Cellular and Molecular Effects of High-Molecular-Weight Heparin on Matrix Metalloproteinase 9 Expression
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Direct Stimulation of Different Cell Types with Anticoagulants Has No Influence on MMP-9 Expression
2.2. Significant Induction of MMP-9 Expression by HMWH in A Co-Culture Including THP-1, Jurkat, and HT Cells
2.3. Significant Induction of MMP-9 Expression by HMWH in the THP-1 and Jurkat Co-Culture
2.4. Significant Induction of MMP-9 Expression in THP-1 Cells in Response to Culture Supernatant Derived from HMWH-Treated Jurkat Cells
2.5. High-Molecular-Weight Heparin Versus Low-Molecular-Weight Heparin
2.6. Identification of Soluble Mediators Secreted in Response to HMWH
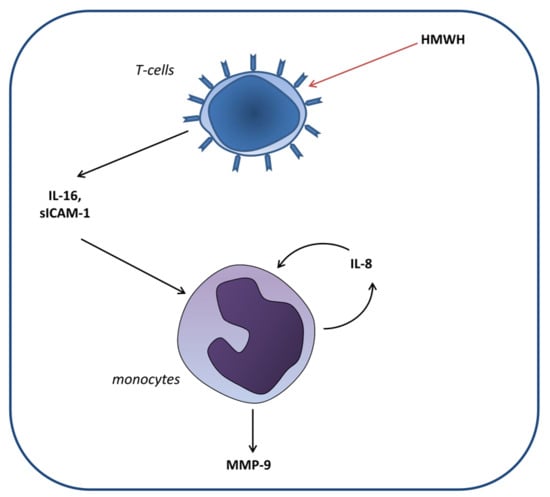
2.7. Regulation of MMP-9 Expression in THP-1 by Jurkat-Derived IL-16 and sICAM-1
2.8. Regulation of IL-8 Expression in THP-1 by IL-16 and Autocrine Activation
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Collection and Storage of Human Heparin Plasma
4.2. Cell Lines and Cell Culture Conditions
4.3. Cell Culture Experiments
4.3.1. Individual and Co-Culture Experiments
4.3.2. Cell Supernatant Transfer Experiments
4.3.3. Cytokine/Chemokine Stimulation Experiments
4.4. RNA Extraction, cDNA Synthesis, and qPCR
4.5. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay
4.6. Proteome Profiler Array
4.7. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AP | Activator protein |
| cDNA | Complementary DNA |
| CCL | CC-chemokine ligand |
| CXCL | CxC-chemokine ligand |
| DSMZ | Deutsche Sammlung von Mikroorganismen und Zellkulturen |
| ECL | Enhanced chemiluminescence |
| ECM | Extracellular matrix |
| EDTA | Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid |
| EGF | Epidermal growth factor |
| ELISA | Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay |
| ERK | Extracellular signal-regulated kinase |
| FCS | Fetal calf serum |
| GAPDH | Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase |
| GM-CSF | granulocyte/macrophage-colony stimulating factor |
| GPR | G-protein-coupled receptor |
| HMGB | High mobility group box |
| HMWH | High-molecular-weight heparin |
| HRP | Horseradish peroxidase |
| IFN | Interferon |
| IKK | IκB kinase |
| IL | Interleukin |
| IL-1RA | IL-1 receptor antagonist |
| IU | International unit |
| Jak | Janus kinase |
| JNK | Jun N-terminal kinase |
| LMWH | Low-molecular-weight heparin |
| MAPK | Mitogen-activated protein kinasesmethyl-accepting chemotaxis protein |
| MCP | Methyl-accepting chemotaxis protein |
| MIF | Macrophage migration inhibitory factor |
| MIP | Macrophage inflammatory protein |
| MMP | Matrix metalloproteinase |
| NF-κB | Nuclear factor κB |
| PDGF | Platelet-derived growth factor |
| PKC | Protein kinase C |
| qPCR | Quantitative polymerase chain reaction |
| SCF | Stem cell factor |
| SD | Standard deviation |
| sICAM | Soluble intercellular adhesion molecule |
| Sp | Specificity protein |
| STAT | Signal transducer and activator of transcription |
| TIMP | Tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases |
| TNF | Tumor necrosis factor |
| VEGF | Vascular endothelial growth factor |
| VTE | Venous thromboembolism |
References
- Nelson, A.R.; Fingleton, B.; Rothenberg, M.L.; Matrisian, L.M. Matrix metalloproteinases: Biologic activity and clinical implications. J. Clin. Oncol. 2000, 18, 1135–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egeblad, M.; Werb, Z. New functions for the matrix metalloproteinases in cancer progression. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2002, 2, 161–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemaitre, V.; D’Armiento, J. Matrix metalloproteinases in development and disease. Birth Defects Res. C Embryo Today 2006, 78, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, V.W. Metalloproteinases: Mediators of pathology and regeneration in the CNS. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2005, 6, 931–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, J.; Van den Steen, P.E.; Sang, Q.X.; Opdenakker, G. Matrix metalloproteinase inhibitors as therapy for inflammatory and vascular diseases. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2007, 6, 480–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gronberg, N.V.; Johansen, F.F.; Kristiansen, U.; Hasseldam, H. Leukocyte infiltration in experimental stroke. J. Neuroinflamm. 2013, 10, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sapojnikova, N.; Kartvelishvili, T.; Asatiani, N.; Zinkevich, V.; Kalandadze, I.; Gugutsidze, D.; Shakarishvili, R.; Tsiskaridze, A. Correlation between MMP-9 and extracellular cytokine HMGB1 in prediction of human ischemic stroke outcome. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2014, 1842, 1379–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rababah, M.; Worthmann, H.; Deb, M.; Tryc, A.B.; Ma, Y.T.; El Bendary, O.M.; Hecker, H.; Goldbecker, A.; Heeren, M.; Brand, K.; et al. Anticoagulants affect matrix metalloproteinase 9 levels in blood samples of stroke patients and healthy controls. Clin. Biochem. 2012, 45, 483–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mannello, F.; Luchetti, F.; Canonico, B.; Papa, S. Effect of anticoagulants and cell separation media as preanalytical determinants on zymographic analysis of plasma matrix metalloproteinases. Clin. Chem. 2003, 49, 1956–1957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannello, F.; Jung, K.; Tonti, G.A.; Canestrari, F. Heparin affects matrix metalloproteinases and tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases circulating in peripheral blood. Clin. Biochem. 2008, 41, 1466–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meisser, A.; Cohen, M.; Bischof, P. Concentrations of circulating gelatinases (matrix metalloproteinase-2 and -9) are dependent on the conditions of blood collection. Clin. Chem. 2005, 51, 274–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerlach, R.F.; Demacq, C.; Jung, K.; Tanus-Santos, J.E. Rapid separation of serum does not avoid artificially higher matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-9 levels in serum versus plasma. Clin. Biochem. 2007, 40, 119–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, E.; Mulloy, B.; Barrowcliffe, T.W. Heparin and low-molecular-weight heparin. Thromb. Haemost. 2008, 99, 807–818. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pineo, G.F.; Hull, R.D. Economic and practical aspects of thromboprophylaxis with unfractionated and low-molecular-weight heparins in hospitalized medical patients. Clin. Appl. Thromb. Hemost. 2009, 15, 489–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banfi, G.; Salvagno, G.L.; Lippi, G. The role of ethylenediamine tetraacetic acid (EDTA) as in vitro anticoagulant for diagnostic purposes. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2007, 45, 565–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van den Besselaar, A.M.; Chantarangkul, V.; Tripodi, A. A comparison of two sodium citrate concentrations in two evacuated blood collection systems for prothrombin time and ISI determination. Thromb. Haemost. 2000, 84, 664–667. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yoffe, J.R.; Taylor, D.J.; Woolley, D.E. Mast-cell products and heparin stimulate the production of mononuclear-cell factor by cultured human monocyte/macrophages. Biochem. J. 1985, 230, 83–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Webster, N.L.; Crowe, S.M. Matrix metalloproteinases, their production by monocytes and macrophages and their potential role in HIV-related diseases. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2006, 80, 1052–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wollbold, J.; Huber, R.; Pohlers, D.; Koczan, D.; Guthke, R.; Kinne, R.W.; Gausmann, U. Adapted Boolean network models for extracellular matrix formation. BMC Syst. Biol. 2009, 3, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page-McCaw, A.; Ewald, A.J.; Werb, Z. Matrix metalloproteinases and the regulation of tissue remodelling. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2007, 8, 221–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van den Steen, P.E.; Dubois, B.; Nelissen, I.; Rudd, P.M.; Dwek, R.A.; Opdenakker, G. Biochemistry and molecular biology of gelatinase B or matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9). Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2002, 37, 375–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, G.; Knäuper, V.; Atkinson, S.; Butler, G.; English, W.; Hutton, M.; Stracke, J.; Clark, I. Matrix metalloproteinases in arthritic disease. Arthritis Res. 2002, 4, S39–S49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kessenbrock, K.; Plaks, V.; Werb, Z. Matrix metalloproteinases: Regulators of the tumor microenvironment. Cell 2010, 141, 52–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert, E.; Dasse, E.; Haye, B.; Petitfrere, E. TIMPs as multifacial proteins. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2004, 49, 187–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.R.; Noh, E.M.; Han, J.H.; Kim, J.M.; Hwang, B.M.; Kim, B.S.; Lee, S.H.; Jung, S.H.; Youn, H.J.; Chung, E.Y.; et al. Sulforaphane controls TPA-induced MMP-9 expression through the NF-kappaB signaling pathway, but not AP-1, in MCF-7 breast cancer cells. BMB Rep. 2013, 46, 201–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, W.R.; Chung, C.L.; Hsiao, C.J.; Chou, Y.C.; Hsueh, P.J.; Yang, P.C.; Jan, J.S.; Cheng, Y.W.; Hsiao, G. Suppression of matrix metalloproteinase-9 expression by andrographolide in human monocytic THP-1 cells via inhibition of NF-kappaB activation. Phytomedicine 2012, 19, 270–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Rashed, F.; Kochumon, S.; Usmani, S.; Sindhu, S.; Ahmad, R. Pam3CSK4 Induces MMP-9 Expression in Human Monocytic THP-1 Cells. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 41, 1993–2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- St-Pierre, Y.; Couillard, J.; Van Themsche, C. Regulation of MMP-9 gene expression for the development of novel molecular targets against cancer and inflammatory diseases. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2004, 8, 473–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Overall, C.M.; Lopez-Otin, C. Strategies for MMP inhibition in cancer: Innovations for the post-trial era. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2002, 2, 657–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manfredi, M.A.; Zurakowski, D.; Rufo, P.A.; Walker, T.R.; Fox, V.L.; Moses, M.A. Increased incidence of urinary matrix metalloproteinases as predictors of disease in pediatric patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2008, 14, 1091–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, K.; Lein, M.; Laube, C.; Lichtinghagen, R. Blood specimen collection methods influence the concentration and the diagnostic validity of matrix metalloproteinase 9 in blood. Clin. Chim. Acta 2001, 314, 241–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, K.; Klotzek, S.; Stephan, C.; Mannello, F.; Lein, M. Impact of blood sampling on the circulating matrix metalloproteinases 1, 2, 3, 7, 8, and 9. Clin. Chem. 2008, 54, 772–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bar-Or, A.; Nuttall, R.K.; Duddy, M.; Alter, A.; Kim, H.J.; Ifergan, I.; Pennington, C.J.; Bourgoin, P.; Edwards, D.R.; Yong, V.W. Analyses of all matrix metalloproteinase members in leukocytes emphasize monocytes as major inflammatory mediators in multiple sclerosis. Brain 2003, 126, 2738–2749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Raphael, I.; Nalawade, S.; Eagar, T.N.; Forsthuber, T.G. T cell subsets and their signature cytokines in autoimmune and inflammatory diseases. Cytokine 2015, 74, 5–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cruikshank, W.W.; Kornfeld, H.; Center, D.M. Interleukin-16. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2000, 67, 757–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mathy, N.L.; Scheuer, W.; Lanzendorfer, M.; Honold, K.; Ambrosius, D.; Norley, S.; Kurth, R. Interleukin-16 stimulates the expression and production of pro-inflammatory cytokines by human monocytes. Immunology 2000, 100, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Park, S.L.; Hwang, B.; Lee, S.Y.; Kim, W.T.; Choi, Y.H.; Chang, Y.C.; Kim, W.J.; Moon, S.K. p21WAF1 Is Required for Interleukin-16-Induced Migration and Invasion of Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells via the p38MAPK/Sp-1/MMP-9 Pathway. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0142153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunther, J.; Vogt, N.; Hampel, K.; Bikker, R.; Page, S.; Muller, B.; Kandemir, J.; Kracht, M.; Dittrich-Breiholz, O.; Huber, R.; et al. Identification of two forms of TNF tolerance in human monocytes: Differential inhibition of NF-kappaB/AP-1- and PP1-associated signaling. J. Immunol. 2014, 192, 3143–3155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, S.C.; Scott, K.A.; Balkwill, F.R. Chemokine stimulation of monocyte matrix metalloproteinase-9 requires endogenous TNF-alpha. Eur. J. Immunol. 2002, 32, 404–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, D.A.; Fang, L.; Chan, W.; Morand, E.F.; Kiriazis, H.; Duffy, S.J.; Taylor, A.J.; Dart, A.M.; Du, X.J.; Gao, X.M. Pro-inflammatory action of MIF in acute myocardial infarction via activation of peripheral blood mononuclear cells. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e76206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Browning, D.D.; Diehl, W.C.; Hsu, M.H.; Schraufstatter, I.U.; Ye, R.D. Autocrine regulation of interleukin-8 production in human monocytes. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 2000, 279, L1129–L1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, F.; Tang, R.; Zhang, X.; Madushi, W.M.; Luo, D.; Dang, Y.; Li, Z.; Wei, K.; Chen, G. Overexpression of MMP Family Members Functions as Prognostic Biomarker for Breast Cancer Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0135544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leber, T.M.; Balkwill, F.R. Regulation of monocyte MMP-9 production by TNF-alpha and a tumour-derived soluble factor (MMPSF). Br. J. Cancer 1998, 78, 724–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doster, A.; Schwarzig, U.; Zygmunt, M.; Rom, J.; Schutz, F.; Fluhr, H. Unfractionated Heparin Selectively Modulates the Expression of CXCL8, CCL2 and CCL5 in Endometrial Carcinoma Cells. Anticancer Res. 2016, 36, 1535–1544. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Biancotto, A.; Feng, X.; Langweiler, M.; Young, N.S.; McCoy, J.P. Effect of anticoagulants on multiplexed measurement of cytokine/chemokines in healthy subjects. Cytokine 2012, 60, 438–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Patil, R.; Shukre, S.; Paranjape, R.; Thakar, M. Heparin and EDTA anticoagulants differentially affect the plasma cytokine levels in humans. Scand. J. Clin. Lab. Investig. 2013, 73, 452–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baram, D.; Rashkovsky, M.; Hershkoviz, R.; Drucker, I.; Reshef, T.; Ben-Shitrit, S.; Mekori, Y.A. Inhibitory effects of low molecular weight heparin on mediator release by mast cells: Preferential inhibition of cytokine production and mast cell-dependent cutaneous inflammation. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 1997, 110, 485–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shastri, M.D.; Stewart, N.; Horne, J.; Peterson, G.M.; Gueven, N.; Sohal, S.S.; Patel, R.P. In-vitro suppression of IL-6 and IL-8 release from human pulmonary epithelial cells by non-anticoagulant fraction of enoxaparin. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0126763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shastri, M.D.; Stewart, N.; Eapen, M.; Peterson, G.M.; Zaidi, S.T.; Gueven, N.; Sohal, S.S.; Patel, R.P. Opposing effects of low molecular weight heparins on the release of inflammatory cytokines from peripheral blood mononuclear cells of asthmatics. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0118798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onishi, A.; St Ange, K.; Dordick, J.S.; Linhardt, R.J. Heparin and anticoagulation. Front. Biosci. (Landmark Ed.) 2016, 21, 1372–1392. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Linhardt, R.J. Chemoenzymatic synthesis of heparan sulfate and heparin. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2014, 31, 1676–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Crowther, M.; Lim, W. Low molecular weight heparin and bleeding in patients with chronic renal failure. Curr. Opin. Pulm. Med. 2007, 13, 409–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Ling, Y.; Huang, M.; Yin, T.; Gou, S.M.; Zhan, N.Y.; Xiong, J.X.; Wu, H.S.; Yang, Z.Y.; Wang, C.Y. Heparin inhibits the inflammatory response induced by LPS and HMGB1 by blocking the binding of HMGB1 to the surface of macrophages. Cytokine 2015, 72, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, N.Y.; Chang, G.W.; Huang, Y.S.; Peng, Y.M.; Hsiao, C.C.; Kuo, M.L.; Lin, H.H. Heparin interacts with the adhesion GPCR GPR56, reduces receptor shedding, and promotes cell adhesion and motility. J. Cell Sci. 2016, 129, 2156–2169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Theroux, P.; Waters, D.; Qiu, S.; McCans, J.; de Guise, P.; Juneau, M. Aspirin versus heparin to prevent myocardial infarction during the acute phase of unstable angina. Circulation 1993, 88, 2045–2048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavender, M.A.; Sabatine, M.S. Bivalirudin versus heparin in patients planned for percutaneous coronary intervention: A meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. Lancet 2014, 384, 599–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grzela, T.; Brawura-Biskupski-Samaha, R.; Jelenska, M.M.; Szmidt, J. Low molecular weight heparin treatment decreases MMP-9 plasma activity in patients with abdominal aortic aneurysm. Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. 2008, 35, 159–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalyani, B.S.; Roberts, C.S. Low molecular weight heparin: Current evidence for its application in orthopaedic surgery. Curr. Vasc. Pharmacol. 2011, 9, 19–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyman, G.H. Thromboprophylaxis with low-molecular-weight heparin in medical patients with cancer. Cancer 2009, 115, 5637–5650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huber, R.; Panterodt, T.; Welz, B.; Christmann, M.; Friesenhagen, J.; Westphal, A.; Pietsch, D.; Brand, K. C/EBPbeta-LAP*/LAP Expression Is Mediated by RSK/eIF4B-Dependent Signalling and Boosted by Increased Protein Stability in Models of Monocytic Differentiation. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0144338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, R.; Kunisch, E.; Gluck, B.; Egerer, R.; Sickinger, S.; Kinne, R.W. Comparison of conventional and real-time RT-PCR for the quantitation of jun protooncogene mRNA and analysis of junB mRNA expression in synovial membranes and isolated synovial fibroblasts from rheumatoid arthritis patients. Z. Rheumatol. 2003, 62, 378–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haas, S.C.; Huber, R.; Gutsch, R.; Kandemir, J.D.; Cappello, C.; Krauter, J.; Duyster, J.; Ganser, A.; Brand, K. ITD- and FL-induced FLT3 signal transduction leads to increased C/EBPbeta-LIP expression and LIP/LAP ratio by different signalling modules. Br. J. Haematol. 2010, 148, 777–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwettmann, L.; Wehmeier, M.; Jokovic, D.; Aleksandrova, K.; Brand, K.; Manns, M.P.; Lichtinghagen, R.; Bahr, M.J. Hepatic expression of A disintegrin and metalloproteinase (ADAM) and ADAMs with thrombospondin motives (ADAM-TS) enzymes in patients with chronic liver diseases. J. Hepatol. 2008, 49, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutsch, R.; Kandemir, J.D.; Pietsch, D.; Cappello, C.; Meyer, J.; Simanowski, K.; Huber, R.; Brand, K. CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein beta inhibits proliferation in monocytic cells by affecting the retinoblastoma protein/E2F/cyclin E pathway but is not directly required for macrophage morphology. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 22716–22729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]








| Cell Line(s) | Identified Cytokines/Chemokines |
|---|---|
| THP-1 | IL-1RA, CCL5, MIF |
| Jurkat | MIF, IL-13, IL-16, sICAM-1, Serpin E1 |
| HT | MIF, IL-13, sICAM-1, Serpin E1, TNF |
| THP-1, Jurkat, and HT | IL-1RA, CCL5, MIF, IL-13, IL-16, sICAM-1, Serpin E1, IL-8 |
| THP-1 and Jurkat | IL-1RA, CCL5, MIF, IL-13, IL-16, sICAM-1, Serpin E1, IL-8 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huber, R.; Attili/Abedalkhader, R.; Küper, D.; Hauke, L.; Lüns, B.; Brand, K.; Weissenborn, K.; Lichtinghagen, R. Cellular and Molecular Effects of High-Molecular-Weight Heparin on Matrix Metalloproteinase 9 Expression. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1595. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20071595
Huber R, Attili/Abedalkhader R, Küper D, Hauke L, Lüns B, Brand K, Weissenborn K, Lichtinghagen R. Cellular and Molecular Effects of High-Molecular-Weight Heparin on Matrix Metalloproteinase 9 Expression. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(7):1595. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20071595
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuber, René, Rozan Attili/Abedalkhader, Daniela Küper, Lara Hauke, Bernadette Lüns, Korbinian Brand, Karin Weissenborn, and Ralf Lichtinghagen. 2019. "Cellular and Molecular Effects of High-Molecular-Weight Heparin on Matrix Metalloproteinase 9 Expression" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 7: 1595. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20071595
APA StyleHuber, R., Attili/Abedalkhader, R., Küper, D., Hauke, L., Lüns, B., Brand, K., Weissenborn, K., & Lichtinghagen, R. (2019). Cellular and Molecular Effects of High-Molecular-Weight Heparin on Matrix Metalloproteinase 9 Expression. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(7), 1595. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20071595