Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Dual-Mode Chemo-Sonodynamic Therapy by Low-Energy Ultrasound
Abstract
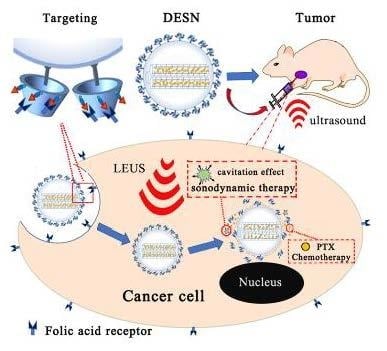
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Materials
2.2. Synthesis of Dual-Effect Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles (DESN)
2.3. Evaluation of PTX Releasing Profiles under LEUS with Different Intensity
2.4. Assay of Intensity of Ultrasound Cavitation by Fluorescence Spectrometry
2.5. Cell Culture
2.6. Cellular Uptake of Fluorescently Labeled DESN
2.7. In Vitro Cytotoxicity Assay
2.8. In Vivo Cytotoxicity Test
2.9. In Vivo Antitumor Effect of DESN upon LEUS Irradiation
2.10. Characterization
3. Result and Discussion
3.1. Preparation and Characterization of the DESN Drug Delivery System
3.2. Evaluation of the Enhancement of the Cavitation Effect
3.3. Evaluation of LEUS-Responsive PTX Release Profiles under LEUS with Different Intensities (1 MHz; 0, 0.4, 0.6, 0.8, and 1.0 W·cm−2)
3.4. In Vitro Antitumor Efficacy
3.5. Safety Evaluation of DESN and In Vivo Tumor-Growth Inhibition Experiment
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zheng, D.W.; Chen, J.L.; Zhu, J.Y.; Rong, L.; Li, B.; Lei, Q.; Fan, J.X.; Zou, M.Z.; Li, C.; Cheng, S.X.; et al. Highly Integrated Nano-Platform for Breaking the Barrier between Chemotherapy and Immunotherapy. Nano Lett. 2016, 16, 4341–4347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Y.C.; Zhou, F.F.; Zhang, D.; Chen, Q.; Xing, D. A graphene oxide based smart drug delivery system for tumor mitochondria-targeting photodynamic therapy. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 3530–3538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, P.; Lin, J.; Wang, S.; Zhou, Z.; Li, Z.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, C.; Yue, X.; Niu, G.; Yang, M.; et al. Photosensitizer-conjugated silica-coated gold nanoclusters for fluorescence imaging-guided photodynamuc therapy. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 4643–4654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paris, J.L.; Cabanas, M.V.; Manzano, M.; Vallet-Regi, M. Polymer-Grafted Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles as Ultrasound-Responsive Drug Carriers. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 11023–11033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, H.-J.; Matsuda, H.; Zhou, H.; Honma, I. Ultrasound-triggered smart drug release from a poly(dimethylsiloxane)-mesoporous silica composite. Adv. Mater. 2006, 18, 3083–3088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, A.K.W.; Sehgal, C.M. A Review of Low-Intensity Ultrasound for Cancer Therapy. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2015, 41, 905–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Bataineh, O.; Jenne, J.; Huber, P. Clinical and future applications of high intensity focused ultrasound in cancer. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2012, 38, 346–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lavon, I.; Kost, J. Mass transport enhancement by ultrasound in non-degradable polymeric controlled release systems. J. Control. Release 1998, 54, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirsi, S.R.; Borden, M.A. State-of-the-art materials for ultrasound-triggered drug delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2014, 72, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yu, T.H.; Wang, Z.B.; Mason, T.J. A review of research into the uses of low level ultrasound in cancer therapy. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2004, 11, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, P.; Qian, X.; Chen, Y.; Yu, L.; Lin, H.; Wang, L.; Zhu, Y.; Shi, J. Metalloporphyrin-encapsulated biodegradable nanosysterms for highly effecient magnetic resonance imaging guided sonodynamic cancer therapy. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 1275–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Q.; Zhou, Q.; Zhu, Q.; Rong, S.K.; Wang, Q.; Guo, R.; Deng, C.; Liu, D.; Yang, G.; Jiang, Y.; et al. Noninvasive cardiac arrhythmia therapy using High-Intensity Focused Ultrasound (HIFU) ablation. Int. J. Cardiol. 2013, 166, E28–E30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; Zhu, H.; Meng, Z.; Chen, Z.; Lin, J.; Shen, Y.; Gao, H. Safety Evaluation of High-Intensity Focused Ultrasound in Patients with Pancreatic Cancer. Onkologie 2013, 36, 88–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y. High-Intensity Focused Ultrasound Treatment for Advanced Pancreatic Cancer. Gastroenterol. Res. Pract. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, M.-K.; Shieh, J.; Lo, C.-W.; Chen, C.-S.; Chen, B.-T.; Huang, C.-W.; Chen, W.S. Reusable tissue-mimicking hydrogel phantoms for focused ultrasound ablation. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2015, 23, 399–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tachibana, K.; Uchida, T.; Tamura, K.; Eguchi, H.; Yamashita, N.; Ogawa, K. Enhanced cytotoxic effect of Ara-C by low intensity ultrasound to HL-60 cells. Cancer Lett. 2000, 149, 189–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marmottant, P.; Hilgenfeldt, S. Controlled vesicle deformation and lysis by single oscillating bubbles. Nature 2003, 423, 153–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lejbkowicz, F.; Salzberg, S. Distinct sensitivity of normal and malignant cells to ultrasound in vitro. Environ. Health Perspect. 1997, 105, 1575–1578. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Schuster, A.; Schwab, T.; Bischof, M.; Klotz, M.; Lemor, R.; Degel, C.; Schäfer, K.H. Cell specific ultrasound effects are dose and frequency dependent. Ann. Anat. 2013, 195, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iida, K.; Luo, H.; Hagisawa, K.; Akima, T.; Shah, P.K.; Naqvi, T.Z.; Siegel, R.J. Noninvasive low-frequency energy causes vasodilation ultrasound in humans. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2006, 48, 532–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lentacker, I.; Geers, B.; Demeester, J.; De Smedt, S.C.; Sanders, N.N. Design and Evaluation of Doxorubicin-containing Microbubbles for Ultrasound-triggered Doxorubicin Delivery: Cytotoxicity and Mechanisms Involved. Mol. Ther. 2010, 18, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schroeder, A.; Honen, R.; Turjeman, K.; Gabizon, A.; Kost, J.; Barenholz, Y. Ultrasound triggered release of cisplatin from liposomes in murine tumors. J. Control. Release 2009, 137, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, P.R.; Williams, R.L. Cavitation and the tensile strength of liquids under dynamic stressing. Mol. Phys. 2004, 102, 2091–2102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurn, W.P.; Schmelzer, J.S.J. Kinetics of bubble formation and the tensile strength of liquids. Atmos. Res. 2011, 25, 303–324. [Google Scholar]
- Pillai, R.; Marinelli, E.R.; Fan, H.; Nanjappan, P.; Song, B.; von Wronski, M.A.; Cherkaoui, S.; Tardy, I.; Pochon, S.; Schneider, M. A Phospholipid-PEG2000 Conjugate of a Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Receptor 2 (VEGFR2)-Targeting Heterodimer Peptide for Contrast-Enhanced Ultrasound Imaging of Angiogenesis. Bioconjug. Chem. 2010, 21, 556–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, F.; Li, Y.X.; Chen, Z.P.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, J.R.; Gu, N. Superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticle-embedded encapsulated microbubbles as dual contrast agents of magnetic resonance and ultrasound imaging. Biomaterials 2009, 30, 3882–3890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belova, V.; Gorin, D.A.; Shchukin, D.G.; Möhwald, H. Selektive Ultraschall-Kavitation an strukturierten hydrophoben Oberflächen. Angew. Chem. 2010, 122, 7285–7289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.; Xu, H.; Chen, H.; Jia, X.; Zhang, K.; Wang, Q.; Zheng, S.; Wu, R.; Yao, M.; Cai, X.; et al. A Drug–Perfluorocarbon Nanoemulsion with an Ultrathin Silica Coating for the Synergistic Effect of Chemotherapy and Ablation by High-Intensity Focused Ultrasound. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 7378–7385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Fu, J.; Wang, L. Effective Cancer Cell Killing by Hydrophobic Nanovoid-Enhanced Cavitation under Safe Low-Energy Ultrasound. Chem. Asian J. 2014, 9, 790–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhu, Y. Synergistic cytotoxicity of low-energy ultrasound and innovative mesoporous silica-based sensitive nanoagents. J. Mater. Sci. 2014, 49, 3665–3673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, S.; Wu, L.; Liu, J.; Xie, M.; Shen, H.; Qi, X.; Yan, Y.; Ge, Y.; Jin, Y. Core-shell structured Fe3O4@TiO2-doxorubicin nanoparticles for targeted chemo-sonodynamic therapy of cancer. Int. J. Pharm. 2015, 486, 380–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, F.Q.; Li, L.L.; Chen, D. Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles: Synthesis, Biocompatibility and Drug Delivery. Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 1504–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.H.; Mou, C.Y.; Lin, H.P. Synthesis of mesoporous silica nanoparticles. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 3862–3875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.; Saha, J.K.; Jang, J. Drying Transition of Water Confined between Hydrophobic Pillars. J. Phys. Chem. C 2012, 116, 19233–19239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.Y.; Wang, X.C.; Jin, P.K.; Zhao, B.; Fan, X. Complexation of anthracene with folic acid studied by FTIR and UV spectroscopies. Spectrochim. Acta Part A-Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2009, 72, 876–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Zhang, Y.-T.; Yu, M.; Guo, J.; Chaudhary, D.; Wang, C.-C. Cancer therapy and fluorescence imaging using the active release of doxorubicin from MSPs/Ni-LDH folate targeting nanoparticles. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 7913–7922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, F.; Zhang, B.; Zeng, S.; Lin, G.; Tian, J.; Yang, C.; Wang, K.; Xu, G.; Yong, K.-T. Folic acid-conjugated organically modified silica nanoparticles for enhanced targeted delivery in cancer cells and tumor in vivo. J. Mater. Chem. B 2015, 3, 6081–6093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLean, J.R.; Mortimer, A.J. A Cavitation and Free-Radical Dosimeter for Ultrasound. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 1988, 14, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mason, T.J.; Lorimer, J.P.; Bates, D.M.; Zhao, Y. Dosimetry in sonochemistry—The use of aqueous terephthalate ion as a fluorescence monitor. Ultrason. Sonochem. 1994, 1, S91–S95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skorb, E.V.; Andreeva, D.V.; Moehwald, H. Generation of a Porous Luminescent Structure through Ultrasonically Induced Pathways of Silicon Modification. Angew. Chem.-Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 5138–5142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bennewitz, M.F.; Lobo, T.L.; Nkansah, M.K.; Ulas, G.; Brudvig, G.W.; Shapiro, E.M. Biocompatible and pH-Sensitive PLGA Encapsulated MnO Nanocrystals for Molecular and Cellular MRI. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 3438–3446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schroeder, A.; Kost, J.; Barenholz, Y. Ultrasound, liposomes, and drug delivery: Principles for using ultrasound to control the release of drugs from liposomes. Chem. Phys. Lipids 2009, 162, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schroeder, A.; Avnir, Y.; Weisman, S.; Najajreh, Y.; Gabizon, A.; Talmon, Y.; Kost, J.; Barenholz, Y. Controlling liposomal drug release with low frequency ultrasound: Mechanism and feasibility. Langmuir 2007, 23, 4019–4025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Croissant, J.G.; Fatieiev, Y.; Almalik, A.; Khashab, N.M. Mesoporous silica and organosilica nanoparticles physical chemistry biosafety delivery strategies and biomedical application. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2018, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Croissant, J.G.; Fatieiev, Y.; Khashab, N.M. Degradability and clearance of silicon organosilica silisesquionxane silica mixed oxide and mesoporous silica nanoparticles. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Liu, Q.; Wang, Z.; Wang, P.; Hao, Q.; Li, C. Bioeffects of Low-Energy Continuous Ultrasound on Isolated Sarcoma 180 Cells. Chemotherapy 2009, 55, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, L.D.; Wu, J.Y. Enhancement of shikonin production in single- and two-phase suspension cultures of Lithospermum erythrorhizon cells using low-energy ultrasound. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2002, 78, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]











| Sample | SBET (m2/g) | D (nm) | Vpore (cm3·g−1) | PTX-Loading Capacity | Zeta Potential a (mV) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MSN | 1000 | 2.38 | 1.089 | 12.4% | −16 ± 1 |
| H-MSN | 640 | 2.30 | 0.56 | - | −58 ± 2 |
| DESN | 247 | 2.17 | 0.28 | 14.83% | 65 ± 3 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, J.; Jiao, Y.; Shao, Y. Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Dual-Mode Chemo-Sonodynamic Therapy by Low-Energy Ultrasound. Materials 2018, 11, 2041. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11102041
Wang J, Jiao Y, Shao Y. Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Dual-Mode Chemo-Sonodynamic Therapy by Low-Energy Ultrasound. Materials. 2018; 11(10):2041. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11102041
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Jingjing, Yajing Jiao, and Yiran Shao. 2018. "Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Dual-Mode Chemo-Sonodynamic Therapy by Low-Energy Ultrasound" Materials 11, no. 10: 2041. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11102041
APA StyleWang, J., Jiao, Y., & Shao, Y. (2018). Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Dual-Mode Chemo-Sonodynamic Therapy by Low-Energy Ultrasound. Materials, 11(10), 2041. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11102041