The Influence of Human Interference on Zooplankton and Fungal Diversity in Poyang Lake Watershed in China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- To analyze the assemblage of zooplankton and fungi to determine whether human activities have led to significant eco-environmental variance between six sub-lakes.
- To study whether the change of microbial assemblage will threaten human health and economic production.
2. Materials and Methods
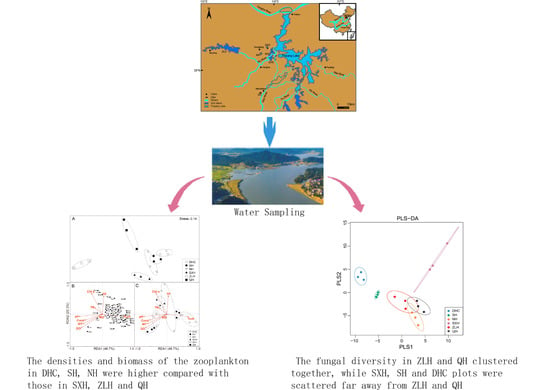
2.1. Study Site Description and Water Sampling
2.2. Densityand Biomass of Zooplankton
2.3. Physiochemical Analysis of Water
2.4. Extraction, Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) Amplification and High-Throughput Sequencing of Aquatic Fungal Genome
2.5. Bioinformatics and Statistics Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Zooplankton and Environment Data from Different Lakes
3.2. The Diversity and Composition of Aquatic Fungi in Six Lakes
3.3. Taxa Abundance and KEGG Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Zooplankton Species | Sub-Lakes | Abbreviate | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DHC | SH | NH | SXH | ZLH | QH | ||
| Rotifera | |||||||
| Lepadella patella | + | Lpa | |||||
| Lepadella ovalis | + | Lov | |||||
| Trichotria tetractis | + | Tte | |||||
| Brachionus calyciflorus | + | + | + | + | + | Bca | |
| Brachionus forficula | + | + | + | Bfo | |||
| Brachionus budapestiensis | + | + | Bbu | ||||
| Brachionus falcatus | + | + | Bfa | ||||
| Brachionus quadridentatus | + | + | + | + | Bca | ||
| Brachionus diversicornis | + | + | + | + | + | Bdi | |
| Platyias militaris | + | Pmi | |||||
| Keratella ticinensis | + | Kti | |||||
| Keratella cochlearis | + | + | + | Kco | |||
| Keratella valga | + | + | Kva | ||||
| Notholca labis | + | Nla | |||||
| Lecane ungulate | + | + | Lun | ||||
| Lecane luna | + | Llu | |||||
| Lecane niothis | + | Lni | |||||
| Monostyla lunaris | + | Mlu | |||||
| Monostyla bulla | + | Mbu | |||||
| Monostyla crenaa | + | Mcr | |||||
| Asplanchna priodonta | + | + | + | + | Apr | ||
| Asplanchna brightwelli | + | Abr | |||||
| Eothinia elongata | + | Eel | |||||
| Cephalodella gibba | + | Cgi | |||||
| Scaridium longicaudum | + | Slo | |||||
| Trichocerca cylindrica | + | + | + | Tcy | |||
| Trichocerca capucina | + | + | + | Tca | |||
| Trichocerca longiseta | + | + | Tlon | ||||
| Trichocerca lophoessa | + | Tlop | |||||
| Trichocerca rousseleti | + | Tro | |||||
| Trichocerca elongata | + | + | + | Tel | |||
| Polyarthra trigla | + | Ptr | |||||
| Polyarthra vulgaris | + | Pvu | |||||
| Filinia longiseta | + | Flo | |||||
| Cladocera | |||||||
| Leptodora Kindti | + | Lki | |||||
| Sida crystallina | + | + | + | + | + | Scr | |
| Diaphanosoma leuchtenbergianum | + | + | + | Dle | |||
| Diaphanosoma brachyurum | + | + | Dbr | ||||
| Diaphanosoma sarsi | + | Dsa | |||||
| Diaphanosoma aspinosum | + | + | + | + | Das | ||
| Bosmina longirostris | + | + | Blo | ||||
| Bosminopsis deitersi | + | + | Bde | ||||
| Daphnia cucullata | + | Dcu | |||||
| Ceriodaphnia quadrangula | + | + | Cqu | ||||
| Alona guttata | + | Agu | |||||
| Pleuroxus laevis | + | Pla | |||||
| Copepoda | |||||||
| Copepod nauplii | + | + | + | + | + | + | Cna |
| Sinocalanus dorrii | + | + | + | Sdo | |||
| Neutrodiaptomus incongruens | + | Nin | |||||
| Tropocyclops prasi | + | Tpr | |||||
| Microcyclops varicans | + | + | + | + | Mva | ||
| Mesocyclops leuckarti | + | + | + | + | Mle | ||
| Neodiaptomus schmackeri | + | Nsc | |||||
References
- Dawen, Z.; Qiegen, L.; Li, Z.; Donggen, W.; Linguang, L.; Yuwei, C.; Jiayou, Z.; Jutao, L. Occurrence and spatial distributions of microcystins in Poyang Lake, the largest freshwater lake in China. Ecotoxicology 2015, 24, 19–28. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Fu, Y.; Kang, S.; Li, Y.; Chen, W. Development of Ecological Fishery in Poyang Lake Area. Asian Agric. Res. 2013, 5, 39–44. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, J.B. Analysis of “three fishery” problems in Poyang Lake area. Acta Agric. Jiangxi 2012, 24, 201–203. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, L. Evaluation on functions of Poyang Lake ecosystem. Chin. J. Ecol. 2004, 23, 47–51. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, L.; Wang, W.; Yang, Y.; Yang, C.; Yuan, Z.; Xiong, S.; Diana, J. Environmental impact of aquaculture and countermeasures to aquaculture pollution in China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2007, 14, 452–462. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Zhou, W.; Hu, C. Status of nitrogen and phosphorus in waters of Lake Poyang Basin. Lake Sci. 2008, 20, 334–338. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, T.; Chen, M. Wetland Ecological Function Deterioration in Poyang Lake and Countermeasures. Chin. J. Ecol. 2001, 20, 74–77. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Jiang, Y.; Ding, M.; Xie, Z. Level, source identification, and risk analysis of heavy metal in surface sediments from river-lake ecosystems in the Poyang Lake, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2017, 24, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.T.; Kim, J.G. Uptake of Cadmium, Copper, Lead, and Zinc from Sediments by an Aquatic Macrophyte and by Terrestrial Arthropods in a Freshwater Wetland Ecosystem. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2016, 71, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Paerl, H.W.; Qin, B.; Zhu, G.; Hall, N.S.; Wu, Y. Determining critical nutrient thresholds needed to control harmful cyanobacterial blooms in eutrophic Lake Taihu, China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 1051–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Du, Y.; Yang, H. Analysis of Wetland Ecosystem Response of Poyang Lake with Water Level Evolution Base on TM Images. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2013, 295–298, 1935–1940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burns, C.W.; Galbraith, L.M. Relating planktonic microbial food web structure in lentic freshwater ecosystems to water quality and land use. J. Plankton Res. 2007, 29, 127–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suda, H. Water quality and compositions of the phytoplankton and zooplankton before and after building construction in lake fukami-ike, Japan. Int. J. Geomate 2016, 10, 1983–1988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elser, J.J.; Foster, D.K.; Hecky, R.E. Effects of zooplankton on sedimentation in pelagic ecosystems: Theory and test in two lakes of the Canadian shield. Biogeochemistry 1995, 30, 143–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutkowska, A.; Paturej, E.; Bowszys, M. Nutrients excretion by zooplankton in two brackish water bodies. Int. Rev. Hydrobiol. 2018, 103, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, W.; Ni, P.; Chen, Y.; Gao, Y.; Shan, B.; Zhan, A. Zooplankton community structure along a pollution gradient at fine geographical scales in river ecosystems: The importance of species sorting over dispersal. Mol. Ecol. 2017, 26, 4351–4360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, J.J.; Lenes, J.M.; Darrow, B.; Parks, A.; Weisberg, R.H. Impacts of combined overfishing and oil spills on the plankton trophodynamics of the West Florida shelf over the last half century of 1965–2011: A two-dimensional simulation analysis of biotic state transitions, from a zooplankton- to a bacterioplankton. Cont. Shelf Res. 2016, 116, 54–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egeren, S.J.V.; Dodson, S.I.; Torke, B.; Maxted, J.T. The relative significance of environmental and anthropogenic factors affecting zooplankton community structure in Southeast Wisconsin Till Plain lakes. Hydrobiologia 2011, 668, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalifa, N.; El, K.; Cairo, A.; Khaled, E.; El-Damhogy, A.; Fishar, M.R.; Nasef, A.; Hegab, M.; El-Damhogy, K. Using zooplankton in some environmental biotic indices to assess water quality of Lake Nasser, Egypt. Int. J. Fish. Aquat. Stud. 2015, 2, 281–289. [Google Scholar]
- Ejsmont-Karabin, J.; Górniak, A.; Jekatierynczuk-Rudczyk, E.; Karpowicz, M.; Więcko, A. Long-term changes in the trophic state of Suwalki lakes—An analysis by means of indices based on abundance and composition of their rotifer fauna. Limnol. Rev. 2017, 16, 199–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hawksworth, D.L. The magnitude of fungal diversity: The 1.5 million species estimate revisited. Mycol. Res. 2001, 105, 1422–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Niquil, N.; Kagami, M.; Urabe, J.; Christaki, U.; Viscogliosi, E.; Simengando, T. Potential role of fungi in plankton food web functioning and stability: A simulation analysis based on Lake Biwa inverse model. Hydrobiologia 2011, 659, 65–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kagami, M.; Miki, T.; Takimoto, G. Mycoloop: Chytrids in aquatic food webs. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kissi, M.; Mountadar, M.; Assobhei, O.; Gargiulo, E.; Palmieri, G.; Giardina, P.; Sannia, G. Roles of two white-rot basidiomycete fungi in decolorisation and detoxification of olive mill waste water. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2001, 57, 221–226. [Google Scholar]
- Magwaza, N.M.; Nxumalo, E.N.; Mamba, B.B.; Msagati, T.A.M. The Occurrence and Diversity of Waterborne Fungi in African Aquatic Systems: Their Impact on Water Quality and Human Health. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nakamura, A.; Matsuno, K.; Abe, Y.; Shimada, H.; Yamaguchi, A.J.Z.S. Length-weight Relationships and Chemical Composition of the Dominant Mesozooplankton Taxa/species in the Subarctic Pacific, with Special Reference to the Effect of Lipid Accumulation in Copepoda. Zool. Stud. 2017, 56, 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, F.; Shu, T.; Jeppesen, E.; Liu, Z.; Chen, Y. Restoration of a subtropical eutrophic shallow lake in China: Effects on nutrient concentrations and biological communities. Hydrobiologia 2013, 718, 59–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trevisan, G.V.; Forsberg, B.R. Relationships among nitrogen and total phosphorus, algal biomass and zooplankton density in the central Amazonia lakes. Hydrobiologia 2007, 586, 357–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgar, R.C. Search and clustering orders of magnitude faster than BLAST. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 2460–2461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lindahl, B.D.; Nilsson, R.H.; Tedersoo, L.; Abarenkov, K.; Carlsen, T.; Kjøller, R.; Kõljalg, U.; Pennanen, T.; Rosendahl, S.; Stenlid, J.; et al. Fungal community analysis by high-throughput sequencing of amplified markers—A user’s guide. New Phytol. 2013, 199, 288–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Quast, C.; Pruesse, E.; Yilmaz, P.; Gerken, J.; Schweer, T.; Yarza, P.; Peplies, J.; Glockner, F.O. The SILVA ribosomal RNA gene database project: Improved data processing and web-based tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, D590–D596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, L.; Zhang, Z.; Zeng, X.; Ma, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Zhou, C. Community Structure of Zooplankton and Water Quality Assessment of Jialing River in Nan Chong. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2011, 10, 1321–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Legendre, P.; Legendre, L. Numerical Ecology; Elsevier Science BV: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Laender, F.; Taub, F.B.; Janssen, C.R. Ecosystem functions and densities of contributing functional groups respond in a different way to chemical stress. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2011, 30, 2892–2898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weyhenmeyer, G.A.; Peter, H.; Willén, E. Shifts in phytoplankton species richness and biomass along a latitudinal gradient—Consequences for relationships between biodiversity and ecosystem functioning. Freshw. Biol. 2013, 58, 612–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krzyk, M.; Drev, D.; Kolbl, S.; Panjan, J. Self-purification processes of Lake Cerknica as a combination of wetland and SBR reactor. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanyal, P.; Bhattacharya, N.; Chakraborty, S.K. Biomonitoring of Four Contrasting Wetlands of Kolkata, West Bengal Based on Zooplankton Ecodynamics and Biotic Indices. J. Environ. Prot. 2015, 6, 683–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Olubode, O.S.; Awodoyin, R.O.; Ogunyemi, S. Floral diversity in the wetlands of Apete River, Eleyele Lake and Oba Dam in Ibadan, Nigeria: Its implication for biodiversity erosion. West Afr. J. Appl. Ecol. 2011, 18, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jacob, A.P.; Culver, D.A.; Lanno, R.P.; Voigt, A. Ecological impacts of fluridone and copper sulphate in catfish aquaculture ponds. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2016, 35, 1183–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.L.; Liao, B. The Major Eco-environmental Problems and its Protection Countermeasures in Zhelin Lake. Jiangxi Sci. 2013, 31, 48–128. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Y.; Wang, Y. Analysis of the lakes plankton miniaturization. J. Aquac. 2012, 33, 4–7. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, L.; Yao, S.; Xue, B.; Li, L.; Liu, J. Long-term change of the assemblages and abundance of cladocerans in different ecotypes of Lake Taihu. J. Lake Sci. 2019, 31, 1670–1684. [Google Scholar]
- Cottenie, K.; Meester, L.D. Connectivity and cladoceran species richness in a metacommunity of shallow lakes. Freshw. Biol. 2003, 48, 823–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aykol, A.; Budakoglu, M.; Kumral, M.; Gultekin, A.H.; Turhan, M.; Esenli, V.; Yavuz, F.; Orgun, Y. Heavy metal pollution and acid drainage from the abandoned Balya Pb-Zn sulfide Mine, NW Anatolia, Turkey. Environ. Geol. 2003, 45, 198–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Dalton, C.; Taylor, D. Cladocera as indicators of trophic state in Irish lakes. J. Paleolimnol. 2010, 44, 465–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shearer, C.A.; Descals, E.; Kohlmeyer, B.; Kohlmeyer, J.; Marvanová, L.; Padgett, D.; Porter, D.; Raja, H.A.; Schmit, J.P.; Thorton, H.A. Fungal biodiversity in aquatic habitats. Biodivers. Conserv. 2007, 16, 49–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hibbett, D.S.; Thorn, R.G. Basidiomycota: Homobasidiomycetes. In Systematics and Evolution; McLaughlin, D.J., McLaughlin, E.G., Lemke, P.A., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2001; pp. 121–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grogan, L.F.; Mulvenna, J.; Gummer, J.P.A.; Scheele, B.C.; Berger, L.; Cashins, S.D.; McFadden, M.S.; Harlow, P.; Hunter, D.A.; Trengove, R.D.; et al. Survival, gene and metabolite responses of Litoria verreauxii alpina frogs to fungal disease chytridiomycosis. Sci. Data 2018, 5, 180033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goh, T.K.; Hyde, K.D. Biodiversity of freshwater fungi. J. Ind. Microbiol. 1996, 17, 328–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yangco, B.G.; Nettlow, A.; Okafor, J.I.; Park, J.; Te Strake, D. Comparative antigenic studies of species of Basidiobolus and other medically important fungi. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1986, 23, 679–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pietryczuk, A.; Cudowski, A.; Hauschild, T.; Świsłocka, M.; Więcko, A.; Karpowicz, M. Abundance and Species Diversity of Fungi in Rivers with Various Contaminations. Curr. Microbiol. 2017, 75, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]






| Studied Sub-Lakes | Code | Max Water Depth (m) | Trophic Status | Water Renewal Time | Lake Area (km2) | Human Interference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dahuchi Lake | DHC | 8.5 | Mesotrophication | June, July | 30 | Nature reserve |
| Shahu Lake | SH | 8 | Mesotrophication | June, July | 14 | Nature reserve |
| Nanhu Lake | NH | 6 | Mesotrophication | June, July | 7 | Natural fishing |
| Sixiahu Lake | SXH | 5 | Eutrophication | July | 8 | Aquaculture |
| Zhelinhu Reservoir | ZLH | 55 | Oligotrophication | July | 308 | Eco-tourism, hydroelectric power and irrigation |
| Qianhu Lake | QH | 3.5 | Eutrophication | Whole year | 1.5 | Urban sewage discharge |
| Sub-Lakes | Density (ind./L) | Rotifera (ind./L) | Cladocera (ind./L) | Copepoda (ind./L) | Biomass (mg/L) | Rotifera (mg/L) | Cladocera (mg/L) | Copepoda (mg/L) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DHC | 394.44 ± 98.73 | 76.13 ± 44.01 | 98.89 ± 16.71 | 219.42 ± 46.78 | 0.761 ± 0.261 | 0.149 ± 0.088 | 0.265 ± 0.054 | 0.346 ± 0.120 |
| SH | 241.82 ± 47.03 | 74.71 ± 27.52 | 25.64 ± 6.27 | 141.47 ± 25.18 | 0.500 ± 0.085 | 0.111 ± 0.026 | 0.042 ± 0.012 | 0.347 ± 0.072 |
| NH | 314.67 ± 57.25 | 126.92 ± 56.39 | 47.47 ± 38.27 | 140.27 ± 75.49 | 0.540 ± 0.060 | 0.222 ± 0.088 | 0.010 ± 0.010 | 0.308 ± 0.138 |
| SXH | 60.00 ± 1.39 | 52.80 ± 2.81 | 2.13 ± 2.13 | 5.07 ± 2.37 | 0.078 ± 0.016 | 0.066 ± 0.015 | 0.002 ± 0.002 | 0.010 ± 0.006 |
| ZLH | 5.03 ± 1.67 | 1.77 ± 0.33 | 0.13 ± 0.13 | 3.13 ± 1.44 | 0.010 ± 0.005 | 0.0004 ± 0.001 | 0.0004 ± 0.0004 | 0.009 ± 0.004 |
| QH | 334.40 ± 146.13 | 18.67 ± 18.67 | 290.13 ± 154.97 | 25.60 ± 16.34 | 0.363 ± 0.191 | 0.001 ± 0.002 | 0.299 ± 0.196 | 0.063 ± 0.043 |
| Sub-Lakes | Species Richness | Diversity Index | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rotifera | Cladocera | Copepoda | D | H’ | J’ | |
| DHC | 20 | 9 | 7 | 2.57 ± 0.19 | 1.11 ± 0.21 | 0.36 ± 0.07 |
| SH | 26 | 6 | 4 | 2.65 ± 0.73 | 1.07 ± 0.16 | 0.36 ± 0.03 |
| NH | 7 | 3 | 3 | 0.83 ± 0.09 | 0.94 ± 0.07 | 0.46 ± 0.04 |
| SXH | 6 | 2 | 2 | 0.94 ± 0.09 | 0.84 ± 0.02 | 0.43 ± 0.03 |
| ZLH | 5 | 1 | 3 | 0.94 ± 0.23 | 0.75 ± 0.19 | 0.49 ± 0.07 |
| QH | 2 | 5 | 2 | 0.50 ± 0.07 | 0.68 ± 0.14 | 0.42 ± 0.08 |
| Total | 34 | 12 | 7 | - | - | - |
| Sub-Lakes | TN (mg/L) | TP (mg/L) | Chlorophyll-a (μg/L) | Water Temperature (°C) | Water Depth (cm) | Turbidity (NTU) | pH | Dissolved Oxygen (mg/L) | Conductivity (uS/cm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DHC | 2.18 ± 0.40 | 0.28 ± 0.05 | 19.34 ± 3.88 | 28.20 ± 0.12 | 56.67 ± 3.33 | 206.37 ± 64.78 | 7.53 ± 0.06 | 3.67 ± 0.52 | 59.47 ± 1.60 |
| SH | 1.56 ± 0.06 | 0.20 ± 0.03 | 22.49 ± 4.09 | 29.07 ± 0.09 | 76.67 ± 12.02 | 43.03 ± 20.52 | 7.41 ± 0.10 | 3.46 ± 0.62 | 76.40 ± 6.07 |
| NH | 2.75 ± 0.62 | 0.38 ± 0.09 | 91.14 ± 33.36 | 30.77 ± 0.71 | 31.67 ± 9.28 | 75.30 ± 14.57 | 7.89 ± 0.33 | 6.00 ± 0.83 | 140.93 ± 14.12 |
| SXH | 2.64 ± 0.12 | 0.45 ± 0.05 | 107.92 ± 6.23 | 29.77 ± 0.09 | 48.33 ± 13.02 | 69.57 ± 12.86 | 8.60 ± 0.04 | 6.04 ± 0.09 | 160.83 ± 0.49 |
| ZLH | 1.28 ± 0.06 | 0.06 ± 0.01 | 1.12 ± 0.01 | 29.53 ± 2.07 | 233.33 ± 66.67 | 1.13 ± 0.50 | 8.00 ± 0.14 | 5.25 ± 0.05 | 56.45 ± 26.60 |
| QH | 3.31 ± 0.24 | 0.26 ± 0.02 | 59.42 ± 5.78 | 35.73 ± 0.09 | 20.00 ± 5.77 | 60.30 ± 6.61 | 8.81 ± 0.18 | 7.50 ± 0.23 | 232.67 ± 15.77 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qin, H.; Cao, X.; Cui, L.; Lv, Q.; Chen, T. The Influence of Human Interference on Zooplankton and Fungal Diversity in Poyang Lake Watershed in China. Diversity 2020, 12, 296. https://doi.org/10.3390/d12080296
Qin H, Cao X, Cui L, Lv Q, Chen T. The Influence of Human Interference on Zooplankton and Fungal Diversity in Poyang Lake Watershed in China. Diversity. 2020; 12(8):296. https://doi.org/10.3390/d12080296
Chicago/Turabian StyleQin, Haiming, Xinyi Cao, Lanyue Cui, Qian Lv, and Tingtao Chen. 2020. "The Influence of Human Interference on Zooplankton and Fungal Diversity in Poyang Lake Watershed in China" Diversity 12, no. 8: 296. https://doi.org/10.3390/d12080296
APA StyleQin, H., Cao, X., Cui, L., Lv, Q., & Chen, T. (2020). The Influence of Human Interference on Zooplankton and Fungal Diversity in Poyang Lake Watershed in China. Diversity, 12(8), 296. https://doi.org/10.3390/d12080296