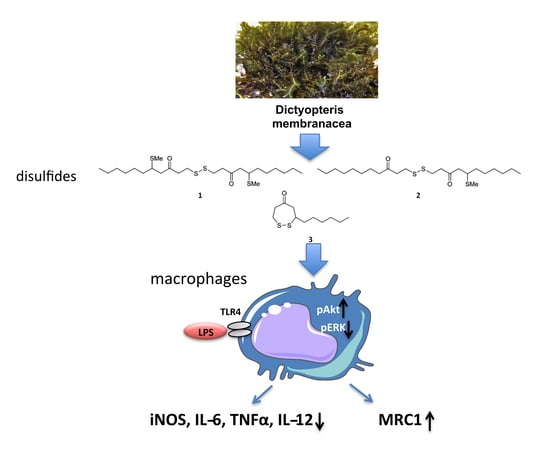
Disulfides from the Brown Alga Dictyopteris membranacea Suppress M1 Macrophage Activation by Inducing AKT and Suppressing MAPK/ERK Signaling Pathways
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Isolation of Metabolites 1–3 and Evaluation of Their Anti-Inflammatory Potency and Toxicity
2.2. Macrophages Exposed to Compounds 1–3 Suppress Expression of Pro-Inflammatory Genes and Alter Metabolic Gene Expression
2.3. Compounds 1–3 Impair TLR4-Mediated Macrophage Activation
2.4. The Effect of Compounds 1–3 in AKT and MAPK/ERK Signaling
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General Experimental Procedures
3.2. Collection of Algal Material
3.3. Isolation of Metabolites 1–3
3.4. Cell Culture and Compound Dilutions
3.5. Nitric Oxide Measurement
3.6. MTT Cell Metabolism Measurement
3.7. RNA Extraction, cDNA Synthesis and Quantitative PCR
3.8. ELISA
3.9. Western Blot
3.10. Isolation of Primary Peritoneal Mouse Macrophages
3.11. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lim, J.J.; Grinstein, S.; Roth, Z. Diversity and Versatility of Phagocytosis: Roles in Innate Immunity, Tissue Remodeling, and Homeostasis. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2017, 7, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hirayama, D.; Iida, T.; Nakase, H. The Phagocytic Function of Macrophage-Enforcing Innate Immunity and Tissue Homeostasis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 19, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Murray, P.J.; Allen, J.E.; Biswas, S.K.; Fisher, E.A.; Gilroy, D.W.; Goerdt, S.; Gordon, S.; Hamilton, J.A.; Ivashkiv, L.B.; Lawrence, T.; et al. Macrophage Activation and Polarization: Nomenclature and Experimental Guidelines. Immunity 2014, 41, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vergadi, E.; Ieronymaki, E.; Lyroni, K.; Vaporidi, K.; Tsatsanis, C. Akt signaling pathway in macrophage activation and m1/m2 polarization. J. Immunol. 2017, 198, 1006–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sarbassov, D.D.; Ali, S.M.; Sengupta, S.; Sheen, J.-H.; Hsu, P.P.; Bagley, A.F.; Markhard, A.L.; Sabatini, D.M. Prolonged Rapamycin Treatment Inhibits mTORC2 Assembly and Akt/PKB. Mol. Cell 2006, 22, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linton, M.F.; Moslehi, J.J.; Babaev, V.R. Akt Signaling in Macrophage Polarization, Survival, and Atherosclerosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Arranz, A.; Doxaki, C.; Vergadi, E.; De La Torre, Y.M.; Vaporidi, K.; Lagoudaki, E.D.; Ieronymaki, E.; Androulidaki, A.; Venihaki, M.; Margioris, A.N.; et al. Akt1 and Akt2 protein kinases differentially contribute to macrophage polarization. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 9517–9522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fruman, D.A.; Chiu, H.; Hopkins, B.D.; Bagrodia, S.; Cantley, L.C.; Abraham, R.T. The PI3K Pathway in Human Disease. Cell 2017, 170, 605–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arkun, Z.Y. Dynamic Modeling and Analysis of the Cross-Talk between Insulin/AKT and MAPK/ERK Signaling Pathways. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0149684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rengasamy, K.R.R.; Mahomoodally, M.F.; Aumeeruddy, M.Z.; Zengin, G.; Xiaoqing, C.; Kim, D.H. Bioactive compounds in seaweeds: An overview of their biological properties and safety. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2020, 135, 111013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zatelli, G.A.; Philippus, A.C.; Falkenberg, M. An overview of odoriferous marine seaweeds of the Dictyopteris genus: Insights into their chemical diversity, biological potential and ecological roles. Rev. Bras. Farm. 2018, 28, 243–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimou, M.; Ioannou, E.; Daskalaki, M.G.; Tziveleka, L.A.; Kampranis, S.C.; Roussis, V. Disulfides with Anti-inflammatory Activity from the Brown Alga Dictyopteris membranacea. J. Nat. Prod. 2016, 79, 584–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daskalaki, M.G.; Tsatsanis, C.; Kampranis, S.C. Histone methylation and acetylation in macrophages as a mechanism for regulation of inflammatory responses. J. Cell. Physiol. 2018, 233, 6495–6507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, K.; Hernandez, L.D.; Galán, J.E.; Janeway, C.A.; Medzhitov, R.; Flavell, R.A. IRAK-M Is a Negative Regulator of Toll-like Receptor Signaling. Cell 2002, 110, 191–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lyroni, K.; Patsalos, A.; Daskalaki, M.G.; Doxaki, C.; Soennichsen, B.; Helms, M.; Liapis, I.; Zacharioudaki, V.; Kampranis, S.C.; Tsatsanis, C. Epigenetic and Transcriptional Regulation of IRAK-M Expression in Macrophages. J. Immunol. 2016, 198, 1297–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, M.M.; Weinberg, S.E.; Chandel, N.S. Mitochondrial control of immunity: Beyond ATP. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2017, 17, 608–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freemerman, A.J.; Johnson, A.R.; Sacks, G.N.; Milner, J.J.; Kirk, E.L.; Troester, M.A.; MacIntyre, A.N.; Goraksha-Hicks, P.; Rathmell, J.C.; Makowski, L. Metabolic Reprogramming of Macrophages: Glucose transporter 1 (glut1)-mediated glucose metabolism drives a proinflammatory phenotype. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 7884–7896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, X.; Liu, R.; Qu, X.; Yu, H.; Chu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, W.; Wu, X.; Gao, H.; Tao, B.; et al. α-Ketoglutarate-Activated NF-κB Signaling Promotes Compensatory Glucose Uptake and Brain Tumor Development. Mol. Cell 2019, 76, 148–162.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.; Kumanogoh, A. The spectrum of macrophage activation by immunometabolism. Int. Immunol. 2020, 32, 467–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.C.-C.; Everts, B.; Ivanova, Y.; O’Sullivan, D.; Nascimento, M.; Smith, S.; Beatty, W.; Love-Gregory, L.; Lam, W.Y.; O’Neill, C.M.; et al. Cell-intrinsic lysosomal lipolysis is essential for alternative activation of macrophages. Nat. Immunol. 2014, 15, 846–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, C.; Shen, M.; Zhang, N.; Wang, S.; Xu, Y.; Chen, S.; Chen, F.; Yang, K.; He, T.; Wang, A.; et al. Reduction Impairs the Antibacterial Activity but Benefits the LPS Neutralization Ability of Human Enteric Defensin 5. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 22875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Buscà, R.; Pouysségur, J.; Lenormand, P. ERK1 and ERK2 Map Kinases: Specific Roles or Functional Redundancy? Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2016, 4, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lu, N.; Malemud, C.J. Extracellular Signal-Regulated Kinase: A Regulator of Cell Growth, Inflammation, Chondrocyte and Bone Cell Receptor-Mediated Gene Expression. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Troutman, T.D.; Bazan, J.F.; Pasare, C. Toll-like receptors, signaling adapters and regulation of the pro-inflammatory response by PI3K. Cell Cycle 2012, 11, 3559–3567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Androulidaki, A.; Iliopoulos, D.; Arranz, A.; Doxaki, C.; Schworer, S.; Zacharioudaki, V.; Margioris, A.N.; Tsichlis, P.N.; Tsatsanis, C. The Kinase Akt1 Controls Macrophage Response to Lipopolysaccharide by Regulating MicroRNAs. Immunity 2009, 31, 220–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]






| Compound | IC50 (μΜ) | No Cytostatic Activity (μΜ) (at 48 h) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2.6 ± 0.35 | <62.5 |
| 2 | 3.8 ± 0.29 | <45 |
| 3 | 14.2 ± 1.67 | <125 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Daskalaki, M.G.; Bafiti, P.; Kikionis, S.; Laskou, M.; Roussis, V.; Ioannou, E.; Kampranis, S.C.; Tsatsanis, C. Disulfides from the Brown Alga Dictyopteris membranacea Suppress M1 Macrophage Activation by Inducing AKT and Suppressing MAPK/ERK Signaling Pathways. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 527. https://doi.org/10.3390/md18110527
Daskalaki MG, Bafiti P, Kikionis S, Laskou M, Roussis V, Ioannou E, Kampranis SC, Tsatsanis C. Disulfides from the Brown Alga Dictyopteris membranacea Suppress M1 Macrophage Activation by Inducing AKT and Suppressing MAPK/ERK Signaling Pathways. Marine Drugs. 2020; 18(11):527. https://doi.org/10.3390/md18110527
Chicago/Turabian StyleDaskalaki, Maria G., Paraskevi Bafiti, Stefanos Kikionis, Maria Laskou, Vassilios Roussis, Efstathia Ioannou, Sotirios C. Kampranis, and Christos Tsatsanis. 2020. "Disulfides from the Brown Alga Dictyopteris membranacea Suppress M1 Macrophage Activation by Inducing AKT and Suppressing MAPK/ERK Signaling Pathways" Marine Drugs 18, no. 11: 527. https://doi.org/10.3390/md18110527
APA StyleDaskalaki, M. G., Bafiti, P., Kikionis, S., Laskou, M., Roussis, V., Ioannou, E., Kampranis, S. C., & Tsatsanis, C. (2020). Disulfides from the Brown Alga Dictyopteris membranacea Suppress M1 Macrophage Activation by Inducing AKT and Suppressing MAPK/ERK Signaling Pathways. Marine Drugs, 18(11), 527. https://doi.org/10.3390/md18110527