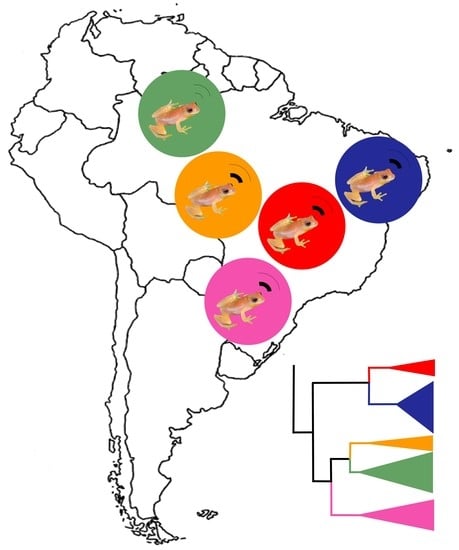
Five Independent Lineages Revealed by Integrative Taxonomy in the Dendropsophus nanus–Dendropsophus walfordi Species Complex
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Taxon Sampling
2.2. Molecular Data
2.2.1. DNA Extraction, Amplification and Sequencing
2.2.2. Phylogenetic Inferences
2.2.3. Analyses of Genetic Divergence
2.2.4. Delimitation of Independently Evolving Lineages Based on DNA Sequences
2.3. Acoustic Analyses
2.4. Morphological Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Phylogenetic Inferences
3.2. Genetic Diversity and Sequence-Based Species Delineation
3.3. Advertisement Calls
3.4. Comparative Acoustic Analyses
3.5. Morphology
4. Discussion
4.1. Comments on Advertisement Call
4.2. Comments on Cytogenetic Data
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wiens, J.J.; Penkrot, T.A. Delimiting species using DNA and morphological variation and discordant species limits in spiny lizards (Sceloporus). Syst. Biol. 2002, 51, 69–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Queiroz, K. The general lineage concept of species, species criteria, and the process of speciation: A conceptual unification and terminological recommendations. In Endless Forms: Species and Speciation; Howard, D.J., Berlocher, S.H., Eds.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1998; pp. 57–75. [Google Scholar]
- Bruschi, D.P.; Lucas, E.M.; Garcia, P.C.; Recco-Pimentel, S.M. Molecular and morphological evidence reveals a new species in the Phyllomedusa hypochondrialis group (Hylidae, Phyllomedusinae) from the Atlantic Forest of the highlands of southern Brazil. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e105608. [Google Scholar]
- Fouquet, A.; Noonan, B.P.; Blanc, M.; Orrico, V.G.D. Phylogenetic position of Dendropsophus gaucheri (Lescure and Marty 2000) highlights the need for an in-depth investigation of the phylogenetic relationships of Dendropsophus (Anura: Hylidae). Zootaxa 2011, 3035, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Funk, W.C.; Caminer, M.; Ron, S.R. High levels of cryptic species diversity uncovered in Amazonian frogs. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2012, 279, 1806–1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guarnizo, C.E.; Escallón, C.; Cannatella, D.; Amézquita, A. Congruence between acoustic traits and genealogical history reveals a new species of Dendropsophus (Anura: Hylidae) in the high Andes of Colombia. Herpetologica 2012, 68, 523–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cocca, W.; Andreone, F.; Belluardo, F.; Rosa, G.M.; Randrianirina, J.E.; Glaw, F.; Crottini, A. Resolving a taxonomic and nomenclatural puzzle in mantellid frogs: Synonymization of Gephyromantis azzurrae with G. corvus, and description of Gephyromantis kintana sp. nov. from the Isalo Massif, western Madagascar. ZooKeys 2020, 951, 133–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Padial, J.M.; Miralles, A.; De la Riva, I.; Vences, M. The integrative future of taxonomy. Front. Zool. 2010, 7, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boulenger, G. On a collection of batrachians made by Prof. Charles Spegazzini at Colonia Resistencia, South Chaco, Argentine Republic. Ann. Mus. Civ. Stor. Nat. Genova Ser. 2 1889, 7, 246–249. [Google Scholar]
- Bokermann, W. Nova espécie de Hyla de Rondônia, Brasil (Amphibia, Salientia). Atas Soc. Biol. Rio Jan. 1962, 6, 52–55. [Google Scholar]
- Jansen, M.; Bloch, R.; Schulze, A.; Pfenninger, M. Integrative inventory of Bolivia’s lowland anurans reveals hidden diversity. Zool. Scr. 2011, 40, 567–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulze, A.; Jansen, M.; Köhler, G. Tadpole diversity of Bolivia’s lowland anuran communities: Molecular identification, morphological characterisation, and ecological assignment. Zootaxa 2015, 4016, 1–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Medeiros, L.R.; Lourenço, L.B.; Rossa-Feres, D.C.; Lima, A.P.; Andrade, G.V.; Giaretta, A.A.; Egito, G.T.; Recco-Pimentel, S.M. Comparative cytogenetic analysis of some species of the Dendropsophus microcephalus group (Anura, Hylidae) in the light of phylogenetic inferences. BMC Genet. 2013, 14, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lutz, B. Brazilian Species of Hyla, 1st ed.; University of Texas Press: Austin, TX, USA, 1973; pp. 1–265. [Google Scholar]
- Langone, J.; Basso, N. Distribución geográfica y sinonimia de Hyla nana Boulenger, 1889 y de Hyla sanborni Schmidt, 1944 (Anura, Hylidae) y observaciones sobre formas afines. Comun. Zoológicas Mus. Hist. Nat. Montev. 1987, 11, 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Teixeira, B.F.V.; Zaracho, V.H.; Giaretta, A.A. Advertisement and courtship calls of Dendropsophus nanus (Boulenger, 1889)(Anura: Hylidae) from its type locality (Resistencia, Argentina). Biota Neotrop. 2016, 16, e20160183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De la Riva, I.; Márquez, R.; Bosch, J. Description of the advertisement calls of some South American Hylidae (Amphibia: Anura): Taxonomic and methodological consequences. Bonn. Zool. Beitr. 1997, 47, 175–186. [Google Scholar]
- De la Riva, I.; Köhler, J.; Lötters, S.; Reichle, S. Ten years of research on Bolivian amphibians: Updated checklist, distribution, taxonomic problems, literature and iconography. Rev. Española Herpetol. 2000, 14, 19–164. [Google Scholar]
- Frost, D.R. Amphibian Species of the World: An Online Reference, Version 6.1; American Museum of Natural History: New York, NY, USA; Available online: http://research.amnh.org/herpetology/amphibia/index.html (accessed on 10 February 2020).
- Ahl, E. Über einige neue Frösche aus Brasilien. Zool. Anz. 1933, 104, 25–30. [Google Scholar]
- Orrico, V.G.; Grant, T.; Faivovich, J.; Rivera-Correa, M.; Rada, M.A.; Lyra, M.L.; Cassini, C.S.; Valdujo, P.H.; Schargel, W.E.; Machado, D.J.; et al. The phylogeny of Dendropsophini (Anura: Hylidae: Hylinae). Cladistics 2021, 37, 73–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graybeal, A. Phylogenetic relationships of bufonid frogs and tests of alternate macroevolutionary hypotheses characterizing their radiation. Zool. J. Linn. Soc. 1997, 119, 297–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Titus, T.A. A phylogenetic Analysis of the Desmognathinae (Caudata: Plethodontidae): Evolutionary Patterns Inferred from Mitochondrial DNA Sequences. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Kansas, Lawrence, KS, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Feller, A.E.; Hedges, S.B. Molecular evidence for the early history of living amphibians. Mol. Phylogenetics Evol. 1998, 9, 509–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Palumbi, S.; Martin, A.; Romano, S.; McMillan, W.; Stice, L.; Grabowski, G. The Simple Fool’s Guide to PCR, Version 2.0; Department of Zoology and Kewalo Marine Laboratory, University of Hawaii: Honolulu, HI, USA, 1991; Available online: http://palumbilab.stanford.edu/SimpleFoolsMaster.pdf (accessed on 12 July 2020).
- Lyra, M.L.; Haddad, C.F.; de Azeredo-Espin, A.M.L. Meeting the challenge of DNA barcoding Neotropical amphibians: Polymerase chain reaction optimization and new COI primers. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2017, 17, 966–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedges, S.B. Molecular evidence for the origin of birds. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 2621–2624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hall, T.A. BioEdit: A user-friendly biological sequence alignment editor and analysis program for Windows 95/98/NT. Nucleic Acids Symp. Ser. 1999, 41, 95–98. [Google Scholar]
- Edgar, R.C. MUSCLE: Multiple sequence alignment with high accuracy and high throughput. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, 1792–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Goloboff, P.; Farris, J.; Nixon, K. TNT: Tree Analysis Using New Technologies. 2003. Available online: http://www.zmuc.dk/public/phylogeny (accessed on 12 July 2020).
- Ronquist, F.; Teslenko, M.; Van Der Mark, P.; Ayres, D.L.; Darling, A.; Höhna, S.; Larget, B.; Liu, L.; Suchard, M.A.; Huelsenbeck, J.P. MrBayes 3.2: Efficient Bayesian phylogenetic inference and model choice across a large model space. Syst. Biol. 2012, 61, 539–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Felsenstein, J. Confidence limits on phylogenies: An approach using the bootstrap. Evolution 1985, 39, 783–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nylander, J. MrModeltest v2. Program Distributed by the Author; Evolutionary Biology Centre, Uppsala University: Uppsala, Sweden, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Rambaut, A.; Suchard, M.A.; Xie, D.; Drummond, A.J. Tracer v.1.6. 2015. Available online: http://beast.bio.ed.ac.uk/Tracer (accessed on 13 September 2020).
- Drummond, A.J.; Suchard, M.A.; Xie, D.; Rambaut, A. Bayesian phylogenetics with BEAUti and the BEAST 1.7. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2012, 29, 1969–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lemmon, E.M.; Lemmon, A.R.; Cannatella, D.C. Geological and climatic forces driving speciation in the continentally distributed trilling chorus frogs (Pseudacris). Evolution 2007, 61, 2086–2103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fouquet, A.; Gilles, A.; Vences, M.; Marty, C.; Blanc, M.; Gemmell, N.J. Underestimation of species richness in Neotropical frogs revealed by mtDNA analyses. PLoS ONE 2007, 2, e1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faivovich, J.; Haddad, C.F.; Garcia, P.C.; Frost, D.R.; Campbell, J.A.; Wheeler, W.C. Systematic review of the frog family Hylidae, with special reference to Hylinae: Phylogenetic analysis and taxonomic revision. Bull. Am. Mus. Nat. Hist. 2005, 2005, 1–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Peterson, D.; Filipski, A.; Kumar, S. MEGA6: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 6.0. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 2725–2729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Excoffier, L.; Smouse, P.E.; Quattro, J.M. Analysis of molecular variance inferred from metric distances among DNA haplotypes: Application to human mitochondrial DNA restriction data. Genetics 1992, 131, 479–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimura, M. A simple method for estimating evolutionary rates of base substitutions through comparative studies of nucleotide sequences. J. Mol. Evol. 1980, 16, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bandelt, H.-J.; Forster, P.; Röhl, A. Median-joining networks for inferring intraspecific phylogenies. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1999, 16, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Kapli, P.; Pavlidis, P.; Stamatakis, A. A general species delimitation method with applications to phylogenetic placements. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 2869–2876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Puillandre, N.; Lambert, A.; Brouillet, S.; Achaz, G. ABGD, Automatic Barcode Gap Discovery for primary species delimitation. Mol. Ecol. 2012, 21, 1864–1877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narins, P.M.; Capranica, R.R. Communicative significance of the two-note call of the treefrog Eleutherodactylus coqui. J. Comp. Physiol. 1978, 127, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerhardt, H.C. Multiple messages in acoustic signals. Semin. Neurosci. 1992, 4, 391–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welch, A.M.; Semlitsch, R.D.; Gerhardt, H.C. Call duration as an indicator of genetic quality in male gray tree frogs. Science 1998, 280, 1928–1930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sousa, V.T.T. Efeitos do Canto de Anúncio e do Tamanho Corporal no Espaçamento Entre Machos em Agregações de Dendropsophus nanus (Anura, Hylidae). Master’s Thesis, São Paulo State University, São Paulo, Brazil, 2012. Available online: https://repositorio.unesp.br/handle/11449/87621 (accessed on 16 December 2020).
- Sueur, J.; Aubin, T.; Simonis, C. Seewave, a free modular tool for sound analysis and synthesis. Bioacoustics 2008, 18, 213–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Team, R.C. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2015; Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 16 December 2020).
- Köhler, J.; Jansen, M.; Rodriguez, A.; Kok, P.; Toledo, L.; Emmrich, M.; Glaw, F.; Haddad, C.; Rödel, M.; Vences, M. The use of bioacoustics in anuran taxonomy: Theory, terminology, methods and recommendations for best practice. Zootaxa 2017, 4251, 1–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liaw, A.; Wiener, M. Classification and regression by randomForest. R News 2002, 2, 18–22. [Google Scholar]
- Duellman, W.E. The Hylid Frogs of Middle America; Natural History Museum of the University of Kansas: Ithaca, NY, USA, 1970. [Google Scholar]
- Heyer, W.R.; Rand, A.S.; da Cruz, C.A.G.; Peixoto, O.L.; Nelson, C.E. Frogs of Boracéia. Arq. Zool. 1990, 31, 231–410. [Google Scholar]
- Napoli, M.; Caramaschi, U. Duas novas espécies de Hyla Laurenti, 1768 do Brasil central afins de H. tritaeniata Bokermann, 1965 (Amphibia, Anura, Hylidae). Bol. Mus. Nac. Nova Sér. Zool. 1998, 391, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Wheeler, B. Package ‘lmPerm’. R Package Version 2.1.0. 2016. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/lmPerm/lmPerm.pdf (accessed on 16 January 2021).
- Legendre, P.; Legendre, L.F. Numerical Ecology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Dray, S.; Dufour, A.-B. The ade4 package: Implementing the duality diagram for ecologists. J. Stat. Softw. 2007, 22, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wilkinson, L. Systat Statistical Package; Systat Inc.: Evanston, IL, USA, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Martins, I.A.; Jim, J. Bioacoustic analysis of advertisement call in Hyla nana and Hyla sanborni (Anura, Hylidae) in Botucatu, São Paulo, Brazil. Braz. J. Biol. 2003, 63, 507–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vences, M.; Thomas, M.; Van der Meijden, A.; Chiari, Y.; Vieites, D.R. Comparative performance of the 16S rRNA gene in DNA barcoding of amphibians. Front. Zool. 2005, 2, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vences, M.; Thomas, M.; Bonett, R.M.; Vieites, D.R. Deciphering amphibian diversity through DNA barcoding: Chances and challenges. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2005, 360, 1859–1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Boul, K.E.; Chris Funk, W.; Darst, C.R.; Cannatella, D.C.; Ryan, M.J. Sexual selection drives speciation in an Amazonian frog. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2006, 274, 399–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reinhold, K. Variation in acoustic signalling traits exhibits footprints of sexual selection. Evolution 2010, 65, 738–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simões, P.I.; Lima, A.P.; Farias, I. The description of a cryptic species related to the pan-Amazonian frog Allobates femoralis. Zootaxa 2010, 2406, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Carvalho, T.R.; Giaretta, A.A. Taxonomic circumscription of Adenomera martinezi (Bokermann, 1956) (Anura: Leptodactylidae: Leptodactylinae) with the recognition of a new cryptic taxon through a bioacoustic approach. Zootaxa 2013, 3701, 207–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thome, M.T.C.; Zamudio, K.R.; Haddad, C.F.B.; Alexandrino, J. Barriers, rather than refugia, underlie the origin of diversity in toads endemic to the Brazilian Atlantic Forest. Mol. Ecol. 2014, 23, 6152–6164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batalha-Filho, H.; Waldschmidt, A.M.; Campos, L.A.; Tavares, M.G.; Fernandes-Salomão, T.M. Phylogeography and historical demography of the neotropical stingless bee Melipona quadrifasciata (Hymenoptera, Apidae): Incongruence between morphology and mitochondrial DNA. Apidologie 2010, 41, 534–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Menezes, R.S.; Brady, S.G.; Carvalho, A.F.; Del Lama, M.A.; Costa, M.A. The roles of barriers, refugia, and chromosomal clines underlying diversification in Atlantic Forest social wasps. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 7689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Saadi, A.; Machette, M.N.; Haller, K.M.; Dart, R.L.; Bradley, L.; Souza, A. Map and Database of Quaternary Faults and Lineaments in Brazil; US Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Costa, L.P. The historical bridge between the Amazon and the Atlantic Forest of Brazil: A study of molecular phylogeography with small mammals. J. Biogeogr. 2003, 30, 71–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Batalha-Filho, H.; Fjeldså, J.; Fabre, P.-H.; Miyaki, C.Y. Connections between the Atlantic and the Amazonian forest avifaunas represent distinct historical events. J. Ornithol. 2013, 154, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prates, I.; Melo-Sampaio, P.R.; Drummond, L.O.; Teixeira, M.; Rodrigues, M.T.; Carnaval, A.C. Biogeographic links between southern Atlantic Forest and western South America: Rediscovery, re-description, and phylogenetic relationships of two rare montane anole lizards from Brazil. Mol. Phylogenetics Evol. 2017, 113, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werneck, F.P. The diversification of eastern South American open vegetation biomes: Historical biogeography and perspectives. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2011, 30, 1630–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Roux, J.P. A review of Tertiary climate changes in southern South America and the Antarctic Peninsula. Part 2: Continental conditions. Sediment. Geol. 2012, 247, 21–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, T.; Silva, V.X.; Silva, M.J.D.J. Phylogenetic relationships within Bothrops neuwiedi group (Serpentes, Squamata): Geographically highly-structured lineages, evidence of introgressive hybridization and Neogene/Quaternary diversification. Mol. Phylogenetics Evol. 2014, 71, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pröhl, H.; Koshy, R.A.; Mueller, U.; Rand, A.S.; Ryan, M.J. Geographic variation of genetic and behavioral traits in northern and southern túngara frogs. Evolution 2006, 60, 1669–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köhler, J.; Lötters, S. A new species of minute Hyla from the southwestern Amazon basin (Amphibia, Anura, Hylidae). Stud. Neotrop. Fauna Environ. 2001, 36, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moravec, J.; Aparicio, J.; Koehler, J. A new species of tree frog, genus Dendropsophus (Anura: Hylidae), from the Amazon of northern Bolivia. Zootaxa 2006, 1327, 23–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yue, X.; Fan, Y.; Xue, F.; Brauth, S.E.; Tang, Y.; Fang, G. The First Call Note Plays a Crucial Role in Frog Vocal Communication. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 10128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Teixeira, B.F.V.; Giaretta, A.A. Setting a fundament for taxonomy: Advertisement calls from the type localities of three species of the Dendropsophus rubicundulus group (Anura: Hylidae). Salamandra 2015, 51, 137–146. [Google Scholar]
- Lynch, J.D.; Duellman, W.E. A review of the centrolenid frogs of Ecuador, with descriptions of new species. Occas. Pap. Mus. Nat. Hist. Univ. Kans. 1973, 16, 1–66. [Google Scholar]
- Duellman, W.E. South American frogs of the Hyla rostrata group (Amphibia, Anura, Hylidae). Zool. Meded. 1972, 47, 177–192. [Google Scholar]
- Duellman, W.E. The genera of Phyllomedusine frogs (Anura: Hylidae). Univ. Kans. Publ. Mus. Nat. Hist. 1968, 18, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basso, N.G.; Perí, S.I.; di Tada, I.E. Revalidación de Hyla sanborni Schmidt, 1944 (Anura: Hylidae). Cuad. Herpetol. 1985, 1, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Márquez, R.; De la Riva, I.; Bosch, J. Advertisement calls of bolivian species of Hyla (Amphibia, Anura, Hylidae). Biotropica 1993, 426–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, J.J. The importance of spectral and temporal properties in species and call recognition in a neotropical treefrog with a complex vocal repertoire. Anim. Behav. 1987, 35, 340–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, J.J.; Wells, K.D. Interspecific acoustic interactions of the neotropical treefrog Hyla ebraccata. Behav. Ecol. Sociobiol. 1984, 14, 211–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, J.J.; Wells, K.D. Vocal behavior of the neotropical treefrog Hyla phlebodes. Herpetologica 1984, 40, 452–463. [Google Scholar]
- Wells, K.D.; Greer, B.J. Vocal responses to conspecific calls in a neotropical hylid frog, Hyla ebraccata. Copeia 1981, 1981, 615–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suárez, P.; Cardozo, D.; Baldo, D.; Pereyra, M.O.; Faivovich, J.; Orrico, V.G.; Catroli, G.F.; Grabiele, M.; Bernarde, P.S.; Nagamachi, C.Y.; et al. Chromosome evolution in Dendropsophini (Amphibia, Anura, Hylinae). Cytogenet. Genome Res. 2013, 141, 295–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teixeira, L.S.; Seger, K.R.; Targueta, C.P.; Orrico, V.G.; Lourenço, L.B. Comparative cytogenetics of tree frogs of tree frogs of the Dendropsophus marmoratus (Laurenti 1768) group: Conserved karyotypes and interstitial telomeric sequences. Comp. Cytogenet. 2016, 10, 753–767. [Google Scholar]







| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Lineage A | 0.5/0.6 | 4.0 | 9.3 | 8.0 | 7.4 |
| 2. Lineage B | 1.7/1.0 | 0.6/1.4 | 7.0 | 6.7 | 7.0 |
| 3. Lineage C | 3.0/1.3 | 3.0/1.8 | 0.7/# | 3.9 | 8.0 |
| 4. Lineage D | 2.8/1.9 | 2.6/1.9 | 2.6/1.7 | 0.5/1.1 | 7.2 |
| 5. Lineage E | 2.7/1.4 | 2.4/1.4 | 3.1/1.3 | 2.5/1.1 | 0.4/1.0 |
| Mean ± SD | Welch’s t-Test | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Species | Acoustic Parameter | Introductory Notes | Secondary Notes | t | p |
| D. nanus | Note duration (ms) | 39.1 ± 7.4 | 19.6 ± 3.8 | 5928 * | <0.001 |
| Pulse duration (ms) | 3.4 ± 0.5 | 3.9 ± 1.1 | 1952.5 * | <0.001 | |
| Pulse number | 11.6 ± 1.6 | 5.1 ± 1.0 | 28.6 | <0.001 | |
| Dominant frequency (Hz) | 4350.8 ± 272.4 | 4338.7 ± 268.2 | 0.3 | 0.8 | |
| Pulse rate | 293.3 ± 39.9 | 268.6 ± 57.4 | 3851.5 * | 0.001 | |
| D. walfordi | Note duration (ms) | 15.4 ± 2.7 | 13.0 ± 2.5 | 3.2 | 0.003 |
| Pulse duration (ms) | 3.8 ± 1.3 | 4.6 ± 2.1 | 241 * | 0.3 | |
| Pulse number | 4.4 ± 1.3 | 3.3 ± 1.0 | 3.3 | 0.002 | |
| Dominant frequency (Hz) | 4492.4 ± 253.8 | 4483.9 ± 246.6 | 0.1 | 0.9 | |
| Pulse rate | 295.3 ± 108.7 | 262.4 ± 92.1 | 1.2 | 0.2 | |
| Notes in Comparison | Source | Df | Pillai’s Trace | F | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Type A notes | Calls (I and II) | 1 | 0.8 | 80.7 | <0.001 |
| Residuals | 99 | ||||
| Type B notes | Calls (I and II) | 1 | 0.5 | 20.1 | <0.001 |
| Residuals | 99 | ||||
| Type A notes of call I and type B notes of call II | Calls (I and II) | 1 | 0.8 | 99.7 | <0.001 |
| Residuals | 99 | ||||
| Type B notes of call I and type A notes of call II | Calls (I and II) | 1 | 0.2 | 6.4 | <0.001 |
| Residuals | 99 |
| Morphometric Ratios | PC1 | PC2 |
|---|---|---|
| HW/HL | −0.497 | −0.251 |
| TD/ED | −0.412 | −0.440 |
| FL/TL | −0.067 | 0.791 |
| TL/SVL | 0.717 | −0.616 |
| HW/SVL | 0.690 | −0.363 |
| FL/SVL | 0.857 | 0.031 |
| HAL/SVL | 0.793 | −0.192 |
| SL/FL | −0.300 | −0.675 |
| TD/HL | −0.523 | −0.491 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Seger, K.R.; da Veiga Teixeira, B.F.; Annibale, F.S.; Rossa-Feres, D.d.C.; Lima, A.P.; Andrade, G.V.; Giaretta, A.A.; Lourenço, L.B. Five Independent Lineages Revealed by Integrative Taxonomy in the Dendropsophus nanus–Dendropsophus walfordi Species Complex. Diversity 2021, 13, 522. https://doi.org/10.3390/d13110522
Seger KR, da Veiga Teixeira BF, Annibale FS, Rossa-Feres DdC, Lima AP, Andrade GV, Giaretta AA, Lourenço LB. Five Independent Lineages Revealed by Integrative Taxonomy in the Dendropsophus nanus–Dendropsophus walfordi Species Complex. Diversity. 2021; 13(11):522. https://doi.org/10.3390/d13110522
Chicago/Turabian StyleSeger, Karin Regina, Bernardo Franco da Veiga Teixeira, Fabiane Santana Annibale, Denise de Cerqueira Rossa-Feres, Albertina Pimentel Lima, Gilda Vasconcellos Andrade, Ariovaldo Antonio Giaretta, and Luciana Bolsoni Lourenço. 2021. "Five Independent Lineages Revealed by Integrative Taxonomy in the Dendropsophus nanus–Dendropsophus walfordi Species Complex" Diversity 13, no. 11: 522. https://doi.org/10.3390/d13110522
APA StyleSeger, K. R., da Veiga Teixeira, B. F., Annibale, F. S., Rossa-Feres, D. d. C., Lima, A. P., Andrade, G. V., Giaretta, A. A., & Lourenço, L. B. (2021). Five Independent Lineages Revealed by Integrative Taxonomy in the Dendropsophus nanus–Dendropsophus walfordi Species Complex. Diversity, 13(11), 522. https://doi.org/10.3390/d13110522