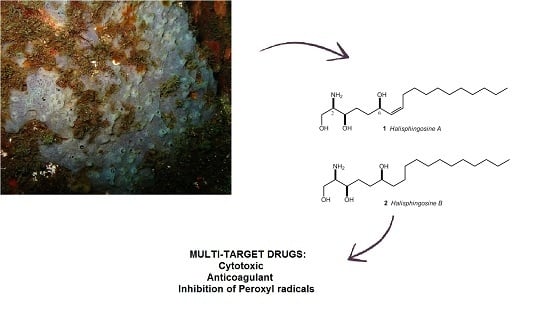
Sphingosines Derived from Marine Sponge as Potential Multi-Target Drug Related to Disorders in Cancer Development
Abstract
:1. Introduction

2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Cytotoxic Evaluation
| H. tubifera Fractions | IC50 (μg/mL) a | |
|---|---|---|
| U87 | SH-SY5Y | |
| Ethyl Acetate | 12.47 ± 1.28 | 16.72 ± 1.24 |
| Aqueous | na | na |
| Hexane | na | na |

2.2. Effects on Blood Coagulation

2.3. Redox Properties
| H. tubifera Fractions | TEAC (μM Trolox/g Marine Sponge) |
|---|---|
| Ethyl Acetate | 8.0 |
| Aqueous | 5.22 |
| Hexane | na |


3. Experimental Section
3.1. Materials
3.2. Sponge Collection
3.3. Preparation of Extracts and Fractions
3.4. Cell Cultures
3.5. Treatments
3.6. Assessment of Glioma and Neuroblastoma Cell Viability
3.7. Evaluation of Antioxidant Activity Using the Total Reactive Antioxidant Potential Method
3.8. Clotting Assay
3.9. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Estimativas 2012: Incidência de Câncer no Brasil. Available online: http://portal.saude.sp.gov.br/resources/ses/perfil/gestor/homepage/estimativas-de-incidencia-de-cancer-2012/estimativas_incidencia_cancer_2012.pdf (accessed on 14 December 2014).
- American Cancer Society (INCA): Information and Resources for Cancer (2013). Available online: www.cancer.org/Cancer/index (accessed on 20 November 2014).
- De Angelis, L.M.; Posner, M.D. Brain Metastases. In Holland-Frei Cancer Medicine; Kufe, D.W., Pollock, R.E., Weichselbaum, R.R., Bast, R.C., Gansler, T.S., Holland, J.F., Frei Hamilton, E., Eds.; BC Decker: Hamilton, ON, Canada, 2004; p. 1227. [Google Scholar]
- Binello, E.; Germano, I.M. Targeting glioma stem cells: A novel framework for brain tumors. Cancer Sci. 2011, 102, 1958–1966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.R.; Eggert, A.; Caron, H. Neuroblastoma: Biology, prognosis, and treatment. Hematol. Oncol. Clin. North Am. 2010, 24, 65–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kvolik, S.; Jukic, M.; Matijevic, M.; Marjanovic, K.; Glavas-Obrovac, L. An overview of coagulation disorders in cancer patients. Surg. Oncol. 2010, 19, e33–e46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, L.V.; Ezban, M. Active site-blocked activated factor VII as an effective antithrombotic agent: Mechanism of action. Blood Coagul. Fibrinol. 2000, 11, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rickles, F.R.; Falanga, A. Molecular basis for the relationship between thrombosis and cancer. Thromb. Res. 2001, 102, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moura, M.B.; dos Santos, L.S.; van Houten, B. Mitochondrial dysfunction in neurodegenerative diseases and cancer. Environ. Mol. Mutagen. 2010, 51, 391–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pelicano, H.; Carney, D.; Huang, P. ROS stress in cancer cells and therapeutic implications. Drug Resist. Update 2004, 7, 97–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shacter, E.; Williams, J.A.; Levine, R.L. Oxidative modification of fibrinogen inhibits thrombin-catalyzed clot formation. Free Radical. Biol. Med. 1995, 18, 815–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blunt, J.W.; Copp, B.R.; Keyzers, R.A.; Munro, M.H.G.; Prinsep, M.R. Marine natural products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2013, 30, 237–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monks, N.R.; Lerner, C.; Henriques, A.T.; Farias, F.M.; Schapoval, E.E.S.; Suyenaga, E.S.; da Rocha, A.B.; Schwartsmann, G.; Mothes, B. Anticancer, antichemotactic and antimicrobial activities of marine sponges collected off coast of Santa Catarina, southern Brazil. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2002, 281, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molinski, T.F.; Biegelmeyer, R.; Stout, E.P.; Wang, X.; Frota, M.L.C.; Henriques, A.T. Halisphingosines A and B, modified sphingoid bases from Haliclona tubifera. Assignment of configuration by circular dichroism and van’t Hoff’s principle of optical superposition. J. Nat. Prod. 2013, 76, 374–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woodcock, J. Sphingosine and ceramide signalling in apoptosis. Life 2006, 58, 462–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manggau, M.; Kim, D.S.; Ruwisch, L.; Vogler, R.; Korting, H.C.; Schäfer-Korting, M.; Kleuser, B. 1a,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3 Protects Human Keratinocytes from Apoptosis by the Formation of Sphingosine-1-Phosphate. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2001, 117, 1241–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dick, T.E.; Hengst, J.A.; Fox, T.E.; Colledge, A.L.; Kale, V.P.; Sung, S.S.; Sharma, A.; Amin, S.; Loughran, T.P., Jr.; et al. The Apoptotic Mechanism of Action of the Sphingosine Kinase 1 Selective Inhibitor SKI-178 in Human Acute Myeloid Leukemia Cell Lines. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2015, 352, 494–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.; Freter, C. Lipid metabolism, apoptosis and cancer therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 924–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muñoz-Sáez, E.; de Munck García, E.; Arahuetes Portero, R.M.; Vicente, F.; Ortiz-López, F.J.; Cantizani, J.; Gómez Miguel, B. Neuroprotective role of sphingosine-1-phosphate in l-BMAA treated neuroblastoma cells (SH-SY5Y). Neurosci. Lett. 2015, 593, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernhart, E.; Damm, S.; Wintersperger, A.; Nusshold, C.; Brunner, A.M.; Plastira, I.; Rechberger, G.; Reicher, H.; Wadsack, C.; Zimmer, A.; et al. Interference with distinct steps of sphingolipid synthesis and signaling attenuates proliferation of U87MG glioma cells. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2015, 96, 119–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drozd, N.N.; Tolstenkov, A.S.; Makarov, V.A.; Kuznetsova, T.A.; Besednova, N.N.; Shevchenko, N.M.; Zvyagintseva, T.N. Pharmacodynamic parameters of anticoagulants based on sulfated polysaccharides from marine algae. B Exp. Biol. Med. 2006, 142, 591–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melo, F.R.; Pereira, M.S.; Foguel, D.; Mourão, P.A.S. Antithrombin-mediated anticoagulant activity of sulfated polysaccharides: Different mechanisms for heparin and sulfated galactans. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 20824–20835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rocha, H.A.; Moraes, F.A.; Trindade, E.S.; Franco, C.R.; Torquato, R.J.; Veiga, S.S.; Valente, A.P.; Mourão, P.A.; Leite, E.L.; Nader, H.B.; et al. Structural and hemostatic activities of a sulfated galactofucan from the brown alga Spatoglossum schroederi. An ideal antithrombotic agent? J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 41278–41288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimura, J.; Ishizuka, E.; Nakao, Y.; Yoshida, W.Y.; Scheuer, P.J.; Kelly-Borges, M. Isolation of 1-Methylherbipoline Salts of Halisulfate-1 and of Suvanine as Serine Protease Inhibitors from a Marine Sponge, Coscinoderma mathewsi. J. Nat. Prod. 1998, 61, 248–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carroll, A.R.; Buchanan, M.S.; Edser, A.; Hyde, E.; Simpson, M.; Quinn, R.J. Dysinosins B−D, inhibitors of factor VIIa and thrombin from the Australian sponge Lamellodysidea chlorea. J. Nat. Prod. 2004, 67, 1291–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abraham, E. Coagulation abnormalities in acute lung injury and sepsis. Am. J. Resp. Cell Mol. 2000, 22, 401–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trachootham, D.; Alexandre, J.; Huang, P. Targeting cancer cells by ROS-mediated mechanisms: A radical therapeutic approach? Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2009, 8, 579–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, E.J.; Pezzuto, J.M. Antioxidant marine products in cancer chemoprevention. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2013, 19, 115–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Booy, E.P.; Johar, D.; Kadkhoda, K.; Bay, G.H.; Los, M. The immune system, involvement in neurodegenerative diseases, ageing and cancer. Curr. Med. Chem. Anti Inflam. Anti Allergy Agents 2005, 4, 349–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boopathy, N.S.; Kathiresan, K. Anticancer drugs from marine flora: An overview. J. Oncol. 2010, 2010, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dresch, M.T.K.; Rossato, S.B.; Kappel, V.D.; Biegelmeyer, R.; Hoff, M.L.M.; Mayorga, P.; Zuanazzi, J.A.S.; Henriques, A.T.; Moreira, J.C.F. Optimization and validation of an alternative method to evaluate Total Reactive Antioxidant Potential (TRAP). Anal. Biochem. 2009, 385, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribeiro, J.M.C.; Schneider, M.; Guimaraes, J.A. Purification and characterization of prolixin S (nitrophorin 2), the salivary anticoagulant of the blood-sucking bug Rhodnius prolixus. Biochem. J. 1995, 308, 243–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Biegelmeyer, R.; Schröder, R.; Rambo, D.F.; Dresch, R.R.; Carraro, J.L.F.; Mothes, B.; Moreira, J.C.F.; Junior, M.L.C.d.F.; Henriques, A.T. Sphingosines Derived from Marine Sponge as Potential Multi-Target Drug Related to Disorders in Cancer Development. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 5552-5563. https://doi.org/10.3390/md13095552
Biegelmeyer R, Schröder R, Rambo DF, Dresch RR, Carraro JLF, Mothes B, Moreira JCF, Junior MLCdF, Henriques AT. Sphingosines Derived from Marine Sponge as Potential Multi-Target Drug Related to Disorders in Cancer Development. Marine Drugs. 2015; 13(9):5552-5563. https://doi.org/10.3390/md13095552
Chicago/Turabian StyleBiegelmeyer, Renata, Rafael Schröder, Douglas F. Rambo, Roger R. Dresch, João L. F. Carraro, Beatriz Mothes, José Cláudio F. Moreira, Mário L. C. da Frota Junior, and Amélia T. Henriques. 2015. "Sphingosines Derived from Marine Sponge as Potential Multi-Target Drug Related to Disorders in Cancer Development" Marine Drugs 13, no. 9: 5552-5563. https://doi.org/10.3390/md13095552
APA StyleBiegelmeyer, R., Schröder, R., Rambo, D. F., Dresch, R. R., Carraro, J. L. F., Mothes, B., Moreira, J. C. F., Junior, M. L. C. d. F., & Henriques, A. T. (2015). Sphingosines Derived from Marine Sponge as Potential Multi-Target Drug Related to Disorders in Cancer Development. Marine Drugs, 13(9), 5552-5563. https://doi.org/10.3390/md13095552