Nanotechnology for Pediatric Retinoblastoma Therapy
Abstract
:1. Retinoblastoma
2. Retinoblastoma Conventional Treatment
2.1. Drug Discovery for Retinoblastoma Treatment
2.2. Drugs in Clinical Trials
2.3. Natural Products
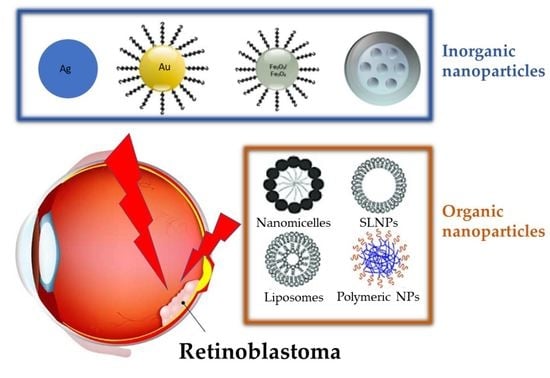
3. Nanoparticles for Treatment of Retinoblastoma
3.1. Inorganic Nanoparticles
3.1.1. Gold Nanoparticles
3.1.2. Silver Nanoparticles
3.1.3. Iron Oxide Nanoparticles
3.1.4. Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles
3.1.5. Cerium Oxide Nanoparticles
3.2. Organic Nanoparticles
3.3. Nanoparticles for Natural Product
4. Future Perspective
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Friend, S.H.; Bernards, R.; Rogelj, S.; Weinberg, R.A.; Rapaport, J.M.; Albert, D.M.; Dryja, T.P. A human DNA segment with properties of the gene that predisposes to retinoblastoma and osteosarcoma. Nature 1986, 323, 643–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grossniklaus, H.E. Retinoblastoma. Fifty Years of Progress. The LXXI Edward Jackson Memorial Lecture. Am. J. Ophtalmol. 2014, 158, 875–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dimaras, H.; Kimani, K.; Dimba, E.A.O.; Gronsdahl, P.; White, A.; Chan, H.S.L.; Gallie, B.L. Retinoblastoma. Lancet 2012, 379, 1436–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karcioglu, Z.A. Fine needle aspiration biopsy (FNAB) for retinoblastoma. Retina 2002, 22, 707–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Jong, M.C.; de Graaf, P.; Noij, D.P.; Göricke, S.; Maeder, P.; Galluzzi, P.; Brisse, H.J.; Moll, A.C.; Castelijns, J.A. Diagnostic performance of magnetic resonance imaging and computed tomography for advanced retinoblastoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ophthalmology 2014, 121, 1109–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Jong, M.C.; Kors, W.A.; Graaf, P.; Castelijns, J.A.; Kivelä, T.; Moll, A.C. Trilateral retinoblastoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Oncol. 2014, 15, 1157–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Global Retinoblastoma Study Group. Global retinoblastoma presentation and analysis by national income level. JAMA Oncol. 2020, 6, 685–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chantada, G.; Fandiño, A.; Manzitti, J.; Urrutia, L.; Schvartzman, E. Late diagnosis of retinoblastoma in a developing country. Arch. Dis. Child. 1999, 80, 1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chawla, B.; Hasan, F.; Azad, R.; Seth, R.; Upadhyay, A.D.; Pathy, S.; Pandey, R.M. Clinical presentation and survival of retinoblastoma in Indian children. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2016, 100, 1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, E.S.; Choy, R.W.; Zhang, Y.; Chu, W.K.; Chen, L.J.; Pang, C.P.; Yam, J.C. Global retinoblastoma survival and globe preservation: A systematic review and meta-analysis of associations with socioeconomic and health-care factors. Lancet Glob. Health 2022, 10, e380–e389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reese, A.B.; Ellsworth, R.M. The evaluation and current concept of retinoblastoma therapy. Am. Acad. Ophthalmol. Otolaryngol. 1963, 67, 164–172. [Google Scholar]
- Murphree, A.L. Intraocular retinoblastoma: The case for a new group classification. Ophthalmol. Clin. N. Am. 2005, 18, 41–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusakevich, A.M.; Schefler, A.C. Retinoblastoma: Recent Trends in Diagnosis and Management. Curr. Surg. Rep. 2022, 10, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://www.childrensoncologygroup.org/index.php/newlydiagnosedwithretinoblastoma (accessed on 21 July 2022).
- Leclerc, R.; Olin, J. An Overview of Retinoblastoma and Enucleation in Pediatric Patients. AORN J. 2020, 111, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://archivio.forumriskmanagement.it/images/FORUMRISK11/LABORATORIO-PDTA/REGIONI/LAZIO/bambingesu-RB.pdf (accessed on 21 July 2022).
- Houston, S.K.; Murray, T.G.; Wolfe, S.Q.; Fernandes, C.E. Current update on retinoblastoma. Int. Ophthalmol. Clin. 2011, 51, 77–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunha-Vaz, J.; Bernardes, R.; Lobo, C. Blood-retinal barrier. Eur. J. Ophthalmol. 2011, 21, S3–S9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balderrama, J.; Carlos Leal-Leal, A.; Alvis-Miranda, H.; Lee, A. Intraarterial chemotherapy for retinoblastoma: A practical review. Rom. Neurosurg. 2013, 20, 327–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Go-bin, Y.P.; Dunkel, I.J.; Marr, B.P.; Brodie, S.E.; Abramson, D.H. Intra-arterial chemotherapy for the management of retinoblastoma: Four-year experience. Arch. Ophthalmol. 2011, 129, 732–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, S.; Yamane, T.; Mohri, M.; Kaneko, A. Selective ophthalmic arterial injection ther-apy for intraocular retinoblastoma: The long-term prognosis. Ophthalmology 2011, 118, 2081–2087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimaras, H.; Corson, T.W.; Cobrinik, D.; White, A.; Zhao, J.; Munier, F.L.; Abramson, D.H.; Shields, C.L.; Chantada, G.L.; Njuguna, F.; et al. Retinoblastoma. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2015, 1, 15021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abramson, D.H.; Dunkel, I.J.; Brodie, S.E.; Kim, J.W.; Gobin, Y.P. A phase I/II study of direct in-traarterial (ophthalmic artery) chemotherapy with melphalan for intraocular retinoblastoma initial results. Ophthalmology 2008, 1151404, 1398–1404.e1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shields, C.L.; Manjandavida, F.P.; Lally, S.E.; Pieretti, G.; Arepalli, S.A.; Caywood, E.H.; Jabbour, P.; Shields, J.A. Intra-arterial chemotherapy for retinoblastoma in 70 eyes: Outcomes based on the international classification of retinoblastoma. Ophthalmology 2014, 121, 1453–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shields, C.L.; Shields, J.A. Retinoblastoma management: Advances in enucleation, intravenous chemoreduction, and intra-arterial chemotherapy. Curr. Opin. Ophthalmol. 2010, 21, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abramson, D.H.; Ellsworth, R.M.; Tretter, P.; Adams, K.; Kitchin, F.D. Simultaneous Bilateral Radiation for Advanced Bilateral Retinoblastoma. Arch. Ophthalmol. 1981, 99, 1763–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warda, O.; Naeem, Z.; Roelofs, K.A.; Sagoo, M.S.; Reddy, M.A. Retinoblastoma and vision. Eye 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gombos, D.S.; Hungerford, J.; Abramson, D.H.; Kingston, J.; Chantada, G.; Dunkel, I.J.; Antoneli, C.B.G.; Greenwald, M.; Haik, B.G.; Leal, C.A.; et al. Secondary Acute Myelogenous Leukemia in Patients with Retinoblastoma. Is Chemotherapy a Factor? Ophthalmology 2007, 114, 1378–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, F.L.; Boice, J.D.; Abramson, D.H.; Tarone, R.E.; Kleinerman, R.A.; Stovall, M.; Goldman, M.B.; Seddon, J.M.; Tarbell, N.; Fraumeni, J.F.; et al. Cancer incidence after retinoblastoma: Radiation dose and sarcoma risk. JAMA 1997, 278, 1262–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qaddoumi, I.; Bass, J.; Wu, J.; Billups, C.A.; Wozniak, A.W.; Merchant, T.E.; Haik, B.G.; Wilson, M.W.; Rodriguez-Galindo, C. Carboplatin-Associated Ototoxicity in Children with Retinoblastoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 30, 1034–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francis, J.H.; Levin, A.M.; Zabor, E.C.; Gobin, Y.P.; Abramson, D.H. Ten-year experience with ophthalmic artery chemosurgery: Ocular and recurrence-free survival. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0197081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abramson, D.H.; Ji, X.; Francis, J.H.; Catalanotti, F.; Brodie, S.E.; Habib, L. Intravitreal chemotherapy in retinoblastoma: Expanded use beyond intravitreal seeds. Br J. Ophthalmol. 2019, 103, 488–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaiquevich, P.; Francis, J.H.; Cancela, M.B.; Montero Carcaboso, A.; Chantada, G.L.; Abramson, D.H. Treatment of Retinoblastoma: What Is the Latest and What Is the Future. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 822330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Available online: https://www.cancer.gov/types/retinoblastoma/hp/retinoblastoma-treatment-pdq (accessed on 21 July 2022).
- Cancela, M.B.; Zugbi, S.; Winter, U.; Martinez, A.L.; Sampor, C.; Sgroi, M.; Francis, J.H.; Garippa, R.; Abramson, D.H.; Chantada, G.; et al. A Decision Process for Drug Discovery in Retinoblastoma. Investig. New Drugs 2020, 39, 426–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pascual-Pasto, G.; Olaciregui, N.G.; Vila-Ubach, M.; Paco, S.; Monterrubio, C.; Rodriguez, E.; Winter, U.; Batalla-Vilacis, M.; Catala, J.; Salvador, H.; et al. Preclinical Platform of Retinoblastoma Xenografts Recapitulating Human Disease and Molecular Markers of Dissemination. Cancer Lett. 2016, 380, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Togashi, K.; Okada, M.; Suzuki, S.; Sanomachi, T.; Seino, S.; Yamamoto, M.; Yamashita, H.; Kitanaka, C. Inhibition of retinoblastoma cell growth by CEP1347 through activation of the P53 pathway. Anticancer. Res. 2020, 40, 4961–4968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomatou, G.; Trontzas, I.; Ioannou, S.; Drizou, M.; Syrigos, N.; Kotteas, E. Mechanisms of resistance to cyclin-dependent kinase 4/6 inhibitors. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2021, 48, 915–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Available online: vvv.clinicaltrials.gov (accessed on 21 July 2022).
- Combs, S.S.; Lee, S.S.; Jame, A. Mechanisms of therapeutic CDK4/6 inhibition in breast cancer. Semin. Oncol. 2017, 44, 385–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherr, C.J.; Beach, D.; Shapiro, G.I. Targeting CDK4 and CDK6: From Discovery to Therapy. Cancer Discov. 2016, 6, 353–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, E.; Infante, J.R. Targeting CDK4/6 in patients with cancer. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2016, 45, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harada, T.; Ijima, A. Pharmacological profile and clinical findings of palbociclib. Nippon. Yakurigaku Zasshi 2018, 152, 306–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardee, A.B.; Li, Y.Z.; Li, C.J. Cancer therapy with beta-lapachone. Curr. Cancer Drug Targets. 2002, 2, 227–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, M.; Murad, W.; Mubin, S.; Ullah, O.; Rehman, N.U.; Rahman, H.M. Multiple health benefits of curcumin and its therapeutic potential. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 43732–43744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moballegh, N.M.; Varzandeh, M.; Pahlavanneshan, S.; Mohamadi, N.; Sarhadi, S.; Samareh Fekri, H.; Mohammadinejad, R.; Ahn, K.S. Curcumin: A potential therapeutic natural product for adenocarcinomas. Phytochem. Lett. 2022, 49, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, A.; Thevenot, P.; Hu, W.; Tang, L. Nanotechnology in the treatment and detection of intraocular cancers. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2008, 4, 410–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhavsar, D.; Subramanian, K.; Sethuraman, S.; Krishnan, U.M. Management of retinoblastoma: Opportunities and challenges. Drug Deliv. 2016, 23, 2488–2496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diebold, Y.; Calonge, M. Applications of nanoparticles in ophthalmology. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2010, 29, 596–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanderwoot, J.; Ludwig, A. Ocular drug delivery: Nanomedicines application. Nanomedicine 2007, 2, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, S.K.; Parveen, S.; Panda, J.J. The present and future of nanotechnology in human health care. Nanomedicine 2007, 3, 20–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Lin, Z.-I.; Chen, J.-A.; Xu, Z.; Gu, J.; Law, W.-C.; Yang, J.H.C.; Chen, C.-K. Organic/inorganic self-assembled hybridnano-architectures for cancer therapy applications. Macromol. Biosci. 2022, 22, 2100349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, T.; Xu, T.; Liu, X. Research progress of the engagement of inorganic nanomaterials in cancer immunotherapy. Drug Deliv. 2022, 29, 1914–1933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, E.; Spallarossa, A.; Tasso, B.; Villa, C.; Brullo, C. Nanotechnology of tyrosine kinase inhibitors in cancer therapy: A perspective. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradi, S.; Mokhtari-Dizaji, M.; Ghassemi, F.; Sheibani, S.; Amoli, F.A. The effect of ultrasound hyperthermia with gold nanoparticles on retinoblastoma Y79 cells. Gold Bull. 2020, 53, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Yang, Q.; Li, M.; Zou, H.; Wang, Z.; Ran, H.; Zheng, Y.; Jian, J.; Zhou, Y.; Luo, Y.; et al. Multifunctional nanoparticles for multimodal imaging-guided low-intensity focused ultrasound/immunosynergistic retinoblastoma therapy. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 5642–5657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darviot, C.; Hardy, P.; Meunier, M. Laser-induced plasmon-mediated treatment of retinoblastoma in viscous vitreous phantom. J. Biophotonics 2019, 12, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalmodia, S.; Parameswaran, S.; Ganapathy, K.; Yang, W.; Barrow, C.J.; Kanwar, J.R.; Roy, K.; Vasudevan, M.; Kulkarni, K.; Elchuri, S.V.; et al. Characterization and molecular mechanism of peptide-conjugated gold nanoparticle inhibiting p53-hdm2 interaction in retinoblastoma. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2017, 9, 349–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitra, M.; Kandalam, M.; Rangasamy, J.; Shankar, B.; Maheswari, U.K.; Swaminathan, S.; Krishnakumar, S. Novel epithelial cell adhesion molecule antibody conjugated polyethyleneimine-capped gold nanoparticles for enhanced and targeted small interfering RNA delivery to retinoblastoma cells. Mol. Vis. 2013, 19, 1029–1038. [Google Scholar]
- Rajanahalli, P.; Stucke, C.J.; Hong, Y. The effects of silver nanoparticles on mouse embryonic stem cell self-renewal and proliferation. Toxicol. Rep. 2015, 2, 758–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirci, H.; Slimani, N.; Pawar, M.; Kumon, R.E.; Vaishnava, P.; Besirli, C.G. Magnetic hyperthermia in y79 retinoblastoma and ARPE-19 retinal epithelial cells: Tumor selective apoptotic activity of iron oxide nanoparticle. Trans. Vis. Sci. Technol. 2019, 8, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sapareto, S.A.; Dewey, W.C. Thermal dose determination in cancer therapy. Int. J. Radiat Oncol. Biol. Phys. 1984, 10, 787–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, W.; Meng, B.; Yu, Y.; Wang, S. EpCAM antibody-conjugated mesoporous silica nanoparticles to enhance the anticancer efficacy of carboplatin in retinoblastoma. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 76, 646–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallud, A.; Warther, D.; Maynadier, M.; Sefta, M.; Poyer, F.; Thomas, C.D.; Rouxel, C.; Mongin, O.; Blanchard-Desce, M.; Morère, A.; et al. Identification of MRC2 and CD209 receptors as targets for photodynamic therapy of retinoblastoma using mesoporous silica nanoparticles. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 75167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gary-Bobo, M.; Mir, Y.; Rouxel, C.; Brevet, D.; Hocine, O.; Maynadier, M.; Gallud, A.; Da Silva, A.; Mongin, O.; Blanchard-Desce, M.; et al. Multifunctionalized mesoporous silica nanoparticles for the in vitro treatment of retinoblastoma: Drug delivery, one and two-photon photodynamic therapy. Int. J. Pharm. 2012, 432, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warther, D.; Mauriello Jimenez, C.; Raehm, L.; Gerardin, C.; Durand, J.-O.; Morère, A.; El Cheikh, K.; Gallud, A.; Gary-Bobo, M.; Maynadier, M.; et al. Small sized mesoporous silica nanoparticles functionalized with mannose for retinoblastoma cell imaging. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 37171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshpande, S.; Patil, S.; Kuchibhatla, S.V.N.T.; Seal, S. Size dependency variation in lattice parameter and valency states in nanocrystalline cerium oxide. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2005, 87, 133113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.-H.; Inbaraj, B.S. Various physicochemical and surface properties controlling the bioactivity of cerium oxide nanoparticles. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2018, 38, 1003–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inbaraj, B.S.; Chen, B.-H. An overview on recent in vivo biological application of cerium oxide nanoparticles. Asian J. Pharm. 2020, 15, 558–575. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, R.; Mitra, R.N.; Zheng, M.; Wang, K.; Dahringer, J.C.; Han, Z. Developing nanoceria-based pH-dependent cancer-directed drug delivery system for retinoblastoma. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1806248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kartha, B.; Thanikachalam, K.; Vijayakumar, N.; Alharbi, N.S.; Kadaikunnan, S.; Khaled, J.M.; Gopinath, K.; Govindarajan, M. Synthesis and characterization of Ce-doped TiO2 nanoparticles and their enhanced anticancer activity in Y79 retinoblastoma cancer cells. Green Process. Synth. 2022, 11, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitra, R.N.; Gao, R.; Zheng, M.; Wu, M.J.; Voinov, M.A.; Smirnov, A.I.; Smirnova, T.I.; Wang, K.; Chavala, S.; Han, Z. Glycol chitosan engineered autoregenerative antioxidant significantly attenuates pathological damages in models of age-related macular degeneration. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 4669–4685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Nogales, C.; Gonzalez-Fernandez, Y.; Aldaz, A.; Couvreur, P.; Blanco-Prieto, M.J. Nanomedicines for Pediatric Cancers. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 7482–7496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Jones, L.; Gu, F.X. Nanomaterials for ocular drug delivery. Macromol. Biosci. 2012, 12, 608–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaurasia, S.S.; Lim, R.R.; Lakshminarayanan, R.; Mohan, R.R. Nanomedicine approaches for corneal diseases. J. Funct. Biomater. 2015, 6, 277–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mudigunda, S.V.; Pemmaraju, D.B.; Paradkar, S.; Puppala, E.R.; Gawali, B.; Upadhyayula, S.M.; Gangamodi, N.V.; Rengan, A.K. Multifunctional polymeric nanoparticles for chemo/phototheranostics of retinoblastoma. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2022, 8, 151–160. [Google Scholar]
- Godse, R.; Rathod, M.; De, A.; Shinde, U. Intravitreal galactose conjugated polymeric nanoparticles of etoposide for retinoblastoma. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2021, 61, 102259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sims, L.B.; Tyo, K.M.; Stocke, S.; Mahmoud, M.Y.; Ramasubramanian, A.; Steinbach-Rankins, J.M. Surface-modified melphalan nanoparticles for intravitreal chemotherapy of retinoblastoma. IOVS 2019, 60, 1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Inomata, M.; Kaneko, A. Chemosensitivity profiles of primary and cultured human retinoblastoma cells in a human tumor clonogenic assay. Jpn. J. Cancer Res. 1987, 78, 858–868. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Silva-Abreu, M.; Calpena, A.C.; Espina, M.; Silva, A.M.; Gimeno, A.; Egea, M.A.; García, M.L. Optimization, biopharmaceutical profile and therapeutic efficacy of pioglitazone-loaded PLGA-PEG nanospheres as a novel strategy for ocular inflammatory disorders. Pharm. Res. 2018, 35, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delrish, E.; Ghassemi, F.; Jabbarvand, M.; Lashay, A.; Atyabi, F.; Soleimani, M.; Dinarvand, R. Biodistribution of cy5-labeled thiolated and methylated chitosan-carboxymethyl dextran nanoparticles in an animal model of retinoblastoma. J. Ophthalmic Vis. Res. 2022, 17, 58–68. [Google Scholar]
- Delrish, E.; Jabbarvand, M.; Ghassemi, F.; Amoli, F.A.; Atyabi, F.; Lashay, A.; Soleimani, M.; Aghajanpour, L.; Dinarvand, R. Efficacy of topotecan nanoparticles for intravitreal chemotherapy of retinoblastoma. Exp. Eye Res. 2021, 204, 108423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passos Gibson, V.; Derbali, R.M.; Phan, H.T.; Tahiri, H.; Allen, C.; Hardy, P.; Chain, J.L. Survivin silencing improved the cytotoxicity of carboplatin and melphalan in Y79 and primary retinoblastoma cells. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 589, 119824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabatabaei, S.N.; Derbali, R.M.; Yang, C.; Superstein, R.; Hamel, P.; Chain, J.L.; Hardy, P. Co-delivery of miR-181a and melphalan by lipid nanoparticles for treatment of seeded retinoblastoma. J. Control. Release 2019, 298, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayana, R.V.L.; Jana, P.; Tomar, N.; Prabhu, V.; Nair, R.M.; Manukonda, R.; Kaliki, S.; Coupland, S.E.; Alexander, J.; Kalirai, H.; et al. Carboplatin and etoposide loaded lactoferrin protein nanoparticles for targeting cancer stem cells in retinoblastoma in vitro. IOVS 2021, 62, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmeda, F.; Ali, M.J.; Kondapi, A.K. Carboplatin loaded protein nanoparticles exhibit improve anti-proliferative activity in retinoblastoma cells. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2014, 70, 572–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shome, D.; Kalita, D.; Jain, V.; Sarin, R.; Maru, G.B.; Bellare, J.R. Carboplatin loaded polymethylmethacrylate nanoparticles in an adjunctive role in retinoblastoma: An animal trial. Indian J. Ophtalm. 2014, 62, 585–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalita, D.; Shome, D.; Jain, V.G.; Chadha, K.; Bellare, J.R. In vivo intraocular distribution and safety of periocular nanoparticle carboplatin for treatment of advanced retinoblastoma in humans. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2014, 157, 1109–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alsaab, H.; Alzhrani, R.M.; Kesharwani, P.; Sau, S.; Boddu, S.H.S.; Iyer, A.K. Folate decorated nanomicelles loaded with a potent curcumin analogue for targeting retinoblastoma. Pharmaceutics 2017, 9, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, Z.; Wu, X.; Li Lin Yao, J.; Sun, L.; Shi, Y.; Zhang, W.; Lin, J.; Liang, D.; Li, Y. Antitumor activity of celastrol nanoparticles in a xenograft retinoblastoma tumor model. Int. J. Nanomed. 2012, 7, 2389–2398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Z.; Shi, L.; Feng, H.; Yang, F.; Li, Z.; Zhang, J.; Jin, L.; Li, J. Reduction-sensitive nanomicelles: Delivery celastrol for retinoblastoma cells effective apoptosis. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2021, 32, 1046–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Guo, Z.; Chu, D.; Feng, H.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, L.; Li, J. Effectively suppressed angiogenesis-mediated retinoblastoma growth using celastrol nanomicelles. Drug Deliv. 2020, 27, 358–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, A.M.; Alvarado, H.L.; Abrego, G.; Martins-Gomes, C.; Garduño-Ramirez, M.L.; García, M.L.; Calpena, A.C.; Souto, E.B. In vitro cytotoxicity of oleanolic/ursolic acids loaded in PLGA nanoparticles in different cell lines. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- N’Diaye, M.; Vergnaud-Gauduchon, J.; Nicolas, V.; Faure, V.; Denis, S.; Abreu, S.; Chaminade, P.; Rosilio, V. Hybrid lipid polymer nanoparticles for combined chemo- and photodynamic therapy. Mol. Pharm. 2019, 16, 4045–4058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remya, R.R.; Radhika Rajasree, S.R.; Suman, T.Y.; Aranganathan, L.; Gayathri, S.; Gobalakrishnan, M.; Karthih, M.G. Laminarin based AgNPs using brown seaweed Turbinaria ornata and its induction of apoptosis in human retinoblastoma Y79 cancer cell lines. Mater. Res. Express 2018, 5, 035403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remya, R.R.; Radhika Rajasree, S.R.; Aranganathan, L.; Suman, T.Y.; Gayathri, S. Enhanced cytotoxic activity of AgNPs on retinoblastoma Y79 cell lines synthesised using marine seaweed Turbinaria ornata. IET Nanobiotechnol. 2017, 11, 18–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, H.; Li, M.; Li, X.; Zheng, W.; Kuang, H.; Wang, M.; Zhang, W.; Ran, H.; Ma, H.; Zhou, X. Multimodal imaging and photothermal synergistic immunotherapy of retinoblastoma with tuftsin-loaded carbonized MOF nanoparticles. Drug Deliv. 2022, 29, 1785–1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Bian, X.; Chen, X.; Fan, N.; Zou, H.; Bao, Y.; Zhou, Y. Multifunctional liposome for photoacoustic/ultrasound imaging-guided chemo/photothermal retinoblastoma therapy. Drug Deliv. 2022, 29, 519–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, C.; Li, L.; Mo, T.; Na, J.; Qian, Z.; Fan, D.; Sun, X.; Yao, M.; Pan, L.; Huang, Y.; et al. Oncolytic viral vectors in the era of diversifed cancer therapy: From preclinical to clinical. Clin. Transl. Oncol. 2022, 24, 1682–1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierce, K.M.; Miklavcic, W.R.; Cook, K.P.; Hennen, M.S.; Bayles, K.W.; Hollingsworth, M.A.; Brooks, A.E.; Pullan, J.E.; Dailey, K.M. The Evolution and Future of Targeted Cancer Therapy: From Nanoparticles, Oncolytic Viruses, and Oncolytic Bacteria to the Treatment of Solid Tumors. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 3018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dick, F.A.; Rubin, S.M. Molecular mechanisms underlying RB protein function. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2013, 14, 297–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascual-Pasto, G.; Bazan-Peregrino, M.; Olaciregui, N.G.; Restrepo-Perdomo, C.A.; Mato-Berciano, A.; Ottaviani, D.; Weber, K.; Correa, G.; Paco, S.; Vila-Ubach, M.; et al. Therapeutic targeting of the RB1 pathway in retinoblastoma with the oncolytic adenovirus VCN-01. Sci. Transl. Med. 2019, 11, eaat9321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, J.; Schober, S.J.; Hindupur, S.V.; Schöning, C.; Klein, F.G.; Mantwill, K.; Ehrenfeld, M.; Schillinger, U.; Hohnecker, T.; Qi, P.; et al. Targeting the Retinoblastoma/E2F repressive complex by CDK4/6 inhibitors amplifies oncolytic potency of an oncolytic adenovirus. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 4689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suryawanshi, Y.R.; Zhang, T.; Razi, F.; Essani, K. Tanapoxvirus: From discovery towards oncolytic immunovirotherapy. J. Cancer Res. Ther. 2020, 16, 708–712. [Google Scholar]
- VanDeusen, H.R.; Kalejta, R.F. The Retinoblastoma Tumor Suppressor Promotes Efficient Human Cytomegalovirus Lytic Replication. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 5012–5021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]


| Group Classification | Morphological Characteristics | Image of Ocular Damage |
|---|---|---|
| Group A | Small tumors (≤3 mm) confined to retina; >3 mm in fovea; 1.5 mm in optic disc |  |
| Group B | Tumors (>3 mm) confined to retina, clear subretinal fluid (≤6 mm from tumor margin) |  |
| Group C | Localized vitreous and/or subretinal seeding (<6 mm from tumor margin) |  |
| Group D | Diffuse vitreous and/or subretinal seeding (>6 mm from tumor margin). Subretinal fluid > 6 mm from tumor margin. |  |
| Group E | No visual potential and poor prognostic features; Retinoblastoma occupying > 50% of the globe, invasion of the optic nerve, choroid, sclera, orbit, anterior chamber |  |
| Drug | Molecular Formula | N. of Trials | N. of Clinical Trials Completed or Terminated | Details |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carboplatinum |  | 34 | 14 | Results available for 6 studies |
| Etoposide |  | 26 | 10 | Results available for 5 studies |
| Vincristine |  | 22 | 7 | Results available for 6 studies |
| Melphalan |  | 18 | 9 | Results available for 2 studies |
| Topotecan |  | 17 | 6 | Results available for 2 studies |
| Doxorubicin |  | 3 | 1 | NCT00186888, active, not recruiting, phase 3; NCT01783535, recruiting, phase 2; NCT00004006, completed, phase 2. |
| Palbociclib |  | 2 | 2 | NCT01291017, phase 2; NCT01320592, phase 1. |
| Cisplatinum |  | 4 | 1 | NCT00554788, phase 3; NCT03567642, phase 1; NCT00002675, phase 2; NCT00003273, phase 2 |
| Drug/NPs | Combination Therapy | Ref. |
|---|---|---|
| Gold NPs | Ultrasonic Hyperthermia | [55] |
| Gold NPs | Laser therapy | [57] |
| Iron oxide NPs | Magnetic Hypertermia | [61] |
| Mesoporous silica NPs | Photodynamic therapy (PDT) | [64] |
| Camptothecin/Mesoporous silica NPs | Chemo/one-photon excitation photodynamic therapy (OPE-PDT) | [65] |
| Doxorubicin/Cerium oxide NPs | tumor targeted/tumor microenvironment (TME) therapy | [70] |
| Palbociclib/polymeric NPs | Chemo/photodermal therapy (PTT) | [76] |
| Beta-lapachone/lipidic NPs | Chemo/photodynamic therapy | [94] |
| Carbon-Metal-tuftsin NPs | Photothermal/Immuno therapy | [97] |
| Doxorubicin/Liposomes | Chemo/Photothermal therapy | [98] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Russo, E.; Spallarossa, A.; Tasso, B.; Villa, C.; Brullo, C. Nanotechnology for Pediatric Retinoblastoma Therapy. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 1087. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15091087
Russo E, Spallarossa A, Tasso B, Villa C, Brullo C. Nanotechnology for Pediatric Retinoblastoma Therapy. Pharmaceuticals. 2022; 15(9):1087. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15091087
Chicago/Turabian StyleRusso, Eleonora, Andrea Spallarossa, Bruno Tasso, Carla Villa, and Chiara Brullo. 2022. "Nanotechnology for Pediatric Retinoblastoma Therapy" Pharmaceuticals 15, no. 9: 1087. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15091087
APA StyleRusso, E., Spallarossa, A., Tasso, B., Villa, C., & Brullo, C. (2022). Nanotechnology for Pediatric Retinoblastoma Therapy. Pharmaceuticals, 15(9), 1087. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15091087