; Haskard, D.O. Differential diagnosis and management of Behcet syndrome. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2013, 9, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakane, T.; Takeno, M.; Suzuki, N.; Inaba, G. Behcet’s disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 1999, 341, 1284–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tursen, U. Pathophysiology of the Behcet’s disease. Pathol. Res. Int. 2012, 2012, 493015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guma, M.; Tiziani, S.; Firestein, G.S. Metabolomics in rheumatic diseases: Desperately seeking biomarkers. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2016, 12, 269–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, J.K.; Kim, S.; Kim, J.; Hwang, J.; Kim, K.H.; Cha, H.S. A Comparative metabolomic evaluation of Behcet’s disease with arthritis and seronegative arthritis using synovial fluid. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0135856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, J.K.; Kim, J.; Hwang, J.; Song, J.; Kim, K.H.; Cha, H.S. Potential metabolomic biomarkers for reliable diagnosis of Behcet’s disease using gas chromatography with time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Jt. Bone Spine 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guleria, A.; Pratap, A.; Dubey, D.; Rawat, A.; Chaurasia, S.; Sukesh, E.; Phatak, S.; Ajmani, S.; Kumar, U.; Khetrapal, C.L.; et al. NMR based serum metabolomics reveals a distinctive signature in patients with Lupus Nephritis. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 35309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapoor, S.R.; Filer, A.; Fitzpatrick, M.A.; Fisher, B.A.; Taylor, P.C.; Buckley, C.D.; McInnes, I.B.; Raza, K.; Young, S.P. Metabolic profiling predicts response to anti-tumor necrosis factor alpha therapy in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2013, 65, 1448–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Wietmarschen, H.A.; Dai, W.; van der Kooij, A.J.; Reijmers, T.H.; Schroen, Y.; Wang, M.; Xu, Z.; Wang, X.; Kong, H.; Xu, G.; et al. Characterization of rheumatoid arthritis subtypes using symptom profiles, clinical chemistry and metabolomics measurements. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e44331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Yang, G.J.; Zhang, J.; Chen, C.; Jia, Z.Y.; Li, J.; Xu, W.D. Plasma, urine and ligament tissue metabolite profiling reveals potential biomarkers of ankylosing spondylitis using NMR-based metabolic profiles. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2016, 18, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weyand, C.M.; Goronzy, J.J. Immunometabolism in early and late stages of rheumatoid arthritis. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2017, 13, 291–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morel, L. Immunometabolism in systemic lupus erythematosus. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2017, 13, 280–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaber, T.; Strehl, C.; Buttgereit, F. Metabolic regulation of inflammation. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2017, 13, 267–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wishart, D. Metabolomics in humans and other mammals. In Metabolome Analysis: An Introduction; Villas-Boas, S.G., Roessner, U., Hansen, M.A.E., Smedsgaard, J., Nielsen, J., Eds.; Wiley-Interscience: New York, NY, USA, 2007; pp. 253–288. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, J.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, R.; He, J.; Song, Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, H.; Wang, L.; Zhan, Q.; Abliz, Z. Global metabolomics reveals potential urinary biomarkers of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma for diagnosis and staging. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 35010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yildirim, M.; Baysal, V.; Inaloz, H.S.; Doguc, D. The significance of serum nitric oxide levels in Behcet’s disease and recurrent aphthous stomatitis. J. Dermatol. 2004, 31, 983–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hodeib, A.A.; Elsharawy, T.A.; Fawzi, H.A. Assessment of serum homocysteine, endothelin-1, and nitric oxide levels in Behcet’s disease. Indian J. Dermatol. 2010, 55, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sogut, S.; Aydin, E.; Elyas, H.; Aksoy, N.; Ozyurt, H.; Totan, Y.; Akyol, O. The activities of serum adenosine deaminase and xanthine oxidase enzymes in Behcet’s disease. Clin. Chim. Acta 2002, 325, 133–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flam, B.R.; Eichler, D.C.; Solomonson, L.P. Endothelial nitric oxide production is tightly coupled to the citrulline-NO cycle. Nitric Oxide 2007, 17, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wanchu, A.; Khullar, M.; Sud, K.; Sakhuja, V.; Thennarasu, K.; Sud, A.; Bambery, P. Serum and urine nitrite and citrulline levels among patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: A possible addition to activity parameters? J. Clin. Rheumatol. 2001, 7, 10–15, discussion 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Consolandi, C.; Turroni, S.; Emmi, G.; Severgnini, M.; Fiori, J.; Peano, C.; Biagi, E.; Grassi, A.; Rampelli, S.; Silvestri, E.; et al. Behcet’s syndrome patients exhibit specific microbiome signature. Autoimmun. Rev. 2015, 14, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouatra, S.; Aziat, F.; Mandal, R.; Guo, A.C.; Wilson, M.R.; Knox, C.; Bjorndahl, T.C.; Krishnamurthy, R.; Saleem, F.; Liu, P.; et al. The human urine metabolome. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e73076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Andersson Hall, U.; Edin, F.; Pedersen, A.; Madsen, K. Whole-body fat oxidation increases more by prior exercise than overnight fasting in elite endurance athletes. Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab. 2016, 41, 430–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Priori, R.; Casadei, L.; Valerio, M.; Scrivo, R.; Valesini, G.; Manetti, C. (1)H-NMR-Based metabolomic study for identifying serum profiles associated with the response to etanercept in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0138537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- International Study Group for Behcet’s Disease. Criteria for diagnosis of Behcet’s disease. Lancet 1990, 335, 1078–1080. [Google Scholar]
- Chan, E.C.; Pasikanti, K.K.; Nicholson, J.K. Global urinary metabolic profiling procedures using gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Nat. Protoc. 2011, 6, 1483–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, D.Y.; Fiehn, O. High quality metabolomic data for Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Plant Methods 2008, 4, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kind, T.; Wohlgemuth, G.; Lee, D.Y.; Lu, Y.; Palazoglu, M.; Shahbaz, S.; Fiehn, O. FiehnLib: Mass spectral and retention index libraries for metabolomics based on quadrupole and time-of-flight gas chromatography/mass spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 10038–10048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, J.; Wishart, D.S. MSEA: A web-based tool to identify biologically meaningful patterns in quantitative metabolomic data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 38, W71–W77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Metabolite | VIP | Fold | AUC | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Metabolites with higher abundances in the BD group than in the control group | ||||
| Guanine | 1.63 | 2.33 | 0.834 | 3.68 × 10−5 |
| Pyrrole-2-carboxylate | 1.40 | 1.95 | 0.806 | 1.01 × 10−4 |
| 3-hydroxypyridine | 1.36 | 2.25 | 0.846 | 2.75 × 10−3 |
| Metabolites with higher abundances in the control group than in the BD group | ||||
| Mannose | 2.02 | 3.28 | 0.860 | 1.11 × 10−8 |
| l-citrulline | 1.87 | 2.08 | 0.884 | 2.19 × 10−8 |
| Galactonate | 1.79 | 1.78 | 0.856 | 1.54 × 10−7 |
| Isothreonate | 1.79 | 1.76 | 0.862 | 1.38 × 10−7 |
| Sedoheptulose | 1.55 | 1.69 | 0.820 | 9.53 × 10−6 |
| Hypoxanthine | 1.48 | 2.25 | 0.849 | 1.06 × 10−4 |
| Gluconic acid lactone | 1.24 | 2.07 | 0.818 | 8.33 × 10−4 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ahn, J.K.; Kim, J.; Hwang, J.; Song, J.; Kim, K.H.; Cha, H.-S. Urinary Metabolomic Profiling to Identify Potential Biomarkers for the Diagnosis of Behcet’s Disease by Gas Chromatography/Time-of-Flight−Mass Spectrometry. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2309. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18112309
Ahn JK, Kim J, Hwang J, Song J, Kim KH, Cha H-S. Urinary Metabolomic Profiling to Identify Potential Biomarkers for the Diagnosis of Behcet’s Disease by Gas Chromatography/Time-of-Flight−Mass Spectrometry. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2017; 18(11):2309. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18112309
Chicago/Turabian StyleAhn, Joong Kyong, Jungyeon Kim, Jiwon Hwang, Juhwan Song, Kyoung Heon Kim, and Hoon-Suk Cha. 2017. "Urinary Metabolomic Profiling to Identify Potential Biomarkers for the Diagnosis of Behcet’s Disease by Gas Chromatography/Time-of-Flight−Mass Spectrometry" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 18, no. 11: 2309. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18112309
APA StyleAhn, J. K., Kim, J., Hwang, J., Song, J., Kim, K. H., & Cha, H. -S. (2017). Urinary Metabolomic Profiling to Identify Potential Biomarkers for the Diagnosis of Behcet’s Disease by Gas Chromatography/Time-of-Flight−Mass Spectrometry. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 18(11), 2309. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18112309