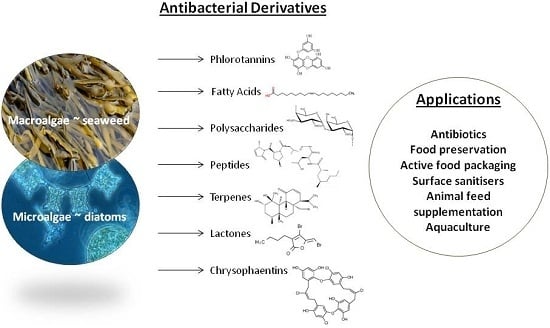
Antibacterial Derivatives of Marine Algae: An Overview of Pharmacological Mechanisms and Applications
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Antibacterial Compounds in Marine Algae and Their Functional Groups
Algal Allelopathy
3. Mechanisms of Pharmacological Action and Potential Applications
3.1. Phlorotannins
3.2. Fatty Acids
3.3. Polysaccharides
3.4. Proteins and Peptides
3.5. Terpenes
3.6. Chrysophaentins
3.7. Lactones
4. Effect of Extraction Methodology on Antibacterial Potency
4.1. Environmental Influences
4.2. Extraction Method and Solvent
4.2.1. Solvent Polarity
4.2.2. Food Grade Solvents
4.3. Novel Extraction Technologies
4.3.1. Supercritical Fluid Extraction
4.3.2. Ultrasound Assisted Extraction
4.3.3. Enzyme Assisted Extraction
5. Marine vs. Terrestrial Antibacterials
6. Inhibition of Foodborne Pathogenic and Spoilage Bacteria in Food Production
6.1. Active Food Packaging Applications
6.2. Animal Feed Supplementation and Aquaculture
6.3. Consumer Acceptance
7. Synergistic Effects
8. Biotechnological Potential of Marine Algae
Omics Studies
9. Chemical Synthesis
10. Conclusions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hu, Y.; Chen, J.; Hu, G.; Yu, J.; Zhu, X.; Lin, Y.; Chen, S.; Yuan, J. Statistical research on the bioactivity of new marine natural products discovered during the 28 years from 1985 to 2012. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 202–221. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Miller, A.A.; Miller, P.F. Emerging Trends in Antibacterial Discovery: Answering the Call to Arms; Caister Academic Press: Norfolk, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Ramanan, R.; Kim, B.-H.; Cho, D.-H.; Oh, H.-M.; Kim, H.-S. Algae-bacteria interactions: Evolution, ecology and emerging applications. Biotechnol. Adv. 2016, 34, 14–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cox, S.; Abu-Ghannam, N.; Gupta, S. An assessment of the antioxidant and antimicrobial activity of six species of edible Irish seaweeds. Int. Food Res. J. 2010, 17, 205–220. [Google Scholar]
- Abu-Ghannam, N.; Rajauria, G. Antimicrobial activity of compounds isolated from algae. In Functional Ingredients from Algae for Foods and Nutraceuticals; Dominguez, H., Ed.; Woodhead Publishing Ltd.: Sawston, UK, 2013; pp. 287–306. [Google Scholar]
- Rizzo, L.; Fraschetti, S.; Alifano, P.; Tredici, M.S.; Stabili, L. Association of Vibrio community with the Atlantic Mediterranean invasive alga Caulerpa cylindracea. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2016, 475, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ördög, V.; Stirk, W.; Lenobel, R.; Bancířová, M.; Strnad, M.; van Staden, J.; Szigeti, J.; Németh, L. Screening microalgae for some potentially useful agricultural and pharmaceutical secondary metabolites. J. Appl. Phycol. 2004, 16, 309–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venugopal, V. Marine Products for Healthcare: Functional and Bioactive Nutraceutical Compounds from the Ocean; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Blunt, J.W.; Munro, M.H.G.; Copp, B.R.; Keyzers, R.A.; Prinsep, M.R. Marine natural products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2015, 32, 116–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayer, A.; Rodríguez, A.D.; Taglialatela-Scafati, O.; Fusetani, N. Marine pharmacology in 2009–2011: Marine compounds with antibacterial, antidiabetic, antifungal, anti-inflammatory, antiprotozoal, antituberculosis, and antiviral activities; affecting the immune and nervous systems, and other miscellaneous mechanisms of action. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 2510–2573. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chojnacka, K.; Kim, S.-K. Introduction of Marine Algae Extracts. In Marine Algae Extracts; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2015; pp. 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Amsler, C.D. Algal Chemical Ecology; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2008; Volume 468. [Google Scholar]
- Hughes, C.C.; Fenical, W. Antibacterials from the Sea. Chemistry 2010, 16, 12512–12525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, A.; Thakur, N.L. Significance of investigating allelopathic interactions of marine organisms in the discovery and development of cytotoxic compounds. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2016, 243, 135–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vieira, C.; Thomas, O.P.; Culioli, G.; Genta-Jouve, G.; Houlbreque, F.; Gaubert, J.; de Clerck, O.; Payri, C.E. Allelopathic interactions between the brown algal genus Lobophora (Dictyotales, Phaeophyceae) and scleractinian corals. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rasher, D.B.; Stout, E.P.; Engel, S.; Kubanek, J.; Hay, M.E. Macroalgal terpenes function as allelopathic agents against reef corals. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 17726–17731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zabaglo, K.; Chrapusta, E.; Bober, B.; Kaminski, A.; Adamski, M.; Bialczyk, J. Environmental roles and biological activity of domoic acid: A review. Algal Res. 2016, 13, 94–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smeti, E.; Roelke, D.; Gremion, G.; Linhart, J.; Danielidis, D.; Spatharis, S. Potential mechanisms of coexistence between two globally important Pseudo-nitzschia (Bacillariophyta) species. Hydrobiologia 2015, 762, 89–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Altares, M.; Tartaglione, L.; Dell’Aversano, C.; Carnicer, O.; Iglesia, P.; Forino, M.; Diogène, J.; Ciminiello, P. The novel ovatoxin-g and isobaric palytoxin (so far referred to as putative palytoxin) from Ostreopsis cf. ovata (NW Mediterranean Sea): Structural insights by LC-high resolution MS. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2015, 407, 1191–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Accoroni, S.; Percopo, I.; Cerino, F.; Romagnoli, T.; Pichierri, S.; Perrone, C.; Totti, C. Allelopathic interactions between the HAB dinoflagellate Ostreopsis cf. ovata and macroalgae. Harmful Algae 2015, 49, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balboa, E.M.; Li, Y.X.; Ahn, B.N.; Eom, S.H.; Domínguez, H.; Jiménez, C.; Rodríguez, J. Photodamage attenuation effect by a tetraprenyltoluquinol chromane meroterpenoid isolated from Sargassum muticum. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2015, 148, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Potin, P.; Bouarab, K.; Salaün, J.-P.; Pohnert, G.; Kloareg, B. Biotic interactions of marine algae. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2002, 5, 308–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibata, T.; Miyasaki, T.; Miyake, H.; Tanaka, R.; Kawaguchi, S. The influence of phlorotannins and bromophenols on the feeding behavior of marine herbivorous gastropod Turbo cornutus. Am. J. Plant Sci. 2014, 5, 387–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eom, S.-H.; Kim, Y.-M.; Kim, S.-K. Antimicrobial effect of phlorotannins from marine brown algae. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2012, 50, 3251–3255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gómez, I.; Huovinen, P. Induction of phlorotannins during UV exposure mitigates inhibition of photosynthesis and DNA damage in the kelp Lessonia nigrescens. Photochem. Photobiol. 2010, 86, 1056–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jormalainen, V.; Honkanen, T.; Koivikko, R.; Eränen, J. Induction of phlorotannin production in a brown alga: Defense or resource dynamics? Oikos 2003, 103, 640–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egan, S.; Harder, T.; Burke, C.; Steinberg, P.; Kjelleberg, S.; Thomas, T. The seaweed holobiont: Understanding seaweed-bacteria interactions. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2013, 37, 462–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pratt, R.; Daniels, T.C.; Eiler, J.J.; Gunnison, J.B.; Kumler, W.D.; Oneto, J.F.; Strait, L.A.; Spoehr, H.A.; Hardin, G.J.; Milner, H.W.; et al. Chlorellin, an antibacterial substance from Chlorella. Science 1944, 99, 351–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willis, R.J. The History of Allelopathy; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Sahoo, D.; Seckbach, J. The Algae World; Springer Science & Business Media: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Heldt, H.-W.; Piechulla, B. Plant Biochemistry; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Xu, Z.; Bach, S.; McAllister, T. Sensitivity of Escherichia coli to seaweed (Ascophyllum nodosum) phlorotannins and terrestrial tannins. Asian-Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2009, 22, 238–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamei, Y.; Isnansetyo, A. Lysis of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus by 2,4-diacetylphloroglucinol produced by Pseudomonas sp. AMSN isolated from a marine alga. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2003, 21, 71–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golan, D.E.; Tashjian, A.H.; Armstrong, E.J. Principles of Pharmacology: The Pathophysiologic Basis of Drug Therapy; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, Y.; Liu, Q.; Xu, C.; Yu, J.; Zhao, L.; Guo, Q. Damage to the membrane permeability and cell death of Vibrio parahaemolyticus caused by phlorotannins with low molecular weight from Sargassum thunbergii. J. Aquat. Food Prod. Technol. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-H.; Eom, S.-H.; Lee, E.-H.; Jung, Y.-J.; Kim, H.-J.; Jo, M.-R.; Son, K.-T.; Lee, H.-J.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, M.-S. In vitro antibacterial and synergistic effect of phlorotannins isolated from edible brown seaweed Eisenia bicyclis against acne-related bacteria. Algae 2014, 29, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Kim, S.K. Biological phlorotannins of Eisenia bicyclis. Mar. Algae Extr. Processes Prod. Appl. 2015, 453–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eom, S.-H.; Lee, D.-S.; Jung, Y.-J.; Park, J.-H.; Choi, J.-I.; Yim, M.-J.; Jeon, J.-M.; Kim, H.-W.; Son, K.-T.; Je, J.-Y.; et al. The mechanism of antibacterial activity of phlorofucofuroeckol-A against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 98, 9795–9804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pradhan, J.; Das, S.; Das, B.K. Antibacterial activity of freshwater microalgae: A review. Afr. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2014, 8, 809–818. [Google Scholar]
- Susilowati, R.; Sabdono, A.; Widowati, I. Isolation and characterization of bacteria associated with brown algae Sargassum spp. from Panjang Island and their antibacterial activities. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2015, 23, 240–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemming, D. Animal Science Reviews 2010; CABI: Wallingford, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, C.J.; Yoo, J.-S.; Lee, T.-G.; Cho, H.-Y.; Kim, Y.-H.; Kim, W.-G. Fatty acid synthesis is a target for antibacterial activity of unsaturated fatty acids. FEBS Lett. 2005, 579, 5157–5162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Shafay, S.M.; Ali, S.S.; El-Sheekh, M.M. Antimicrobial activity of some seaweeds species from Red sea, against multidrug resistant bacteria. Egypt. J. Aquat. Res. 2016, 42, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Čermák, L.; Pražáková, Š.; Marounek, M.; Skřivan, M.; Skřivanová, E. Effect of green alga Planktochlorella nurekis on selected bacteria revealed antibacterial activity in vitro. Czech J. Anim. Sci. 2015, 60, 427–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amorim, R.d.N.d.S.; Rodrigues, J.A.G.; Holanda, M.L.; Quinderé, A.L.G.; Paula, R.C.M.D.; Melo, V.M.M.; Benevides, N.M.B. Antimicrobial effect of a crude sulfated polysaccharide from the red seaweed Gracilaria ornata. Braz. Arch. Biol. Technol. 2012, 55, 171–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierre, G.; Sopena, V.; Juin, C.; Mastouri, A.; Graber, M.; Maugard, T. Antibacterial activity of a sulfated galactan extracted from the marine alga Chaetomorpha aerea against Staphylococcus aureus. Biotechnol. Bioprocess Eng. 2011, 16, 937–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, F.; Yang, Y.; Yang, G.; Yu, L. Studies on antibacterial activity and antibacterial mechanism of a novel polysaccharide from Streptomyces virginia H03. Food Control 2010, 21, 1257–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadam, S.U.; O’Donnell, C.P.; Rai, D.K.; Hossain, M.B.; Burgess, C.M.; Walsh, D.; Tiwari, B.K. Laminarin from Irish brown seaweeds Ascophyllum nodosum and Laminaria hyperborea: Ultrasound assisted extraction, characterization and bioactivity. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 4270–4280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Besednova, N.N.; Zaporozhets, T.S.; Somova, L.M.; Kuznetsova, T.A. Review: Prospects for the use of extracts and polysaccharides from marine algae to prevent and treat the diseases caused by Helicobacter pylori. Helicobacter 2015, 20, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernández, A.J.; Romero, A.; Gonzalez-Stegmaier, R.; Dantagnan, P. The effects of supplemented diets with a phytopharmaceutical preparation from herbal and macroalgal origin on disease resistance in rainbow trout against Piscirickettsia salmonis. Aquaculture 2016, 454, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.-H.; Wu, S.-J.; Wu, J.-Y.; Wen, D.-Y.; Mi, F.-L. Preparation of fucoidan-shelled and genipin-crosslinked chitosan beads for antibacterial application. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 126, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abou Zeid, A.H.; Aboutabl, E.A.; Sleem, A.A.; El-Rafie, H.M. Water soluble polysaccharides extracted from Pterocladia capillacea and Dictyopteris membranacea and their biological activities. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 113, 62–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vijayabaskar, P.; Vaseela, N.; Thirumaran, G. Potential antibacterial and antioxidant properties of a sulfated polysaccharide from the brown marine algae Sargassum swartzii. Chin. J. Nat. Med. 2012, 10, 421–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, L.T.; Haney, E.F.; Vogel, H.J. The expanding scope of antimicrobial peptide structures and their modes of action. Trends Biotechnol. 2011, 29, 464–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pimenta, D.C.; Lebrun, I. Cryptides: Buried secrets in proteins. Peptides 2007, 28, 2403–2410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lordan, S.; Ross, R.P.; Stanton, C. Marine bioactives as functional food ingredients: Potential to reduce the incidence of chronic diseases. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 1056–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bahar, A.A.; Ren, D. Antimicrobial Peptides. Pharmaceuticals 2013, 6, 1543–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maverakis, E.; Kim, K.; Shimoda, M.; Gershwin, M.E.; Patel, F.; Wilken, R.; Raychaudhuri, S.; Ruhaak, L.R.; Lebrilla, C.B. Glycans in the Immune system and the Altered Glycan Theory of Autoimmunity: A Critical Review. J. Autoimmun. 2015, 57, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheung, R.C.F.; Wong, J.H.; Pan, W.; Chan, Y.S.; Yin, C.; Dan, X.; Ng, T.B. Marine lectins and their medicinal applications. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 99, 3755–3773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weis, W.I.; Drickamer, K. Structural Basis of Lectin-Carbohydrate Recognition. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1996, 65, 441–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharon, N.; Lis, H. Lectins; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Hudson, K.L.; Bartlett, G.J.; Diehl, R.C.; Agirre, J.; Gallagher, T.; Kiessling, L.L.; Woolfson, D.N. Carbohydrate-Aromatic Interactions in Proteins. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 15152–15160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holanda, M.L.; Melo, V.M.M.; Silva, L.M.C.M.; Amorim, R.C.N.; Pereira, M.G.; Benevides, N.M.B. Differential activity of a lectin from Solieria filiformis against human pathogenic bacteria. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 2005, 38, 1769–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strathmann, M.; Wingender, J.; Flemming, H.-C. Application of fluorescently labelled lectins for the visualization and biochemical characterization of polysaccharides in biofilms of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Microbiol. Methods 2002, 50, 237–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, J.H.; Ilag, L.L. Cryptic protein fragments as an emerging source of peptide drugs. IDrugs Investig. Drugs J. 2006, 9, 343–346. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, X.; Bai, L.; Zhu, L.; Yang, L.; Zhang, X. Marine Algae-Derived Bioactive Peptides for Human Nutrition and Health. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 9211–9222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nair, R.; Chabhadiya, R.; Chanda, S. Marine algae: Screening for a potent antibacterial agent. J. Herb. Pharmacother. 2007, 7, 73–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beaulieu, L.; Bondu, S.; Doiron, K.; Rioux, L.-E.; Turgeon, S.L. Characterization of antibacterial activity from protein hydrolysates of the macroalga Saccharina longicruris and identification of peptides implied in bioactivity. J. Funct. Foods 2015, 17, 685–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Tang, W.; Bidigare, R.R. Terpenoids as therapeutic drugs and pharmaceutical agents. In Natural Products; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2005; pp. 197–227. [Google Scholar]
- Kuete, V.; Efferth, T. Biodiversity, Natural Products and Cancer Treatment; World Scientific: London, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Lane, A.L.; Stout, E.P.; Lin, A.-S.; Prudhomme, J.; le Roch, K.; Fairchild, C.R.; Franzblau, S.G.; Hay, M.E.; Aalbersberg, W.; Kubanek, J. Antimalarial bromophycolides J-Q from the Fijian red alga Callophycus serratus. J. Org. Chem. 2009, 74, 2736–2742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues, D.; Alves, C.; Horta, A.; Pinteus, S.; Silva, J.; Culioli, G.; Thomas, O.P.; Pedrosa, R. Antitumor and antimicrobial potential of bromoditerpenes isolated from the red alga, Sphaerococcus coronopifolius. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 713–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Etahiri, S.; Bultel-Poncé, V.; Caux, C.; Guyot, M. New bromoditerpenes from the red alga Sphaerococcus coronopifolius. J. Nat. Prod. 2001, 64, 1024–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, S.; Llewellyn, C.A.; Egeland, E.S.; Johnsen, G. Phytoplankton Pigments: Characterization, Chemotaxonomy and Applications in Oceanography; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.K. Springer Handbook of Marine Biotechnology; Springer: Berlin, Germany; Heidelberg, Germany, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, S.; Wang, K.; Wan, L.; Li, A.; Hu, Q.; Zhang, C. Production, characterization, and antioxidant activity of fucoxanthin from the marine diatom Odontella aurita. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 2667–2681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larkum, A.; Douglas, S.; Raven, J.A. Photosynthesis in Algae; Springer Science & Business Media: New York, NY, USA, 2012; Volume 14. [Google Scholar]
- Posten, C.; Walter, C. Microalgal Biotechnology: Potential and Production; De Gruyter: Berlin, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Rajauria, G.; Abu-Ghannam, N. Isolation and partial characterization of bioactive fucoxanthin from Himanthalia elongata brown seaweed: A TLC-based approach. Int. J. Anal. Chem. 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deyab, M.A.; Abou-Dobara, M.I. Antibacterial activity of some marine algal extracts against most nosocomial bacterial infections. Egypt. J. Exp. Biol. (Bot.) 2013, 9, 281–286. [Google Scholar]
- Plaza, A.; Keffer, J.L.; Bifulco, G.; Lloyd, J.R.; Bewley, C.A. Chrysophaentins A–H, antibacterial bisdiarylbutene macrocycles that inhibit the bacterial cell division protein FtsZ. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 9069–9077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keffer, J.L.; Huecas, S.; Hammill, J.T.; Wipf, P.; Andreu, J.M.; Bewley, C.A. Chrysophaentins are competitive inhibitors of FtsZ and inhibit Z-ring formation in live bacteria. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2013, 21, 5673–5678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Ma, S. Advances in the discovery of novel antimicrobials targeting the assembly of bacterial cell division protein FtsZ. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 95, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brameyer, S.; Heermann, R. Specificity of signal-binding via non-AHL LuxR-type receptors. PLoS ONE 2015, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hentzer, M.; Givskov, M. Pharmacological inhibition of quorum sensing for the treatment of chronic bacterial infections. J. Clin. Investig. 2003, 112, 1300–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, D.; Bedzyk, L.A.; Ye, R.W.; Thomas, S.M.; Wood, T.K. Differential gene expression shows natural brominated furanones interfere with the autoinducer-2 bacterial signaling system of Escherichia coli. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2004, 88, 630–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manefield, M.; Welch, M.; Givskov, M.; Salmond, G.P.C.; Kjelleberg, S. Halogenated furanones from the red alga, Delisea pulchra, inhibit carbapenem antibiotic synthesis and exoenzyme virulence factor production in the phytopathogen Erwinia carotovora. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2001, 205, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castillo, S.; Heredia, N.; García, S. 2 (5H)-Furanone, epigallocatechin gallate, and a citric-based disinfectant disturb quorum-sensing activity and reduce motility and biofilm formation of Campylobacter jejuni. Folia Microbiol. 2015, 60, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stewart, L.D.; Elliott, C.T. The impact of climate change on existing and emerging microbial threats across the food chain: An island of Ireland perspective. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 44, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, M.; Anju, C.P.; Biswas, L.; Anil Kumar, V.; Gopi Mohan, C.; Biswas, R. Antibiotic resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa and alternative therapeutic options. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2016, 306, 48–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mueller, R.; Fischer, A.M.; Bolch, C.J.; Wright, J.T. Environmental correlates of phenotypic variation: Do variable tidal regimes influence morphology in intertidal seaweeds? J. Phycol. 2015, 51, 859–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schiener, P.; Black, K.D.; Stanley, M.S.; Green, D.H. The seasonal variation in the chemical composition of the kelp species Laminaria digitata, Laminaria hyperborea, Saccharina latissima and Alaria esculenta. J. Appl. Phycol. 2014, 27, 363–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marinho-Soriano, E.; Fonseca, P.C.; Carneiro, M.A.A.; Moreira, W.S.C. Seasonal variation in the chemical composition of two tropical seaweeds. Bioresour. Technol. 2006, 97, 2402–2406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moorthi, P.V.; Balasubramanian, C. Antimicrobial properties of marine seaweed, Sargassum muticum against human pathogens. J. Coast. Life Med. 2015, 3, 122–125. [Google Scholar]
- Rosaline, X.D.; Sakthivelkumar, S.; Rajendran, K.; Janarthanan, S. Screening of selected marine algae from the coastal Tamil Nadu, South India for antibacterial activity. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Biomed. 2012, 2, S140–S146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jebasingh, S.E.J.; Rosemary, S.; Elaiyaraja, S.; Sivaraman, K.; Lakshmikandan, M.; Murugan, A.; Raja, P. Potential antibacterial activity of selected green and red seaweeds. J. Pharm. Biomed. Sci. 2011, 5, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Mendiola, J.A.; Torres, C.F.; Toré, A.; Martín-Álvarez, P.J.; Santoyo, S.; Arredondo, B.O.; Señoráns, F.J.; Cifuentes, A.; Ibáñez, E. Use of supercritical CO2 to obtain extracts with antimicrobial activity from Chaetoceros muelleri microalga. A correlation with their lipidic content. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2007, 224, 505–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajauria, G.; Jaiswal, A.K.; Abu-Ghannam, N.; Gupta, S. Antimicrobial, antioxidant and free radical-scavenging capacity of brown seaweed Himanthalia elongata from western coast of Ireland. J. Food Biochem. 2012, 37, 322–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United States Pharmacopeia. Food Chemicals Codex; The United States Pharmacopeial Convention: Rockville, MD, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- EU. Commission Directive (2010) 2010/67/EU of 20 October 2010 amending Directive 2008/84/EC laying down specific purity criteria on food additives other than colours and sweeteners. Off. J. Eur. Union (L Ser.) 2010, 277, 17–26. [Google Scholar]
- FDA. Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act (FD & C Act) 2002. In United States Code, Title 21; The Food and Drug Administration: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Boisvert, C.; Beaulieu, L.; Bonnet, C.; Pelletier, É. Assessment of the Antioxidant and Antibacterial Activities of Three Species of Edible Seaweeds. J. Food Biochem. 2015, 39, 377–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grosso, C.; Valentao, P.; Ferreres, F.; Andrade, P.B. Alternative and efficient extraction methods for marine-derived compounds. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 3182–3230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Da Silva, R.P.; Rocha-Santos, T.A.; Duarte, A.C. Supercritical fluid extraction of bioactive compounds. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2016, 76, 40–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, H.; Barbosa-Cánovas, G.V.; Weiss, J. Ultrasound Technologies for Food and Bioprocessing; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2011; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Greenly, J.M.; Tester, J.W. Ultrasonic cavitation for disruption of microalgae. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 184, 276–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.-K. Handbook of Marine Macroalgae: Biotechnology and Applied Phycology; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Rhein-Knudsen, N.; Ale, M.T.; Meyer, A.S. Seaweed hydrocolloid production: An update on enzyme assisted extraction and modification technologies. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 3340–3359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wijesinghe, W.; Jeon, Y.-J. Enzyme-assistant extraction (EAE) of bioactive components: A useful approach for recovery of industrially important metabolites from seaweeds: A review. Fitoterapia 2012, 83, 6–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Je, J.-Y.; Park, P.-J.; Kim, E.-K.; Park, J.-S.; Yoon, H.-D.; Kim, K.-R.; Ahn, C.-B. Antioxidant activity of enzymatic extracts from the brown seaweed Undaria pinnatifida by electron spin resonance spectroscopy. Food Sci. Technol. 2009, 42, 874–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, D.; Sousa, S.; Silva, A.; Amorim, M.; Pereira, L.; Rocha-Santos, T.A.P.; Gomes, A.M.P.; Duarte, A.C.; Freitas, A.C. Impact of enzyme- and ultrasound-assisted extraction methods on biological properties of red, brown, and green seaweeds from the central west coast of Portugal. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 3177–3188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuorro, A.; Fidaleo, M.; Lavecchia, R. Enzyme-assisted extraction of lycopene from tomato processing waste. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 2011, 49, 567–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Billakanti, J.M.; Catchpole, O.J.; Fenton, T.A.; Mitchell, K.A.; MacKenzie, A.D. Enzyme-assisted extraction of fucoxanthin and lipids containing polyunsaturated fatty acids from Undaria pinnatifida using dimethyl ether and ethanol. Process Biochem. 2013, 48, 1999–2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, T.O.; Smedsgaard, J.; Nielsen, K.F.; Hansen, M.E.; Frisvad, J.C. Phenotypic taxonomy and metabolite profiling in microbial drug discovery. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2005, 22, 672–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bixler, G.D.; Bhushan, B. Biofouling: Lessons from nature. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2012, 370, 2381–2417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.-Y.; Yan, X.; Jackson, C.R. Antimicrobial Resistance and Food Safety: Methods and Techniques; Elsevier: New York, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, S.; Rajauria, G.; Abu-Ghannam, N. Study of the microbial diversity and antimicrobial properties of Irish edible brown seaweeds. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2010, 45, 482–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dussault, D.; Vu, K.D.; Vansach, T.; Horgen, F.D.; Lacroix, M. Antimicrobial effects of marine algal extracts and cyanobacterial pure compounds against five foodborne pathogens. Food Chem. 2016, 199, 114–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tavassoli-Kafrani, E.; Shekarchizadeh, H.; Masoudpour-Behabadi, M. Development of edible films and coatings from alginates and carrageenans. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 137, 360–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alboofetileh, M.; Rezaei, M.; Hosseini, H.; Abdollahi, M. Antimicrobial activity of alginate/clay nanocomposite films enriched with essential oils against three common foodborne pathogens. Food Control 2014, 36, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olaimat, A.N.; Fang, Y.; Holley, R.A. Inhibition of Campylobacter jejuni on fresh chicken breasts by κ-carrageenan/chitosan-based coatings containing allyl isothiocyanate or deodorized oriental mustard extract. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2014, 187, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anjum, A.; Brathwaite, K.J.; Aidley, J.; Connerton, P.L.; Cummings, N.J.; Parkhill, J.; Connerton, I.; Bayliss, C.D. Phase variation of a Type IIG restriction-modification enzyme alters site-specific methylation patterns and gene expression in Campylobacter jejuni strain NCTC11168. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-Martínez, A.V.; Sendón, R.; Abad, M.J.; González-Rodríguez, M.V.; Barros-Velázquez, J.; Aubourg, S.P.; Paseiro-Losada, P.; Rodríguez-Bernaldo de Quirós, A. Migration kinetics of sorbic acid from polylactic acid and seaweed based films into food simulants. Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 65, 630–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lück, E.; Jager, M. Antimicrobial Food Additives: Characteristics-Uses-Effects; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Evans, F.; Critchley, A. Seaweeds for animal production use. J. Appl. Phycol. 2014, 26, 891–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makkar, H.P.S.; Tran, G.; Heuzé, V.; Giger-Reverdin, S.; Lessire, M.; Lebas, F.; Ankers, P. Seaweeds for livestock diets: A review. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2016, 212, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moroney, N.C.; O’Grady, M.N.; Robertson, R.C.; Stanton, C.; O’Doherty, J.V.; Kerry, J.P. Influence of level and duration of feeding polysaccharide (laminarin and fucoidan) extracts from brown seaweed (Laminaria digitata) on quality indices of fresh pork. Meat Sci. 2015, 99, 132–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vatsos, I.N.; Rebours, C. Seaweed extracts as antimicrobial agents in aquaculture. J. Appl. Phycol. 2014, 27, 2017–2035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roohi Fatima, M.; Dinesh, S.; Mekata, T.; Itami, T.; Sudhakaran, R. Therapeutic efficiency of Portieria hornemannii (Rhodophyta) against Vibrio parahaemolyticus in experimentally infected Oreochromis mossambicus. Aquaculture 2016, 450, 369–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutierrez, J.; Barry-Ryan, C.; Bourke, P. The antimicrobial efficacy of plant essential oil combinations and interactions with food ingredients. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2008, 124, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tallarida, R.J. Quantitative methods for assessing drug synergism. Genes Cancer 2011, 2, 1003–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.-Y.; Jeong, M.-R.; Choi, S.-M.; Na, S.-S.; Cha, J.-D. Synergistic effect of fucoidan with antibiotics against oral pathogenic bacteria. Arch. Oral Biol. 2013, 58, 482–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, X.; Hwang, H.-m.; Aker, W.G.; Wang, P.; Lin, Y.; Jiang, X.; He, X. Synergistic combination of marine oligosaccharides and azithromycin against Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Microbiol. Res. 2014, 169, 759–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borowitzka, M. Algal Biotechnology. In The Algae World; Sahoo, D., Seckbach, J., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2015; Volume 26, pp. 319–338. [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Amotz, A.; Avron, M. Dunaliella: Physiology, Biochemistry, and Biotechnology; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Guzmán-Zapata, D.; Macedo-Osorio, K.; Almaraz-Delgado, A.; Durán-Figueroa, N.; Badillo-Corona, J. Production of recombinant proteins in the chloroplast of the green alga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. In Recombinant Proteins from Plants; MacDonald, J., Kolotilin, I., Menassa, R., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2016; Volume 1385, pp. 69–85. [Google Scholar]
- Manivasagan, P.; Oh, J. Marine polysaccharide-based nanomaterials as a novel source of nanobiotechnological applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 82, 315–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stengel, D.B.; Connan, S. Marine algae: A source of biomass for biotechnological applications. In Natural Products from Marine Algae; Stengel, D.B., Connan, S., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2015; Volume 1308, pp. 1–37. [Google Scholar]
- Guarnieri, M.T.; Pienkos, P.T. Algal omics: Unlocking bioproduct diversity in algae cell factories. Photosynth. Res. 2014, 123, 255–263. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kumar, M.; Kuzhiumparambil, U.; Pernice, M.; Jiang, Z.; Ralph, P.J. Metabolomics: An emerging frontier of systems biology in marine macrophytes. Algal Res. 2016, 16, 76–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piganeau, G. Genomic Insights into the Biology of Algae; Elsevier Science: Oxford, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Prakash, D.; Sharma, G. Phytochemicals of Nutraceutical Importance; CABI: Oxfordshire, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Hovde, B.T.; Deodato, C.R.; Hunsperger, H.M.; Ryken, S.A.; Yost, W.; Jha, R.K.; Patterson, J.; Monnat, R.J., Jr.; Barlow, S.B.; Starkenburg, S.R. Genome sequence and transcriptome analyses of Chrysochromulina tobin: Metabolic tools for enhanced algal fitness in the prominent order Prymnesiales (Haptophyceae). PLoS Genet. 2015, 11, e1005469. [Google Scholar]
- De Oliveira, L.S.; Gregoracci, G.B.; Silva, G.G.Z.; Salgado, L.T.; Filho, G.A.; Alves-Ferreira, M.; Pereira, R.C.; Thompson, F.L. Transcriptomic analysis of the red seaweed Laurencia dendroidea (Florideophyceae, Rhodophyta) and its microbiome. BMC Genom. 2012, 13, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hurd, C.L.; Harrison, P.J.; Bischof, K.; Lobban, C.S. Seaweed Ecology and Physiology; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Urosa, A.; Marcos, I.; Díez, D.; Lithgow, A.; Plata, G.; Padrón, J.; Basabe, P. Synthesis and bioactivity of Luffarin I. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 2407–2423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Oliveira, L.; Tschoeke, D.; de Oliveira, A.; Hill, L.; Paradas, W.; Salgado, L.; Thompson, C.; Pereira, R.; Thompson, F. New insights on the terpenome of the red seaweed Laurencia dendroidea (Florideophyceae, Rhodophyta). Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 879–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montaser, R.; Luesch, H. Marine natural products: A new wave of drugs? Future Med. Chem. 2011, 3, 1475–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kilcoyne, A.; O’Connor, D.; Ambery, P. Pharmaceutical Medicine; OUP Oxford: Oxford, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Howard, S.J.; Hopwood, S.; Davies, S.C. Antimicrobial resistance: A global challenge. Sci. Transl. Med. 2014, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shannon, E.; Abu-Ghannam, N. Antibacterial Derivatives of Marine Algae: An Overview of Pharmacological Mechanisms and Applications. Mar. Drugs 2016, 14, 81. https://doi.org/10.3390/md14040081
Shannon E, Abu-Ghannam N. Antibacterial Derivatives of Marine Algae: An Overview of Pharmacological Mechanisms and Applications. Marine Drugs. 2016; 14(4):81. https://doi.org/10.3390/md14040081
Chicago/Turabian StyleShannon, Emer, and Nissreen Abu-Ghannam. 2016. "Antibacterial Derivatives of Marine Algae: An Overview of Pharmacological Mechanisms and Applications" Marine Drugs 14, no. 4: 81. https://doi.org/10.3390/md14040081
APA StyleShannon, E., & Abu-Ghannam, N. (2016). Antibacterial Derivatives of Marine Algae: An Overview of Pharmacological Mechanisms and Applications. Marine Drugs, 14(4), 81. https://doi.org/10.3390/md14040081