Luteolin-7-O-β-d-Glucoside Inhibits Cellular Energy Production Interacting with HEK2 in Keratinocytes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Metabolic Analysis in LUT-7G Treated Keratinocytes
2.2. Metabolic Analysis in Calcium Differentiating Keratinocytes
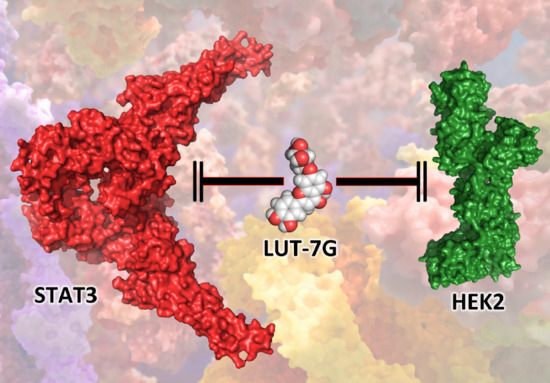
2.3. The Role of LUT-7G in the Regulation of Hexokinase 2 Activity
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Molecular Docking Simulations
4.2. ATP Levels Detection
4.3. Cell culture and Treatments
4.4. Metabolomic Analysis
4.5. Hexokinase Activity
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| LUT-7G | luteolin-7glucoside |
| HEK2 | hexokinase 2 |
| GLUT-4 | glucose transporter type 4 |
| TCA | tricarboxylic Acid Cycle or Krebs cycle |
| PEP | phosphoenolpyruvate |
| 3PG | 3-phosphoglycerate |
| G6P | glucose-6-phosphate |
| IMQ | imiquimod |
| IL-22 | interleukin-22 |
| IL6 | interleukin-6 |
| STAT3 | transcription of Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 |
| HEKn | human epidermal keratinocytes neonatal |
| TG1, TG3 | transglutaminase 1 and 3 |
| K10 | keratin 10 |
References
- Reuter, J.; Merfort, I.; Schempp, C.M. Botanicals in dermatology: An evidence-based review. Am. J. Clin. Dermatol. 2010, 11, 247–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kostyuk, V.; Potapovich, A.; de Luca, C. The promise of plant polyphenols as the golden standard skin anti-inflammatory agents. Curr. Drug Metab. 2010, 11, 414–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez-Lazaro, M. Distribution and biological activities of the flavonoid luteolin. Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 2009, 9, 31–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Leary, K.A.; de Pascual-Teresa, S.; Needs, P.W.; Bao, Y.P.; O’Brien, N.M.; Williamson, G. Effect of flavonoids and vitamin E on cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) transcription. Mutat. Res. 2004, 551, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakata, K.; Hirose, Y.; Qiao, Z.; Tanaka, T.; Mori, H. Inhibition of inducible isoforms of cyclooxygenase and nitric oxide synthase by flavonoid hesperidin in mouse macrophage cell line. Cancer Lett. 2003, 199, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, S.Y.; Park, S.J.; Kwon, M.J.; Jeong, T.S.; Bok, S.H.; Choi, W.Y.; Jeong, W.I.; Ryu, S.Y.; Do, S.H.; Lee, C.S.; et al. Quercetin suppresses proinflammatory cytokines production through MAP kinases andNF-kappaB pathway in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated macrophage. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2003, 243, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicentini, F.T.; He, T.; Shao, Y.; Fonseca, M.J.; Verri, W.A., Jr.; Fisher, G.J.; Xu, Y. Quercetin inhibits UV irradiation-induced inflammatory cytokine production in primary human keratinocytes by suppressing NF-kappaB pathway. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2011, 61, 162–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.C.; Hsieh, L.M.; Chen, H.W.; Lin, Y.S.; Chen, J.S. Effects of baicalein and esculetin on transduction signals and growth factors expression in T-lymphoid leukemia cells. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1994, 268, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCabe, M.J., Jr.; Orrenius, S. Genistein induces apoptosis in immature human thymocytes by inhibiting topoisomerase-II. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1993, 194, 944–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Middleton, E., Jr.; Kandaswami, C.; Theoharides, T.C. The effects of plant flavonoids on mammalian cells: Implications for inflammation, heart disease, and cancer. Pharmacol. Rev. 2000, 52, 673–751. [Google Scholar]
- Del Rio, D.; Rodriguez-Mateos, A.; Spencer, J.P.; Tognolini, M.; Borges, G.; Crozier, A. Dietary (poly)phenolics in human health: Structures, bioavailability, and evidence of protective effects against chronic diseases. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2013, 18, 1818–1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palombo, R.; Savini, I.; Avigliano, L.; Madonna, S.; Cavani, A.; Albanesi, C.; Mauriello, A.; Melino, G.; Terrinoni, A. Luteolin-7-glucoside inhibits IL-22/STAT3 pathway, reducing proliferation, acanthosis, and inflammation in keratinocytes and in mouse psoriatic model. Cell. Death Dis. 2016, 7, e2344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, J.Q. Targeting interleukin-22 in psoriasis. Inflammation 2014, 37, 94–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Belle, A.B.; de Heusch, M.; Lemaire, M.M.; Hendrickx, E.; Warnier, G.; Dunussi-Joannopoulos, K.; Fouser, L.A.; Renauld, J.C.; Dumoutier, L. IL-22 is required for imiquimod-induced psoriasiform skin inflammation in mice. J. Immunol. 2012, 188, 462–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bikle, D.D.; Ng, D.; Tu, C.L.; Oda, Y.; Xie, Z. Calcium- and vitamin D-regulated keratinocyte differentiation. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2001, 177, 161–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrne, C.; Tainsky, M.; Fuchs, E. Programming gene expression in developing epidermis. Development 1994, 120, 2369–2383. [Google Scholar]
- Candi, E.; Schmidt, R.; Melino, G. The cornified envelope: A model of cell death in the skin. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2005, 6, 328–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melino, G.; De Laurenzi, V.; Catani, M.V.; Terrinoni, A.; Ciani, B.; Candi, E.; Marekov, L.; Steinert, P.M. The cornified envelope: A model of cell death in the skin. Results Probl. Cell. Differ. 1998, 24, 175–212. [Google Scholar]
- Melstrom, L.G.; Salabat, M.R.; Ding, X.Z.; Milam, B.M.; Strouch, M.; Pelling, J.C.; Bentrem, D.J. Apigenin inhibits the GLUT-1 glucose transporter and the phosphoinositide 3-kinase/Akt pathway in human pancreatic cancer cells. Pancreas 2008, 37, 426–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hennings, H.; Kruszewski, F.H.; Yuspa, S.H.; Tucker, R.W. Intracellular calcium alterations in response to increased external calcium in normal and neoplastic keratinocytes. Carcinogenesis 1989, 10, 777–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuspa, S.H.; Kilkenny, A.E.; Steinert, P.M.; Roop, D.R. Expression of murine epidermal differentiation markers is tightly regulated by restricted extracellular calcium concentrations in vitro. J. Cell. Biol. 1989, 109, 1207–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smirnov, A.; Lena, A.M.; Cappello, A.; Panatta, E.; Anemona, L.; Bischetti, S.; Annicchiarico-Petruzzelli, M.; Mauriello, A.; Melino, G.; Candi, E. ZNF185 is a p63 target gene critical for epidermal differentiation and squamous cell carcinoma development. Oncogene 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poumay, Y.; Pittelkow, M. Cell density and culture factors regulate keratinocyte commitment to differentiation and expression of suprabasal K1/K10 keratins. J. Investig. Dermatol 1995, 104, 271–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terrinoni, A.; Didona, B.; Caporali, S.; Chillemi, G.; Lo Surdo, A.; Paradisi, M.; Annichiarico-Petruzzelli, M.; Candi, E.; Bernardini, S.; Melino, G. Role of the keratin 1 and keratin 10 tails in the pathogenesis of ichthyosis hystrix of Curth Macklin. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0195792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettersen, E.F.; Goddard, T.D.; Huang, C.C.; Couch, G.S.; Greenblatt, D.M.; Meng, E.C.; Ferrin, T.E. UCSF Chimera--a visualization system for exploratory research and analysis. J. Comput. Chem. 2004, 25, 1605–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laskowski, R.A.; Swindells, M.B. LigPlot+: Multiple ligand-protein interaction diagrams for drug discovery. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2011, 51, 2778–2786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Lano, W.L. The PyMOL Molecular Graphics System. Available online: https://pymol.org/2/support.html (accessed on 6 May 2019).
- Amat, A.; Clementi, C.; De Angelis, F.; Sgamellotti, A.; Fantacci, S. Absorption and emission of the apigenin and luteolin flavonoids: A TDDFT investigation. J. Phys. Chem. A 2009, 113, 15118–15126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leopoldini, M.; Prieto Pitarch, I.; Russo, N.; Toscano, M. Structure, Conformation, and Electronic Properties of Apigenin, Luteolin, and Taxifolin Antioxidants. A First Principle Theoretical Study. J. Phys. Chem. A 2004, 108, 92–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanpain, C.; Fuchs, E. Epidermal stem cells of the skin. Annu. Rev. Cell. Dev. Biol. 2006, 22, 339–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Candi, E.; Rufini, A.; Terrinoni, A.; Dinsdale, D.; Ranalli, M.; Paradisi, A.; De Laurenzi, V.; Spagnoli, L.G.; Catani, M.V.; Ramadan, S.; et al. Differential roles of p63 isoforms in epidermal development: Selective genetic complementation in p63 null mice. Cell. Death Differ. 2006, 13, 1037–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koster, M.I.; Dai, D.; Marinari, B.; Sano, Y.; Costanzo, A.; Karin, M.; Roop, D.R. p63 induces key target genes required for epidermal morphogenesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 3255–3260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Serra, V.; Castori, M.; Paradisi, M.; Bui, L.; Melino, G.; Terrinoni, A. Functional characterization of a novel TP63 mutation in a family with overlapping features of Rapp-Hodgkin/AEC/ADULT syndromes. Am. J. Med. Genet. A 2011, 155A, 3104–3109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viticchie, G.; Agostini, M.; Lena, A.M.; Mancini, M.; Zhou, H.; Zolla, L.; Dinsdale, D.; Saintigny, G.; Melino, G.; Candi, E. p63 supports aerobic respiration through hexokinase II. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 11577–11582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Candi, E.; Terrinoni, A.; Rufini, A.; Chikh, A.; Lena, A.M.; Suzuki, Y.; Sayan, B.S.; Knight, R.A.; Melino, G. p63 is upstream of IKK alpha in epidermal development. J. Cell. Sci. 2006, 119, 4617–4622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frezza, V.; Fierro, C.; Gatti, E.; Peschiaroli, A.; Lena, A.M.; Petruzzelli, M.A.; Candi, E.; Anemona, L.; Mauriello, A.; Pelicci, P.G.; et al. DeltaNp63 promotes IGF1 signalling through IRS1 in squamous cell carcinoma. Aging (Albany NY) 2018, 10, 4224–4240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Chen, H.; Xu, P.; Cong, L.N.; Sciacchitano, S.; Li, Y.; Graham, D.; Jacobs, A.R.; Taylor, S.I.; Quon, M.J. Action of insulin receptor substrate-3 (IRS-3) and IRS-4 to stimulate translocation of GLUT4 in rat adipose cells. Mol. Endocrinol. 1999, 13, 505–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Zeng, J.; Xie, R.; Schulz, M.J.; Tedesco, R.; Qu, J.; Erhard, K.F.; Mack, J.F.; Raha, K.; Rendina, A.R.; et al. Discovery of a Novel 2,6-Disubstituted Glucosamine Series of Potent and Selective Hexokinase 2 Inhibitors. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2016, 7, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chang, J.; Hsu, Y.; Kuo, P.; Kuo, Y.; Chiang, L.; Lin, C. Increase of Bax/ Bcl-XL ratio and arrest of cell cycle by luteolin in immortalized human hepatoma cell line. Life Sci. 2005, 76, 1883–1893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.H.; Park, H.S.; Lee, J.H.; Chi, G.Y.; Kim, G.Y.; Moon, S.K.; Chang, Y.C.; Hyun, J.W.; Kim, W.J.; Choi, Y.H. Induction of endoplasmic reticulum stress-mediated apoptosis and non-canonical autophagy by luteolin in NCI-H460 lung carcinoma cells. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2013, 56, 100–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, W.; Wang, X.; Shi, H.; Chen, W.; Belinsky, S.A.; Lin, Y. A critical role of luteolin-induced reactive oxygen species in blockage of tumor necrosis factor-activated nuclear factor-kappaB pathway and sensitization of apoptosis in lung cancer cells. Mol. Pharmacol. 2007, 71, 1381–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warburg, O. The metabolism of carcinoma cells. J. Cancer Res. 1925, 1, 148–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liberti, M.V.; Locasale, J.W. The Warburg Effect: How Does it Benefit Cancer Cells? Trends Biochem. Sci. 2016, 41, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Amelio, I.; Antonov, A.A.; Catani, M.V.; Massoud, R.; Bernassola, F.; Knight, R.A.; Melino, G.; Rufini, A. TAp73 promotes anabolism. Oncotarget 2014, 5, 12820–12934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Dai, D.; Chen, B.; Tang, H.; Xie, X.; Wei, W. Efficacy of PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway inhibitors for the treatment of advanced solid cancers: A literature-based meta-analysis of 46 randomised control trials. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0192464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhullar, K.S.; Lagaron, N.O.; McGowan, E.M.; Parmar, I.; Jha, A.; Hubbard, B.P.; Rupasinghe, H.P.V. Kinase-targeted cancer therapies: Progress, challenges and future directions. Mol. Cancer 2018, 17, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trott, O.; Olson, A.J. AutoDock Vina: Improving the speed and accuracy of docking with a new scoring function, efficient optimization, and multithreading. J. Comput. Chem. 2010, 31, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seeliger, D.; de Groot, B.L. Ligand docking and binding site analysis with PyMOL and Autodock/Vina. J. Comput. Aided Mol. Des. 2010, 24, 417–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Palombo, R.; Porta, G.; Bruno, E.; Provero, P.; Serra, V.; Neduri, K.; Viziano, A.; Alessandrini, M.; Micarelli, A.; Ottaviani, F.; et al. OTX2 regulates the expression of TAp63 leading to macular and cochlear neuroepithelium development. Aging (Albany NY) 2015, 7, 928–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]






© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Palombo, R.; Caporali, S.; Falconi, M.; Iacovelli, F.; Morozzo Della Rocca, B.; Lo Surdo, A.; Campione, E.; Candi, E.; Melino, G.; Bernardini, S.; et al. Luteolin-7-O-β-d-Glucoside Inhibits Cellular Energy Production Interacting with HEK2 in Keratinocytes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2689. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20112689
Palombo R, Caporali S, Falconi M, Iacovelli F, Morozzo Della Rocca B, Lo Surdo A, Campione E, Candi E, Melino G, Bernardini S, et al. Luteolin-7-O-β-d-Glucoside Inhibits Cellular Energy Production Interacting with HEK2 in Keratinocytes. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(11):2689. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20112689
Chicago/Turabian StylePalombo, Ramona, Sabrina Caporali, Mattia Falconi, Federico Iacovelli, Blasco Morozzo Della Rocca, Alessandro Lo Surdo, Elena Campione, Eleonora Candi, Gerry Melino, Sergio Bernardini, and et al. 2019. "Luteolin-7-O-β-d-Glucoside Inhibits Cellular Energy Production Interacting with HEK2 in Keratinocytes" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 11: 2689. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20112689
APA StylePalombo, R., Caporali, S., Falconi, M., Iacovelli, F., Morozzo Della Rocca, B., Lo Surdo, A., Campione, E., Candi, E., Melino, G., Bernardini, S., & Terrinoni, A. (2019). Luteolin-7-O-β-d-Glucoside Inhibits Cellular Energy Production Interacting with HEK2 in Keratinocytes. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(11), 2689. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20112689