Oral Delivery of a Tetrameric Tripeptide Inhibitor of VEGFR1 Suppresses Pathological Choroid Neovascularization
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Synthesis of iVR1
2.2. FT-IR Characterization of Peptides Before and after Counter-Ion Exchange
2.3. iVR1Ac Shows Increased Inhibitory Activity Compared to iVR1-TFA
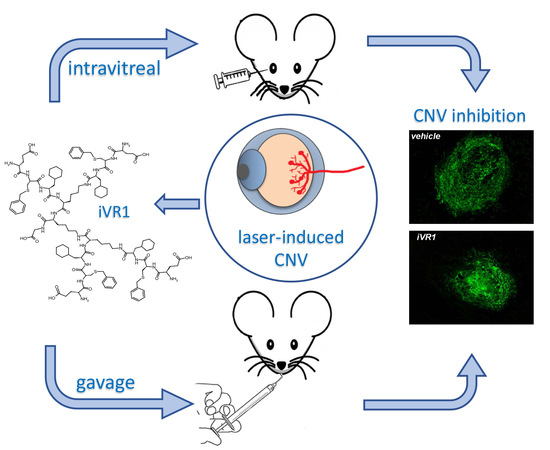
2.4. Intravitreal Delivery of iVR1-Ac Potently Inhibit Laser-Induced CNV
2.5. iVR1-Ac Delivered by Gavage Provides Effective CNV Inhibition
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Peptide Synthesis
4.2. FT-IR Characterization of Peptides Before and After Counter-Ion Exchange
4.3. Competitive ELISA for VEGF-A/VEGFR-1 Interaction
4.4. Animals
4.5. Choroidal Neo-Vascularization Model: Intravitreal Delivery
4.6. Choroidal Neo-Vascularization Model: Oral Delivery by Gavage
4.7. Choroidal Neo-Vascularization Volume Quantification
4.8. Statistical Analysis
5. Patents
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AMD | age-related macular degeneration |
| CNV | choroid neovascularization |
| CRVO | central retinal vein occlusion |
| DR | diabetic retinopathy |
| iVR1 | inhibitor of VEGF receptor 1 |
| ROP | retinopathy of prematurity |
| RPE | retinal pigment epithelium |
| TFA | trifluoroacetate |
| TKi | tyrosine kinase inhibitors |
| VEGF | vascular endothelial growth factor |
| VEGFR1 | vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 1 |
| VEGFR2 | vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 |
References
- Wong, W.L.; Su, X.; Li, X.; Cheung, C.M.; Klein, R.; Cheng, C.Y.; Wong, T.Y. Global prevalence of age-related macular degeneration and disease burden projection for 2020 and 2040: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Glob. Health 2014, 2, e106–e116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gelfand, B.D.; Ambati, J. A Revised Hemodynamic Theory of Age-Related Macular Degeneration. Trends Mol. Med. 2016, 22, 656–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ferrara, N.; Mass, R.D.; Campa, C.; Kim, R. Targeting VEGF-A to treat cancer and age-related macular degeneration. Annu. Rev. Med. 2007, 58, 491–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarallo, V.; De Falco, S. The vascular endothelial growth factors and receptors family: Up to now the only target for anti-angiogenesis therapy. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2015, 64, 185–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Group, C.R.; Martin, D.F.; Maguire, M.G.; Ying, G.S.; Grunwald, J.E.; Fine, S.L.; Jaffe, G.J. Ranibizumab and bevacizumab for neovascular age-related macular degeneration. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 364, 1897–1908. [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt-Erfurth, U.; Kaiser, P.K.; Korobelnik, J.F.; Brown, D.M.; Chong, V.; Nguyen, Q.D.; Ho, A.C.; Ogura, Y.; Simader, C.; Jaffe, G.J.; et al. Intravitreal aflibercept injection for neovascular age-related macular degeneration: Ninety-six-week results of the VIEW studies. Ophthalmology 2014, 121, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lux, A.; Llacer, H.; Heussen, F.M.; Joussen, A.M. Non-responders to bevacizumab (Avastin) therapy of choroidal neovascular lesions. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2007, 91, 1318–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Krebs, I.; Glittenberg, C.; Ansari-Shahrezaei, S.; Hagen, S.; Steiner, I.; Binder, S. Non-responders to treatment with antagonists of vascular endothelial growth factor in age-related macular degeneration. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2013, 97, 1443–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treins, C.; Giorgetti-Peraldi, S.; Murdaca, J.; Van Obberghen, E. Regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor expression by advanced glycation end products. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 43836–43841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nishijima, K.; Ng, Y.S.; Zhong, L.; Bradley, J.; Schubert, W.; Jo, N.; Akita, J.; Samuelsson, S.J.; Robinson, G.S.; Adamis, A.P.; et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor-A is a survival factor for retinal neurons and a critical neuroprotectant during the adaptive response to ischemic injury. Am. J. Pathol. 2007, 171, 53–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kurihara, T.; Westenskow, P.D.; Bravo, S.; Aguilar, E.; Friedlander, M. Targeted deletion of Vegfa in adult mice induces vision loss. J. Clin. Investig. 2012, 122, 4213–4217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rofagha, S.; Bhisitkul, R.B.; Boyer, D.S.; Sadda, S.R.; Zhang, K.; SEVEN-UP Study Group. Seven-year outcomes in ranibizumab-treated patients in ANCHOR, MARINA, and HORIZON: A multicenter cohort study (SEVEN-UP). Ophthalmology 2013, 120, 2292–2299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grunwald, J.E.; Daniel, E.; Huang, J.; Ying, G.S.; Maguire, M.G.; Toth, C.A.; Jaffe, G.J.; Fine, S.L.; Blodi, B.; Klein, M.L.; et al. Risk of geographic atrophy in the comparison of age-related macular degeneration treatments trials. Ophthalmology 2014, 121, 150–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Falavarjani, K.G.; Nguyen, Q.D. Adverse events and complications associated with intravitreal injection of anti-VEGF agents: A review of literature. Eye 2013, 27, 787–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fischer, C.; Mazzone, M.; Jonckx, B.; Carmeliet, P. FLT1 and its ligands VEGFB and PlGF: Drug targets for anti-angiogenic therapy? Nat. Rev. Cancer 2008, 8, 942–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waltenberger, J.; Claesson-Welsh, L.; Siegbahn, A.; Shibuya, M.; Heldin, C.H. Different signal transduction properties of KDR and Flt1, two receptors for vascular endothelial growth factor. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 26988–26995. [Google Scholar]
- Koch, S.; Claesson-Welsh, L. Signal transduction by vascular endothelial growth factor receptors. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2012, 2, a006502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiratsuka, S.; Maru, Y.; Okada, A.; Seiki, M.; Noda, T.; Shibuya, M. Involvement of Flt-1 tyrosine kinase (vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-1) in pathological angiogenesis. Cancer Res. 2001, 61, 1207–1213. [Google Scholar]
- Carmeliet, P.; Moons, L.; Luttun, A.; Vincenti, V.; Compernolle, V.; De Mol, M.; Wu, Y.; Bono, F.; Devy, L.; Beck, H.; et al. Synergism between vascular endothelial growth factor and placental growth factor contributes to angiogenesis and plasma extravasation in pathological conditions. Nat. Med. 2001, 7, 575–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apicella, I.; Cicatiello, V.; Acampora, D.; Tarallo, V.; De Falco, S. Full Functional Knockout of Placental Growth Factor by Knockin with an Inactive Variant Able to Heterodimerize with VEGF-A. Cell Rep. 2018, 23, 3635–3646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellomo, D.; Headrick, J.P.; Silins, G.U.; Paterson, C.A.; Thomas, P.S.; Gartside, M.; Mould, A.; Cahill, M.M.; Tonks, I.D.; Grimmond, S.M.; et al. Mice lacking the vascular endothelial growth factor-B gene (Vegfb) have smaller hearts, dysfunctional coronary vasculature, and impaired recovery from cardiac ischemia. Circ. Res. 2000, 86, e29–e35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wu, Y.; Zhong, Z.; Huber, J.; Bassi, R.; Finnerty, B.; Corcoran, E.; Li, H.; Navarro, E.; Balderes, P.; Jimenez, X.; et al. Anti-vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-1 antagonist antibody as a therapeutic agent for cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2006, 12, 6573–6584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fischer, C.; Jonckx, B.; Mazzone, M.; Zacchigna, S.; Loges, S.; Pattarini, L.; Chorianopoulos, E.; Liesenborghs, L.; Koch, M.; De Mol, M.; et al. Anti-PlGF inhibits growth of VEGF(R)-inhibitor-resistant tumors without affecting healthy vessels. Cell 2007, 131, 463–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bae, D.G.; Kim, T.D.; Li, G.; Yoon, W.H.; Chae, C.B. Anti-flt1 peptide, a vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 1-specific hexapeptide, inhibits tumor growth and metastasis. Clin. Cancer Res. 2005, 11, 2651–2661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Taylor, A.P.; Goldenberg, D.M. Role of placenta growth factor in malignancy and evidence that an antagonistic PlGF/Flt-1 peptide inhibits the growth and metastasis of human breast cancer xenografts. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2007, 6, 524–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Falco, S. Antiangiogenesis therapy: An update after the first decade. Korean J. Intern. Med. 2014, 29, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ponticelli, S.; Marasco, D.; Tarallo, V.; Albuquerque, R.J.; Mitola, S.; Takeda, A.; Stassen, J.M.; Presta, M.; Ambati, J.; Ruvo, M.; et al. Modulation of angiogenesis by a tetrameric tripeptide that antagonizes vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 1. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 34250–34259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cicatiello, V.; Apicella, I.; Tudisco, L.; Tarallo, V.; Formisano, L.; Sandomenico, A.; Kim, Y.; Bastos-Carvalho, A.; Orlandi, A.; Ambati, J.; et al. Powerful anti-tumor and anti-angiogenic activity of a new anti-vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 1 peptide in colorectal cancer models. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 10563–10576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Caporale, A.; Doti, N.; Monti, A.; Sandomenico, A.; Ruvo, M. Automatic procedures for the synthesis of difficult peptides using oxyma as activating reagent: A comparative study on the use of bases and on different deprotection and agitation conditions. Peptides 2018, 102, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valenti, L.E.; Paci, M.B.; De Pauli, C.P.; Giacomelli, C.E. Infrared study of trifluoroacetic acid unpurified synthetic peptides in aqueous solution: Trifluoroacetic acid removal and band assignment. Anal. Biochem. 2011, 410, 118–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barth, A. Infrared spectroscopy of proteins. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2007, 1767, 1073–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, S.; Chen, T.T.; Barber, C.L.; Jordan, M.C.; Murdock, J.; Desai, S.; Ferrara, N.; Nagy, A.; Roos, K.P.; Iruela-Arispe, M.L. Autocrine VEGF signaling is required for vascular homeostasis. Cell 2007, 130, 691–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dewerchin, M.; Carmeliet, P. PlGF: A multitasking cytokine with disease-restricted activity. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2012, 2, a011056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jakobsson, L.; Franco, C.A.; Bentley, K.; Collins, R.T.; Ponsioen, B.; Aspalter, I.M.; Rosewell, I.; Busse, M.; Thurston, G.; Medvinsky, A.; et al. Endothelial cells dynamically compete for the tip cell position during angiogenic sprouting. Nat. Cell Biol. 2010, 12, 943–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clauss, M.; Weich, H.; Breier, G.; Knies, U.; Rockl, W.; Waltenberger, J.; Risau, W. The vascular endothelial growth factor receptor Flt-1 mediates biological activities. Implications for a functional role of placenta growth factor in monocyte activation and chemotaxis. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 17629–17634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- McLaughlin, M.M.; Paglione, M.G.; Slakter, J.; Tolentino, M.; Ye, L.; Xu, C.F.; Suttle, A.B.; Kim, R.Y. Initial exploration of oral pazopanib in healthy participants and patients with age-related macular degeneration. JAMA Ophthalmol. 2013, 131, 1595–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meredith, E.L.; Mainolfi, N.; Poor, S.; Qiu, Y.; Miranda, K.; Powers, J.; Liu, D.; Ma, F.; Solovay, C.; Rao, C.; et al. Discovery of Oral VEGFR-2 Inhibitors with Prolonged Ocular Retention That Are Efficacious in Models of Wet Age-Related Macular Degeneration. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 58, 9273–9286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Zhang, T.; Yao, Y.; Zeng, S.; Li, M.; Xiang, H.; Zhao, C.; Cao, G.; Li, M.; Wan, R.; et al. Efficacy of Lenvatinib, a multitargeted tyrosine kinase inhibitor, on laser-induced CNV mouse model of neovascular AMD. Exp. Eye Res. 2018, 168, 2–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tarallo, V.; Iaccarino, E.; Cicatiello, V.; Sanna, R.; Ruvo, M.; De Falco, S. Oral Delivery of a Tetrameric Tripeptide Inhibitor of VEGFR1 Suppresses Pathological Choroid Neovascularization. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 410. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21020410
Tarallo V, Iaccarino E, Cicatiello V, Sanna R, Ruvo M, De Falco S. Oral Delivery of a Tetrameric Tripeptide Inhibitor of VEGFR1 Suppresses Pathological Choroid Neovascularization. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(2):410. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21020410
Chicago/Turabian StyleTarallo, Valeria, Emanuela Iaccarino, Valeria Cicatiello, Riccardo Sanna, Menotti Ruvo, and Sandro De Falco. 2020. "Oral Delivery of a Tetrameric Tripeptide Inhibitor of VEGFR1 Suppresses Pathological Choroid Neovascularization" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 2: 410. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21020410
APA StyleTarallo, V., Iaccarino, E., Cicatiello, V., Sanna, R., Ruvo, M., & De Falco, S. (2020). Oral Delivery of a Tetrameric Tripeptide Inhibitor of VEGFR1 Suppresses Pathological Choroid Neovascularization. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(2), 410. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21020410