MiR&moRe2: A Bioinformatics Tool to Characterize microRNAs and microRNA-Offset RNAs from Small RNA-Seq Data
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
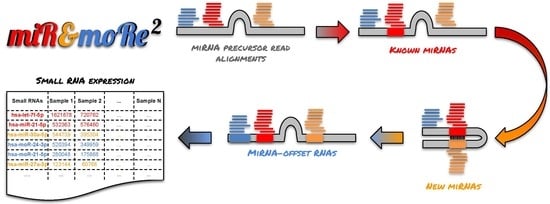
2.1. The MiR&moRe2 Software Pipeline
2.2. MiR&moRe2 Recovers Known MoRNAs
2.3. MoRNA Expression Is Impaired upon Knock-Down of the miRNA Biogenesis Pathway
2.4. MoRNAs Expression in Seven Human Blood Cell Populations
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. MiR&moRe2 Implementation Details
4.2. Dataset Features and Accession Numbers
4.3. MiR&moRe2 Parameters and Expression Analysis
4.4. Additional Software and Packages
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| miRNA | microRNA |
| moRNA | miRNA-offset RNA |
| sRNA | small RNA |
| RNA-seq | RNA sequencing |
| sRNA-seq | small RNA sequencing |
| SRA | Sequence Read Archive |
| CPM | Count Per Million mapped reads |
| LFC | Log2 Fold Change |
References
- Bartel, D.P. MicroRNAs: Genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 2004, 116, 281–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bortolomeazzi, M.; Gaffo, E.; Bortoluzzi, S. A survey of software tools for microRNA discovery and characterization using RNA-seq. Brief. Bioinform. 2019, 20, 918–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.; Hendrix, D.; Levine, M.; Haley, B. A distinct class of small RNAs arises from pre-miRNA–proximal regions in a simple chordate. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2009, 16, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bofill-De Ros, X.; Yang, A.; Gu, S. IsomiRs: Expanding the miRNA repression toolbox beyond the seed. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gene Regul. Mech. 2019, 194373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Umbach, J.L.; Strelow, L.I.; Wong, S.W.; Cullen, B.R. Analysis of rhesus rhadinovirus microRNAs expressed in virus-induced tumors from infected rhesus macaques. Virology 2010, 405, 592–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Berezikov, E.; Robine, N.; Samsonova, A.; Westholm, J.O.; Naqvi, A.; Hung, J.-H.; Okamura, K.; Dai, Q.; Bortolamiol-Becet, D.; Martin, R.; et al. Deep annotation of Drosophila melanogaster microRNAs yields insights into their processing, modification, and emergence. Genome Res. 2011, 21, 203–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhou, H.; Arcila, M.L.; Li, Z.; Lee, E.J.; Henzler, C.; Liu, J.; Rana, T.M.; Kosik, K.S. Deep annotation of mouse iso-miR and iso-moR variation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, 5864–5875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gaffo, E.; Zambonelli, P.; Bisognin, A.; Bortoluzzi, S.; Davoli, R. miRNome of Italian Large White pig subcutaneous fat tissue: New miRNAs, isomiRs and moRNAs. Anim. Genet. 2014, 45, 685–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donohoe, O.H.; Henshilwood, K.; Way, K.; Hakimjavadi, R.; Stone, D.M.; Walls, D. Identification and Characterization of Cyprinid Herpesvirus-3 (CyHV-3) Encoded MicroRNAs. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0125434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coucheron, D.H.; Wojewodzic, M.W.; Bøhn, T. MicroRNAs in Daphnia magna identified and characterized by deep sequencing, genome mapping and manual curation. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 15945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taft, R.J.; Simons, C.; Nahkuri, S.; Oey, H.; Korbie, D.J.; Mercer, T.R.; Holst, J.; Ritchie, W.; Wong, J.J.-L.; Rasko, J.E.J.; et al. Nuclear-localized tiny RNAs are associated with transcription initiation and splice sites in metazoans. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2010, 17, 1030–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meiri, E.; Levy, A.; Benjamin, H.; Ben-David, M.; Cohen, L.; Dov, A.; Dromi, N.; Elyakim, E.; Yerushalmi, N.; Zion, O.; et al. Discovery of microRNAs and other small RNAs in solid tumors. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 38, 6234–6246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bortoluzzi, S.; Bisognin, A.; Biasiolo, M.; Guglielmelli, P.; Biamonte, F.; Norfo, R.; Manfredini, R.; Vannucchi, A.M.; AGIMM (Associazione Italiana per la Ricerca sul Cancro–Gruppo Italiano Malattie Mieloproliferative) Investigators. Characterization and discovery of novel miRNAs and moRNAs in JAK2V617F-mutated SET2 cells. Blood 2012, 119, e120–e130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Asikainen, S.; Heikkinen, L.; Juhila, J.; Holm, F.; Weltner, J.; Trokovic, R.; Mikkola, M.; Toivonen, S.; Balboa, D.; Lampela, R.; et al. Selective microRNA-Offset RNA expression in human embryonic stem cells. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0116668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guglielmelli, P.; Bisognin, A.; Saccoman, C.; Mannarelli, C.; Coppe, A.; Vannucchi, A.M.; Bortoluzzi, S. Small RNA Sequencing Uncovers New miRNAs and moRNAs Differentially Expressed in Normal and Primary Myelofibrosis CD34+ Cells. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0140445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irimie, A.I.; Zimta, A.-A.; Ciocan, C.; Mehterov, N.; Dudea, D.; Braicu, C.; Berindan-Neagoe, I. The Unforeseen Non-Coding RNAs in Head and Neck Cancer. Genes 2018, 9, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Agnelli, L.; Bisognin, A.; Todoerti, K.; Manzoni, M.; Taiana, E.; Galletti, S.; Cutrona, G.; Gaffo, E.; Bortoluzzi, S.; Neri, A. Expanding the repertoire of miRNAs and miRNA-offset RNAs expressed in multiple myeloma by small RNA deep sequencing. Blood Cancer J. 2019, 9, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Langenberger, D.; Bermudez-Santana, C.; Hertel, J.; Hoffmann, S.; Khaitovich, P.; Stadler, P.F. Evidence for human microRNA-offset RNAs in small RNA sequencing data. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 2298–2301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Davoli, R.; Gaffo, E.; Zappaterra, M.; Bortoluzzi, S.; Zambonelli, P. Identification of differentially expressed small RNAs and prediction of target genes in Italian Large White pigs with divergent backfat deposition. Anim. Genet. 2018, 49, 205–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burroughs, A.M.; Kawano, M.; Ando, Y.; Daub, C.O.; Hayashizaki, Y. pre-miRNA profiles obtained through application of locked nucleic acids and deep sequencing reveals complex 5′/3’ arm variation including concomitant cleavage and polyuridylation patterns. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, 1424–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Schnitzler, G.R.; Iyer, L.K.; Aronovitz, M.J.; Baur, W.E.; Karas, R.H. MicroRNA-Offset RNA Alters Gene Expression and Cell Proliferation. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0156772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozomara, A.; Birgaoanu, M.; Griffiths-Jones, S. miRBase: From microRNA sequences to function. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D155–D162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haeussler, M.; Zweig, A.S.; Tyner, C.; Speir, M.L.; Rosenbloom, K.R.; Raney, B.J.; Lee, C.M.; Lee, B.T.; Hinrichs, A.S.; Gonzalez, J.N.; et al. The UCSC Genome Browser database: 2019 update. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D853–D858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cunningham, F.; Achuthan, P.; Akanni, W.; Allen, J.; Amode, M.R.; Armean, I.M.; Bennett, R.; Bhai, J.; Billis, K.; Boddu, S.; et al. Ensembl 2019. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D745–D751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Friedländer, M.R.; Mackowiak, S.D.; Li, N.; Chen, W.; Rajewsky, N. miRDeep2 accurately identifies known and hundreds of novel microRNA genes in seven animal clades. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, 37–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuperus, J.T.; Fahlgren, N.; Carrington, J.C. Evolution and Functional Diversification of MIRNA Genes. Plant. Cell 2011, 23, 431–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Burroughs, A.M.; Ando, Y.; de Hoon, M.J.L.; Tomaru, Y.; Nishibu, T.; Ukekawa, R.; Funakoshi, T.; Kurokawa, T.; Suzuki, H.; Hayashizaki, Y.; et al. A comprehensive survey of 3′ animal miRNA modification events and a possible role for 3’ adenylation in modulating miRNA targeting effectiveness. Genome Res. 2010, 20, 1398–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Landgraf, P.; Rusu, M.; Sheridan, R.; Sewer, A.; Iovino, N.; Aravin, A.; Pfeffer, S.; Rice, A.; Kamphorst, A.O.; Landthaler, M.; et al. A mammalian microRNA expression atlas based on small RNA library sequencing. Cell 2007, 129, 1401–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mahlab-Aviv, S.; Boulos, A.; Peretz, A.R.; Eliyahu, T.; Carmel, L.; Sperling, R.; Linial, M. Small RNA sequences derived from pre-microRNAs in the supraspliceosome. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, 11014–11029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedländer, M.R.; Lizano, E.; Houben, A.J.S.; Bezdan, D.; Báñez-Coronel, M.; Kudla, G.; Mateu-Huertas, E.; Kagerbauer, B.; González, J.; Chen, K.C.; et al. Evidence for the biogenesis of more than 1,000 novel human microRNAs. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, R57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Juzenas, S.; Venkatesh, G.; Hübenthal, M.; Hoeppner, M.P.; Du, Z.G.; Paulsen, M.; Rosenstiel, P.; Senger, P.; Hofmann-Apitius, M.; Keller, A.; et al. A comprehensive, cell specific microRNA catalogue of human peripheral blood. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, 9290–9301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lappalainen, T.; Sammeth, M.; Friedländer, M.R.; ’t Hoen, P.A.C.; Monlong, J.; Rivas, M.A.; Gonzàlez-Porta, M.; Kurbatova, N.; Griebel, T.; Ferreira, P.G.; et al. Transcriptome and genome sequencing uncovers functional variation in humans. Nature 2013, 501, 506–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.-Q.; Chen, D.-J.; He, H.-B.; Chen, D.-S.; Chen, L.-L.; Chen, H.-C.; Liu, Z.-F. Pseudorabies Virus Infected Porcine Epithelial Cell Line Generates a Diverse Set of Host MicroRNAs and a Special Cluster of Viral MicroRNAs. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e30988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Timoneda, O.; Núñez-Hernández, F.; Balcells, I.; Muñoz, M.; Castelló, A.; Vera, G.; Pérez, L.J.; Egea, R.; Mir, G.; Córdoba, S.; et al. The Role of Viral and Host MicroRNAs in the Aujeszky’s Disease Virus during the Infection Process. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e86965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stark, R.; Grzelak, M.; Hadfield, J. RNA sequencing: The teenage years. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2019, 20, 631–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaffo, E.; Bonizzato, A.; Kronnie, G.T.; Bortoluzzi, S. CirComPara: A Multi-Method Comparative Bioinformatics Pipeline to Detect and Study circRNAs from RNA-seq Data. Noncoding RNA 2017, 3, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Memczak, S.; Jens, M.; Elefsinioti, A.; Torti, F.; Krueger, J.; Rybak, A.; Maier, L.; Mackowiak, S.D.; Gregersen, L.H.; Munschauer, M.; et al. Circular RNAs are a large class of animal RNAs with regulatory potency. Nature 2013, 495, 333–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salzman, J.; Gawad, C.; Wang, P.L.; Lacayo, N.; Brown, P.O. Circular RNAs are the predominant transcript isoform from hundreds of human genes in diverse cell types. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e30733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hendrix, D.; Levine, M.; Shi, W. miRTRAP, a computational method for the systematic identification of miRNAs from high throughput sequencing data. Genome Biol. 2010, 11, R39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martin, M. Cutadapt removes adapter sequences from high-throughput sequencing reads. EMBnet. J. 2011, 17, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziemann, M.; Kaspi, A.; El-Osta, A. Evaluation of microRNA alignment techniques. RNA 2016, 22, 1120–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lorenz, R.; Bernhart, S.H.; Höner Zu Siederdissen, C.; Tafer, H.; Flamm, C.; Stadler, P.F.; Hofacker, I.L. ViennaRNA Package 2.0. Algorithms Mol. Biol. 2011, 6, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desvignes, T.; Batzel, P.; Berezikov, E.; Eilbeck, K.; Eppig, J.T.; McAndrews, M.S.; Singer, A.; Postlethwait, J.H. miRNA Nomenclature: A View Incorporating Genetic Origins, Biosynthetic Pathways, and Sequence Variants. Trends Genet. 2015, 31, 613–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Langmead, B.; Trapnell, C.; Pop, M.; Salzberg, S.L. Ultrafast and memory-efficient alignment of short DNA sequences to the human genome. Genome Biol. 2009, 10, R25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Quinlan, A.R. BEDTools: The Swiss-Army Tool for Genome Feature Analysis. Curr. Protoc. Bioinform. 2014, 47, 11–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Handsaker, B.; Wysoker, A.; Fennell, T.; Ruan, J.; Homer, N.; Marth, G.; Abecasis, G.; Durbin, R.; 1000 Genome Project Data Processing Subgroup. The Sequence Alignment/Map format and SAMtools. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 2078–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Anders, S.; Pyl, P.T.; Huber, W. HTSeq—A Python framework to work with high-throughput sequencing data. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 166–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leinonen, R.; Sugawara, H.; Shumway, M.; International Nucleotide Sequence Database Collaboration. The sequence read archive. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, D19–D21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Robinson, M.D.; McCarthy, D.J.; Smyth, G.K. edgeR: A Bioconductor package for differential expression analysis of digital gene expression data. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 139–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Love, M.I.; Huber, W.; Anders, S. Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ritchie, M.E.; Phipson, B.; Wu, D.; Hu, Y.; Law, C.W.; Shi, W.; Smyth, G.K. limma powers differential expression analyses for RNA-sequencing and microarray studies. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, e47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickham, H. ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin, Germany, 2009; ISBN 9780387981413. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.; Boutros, P.C. VennDiagram: A package for the generation of highly-customizable Venn and Euler diagrams in R. BMC Bioinform. 2011, 12, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]




| Acronym | Cell of Origin | Reference | SRA IDs |
|---|---|---|---|
| ASI | hESC, fibroblasts | Asikainen et al. 2015 | SRR1616134-36 |
| SRR026761-62 | |||
| BUR | HeLa | Burroughs et al. 2012 | DRR001488-89 |
| MAV | HeLa | Mahlab-Aviv et al. 2018 | SRR6155355-58 |
| SRR5804909-14 | |||
| FRI | SH-SY5Y | Friedländer et al. 2014 | SRR952248-49 |
| SRR952288-89 | |||
| SRR952290 | |||
| SRR952309-11 | |||
| JUZ | Monocytes, neutrophils, red blood cells, helper T-cells, cytotoxic T-cells, B-cells, natural killers | Juzenas et al. 2017 | SRR5755813-6109 |
| LAP | Lymphoblastoid cell line cells | Lappalainen et al. 2013 | ERR187515 |
| ERR187573 | |||
| ERR187587 | |||
| ERR187595 | |||
| ERR187647 | |||
| ERR187758 | |||
| ERR187761 | |||
| ERR187786 | |||
| ERR187791 | |||
| ERR187813 | |||
| ERR187918 | |||
| ERR187922 | |||
| ERR204769 |
| Small RNA | B-Cell | Natural Killer | Cytotoxic T-Cell | Helper T-Cell | Monocyte | Neutrophil |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| miR-2110-3p | 11.0 | 29.5 | 17.8 | 13.3 | 17.6 | 22.8 |
| moR-150-3p | 16.2 | 12.6 | 17.6 | 20.2 | 1.2 | 1.2 |
| moR-421-5p | 4.1 | 10.7 | 6.8 | 12.8 | 7.9 | 1.4 |
| miR-4424-3p | 33.5 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.2 |
| moR-103a-2-3p | 4.5 | 7.5 | 5.7 | 5.5 | 7.0 | 1.2 |
| moR-103a-2-5p | 1.4 | 2.7 | 4.6 | 4.4 | 7.7 | 1.5 |
| moR-150-5p | 10.5 | 3.6 | 1.9 | 3.0 | 1.2 | 1.2 |
| moR-16-1-5p | 6.6 | 1.9 | 1.5 | 2.5 | 4.6 | 1.3 |
| moR-24-2-5p | 3.9 | 5.3 | 1.6 | 2.8 | 3.5 | 1.2 |
| moR-7-1-5p | 1.7 | 2.7 | 4.1 | 4.8 | 2.0 | 1.2 |
| miR-5696-3p | 1.3 | 2.7 | 2.6 | 5.4 | 1.2 | 1.2 |
| moR-21-5p | 1.2 | 1.6 | 1.4 | 2.0 | 1.3 | 2.8 |
| miR-3648-1/2-3p | 2.8 | 1.4 | 1.6 | 1.9 | 1.2 | 1.2 |
| moR-876-5p | 1.2 | 3.5 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.2 |
| moR-27a-5p | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.3 | 3.0 | 1.2 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gaffo, E.; Bortolomeazzi, M.; Bisognin, A.; Di Battista, P.; Lovisa, F.; Mussolin, L.; Bortoluzzi, S. MiR&moRe2: A Bioinformatics Tool to Characterize microRNAs and microRNA-Offset RNAs from Small RNA-Seq Data. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1754. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21051754
Gaffo E, Bortolomeazzi M, Bisognin A, Di Battista P, Lovisa F, Mussolin L, Bortoluzzi S. MiR&moRe2: A Bioinformatics Tool to Characterize microRNAs and microRNA-Offset RNAs from Small RNA-Seq Data. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(5):1754. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21051754
Chicago/Turabian StyleGaffo, Enrico, Michele Bortolomeazzi, Andrea Bisognin, Piero Di Battista, Federica Lovisa, Lara Mussolin, and Stefania Bortoluzzi. 2020. "MiR&moRe2: A Bioinformatics Tool to Characterize microRNAs and microRNA-Offset RNAs from Small RNA-Seq Data" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 5: 1754. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21051754
APA StyleGaffo, E., Bortolomeazzi, M., Bisognin, A., Di Battista, P., Lovisa, F., Mussolin, L., & Bortoluzzi, S. (2020). MiR&moRe2: A Bioinformatics Tool to Characterize microRNAs and microRNA-Offset RNAs from Small RNA-Seq Data. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(5), 1754. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21051754